e8d74ee2dbff832168712ed6d8e54075.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Welcome to Duke Hospital
Welcome to Duke Hospital
 Teaching Technology Teamwork Rebecca Johnson, RN, Lupino Washington, BSN Duke University Health System, Durham, NC
Teaching Technology Teamwork Rebecca Johnson, RN, Lupino Washington, BSN Duke University Health System, Durham, NC
 CCU Description • 16 bed cardiac intensive care unit • Major Diagnoses include • Cardiogenic shock • Acute myocardial infarctions • Cardiomyopathy • Unstable angina • Life threatening arrhythmias • Overflow of patients other than cardiac
CCU Description • 16 bed cardiac intensive care unit • Major Diagnoses include • Cardiogenic shock • Acute myocardial infarctions • Cardiomyopathy • Unstable angina • Life threatening arrhythmias • Overflow of patients other than cardiac
 CCU Staffing • Charge Nurses - act as resources to nurses and physicians • Charge Nurses do not take patients • The staff is 90% Registered Nurses • There are 60 RN’s in the CCU • Nurse patient ratio is 1: 1 to 1: 2
CCU Staffing • Charge Nurses - act as resources to nurses and physicians • Charge Nurses do not take patients • The staff is 90% Registered Nurses • There are 60 RN’s in the CCU • Nurse patient ratio is 1: 1 to 1: 2
 CCU Staffing Nurse Clinician • Liaison between the patient, family and healthcare team • Assists in end-of-life issues Patient Resource Manager • Manages discharge planning and insurance issues
CCU Staffing Nurse Clinician • Liaison between the patient, family and healthcare team • Assists in end-of-life issues Patient Resource Manager • Manages discharge planning and insurance issues
 CCU Staffing Attending physicians • Round morning and evening • Available 24 hours a day Cardiology fellow, resident, and intern • On the unit 24 hours a day Pharmacists • Available on the unit for rounds and consultation from 7: 00 AM to 11: 00 PM
CCU Staffing Attending physicians • Round morning and evening • Available 24 hours a day Cardiology fellow, resident, and intern • On the unit 24 hours a day Pharmacists • Available on the unit for rounds and consultation from 7: 00 AM to 11: 00 PM
 Patient Room Cardiac Care Unit
Patient Room Cardiac Care Unit
 Progressive Care Unit Description • Two 31 bed medical cardiology progressive care units • All beds have telemetry • Patient populations consist of • Unstable angina and post acute MI • Cardiomyopathy • Pre-heart transplants • Dysrhythmias • These units offer opportunities to use innovative technologies, participate in research based practice, and facilitate patient education
Progressive Care Unit Description • Two 31 bed medical cardiology progressive care units • All beds have telemetry • Patient populations consist of • Unstable angina and post acute MI • Cardiomyopathy • Pre-heart transplants • Dysrhythmias • These units offer opportunities to use innovative technologies, participate in research based practice, and facilitate patient education
 Progressive Care Unit
Progressive Care Unit
 Patient Room Progressive Care Unit
Patient Room Progressive Care Unit
 Typical Day on the CCU Nurse-to-nurse report using computerized charting
Typical Day on the CCU Nurse-to-nurse report using computerized charting
 Daily Rounds using computerized physician order entry • The entire team rounds daily on each patient • Every team member has input in creating the plan of care: Attending Fellows House staff Care nurse Clinical pharmacist Patient Resource Manager Respiratory therapist
Daily Rounds using computerized physician order entry • The entire team rounds daily on each patient • Every team member has input in creating the plan of care: Attending Fellows House staff Care nurse Clinical pharmacist Patient Resource Manager Respiratory therapist
 Nursing Contribution to Rounds • Update team on vital signs and hemodynamics • Relate patient response to medication (vasopressors and oral agents that have been titrated by nurse) • General changes in patient status • Input into the decision whether or not the patient is able to transfer to another unit or rehab facility • Identify patient and family concerns and questions
Nursing Contribution to Rounds • Update team on vital signs and hemodynamics • Relate patient response to medication (vasopressors and oral agents that have been titrated by nurse) • General changes in patient status • Input into the decision whether or not the patient is able to transfer to another unit or rehab facility • Identify patient and family concerns and questions
 Education, Leadership and Responsibility Nurses are responsible for monitoring patients and interpretation of information as well as operating a wide variety of equipment such as: • • Intra aortic balloon pumps Pulmonary artery catheters Continuous venous-venous hemodialysis Temporary transvenous pacemakers Ventilators Defibrillators/cardioversion Pericardial drains
Education, Leadership and Responsibility Nurses are responsible for monitoring patients and interpretation of information as well as operating a wide variety of equipment such as: • • Intra aortic balloon pumps Pulmonary artery catheters Continuous venous-venous hemodialysis Temporary transvenous pacemakers Ventilators Defibrillators/cardioversion Pericardial drains
 Routine Care
Routine Care
 Responsibilities and Nurse Driven Protocols • Titration of vasopressors to patient hemodynamics • Phase I Cardiac Rehab • Nurse Driven protocols • Heparin – titrate according to nomogram • Potassium – supplement according patient lab value • Magnesium - supplement according patient lab value • Tube feedings
Responsibilities and Nurse Driven Protocols • Titration of vasopressors to patient hemodynamics • Phase I Cardiac Rehab • Nurse Driven protocols • Heparin – titrate according to nomogram • Potassium – supplement according patient lab value • Magnesium - supplement according patient lab value • Tube feedings
 Staff Nurse using critical thinking skills to titrate vasopressor to patient hemodynamics
Staff Nurse using critical thinking skills to titrate vasopressor to patient hemodynamics
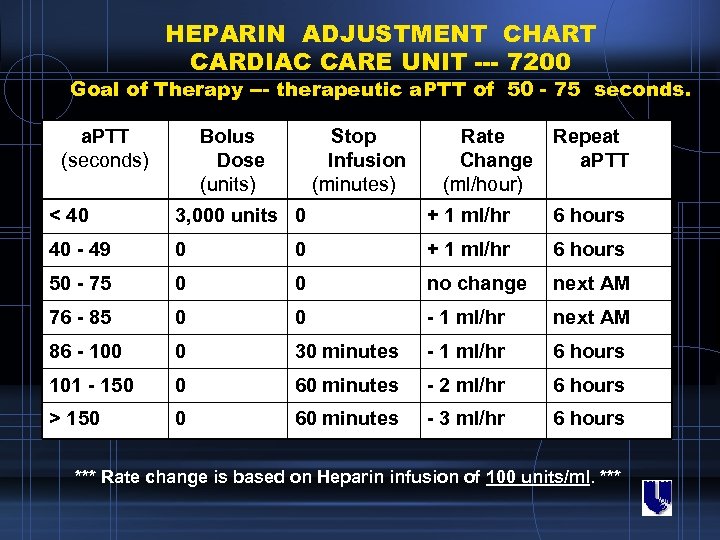 HEPARIN ADJUSTMENT CHART CARDIAC CARE UNIT --- 7200 Goal of Therapy --- therapeutic a. PTT of 50 - 75 seconds. a. PTT (seconds) Bolus Dose (units) Stop Infusion (minutes) Rate Change (ml/hour) Repeat a. PTT < 40 3, 000 units 0 + 1 ml/hr 6 hours 40 - 49 0 0 + 1 ml/hr 6 hours 50 - 75 0 0 no change next AM 76 - 85 0 0 - 1 ml/hr next AM 86 - 100 0 30 minutes - 1 ml/hr 6 hours 101 - 150 0 60 minutes - 2 ml/hr 6 hours > 150 0 60 minutes - 3 ml/hr 6 hours *** Rate change is based on Heparin infusion of 100 units/ml. ***
HEPARIN ADJUSTMENT CHART CARDIAC CARE UNIT --- 7200 Goal of Therapy --- therapeutic a. PTT of 50 - 75 seconds. a. PTT (seconds) Bolus Dose (units) Stop Infusion (minutes) Rate Change (ml/hour) Repeat a. PTT < 40 3, 000 units 0 + 1 ml/hr 6 hours 40 - 49 0 0 + 1 ml/hr 6 hours 50 - 75 0 0 no change next AM 76 - 85 0 0 - 1 ml/hr next AM 86 - 100 0 30 minutes - 1 ml/hr 6 hours 101 - 150 0 60 minutes - 2 ml/hr 6 hours > 150 0 60 minutes - 3 ml/hr 6 hours *** Rate change is based on Heparin infusion of 100 units/ml. ***
 Instructions for Heparin Nomogram For patients who received thrombolytic therapy: (ie, t. PA, TNK, r. PA) From 6 - 12 hours after start of thrombolytic agent ---1. Do NOT discontinue or decrease the infusion unless significant bleeding occurs or the a. PTT is > 120. 2. Adjust the infusion upward if a. PTT is < 50. 12 or more hours after start of thrombolytic agent ---Adjust Heparin using the entire chart. Deliver the bolus, stop the infusion and/or change the rate of infusion based on a. PTT result. For all patients who did NOT have thrombolytic therapy: Adjust Heparin using the entire chart. Deliver the bolus, stop the infusion, and/or change the rate of infusion based on a. PTT result. HO should weight, age and gender adjust the initial infusion rate to the patient. If patient has not reached therapeutic range after 2 adjustments are made using the chart, ask HO to write order for additional bolus or additional increase in drip rate, if appropriate.
Instructions for Heparin Nomogram For patients who received thrombolytic therapy: (ie, t. PA, TNK, r. PA) From 6 - 12 hours after start of thrombolytic agent ---1. Do NOT discontinue or decrease the infusion unless significant bleeding occurs or the a. PTT is > 120. 2. Adjust the infusion upward if a. PTT is < 50. 12 or more hours after start of thrombolytic agent ---Adjust Heparin using the entire chart. Deliver the bolus, stop the infusion and/or change the rate of infusion based on a. PTT result. For all patients who did NOT have thrombolytic therapy: Adjust Heparin using the entire chart. Deliver the bolus, stop the infusion, and/or change the rate of infusion based on a. PTT result. HO should weight, age and gender adjust the initial infusion rate to the patient. If patient has not reached therapeutic range after 2 adjustments are made using the chart, ask HO to write order for additional bolus or additional increase in drip rate, if appropriate.
 Nurse Physician Collaboration
Nurse Physician Collaboration
 Responding to Emergencies Nurses use critical thinking to pull together the patient assessment data, effects of medications and hemodynamic numbers to respond to emergency situations
Responding to Emergencies Nurses use critical thinking to pull together the patient assessment data, effects of medications and hemodynamic numbers to respond to emergency situations
 How are our nurses prepared to practice ?
How are our nurses prepared to practice ?
 Nursing Education AD – Associate degree – 2 years Diploma in Nursing – 3 years BSN – Bachelor of Science in Nursing – 4 years MSN – Master or Science in nursing – 2 -3 years NP – Nurse Practitioner CRNA – Certified Nurse Anesthetist CNS - Clinical Nurse Specialist MHA – Masters in Hospital Administration
Nursing Education AD – Associate degree – 2 years Diploma in Nursing – 3 years BSN – Bachelor of Science in Nursing – 4 years MSN – Master or Science in nursing – 2 -3 years NP – Nurse Practitioner CRNA – Certified Nurse Anesthetist CNS - Clinical Nurse Specialist MHA – Masters in Hospital Administration
 Men in Nursing
Men in Nursing
 Nursing Education Ph. D. – Doctorate in Nursing • Researchers • Administrators of practice • Educators Dr. Bradi Granger Heart Center Nurse Researcher
Nursing Education Ph. D. – Doctorate in Nursing • Researchers • Administrators of practice • Educators Dr. Bradi Granger Heart Center Nurse Researcher
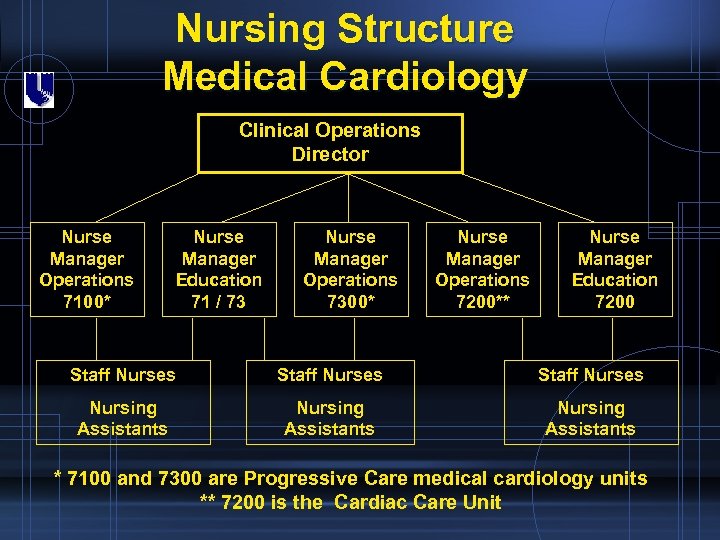 Nursing Structure Medical Cardiology Clinical Operations Director Nurse Manager Operations 7100* Nurse Manager Education 71 / 73 Nurse Manager Operations 7300* Nurse Manager Operations 7200** Nurse Manager Education 7200 Staff Nurses Nursing Assistants * 7100 and 7300 are Progressive Care medical cardiology units ** 7200 is the Cardiac Care Unit
Nursing Structure Medical Cardiology Clinical Operations Director Nurse Manager Operations 7100* Nurse Manager Education 71 / 73 Nurse Manager Operations 7300* Nurse Manager Operations 7200** Nurse Manager Education 7200 Staff Nurses Nursing Assistants * 7100 and 7300 are Progressive Care medical cardiology units ** 7200 is the Cardiac Care Unit
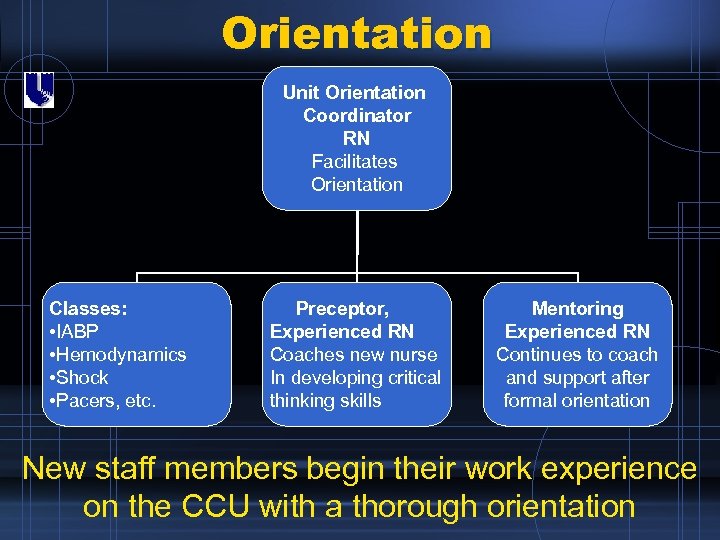 Orientation Unit Orientation Coordinator RN Facilitates Orientation Classes: • IABP • Hemodynamics • Shock • Pacers, etc. Preceptor, Experienced RN Coaches new nurse In developing critical thinking skills Mentoring Experienced RN Continues to coach and support after formal orientation New staff members begin their work experience on the CCU with a thorough orientation
Orientation Unit Orientation Coordinator RN Facilitates Orientation Classes: • IABP • Hemodynamics • Shock • Pacers, etc. Preceptor, Experienced RN Coaches new nurse In developing critical thinking skills Mentoring Experienced RN Continues to coach and support after formal orientation New staff members begin their work experience on the CCU with a thorough orientation
 Beginning the Clinical Ladder Orienting New Staff Nurses ( Clinical Nurse I )
Beginning the Clinical Ladder Orienting New Staff Nurses ( Clinical Nurse I )
 Clinical Ladder Program Advancement for the Staff Nurse
Clinical Ladder Program Advancement for the Staff Nurse
 Education, Leadership and Responsibility Nurses are responsible for many areas of their own practice: • Scheduling • Interviewing potential staff members • Create policies and procedures • Conduct yearly skills validation • Ongoing inservices and education • Evaluate new product for hospital use
Education, Leadership and Responsibility Nurses are responsible for many areas of their own practice: • Scheduling • Interviewing potential staff members • Create policies and procedures • Conduct yearly skills validation • Ongoing inservices and education • Evaluate new product for hospital use
 Teamwork Nurses have the additional responsibility to participate in hospital wide multidisciplinary committees • Mortality and Morbidity • Cardiovascular Medicine Performance Improvement • Cardiovascular Serviceline Council • Medical Directors meeting • Heart Center Discharge meeting
Teamwork Nurses have the additional responsibility to participate in hospital wide multidisciplinary committees • Mortality and Morbidity • Cardiovascular Medicine Performance Improvement • Cardiovascular Serviceline Council • Medical Directors meeting • Heart Center Discharge meeting
 How do nurses maintain their proficiency as well as learn new competencies? • Yearly skills revalidation on the unit • Unit inservices of new equipment and techniques • Hospital wide programs • Local Conferences – present as well as participate • National Conferences – present as well as participate
How do nurses maintain their proficiency as well as learn new competencies? • Yearly skills revalidation on the unit • Unit inservices of new equipment and techniques • Hospital wide programs • Local Conferences – present as well as participate • National Conferences – present as well as participate
 Nurses Presenting at National Critical Care Conference
Nurses Presenting at National Critical Care Conference
 Teamwork Education, experience, autonomy and responsibility prepare nurses to be competent and respected members of the healthcare team.
Teamwork Education, experience, autonomy and responsibility prepare nurses to be competent and respected members of the healthcare team.
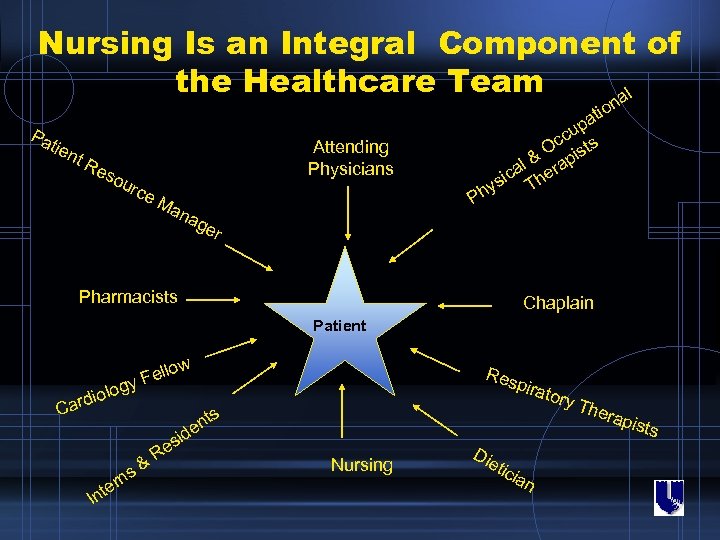 Nursing Is an Integral Component of the Healthcare Team al n o ati Pa tien Attending Physicians t. R eso u rce p cu s Oc ist & p al era ic ys Th h Ma P na ge r Pharmacists Chaplain Patient w olo ardi o Fell y g C e rn s& Re tory nts ide s Int Res pira Nursing Die tic ian The rapi sts
Nursing Is an Integral Component of the Healthcare Team al n o ati Pa tien Attending Physicians t. R eso u rce p cu s Oc ist & p al era ic ys Th h Ma P na ge r Pharmacists Chaplain Patient w olo ardi o Fell y g C e rn s& Re tory nts ide s Int Res pira Nursing Die tic ian The rapi sts
 Team Collaboration at Duke It’s More than just the doctors and nurses. . .
Team Collaboration at Duke It’s More than just the doctors and nurses. . .
 In addition to the healthcare team, we value families Family presence is important for the -being of our patients well
In addition to the healthcare team, we value families Family presence is important for the -being of our patients well
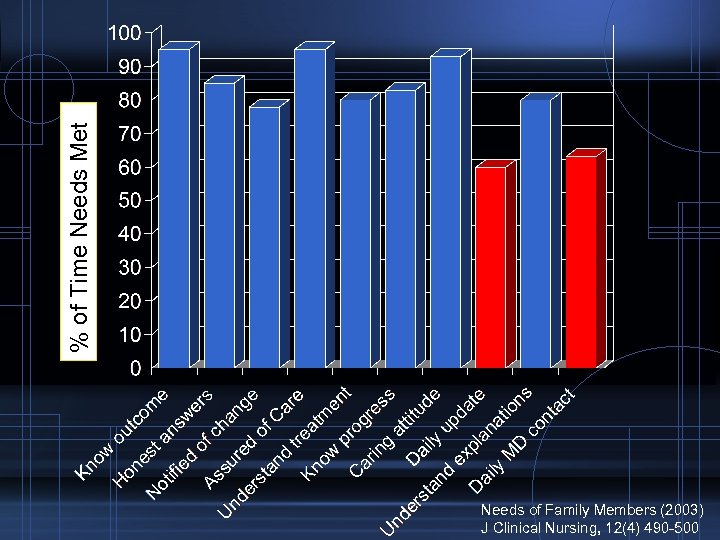 % of Time Needs Met Needs of Family Members (2003) J Clinical Nursing, 12(4) 490 -500
% of Time Needs Met Needs of Family Members (2003) J Clinical Nursing, 12(4) 490 -500
 Physicians speak with families daily Family Conference with Physician, Care Nurse and Charge Nurse
Physicians speak with families daily Family Conference with Physician, Care Nurse and Charge Nurse
 Family Visitation • Visiting hours are daily from morning until bedtime and are open, but not unlimited • Visitors are requested to use an intercom system to call back before entering the unit • Staff members have the right to ask family to wait before coming Yes, He is in room 7214. Mr. ve Can g ha n usi ors? Cla isit v
Family Visitation • Visiting hours are daily from morning until bedtime and are open, but not unlimited • Visitors are requested to use an intercom system to call back before entering the unit • Staff members have the right to ask family to wait before coming Yes, He is in room 7214. Mr. ve Can g ha n usi ors? Cla isit v
 If life support has been withdrawn, we encourage families to be present as much as they wish - 24 hours per day
If life support has been withdrawn, we encourage families to be present as much as they wish - 24 hours per day
 There are times when children are allowed to visit
There are times when children are allowed to visit
 Teaching, Technology, Teamwork Teaching, technology and team work have allowed Duke to successfully achieve extraordinary care for our patients and their families. and Through education, responsibility and autonomy, nurses have a strong impact on patient care and outcomes.
Teaching, Technology, Teamwork Teaching, technology and team work have allowed Duke to successfully achieve extraordinary care for our patients and their families. and Through education, responsibility and autonomy, nurses have a strong impact on patient care and outcomes.
 Duke Hospital achieved Magnet Status for excellence in Nursing Services in 2006 First Critical Care Unit in North Carolina to receive the Beacon Award for Excellence in Nursing practice
Duke Hospital achieved Magnet Status for excellence in Nursing Services in 2006 First Critical Care Unit in North Carolina to receive the Beacon Award for Excellence in Nursing practice
 Teamwork!
Teamwork!



