3958df98c5823ed41ed50a58a5bbbe4d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 99

Welcome to Nanofabrication Laboratory at MC 2 Clean Room Introduction and safety course

l 10: 15 Introduction l MC 2 cleanroom facility l Cleanroom design and layout l 11. 15 Administrative guidelines l l l Cleanroom behaviour DVD-Cleanroom behaviour (15 min) Cleanroom access LIMS Process tools/driving license Working hours/lab buddy/ visitors l 12: 00 Lunch break l 13: 15 Work Environment and Safety gear l Risks with chemicals (Kaija Matikainen) l Categories of chemicals (acids, bases, solvents, photochemicals) l Handling of chemical waste (Svante l 14: 15 Pålsson) Safety first l Safety policy at MC 2 and Chalmers l DVD- Cleanroom safety (25 min) l Alarm systems l 15: 30 Lab tour (Ulf Södervall) Clean Room Introduction and safety course

MC 2 Building • Inauguration: Year 2000 • Measurements Lab- & Office Area: 18 000 m 2 • Cleanroom operation starts: Year 2001 • Process Lab Area: 1 240 m 2 • Cleanroom Class: 1 - 1 000 • Investment: 90 M€ Clean Room Introduction and safety course

The Aim of this course; To inform about the regulations and rules regarding safety and work environment associated with 14: 50 reak work in the MC 2 Nanofabrication laboratories. Safety declaration Safety regulations, procedures and potential dangers Clean Room Introduction and safety course

The Aim of this course; Anyone who violates the safety regulations, or in any way Exposes himself/herself or others to danger Will be denied accesss to the laboratory by the decision of the executive management Clean Room Introduction and safety course
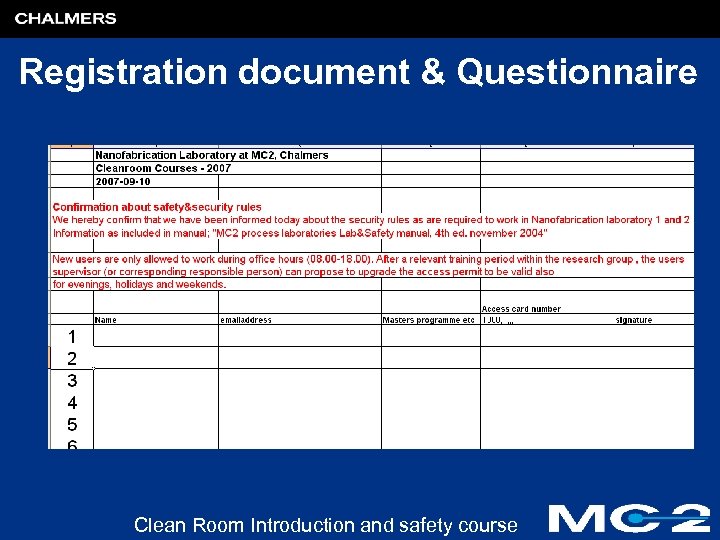
Registration document & Questionnaire Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Working in a Cleanroom environment Sources of contamination Cleanroom garments Cleanroom behaviour Training in the gowning procedure Clean Room Introduction and safety course

MC 2 Nano. Fabrication laboratory l Cleanrooms often found in processing industry – electronics, pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical, medical device industries, food and critical manufacturing environments (semiconductor, biology) and hospitals. – The only way to control contamination is to control the total environment. Air flow rates and direction, pressurization Temperature Humidity and specialized filtration Clean Room Introduction and safety course

MC 2 Nano. Fabrication laboratory l A cleanroom is laboratory with a controlled environment, where products are manufactured. A room in which the concentration of airborne particles is controlled, and which is constructed and used in a manner to minimize the introduction, generation and retention of particles inside the room and in which the other relevant parameters e. g. temperature, humidity and pressure are controlled as neccessary (ISO 14644 -1) l Typical office building contains ca 1 million particles/foot 3. The Federal standard 209 E (ISO 14644) is a document that establishes standard classes of air cleanliness for airborne particulate levels in cleanrooms Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Origin of contamination l Personal 35% l Process equipment 25% l Process 20% l Chemicals 20% Clean Room Introduction and safety course
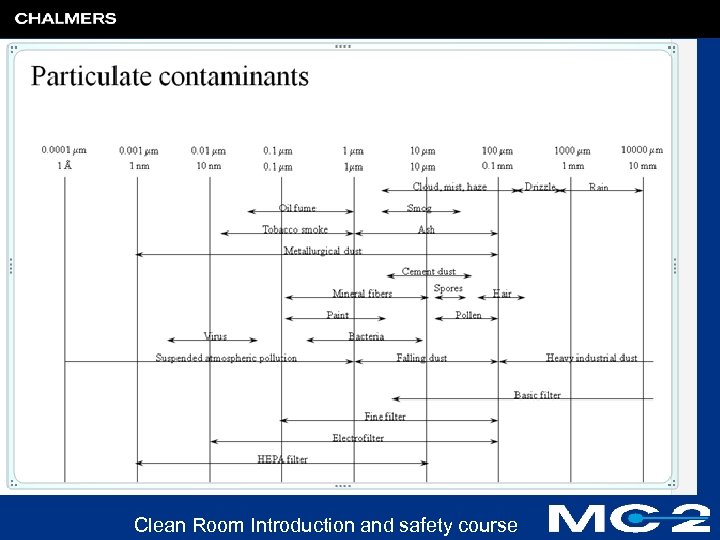
Clean Room Introduction and safety course
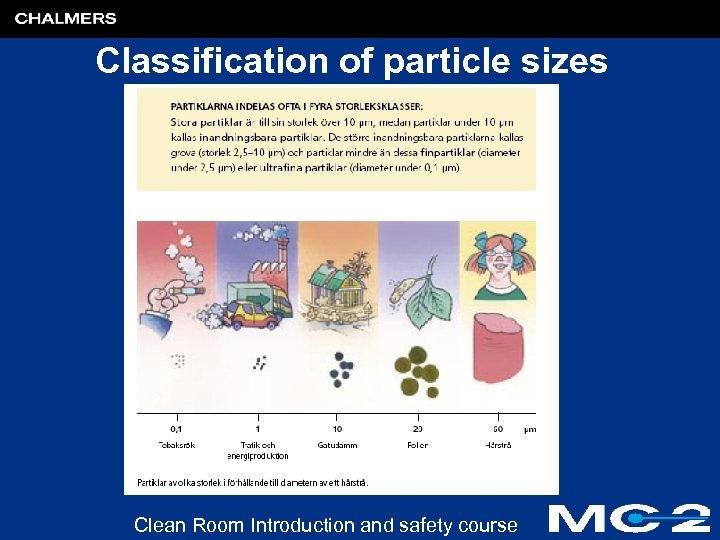
Classification of particle sizes Clean Room Introduction and safety course

The cleanroom garments l Filtering function – Low penetration for particles>0, 3 my. The garments should be worn properly sealed l Wear resistant – Strong material, wear, laundry resistant l ESD (Electro Static Discharge) safe – Conductive fibres in the hood, cleanroom suit and boots including the sole l Comfort – Breathing material and comfortable fit l Size – Choose the correct size. Too tight garments cause friction and increase particle generation. Too large garments may cause the ”air balloon effect” resulting in excessive release of particles Clean Room Introduction and safety course

l Contamination from personal – particles of >0, 5 my diam. generated/minute from the human body Action Ordinary clothes Clean room clothes Sitting Standing up Walking slowly Running 500, 000 2, 500, 000 5, 000 10, 000 15, 000 80, 000 150, 000 300, 000 Clean Room Introduction and safety course
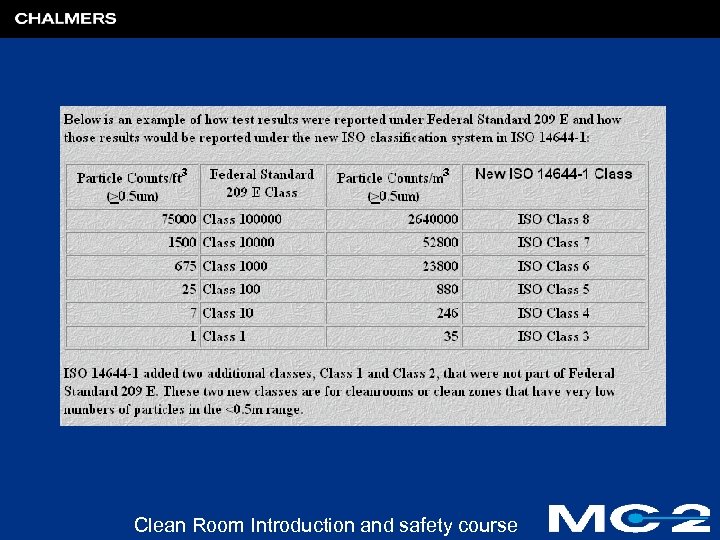
Clean Room Introduction and safety course

l Cleanroom areas in the Nanofabrication laboratory – – – – Processlab 1 (cleanroom- class 100/10) Processlab 2: (”The training lab”- class 1, 000) MBE-lab (class 10, 000) Dicing and CMP room (class 100, 000) Chemical preparation room ( class 1, 000) Visitors corridor, (class 10, 000) air-locks and gowning rooms (class 100, 000) l Other areas: – – – Media basement (below process lab 1) Machine hall; Fans, pressurised air, central vacuum, CVC, Water purification pump service and UHV preparation room Media attic(above process lab 1, 2) Scrubber room Steamer room l House E: House gases, Nitrogen purifier, Neutralisation plant, waste tanks, Emergancy power facility l House G: Special gases Clean Room Introduction and safety course

”Fan tower” Media basement HEPA filter Plenum MC 2 Cleanroom ventilation system, PL 1 Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Technical Data; Process laboratory 1 l 360 000 m 3/h of air is circulated (c: a 500 HEPA) l 90% of the air is recirculated, 10% is evacuated l Temperature= 21 C +/- 1 C l Relative humidity=43% +/- 5% l Air Velocity= 0. 4 m/s l Noise level specification=53 d. B l Vibration level=BBN-E Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Cleanliness & Climate Control l Particles: – Class 10 -100 l Clothing: – Full body suits to limit particle generation l Ventilation: – 520 000 m 3/hour capacity l Climate control: – Humidity control within ± 3% RH, – Temperature control within ± 1°C (± 0, 1°C around ebeam column) Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Vibration Minimization l Cleanroom has independent support from rest of building l Multiple layers of vibration insulated pillars l 3 µm/sec (curve E) is met with good margins l Vibration sensitive equipment not in contact with cleanroom floor l Roughing pumps located on media level Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Cleanroom functions and Media l Static electricity and ESD l General media – – House gases Special gases Drain Ventilatiojn exhaust (solvent, Acid, Toxic) – Electrical power – DI water – CDA, Vacuum, LN 2 Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Entry and Exit to Cleanroom On and Off garment procedure Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Cleanroom rules To consider before entering the Cleanroom l A proper personal hygiene is a condition for working in the cleanroom l Persons suffering from a cold or eczema should not enter the cleanroom l Cosmetics, rings and wristwatches have to be removed before entering the gowning area l Persons wearing glasses must clean those before entering the gowning area l Mobile phones are not allowed in the cleanroom areas l Men with a beard have to use a beard cover l Smokers should wait at least 10 minutes after smoking before entering the cleanrrom l Smokers and snuff users have to rinse their mouth before entering the cleanroom Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Cleanroom rules To consider in the cleanroom l l l l All movements should be slow and well planned Avoid crowding as this concentrates the contamination Do not carry items close to your body Do not touch your face or garment with your clean gloves Avoid touching any clean surfaces; such as load locks, etc Avoid talking while near your component/product No food (including chewing gum) or beverages are allowed in the cleanroom. Only ”cleanroom compatible matters/materials” are allowed. l Garments that are wet or stained have substantially reduced filtering effect and have to be exchanged immediately Clean Room Introduction and safety course

DVD- Cleanroom behaviour l Contamination and people l Human microenvironment – Speed of movement – Carrying materials – Correct working behaviour Clean Room Introduction and safety course

MC 2 ; Administrative guidelines Design dictated by – – Cleanliness Vibration minimization Safety Support access l Professional lab staff of 14 engineers specialized in – Lithography and Nano Processing – Thin Film and Plasma Processing – Thermal and Chemical Processing and 6 technicians working with – Service & Maintenance Clean Room Introduction and safety course
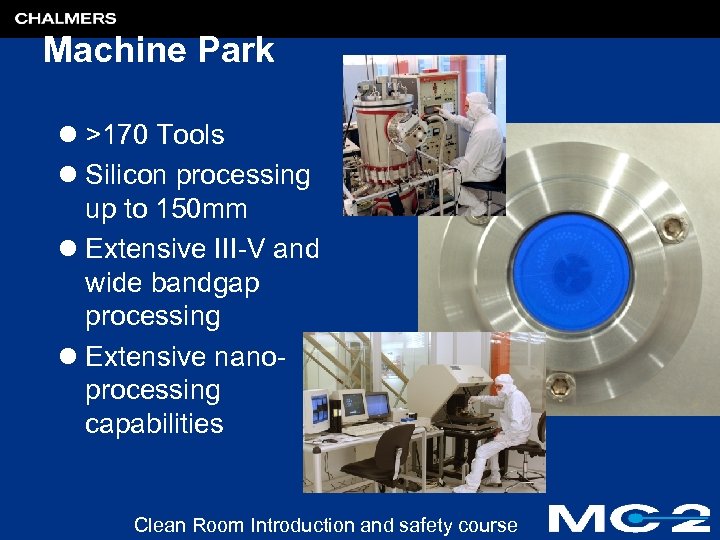
Machine Park l >170 Tools l Silicon processing up to 150 mm l Extensive III-V and wide bandgap processing l Extensive nanoprocessing capabilities Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Nanofabrication Laboratory Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Nanofabrication laboratory organisation l Lab Manager; Peter Modh l Process specialists – – – _ Johan Andersson Bengt Nilsson Piotr Jedrasik John Halonen Karin Hedsten Göran Alestig Mahdad Sadeghi Mats Hagberg Henrik Frederiksen Ulf Södervall Martin Hollerz Göran Pettersson Zonghe Lai l Service and Maintenance – – – – Svante Pålsson Göran Reivall Lars-Åke Sidengren Christer Andersson Kaija Matikainen Fredrik Johansson Emmy Nilsson Clean Room Introduction and safety course

l Cleanroom introduction course – – – Compulsory for all cleanroom users Over 600 participants so far Safety Rules & regulations Proper cleanroom behavior l “Driving licence”-training – To use any equipment in the cleanroom it is compulsory to have the relevant training before using it. l Ph D Processing course – For graduate students in applicable programs – Theoretical background and demonstrations of a wide variety of micro/nano processing techniques – Course for Masters students Clean Room Introduction and safety course
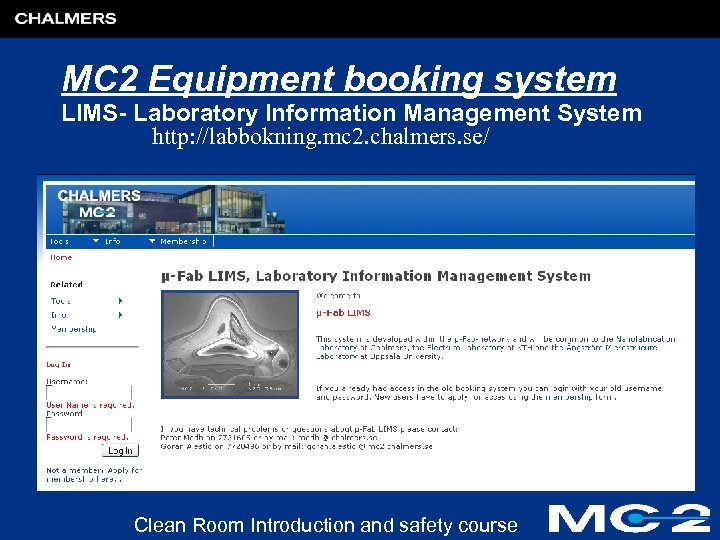
MC 2 Equipment booking system LIMS- Laboratory Information Management System http: //labbokning. mc 2. chalmers. se/ Clean Room Introduction and safety course
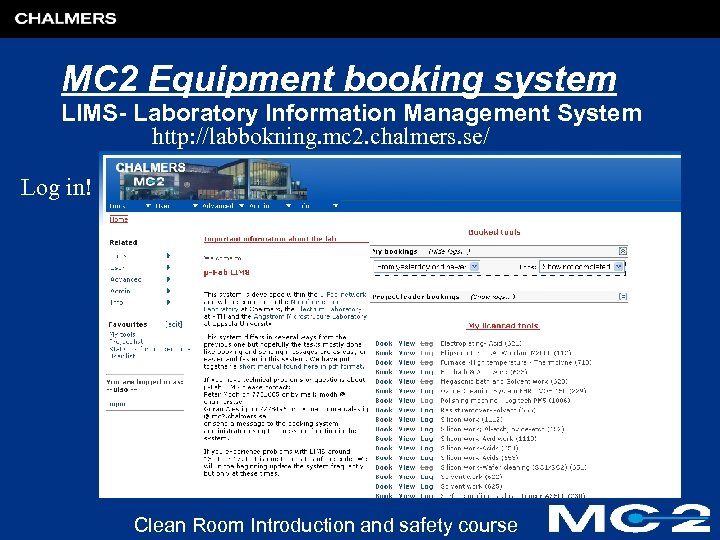
MC 2 Equipment booking system LIMS- Laboratory Information Management System http: //labbokning. mc 2. chalmers. se/ Log in! Clean Room Introduction and safety course
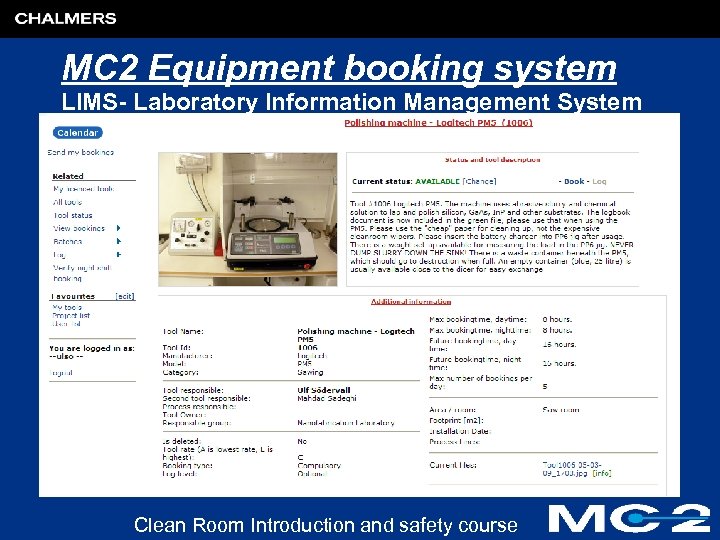
MC 2 Equipment booking system LIMS- Laboratory Information Management System Clean Room Introduction and safety course
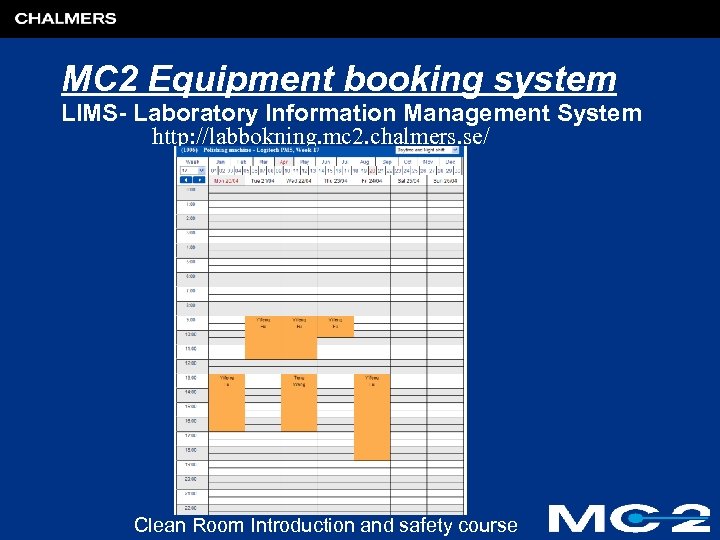
MC 2 Equipment booking system LIMS- Laboratory Information Management System http: //labbokning. mc 2. chalmers. se/ Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Consider the following when you book equipment l Plan your process steps. Do not book more time than you need. l Make sure that your process step is finished by 18. 00, unless you have a backup( see ”lab buddy” system) l Cancel booked time that you do not intend to use. l In case somebody do not show up at the booked hour, another user can take the time after 30 min. l Apply a professional attitude to your work, and keep your booked time strictly. Delays will cause irritation among the subsequent users. l Make sure that you have booked sufficient time for cleanup and resetting the equipment to original state. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Lab usage l Only authorized users may use the process equipment in the lab. You need a ”drivers licence” for ALL tools (including microscopes, wet benches) l How to acquire an equipment drivers license? ? – The purpose of the drivers license is to make sure that the user is able to handle the tool in a manner that is l Safe for the user, l Safe for the tool itself l Safe for the process running at the tool. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

l The following outline should be applied for complex tools: – Find someone in your group who is already experienced with the tool, and work with him/her until you are both satisfied with your basic handling of the tool. – Once both you and your teacher agree that you are able to work independently with the tool, your teacher should contact the tool responsible and state that you are trained well enough for independent work. Please note that you are under no circumstances allowed to actually work with the tool without supervision without a license. Your teacher must be present at all times during training. – The tool responsible person will give the training needed, and you will be granted the ”driving license” Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Opening hours l Approved users have access to the process laboratories 24 hours a day, all year, with the exeption of certain holidays. When the lab is closed, an announcment is always displayed at http: //processlab. mc 2. chalmers. se/information. html BUT! If you want to use the process laboratory late at night or at other times outside normal working hours (08. 00 -18. 00) you need to use the back-up or lab buddy system Also; new users will automatically only have access during office hours. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Back-up system; ”lab-buddy” ”if there is any risk of accidental personal injury occuring while working alone, then the worker must be assured quick access to help in case of an emergency” When you use the ”lab-buddy” system it is required that l Another approved user is present in the lab (or close by) to assist you in the event of an accident/emergency l Lab-buddies have close contact (not by mobile-telephone) for the system to work efficiently l The backup person must be an experienced lab user, familiar with the process lab and its safety devices and alarm system. (Arbets. MiljöLagen , AML, 3 Chp ; 2§ paragraph) https: //www. chalmers. se/insidan/SV/om-chalmers/arbetsmiljo/halsa-olycksfall/ensamarbete Clean Room Introduction and safety course

User responsiblities; MC 2 assumes that every user l l l l l Has read and understood the lab-safety manual Has attended the training course given by MC 2 for new users Carefully follows the MC 2 rules and regulations for cleanroom work Does not lend or copy keys or card-keys for the MC 2 facility Follows the directives given from the MC 2 staff Maintains a proper personal hygiene Acknowledges the established work and access hours Pays attention to the information updates issued by MC 2 Acts in a professional manner Register his/her emailadress to the MC 2 introduction course manager Users with experience from smaller process laboratories may see the MC 2 regulation framwork as complex and over-worked. However, both the size and cleanliness level of the facility calls for rigorous safety rules and cleanroom discipline. In the end, it is the user who benefits from a safe and functional working place Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Lab staff responsibilities The MC 2 facility staff has the following functions and responsibilities l l l l To give advice and suggestions regarding process issues Execute projects according to process plans Ensure that safety, cleanliness and equipment standards are maintained Perform service and maintenance Maintain booking systems and other administrative functions connected to the lab Train new users in cleanroom behaviour and dress code Inform users via email about changes related to the process lab Please note that it is NOT within the responsibility of the lab group staff to l Clean the equipment after other users l Execute process steps or tasks without approval from the project manager Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Lab usage- Storage l Every user will be assigned a personal storage space with a corresponding storage box – Intended for temporary storage of work material such as tweezers, ”personal items”, cleanroom pens and notebooks, etc – Only ”harmless” materials may be stored in the personal storage boxes – Personal storage boxes are personal. You should not borrow items from a box that belongs to someone else. – Materials with high probability of contamination or which may impose a safety risk, may under no circumstances be stored in the personal storage boxes. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Lab usage- Visitors l Every user have the possibility to bring a visitor in the laboratory only with the following restrictions – Visitors corridor: You may bring visitors without special permission. Visitors muct be accompanied all the time and must be properly gowned (cleanroom coat and hair cover). No bags, mobil phones, coats are allowed – Process lab 1 -requires special permission from the lab manager. All guests must be informed about safety rules and cleanroom behaviour – Process lab 2. Normally not accessable for visitors. Guests must be accompanied all the time. Make sure that your guests are gowned properly and instruct them not to touch anything. – MBE lab, CMP and chemical preparation room- Normally not accessable for visitors. You need permission from the lab staff if you want to bring visitors here. . Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Lab usage l It is the responsibility of the user to clean and reset the process equipment after use l A user can be banned from the cleanroom, or be ordered further cleanroom training, if persistent or serios errors in the work procedure are observed Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Work environment risks (Kaija Matikainen) Clean Room Introduction and safety course

The objective of this chemical safety training course is to identify potentially hazardous chemicals, and to establish safety routines for work in the lab. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Hazardous Chemicals at MC 2 Nanofabrication Laboratories l l Acids Bases Oxidizers Solvents Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Potential hazards using liquid chemicals 1. Liquid chemicals requires a lot of handling in your work. 2. There are many liquid chemicals used throughout the lab, each with a different set of hazards and precautionary measures required for use. 3. Unconventional use of standard chemicals can present unexpected hazards not associated with normal use in the lab. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Material Safety Data Sheet, MSDS l l l l l Material identification – name, CAS #, formula. Physical data – chemistry (boiling point, solubility etc. ). Hazardous ingredients – TLV (Threshold Limit Value). Fire and explosion data – AIT, LEL, UEL. Health hazard data – overexposure, first aid. Reactivity data – stability, incompabilities. Spill or leak procedures – what steps to take. Special precautions – handling and storage. Emergency phone contact Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Risk analysis: Acids l Hydrofluoric acid, HF l BOE/BHF, Buffered Oxide Etch (HF/NH 4 F) l Sulphuric acid, H 2 SO 4 l Nitric acid, HNO 3 l Hydrochloric acid, HCl Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Risk analysis: Nitric acid, HNO 3 Nitrous gases are highly toxic – and you can’t smell them! Nitric acid could form ignition at reaction with organic substances (e. g. alcohols), and form highly toxic nitrous gases, especially when heated. Reaction could be explosive. Nitric acid could form ignition at reaction with organic substances! Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Risk analysis: HF and BOE Exposure to diluted HF or BOE can produce harmful health effects that may not be immediately apparent. Diluted HF or BOE penetrates the skin with no immediate pain. And then cause serious tissue and bone damage before pain begins. This attack could be inhibited by treatment with HF-Antidote Gel. Immedately flush the exposed area with water at least one min. Flush well but briefly. It is critical to apply antidote as soon as possible. Carefully remove contaminated clothing at once, wipe dry and apply HF-Antidote Gel to exposed area gently and freely. Aggressively massage the gel into the skin (wearing gloves) and continue to reapply and massage until pain and/or redness disappear or until medical treatment is available. Seek medical attention as soon as possible for all burns regardless of how minor they may appear initially. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

A. A. A. – Always Add Acid into the water rule Do not add water to an acid solution; instead, gradually add the acid to the water. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Risk analysis: Bases l Ammonium hydroxide, NH 4 OH l Potassium hydroxide, KOH l Developers: AZ 351 B(Na. OH), MF 312, MF 319… l TMAH (Tetra Methyl Ammonium Hydroxide) could produce toxic nitrous gases! Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Risk analysis: Oxidizers l Hydrogen peroxide, H 2 O 2 l Sodium persulfate, Na 2 S 2 O 3 l Ammonium peroxidesulfate, (NH 4)2 S 2 O 8 l Nitric acid, HNO 3 Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Symptoms: Acids, Bases, and Oxidizers After inhalation: Depending on the concentration of the chemical and length of time symptoms may result in corrosive attack on the respiratory passages and lungs. Exposure may produce upper airway oedema, respiratory failure, pulmonary oedema (lung water) and inflammation (pnemonitis). A person may get better but then worse again from 30 hours up to 1 week later. After skin contact: Contact with skin cause redness, pain, blistering, or severe tissue burns. After eye contact: Corrosive to eyes. Symptoms of redness, pain, blurred vision, and permanent eye damage can occur. Possibly delayed (up to one week), possible blindness. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

First aid measures: Acids, Bases and Oxidizers After inhalation: Remove to fresh air. Keep warm and resting. Get medical attention immediately. Report incident to safety responsible person. After skin contact: Immediately flush with water for at least 15 minutes and rinse thoroughly. Remove contaminated clothing. Get medical attention in case of symptoms. If skin contact results in severe tissue burns, have someone call 112 for prompt emergency transport while you continue flushing the affected area with water, or have someone to make arrangement for transport to nearest “akutintag”, emergency room unit. After eye contact: Immediately flush thoroughly with water continuously for at least 15 -30 minutes, forcibly hold eye open to ensure effective wash behind eyelids. Get medical attention immediately. Report incident to safety responsible person. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Risk analysis: Solvents l Cleaning solvents: Methanol, IPA, acetone. l Resists for optical and e-beam lithography. l Resist removers: Shipley Microposit Remover 1165 (NMP), MEK, DEK, and acetone. l Developers: Toluene, xylene, MIBK, and XP SU-8. l Resist thinners: Anisole, EC-solvent, cyclopentanone, and chlorobenzene. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Risk analysis: Solvents There is no safe way of heating up flammables! Because the vapours can travel a considerable distance, the source of ignition can be far away from the flammable container itself. Always make sure that your work bench has 100% exhaustion when working with flammables, and that flammable containers should be restored back to the flammables cabinet immediately after use. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Symptoms: Solvents After inhalation: Can cause irritation of eyes, nose and throat. Prolonged exposure can cause headache, sickness (nausea), confusion, drowsiness, convulsion and coma. After skin contact: Prolonged or repeated exposure may cause irritation, itching, skin dryness or cracking characterised by redness and inflammation. After eye contact: Vapours may cause severe irritation with redness, pain, tearing and inflammation. Splashes may cause eye damage. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

First aid measures: Solvents After inhalation: Remove to fresh air. Report incident to safety responsible person. Get medical attention in case of symptoms. After skin contact: Immediately wash with water and rinse thoroughly. Remove contaminated clothing. Get medical attention in case of symptoms. Report incident to safety responsible person. After eye contact: Immediately flush thoroughly with water continously for at least 15 -20 minutes, with eyelids held wide open during flushing. Get immediate medical attention. Report incident to safety responsible person. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

PPE, Personal Protective Equipment: Gloves l Put chemical protection gloves outside the disposable gloves before you start working with hazardous chemicals at the wet benches. l Inspect your chemical protection gloves carefully. If the gloves are discoloured or damaged, they should be disposed immediately. Rinse the gloves carefully before disposing them. l When your work in the process wet bench has been completed, the chemical protection gloves should be rinsed and put back to their designated place, without touching any surface outside the process wet bench. l Gloves should always be rinsed with water before handling wash bottles or other laboratory fixtures. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

PPE, Personal Protective Equipment: Eye protection IT IS MANDATORY TO WEAR SAFETY GLASSES IN THE LABORATORY! l Use apron and face shield when mixing or using strong acids, bases or oxidizers. l Put on face shield when you are wet etching. l Use apron and safety glasses when dicing materials and at CMP (Chemical Mechanical Polishing) machines. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Safety routines at MC 2 Processlabs l Do not leave your chemicals unattended. Clearly mark the content of your chemicals, your name, phone, and date plus time on a clean room note. l You are responsible for removing and disposing of your personal chemical containers when they are no longer in use. l Chemical containers, that are not clearly labelled, should be disposed immediately. Mark the container “ unknown content “ and contact the lab staff. l Put the cap back on each chemical bottle securely. Rinse and dry the outside of the bottle before returning it back to the storage. l Never mix chemicals without prior knowledge about the consequences! l You are responsible for the security when handling chemicals at your wet bench. Clean up your wet bench when you have finished your work. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

The MC 2 Process laboratory safety declaration Remember, you are responsible for your own safety, and that for others around you. MC 2 provides you with information, recommendations, and necessary resources for you to be able to do your work safely. It is up to you to ensure that you take appropriate precautions for your safety and your fellow lab members. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Clean Room Introduction and safety course

CHEMICALS (Svante Pålsson) l. Chemical supply to lab l. Chemical waste from the lab. 70

CHEMICAL SUPPLY TO THE LAB. l Please, order standard chemical by e-mail, a day ahead from kaija@chalmers. se l Special chemicals have to be requested and granted by MC 2. 71

CHEMICAL SUPPLY TO THE LAB. l Major stock in basement. 72

CHEMICAL SUPPLY TO THE LAB. l Minor stock for day use close to the lab. 73

CHEMICAL WASTE FROM THE LAB. l Waste has to be marked with adequate marking for disposal. 74

CHEMICAL WASTE FROM THE LAB. l Diluted chemicals can be disposed down the drains. Acid drains in wet benches. l Neutralization in basement. 75

CHEMICAL WASTE FROM THE LAB. l Solvent drain for acetone, and alcohol to tank. l Emergency drain to tank. l Tanks are emptied with a truck. 76

CHEMICAL WASTE FROM THE LAB. l Place empty chemical bottles on the trolley. l Please rinse the bottles with water before disposing. 77

CHEMICAL WASTE FROM THE LAB. l Material waste are disposed in special waste basket inside the lab. 78

Clean Room Introduction and safety course

“Safety First” l l l Chalmers safety plan and organisation 4. 6 MC 2 safety policy 4. 7 Alarms (gas, fire and process) 4. 7. 1 Evacuation of cleanroom 5. 1 First aid 5. 2 Safety gear 5. 3 Fire extinguisher 5. 4 -5. 5 Eye and body showers 5. 6 Antidote gel In case of an emergency Chemical spill l Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Wet bench training, 4. 4 -4. 5 l 1 hour hands on demonstration in lab. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Chalmers safety organisation l President – – a) information group b) catastrophe organisation l MC 2 Prefekt – a) Alarm levels l MC 2 lab manager – – a) work delegation b) Education Clean Room Introduction and safety course

http: //www. adm. chalmers. se/Intern/Soseng/general. html Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Clean Room Introduction and safety course
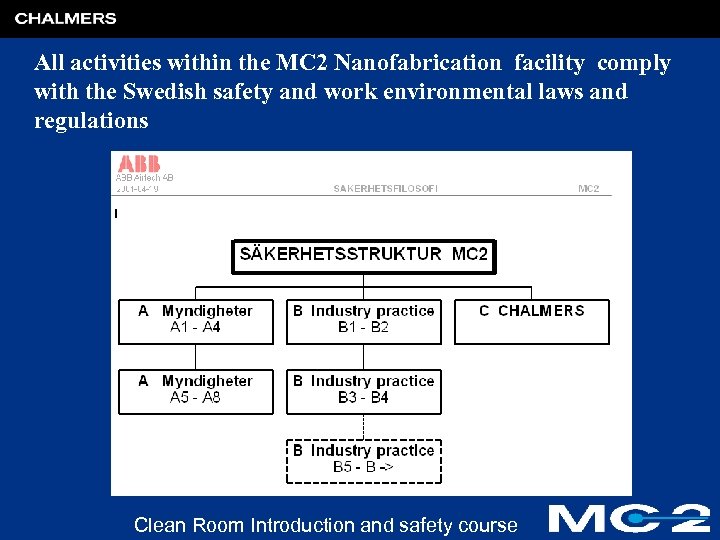
All activities within the MC 2 Nanofabrication facility comply with the Swedish safety and work environmental laws and regulations Clean Room Introduction and safety course

DVD- Safety in Cleanroom l Cleanroom hazards (fire, explosions, toxicity, physical l Hazardous materials (flammable, reactive, corrosive, poison/toxic) l Hazardous materials (handling & storage) l Dealing with emergencies (water based, foam, carbon dioxide, powder) Clean Room Introduction and safety course

ALARM SYSTEM l Smoke detector/ alarm l Fire sensors and alarms in wet bench units with solvents l Sprinkler system Clean Room Introduction and safety course

ALARMS l Fire alarm – acoustic signal and flashing red light ACTION: Evacuation of laboratories l Gas alarm – acoustic signal and flashing red light ACTION: Evacuation of laboratories l Process alarm – acoustic signal and flashing blue light ACTION: Contact the lab staff Clean Room Introduction and safety course

In case of emergency (fire, gas, etc)! l Manual Alarm – Push the knob to evacuationalarm; this also gives an alarm to Rescue service – Automatic alarm from fire, gas sensors l Rescue those who are in danger l Evacuate building l Call (00) 112 and inform about; – what has happened – if there any people locked in – who is calling ( see last page in lab manual) Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Meeting point after evacuation l In case of evacuation alarm! l Put out fire using extinguisher ONLY ”if it is possible without danger for your health) and you have the proper training l Use ”Fire choking cloth” l l l Evacuate from building via emergency exits. Local evacuation officers in house Do not use elevators at evacuation Close doors to minimize smoke spreading Point of assembly after evacuation from MC 2 (“VASA square”), wait for further information l Do not enter building again unless red alarm lamps has stopped flashing Clean Room Introduction and safety course

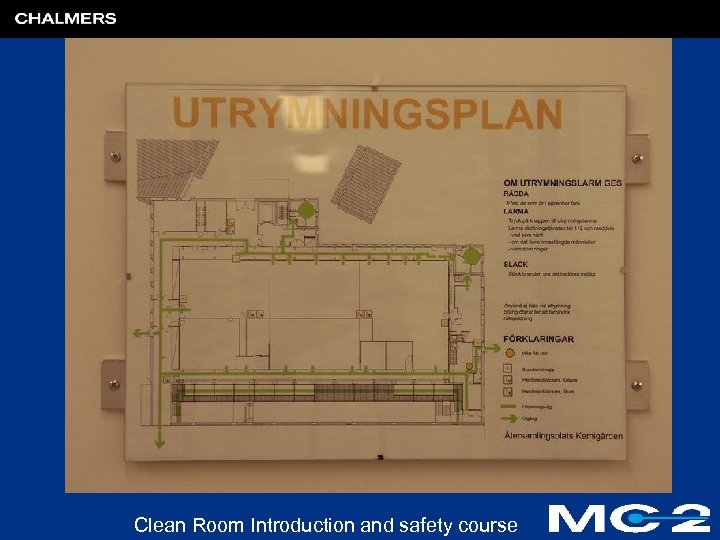
Preventive actions; what to know before entering laboratory!? l Look at evacuation plans (”close to exits”) and recognize evacuation exits l At least 2 escape ways from each position! Clean Room Introduction and safety course
Clean Room Introduction and safety course

First aid kit Eye and body showers Clean Room Introduction and safety course

In case of Fire extinguisher classes: A, B, C, D Foam, S (Skumsläckare, A+B); for wood, paper, gases, liquids, CO 2 , K (Kolsyresläckare; B) for gases, liquids and electrical equipment risk for choking Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Chemical Spill; l Isolate the area l Call the lab staff l If possible use absorbing material (is available in cupboard in Processlab ) l If you spill chemicals onto yourself, use the emergency showers and let somebody else take care of the items above. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Nanomaterial hazards l Nanomaterials (4. 2. 8) l Nanomaterials are applications with morphological features smaller than a one tenth of a micrometer in at least one dimension. Despite the fact that there is no consensus upon the minimum or maximum size of nanomaterials, with some authors restricting their size to as low as 1 to ~30 nm, a logical definition would situate the nanoscale between microscale (0. 1 micrometer) and atomic/molecular scale (about 0. 2 nanometers). l The hazards associated with handling of novel nanomaterials are still under debate, but first of all those new materials are not yet proven to be non-hazardous. We require that our users keep updated on information about the potential risks with their material, and using the appropriate precautions during handling. l A good recommendation is to start reading the following 2 links; l (http: //membership. acs. org/c/ccs/nano. htm) and the European project Nanosafe (http: //www. nanosafe. org/) Clean Room Introduction and safety course

Clean Room Introduction and safety course

l You are strongly encouraged to recommend changes that make the cleanroom facility; safer, cleaner, easier to use, or less expensive to maintain! l When in the cleanroom, be aware of your knowledge limitations. It is extremely important that you ask someone for help if you are unsure about the operation of these facilities. Clean Room Introduction and safety course

l. Laboratory tour; – Entering main cleanroom area; shoe protection/change, hair protection – Entering procedure for the Processlab 2 and visitors corridor(visitors gowning room), – Enter procedure for Processlab 1; handwash, new garments (hood, overall, shoes, personal hanger), gloves – Processlab 1; equipment layout, ventilation circulation, alarm system, emergency escape ways, eye and body showers, cloth/cushion for chemical spill – Undress cleanroom garment procedure – Exit from clean room zone Clean Room Introduction and safety course
3958df98c5823ed41ed50a58a5bbbe4d.ppt