ce0ab5d770e9332eb06605a6ca672192.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Welcome to Department of Computer and Systems Sciences – DSV
Welcome to Department of Computer and Systems Sciences – DSV
 Introduction • Established in 1965 -1966 • Faculty of Social Sciences • Research, graduate and undergraduate education • Cooperation with society at large • Located in Kista Science City – one of the largest IT clusters in the world 2
Introduction • Established in 1965 -1966 • Faculty of Social Sciences • Research, graduate and undergraduate education • Cooperation with society at large • Located in Kista Science City – one of the largest IT clusters in the world 2
 We focus on bridging the gap between, on one hand information technology, on the other hand the social and the behavioural sciences and the humanities 3
We focus on bridging the gap between, on one hand information technology, on the other hand the social and the behavioural sciences and the humanities 3
 Our focus in the field is on design, construction and use of IT systems in their context – and on their relation to people, organizations and society 4
Our focus in the field is on design, construction and use of IT systems in their context – and on their relation to people, organizations and society 4
 DSV in approximate figures 2011 • • Turnover: 200 MSEK Number of employees: 211 (about 270 persons) Total number of students per year: 5400; 40% women Number of freshmen for larger course blocks: 800 Number of undergraduate students: 1 350 Number of master’s students: 200 Number of doctoral students: 73; 23 women 5
DSV in approximate figures 2011 • • Turnover: 200 MSEK Number of employees: 211 (about 270 persons) Total number of students per year: 5400; 40% women Number of freshmen for larger course blocks: 800 Number of undergraduate students: 1 350 Number of master’s students: 200 Number of doctoral students: 73; 23 women 5
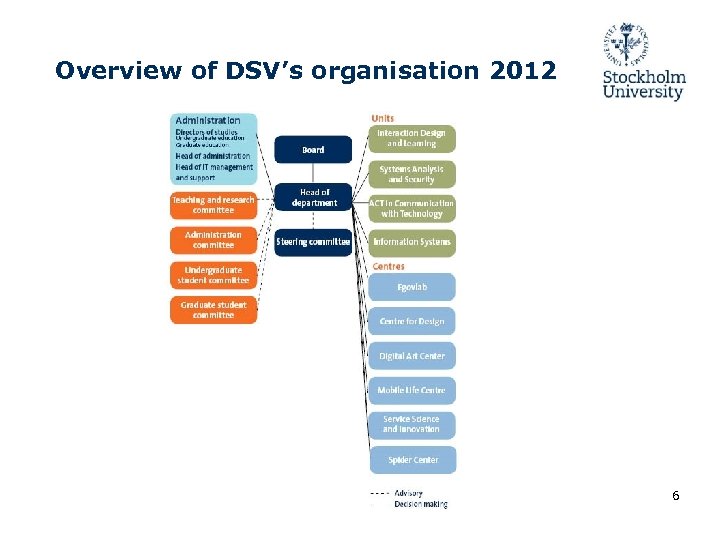 Overview of DSV’s organisation 2012 6
Overview of DSV’s organisation 2012 6
 Four strong profile areas • Conduct highly acclaimed research and have a leading position in four profile areas: – Artistic Technologies – E-government – ICT for Development (ICT 4 D) – Technology Enhanced Learning (TEL) 7
Four strong profile areas • Conduct highly acclaimed research and have a leading position in four profile areas: – Artistic Technologies – E-government – ICT for Development (ICT 4 D) – Technology Enhanced Learning (TEL) 7
 Research areas • Business Process Management and Enterprise Modeling • Consumer-oriented mobile services • Data and text mining • Digital games • Digital Systems Security • E-government and E-democracy • ICT for Development (ICT 4 D) • Health Informatics • Immersive Participation • Interaction design • IT Management • Language Technology • Risk and decision analysis • Services Science • Technology Enhanced Learning 8
Research areas • Business Process Management and Enterprise Modeling • Consumer-oriented mobile services • Data and text mining • Digital games • Digital Systems Security • E-government and E-democracy • ICT for Development (ICT 4 D) • Health Informatics • Immersive Participation • Interaction design • IT Management • Language Technology • Risk and decision analysis • Services Science • Technology Enhanced Learning 8
 Unit of Systems Analysis and Security (SAS) Key activities • decision and risk analysis • data mining • simulation of complex systems. • security, privacy and trust in systems • cyber security and forensics Cooperation and projects: • COINS: Controlled information security placing the reins of information security in the hands of the management and in cooperation with FOI and funded by MSO/KBM • University of Applied Sciences (CH), University of Ljubljana (SI), ENISA, . • Security, risk and sustainability in ICT 4 D • Building Cyber Scene Investigation lab 9
Unit of Systems Analysis and Security (SAS) Key activities • decision and risk analysis • data mining • simulation of complex systems. • security, privacy and trust in systems • cyber security and forensics Cooperation and projects: • COINS: Controlled information security placing the reins of information security in the hands of the management and in cooperation with FOI and funded by MSO/KBM • University of Applied Sciences (CH), University of Ljubljana (SI), ENISA, . • Security, risk and sustainability in ICT 4 D • Building Cyber Scene Investigation lab 9
 Unit of Interaction, Design and Learning (IDEAL) • Flexible learning • Virtual cases f learning & assessment • Simulation for learning • ICT 4 D • Cooperation and projects: – Sci-Pro: An IT system that supports and controls thesis process – Video/Hyper. Caster: Video storage and non-linear video in education – Virtual cases: Virtual patients, Virtual cases for assessment, Virtual cases in law – Simulation: Virtual scenarios for Rehabilltation of violent offenders – Cooperation with various partners such as Karolinska Institutet, Open University (UK), Delft, U. Of Eastern Finland, Copenhagen University, Stanford Univ etc. 10
Unit of Interaction, Design and Learning (IDEAL) • Flexible learning • Virtual cases f learning & assessment • Simulation for learning • ICT 4 D • Cooperation and projects: – Sci-Pro: An IT system that supports and controls thesis process – Video/Hyper. Caster: Video storage and non-linear video in education – Virtual cases: Virtual patients, Virtual cases for assessment, Virtual cases in law – Simulation: Virtual scenarios for Rehabilltation of violent offenders – Cooperation with various partners such as Karolinska Institutet, Open University (UK), Delft, U. Of Eastern Finland, Copenhagen University, Stanford Univ etc. 10
 Unit of ACT in Communication with Technology • Internet of Things – Sensors and more • Games and gaming – Mobile games – Social games – Game Development • Computer Science & Software Engineering 11
Unit of ACT in Communication with Technology • Internet of Things – Sensors and more • Games and gaming – Mobile games – Social games – Game Development • Computer Science & Software Engineering 11
 Unit for Information Systems (IS) • Information systems design and use • Business process management • Enterprise modelling • IT management • Service science and innovation • Cooperation and projects: – Open Services in Social Care – IMAIL-Intelligent e-mail answering service for e-Government – HEXAnord – HEalth te. Xt Analysis network in the Nordic and Baltic countries – SAMMET – Methods for Customer Interactive Service Design – Service oriented business models for enterprise systems 12
Unit for Information Systems (IS) • Information systems design and use • Business process management • Enterprise modelling • IT management • Service science and innovation • Cooperation and projects: – Open Services in Social Care – IMAIL-Intelligent e-mail answering service for e-Government – HEXAnord – HEalth te. Xt Analysis network in the Nordic and Baltic countries – SAMMET – Methods for Customer Interactive Service Design – Service oriented business models for enterprise systems 12
 Undergraduate education – B. Sc. programmes • Computer and Systems Sciences • Computer Science (and Software Engineering) • Computer Game Development – Construction • Computer Game Development – Design • Digital Media (with Dept. of Education and Dept. of Journalism, Media, and Communication) • Business Administration and Information Technology (with Dept. of Business Administration) • Enterprise Systems and Service Design • Interaction Design • Market Communication and Information Technology (with Dept. of Advertising and Public Relations) 13
Undergraduate education – B. Sc. programmes • Computer and Systems Sciences • Computer Science (and Software Engineering) • Computer Game Development – Construction • Computer Game Development – Design • Digital Media (with Dept. of Education and Dept. of Journalism, Media, and Communication) • Business Administration and Information Technology (with Dept. of Business Administration) • Enterprise Systems and Service Design • Interaction Design • Market Communication and Information Technology (with Dept. of Advertising and Public Relations) 13
 Graduate education – M. Sc. programmes • Computer and Systems Sciences (One year M. Sc. ) • Computer and Systems Sciences; incl. special tracks • Health Informatics (joint degree with Karolinska Institutet) • Information Systems Management • Strategic Management and Information Technology (with Dept. of Business Administration) • Information and Communication Technology for Development (ICT 4 D) • ICT, learning and educational design (with Dept. of Education) • Online IT Project Management (Distance M. Sc. program) 14
Graduate education – M. Sc. programmes • Computer and Systems Sciences (One year M. Sc. ) • Computer and Systems Sciences; incl. special tracks • Health Informatics (joint degree with Karolinska Institutet) • Information Systems Management • Strategic Management and Information Technology (with Dept. of Business Administration) • Information and Communication Technology for Development (ICT 4 D) • ICT, learning and educational design (with Dept. of Education) • Online IT Project Management (Distance M. Sc. program) 14
 Post-Graduate education • Computer and Systems Sciences • Man-Machine Interaction • IT and Learning (coming up) • – Ph. D programmes “Industry Ph. Ds” 15
Post-Graduate education • Computer and Systems Sciences • Man-Machine Interaction • IT and Learning (coming up) • – Ph. D programmes “Industry Ph. Ds” 15
 Collaborations within education • Stockholm Academy of Dramatic Arts • Karolinska Institutet • KTH Royal Institute of Technology – School of Information and Communication Technology • Royal Institute of Art • Royal College of Music in Stockholm • Stockholm University: – Dept. of Education – Dept. of Journalism, Media, and Communication – Dept. of Business Administration – Dept. of Advertising and Public Relations – Dept. for Musicology and Performance Studies – Dept. of Cinema Studies 16
Collaborations within education • Stockholm Academy of Dramatic Arts • Karolinska Institutet • KTH Royal Institute of Technology – School of Information and Communication Technology • Royal Institute of Art • Royal College of Music in Stockholm • Stockholm University: – Dept. of Education – Dept. of Journalism, Media, and Communication – Dept. of Business Administration – Dept. of Advertising and Public Relations – Dept. for Musicology and Performance Studies – Dept. of Cinema Studies 16
 International student exchange Numerous university-wide agreements and departemental agreements in: Europe: • Austria (3) • Bulgaria • Finland (2) • France (5) • Germany (3) • Greece • Lithuania • The Netherlands • Portugal • Switzerland • Turkey (4) Africa: • Morocco Asia: • China (5) 17
International student exchange Numerous university-wide agreements and departemental agreements in: Europe: • Austria (3) • Bulgaria • Finland (2) • France (5) • Germany (3) • Greece • Lithuania • The Netherlands • Portugal • Switzerland • Turkey (4) Africa: • Morocco Asia: • China (5) 17
 Spider – Swedish Program for ICT in Developing Regions • Sida funded • 2003– 2013 • Promotion and diffusion of Information and Communication Technology by building human capacity and enhancing knowledge for societal sustainability and progress in developing regions 18
Spider – Swedish Program for ICT in Developing Regions • Sida funded • 2003– 2013 • Promotion and diffusion of Information and Communication Technology by building human capacity and enhancing knowledge for societal sustainability and progress in developing regions 18
 Mobile Life Centre • Government funded (Vinnex) • 2007– 2017 • The Centre includes research on consumer-oriented mobile and ubiquitous services • Partners: Ericsson AB, Nokia Corporation, Microsoft Research, Telia. Sonera, City of Stockholm, Kista Science City, STING, Company P, Bambuser 19
Mobile Life Centre • Government funded (Vinnex) • 2007– 2017 • The Centre includes research on consumer-oriented mobile and ubiquitous services • Partners: Ericsson AB, Nokia Corporation, Microsoft Research, Telia. Sonera, City of Stockholm, Kista Science City, STING, Company P, Bambuser 19
 DAC – Digital Art Center • A real place where research and innovation in technology, media, and art are created and centered around the visibility and prominence of Kista • Established in 2010 • Key players in the DAC are Stockholm University, Atrium Ljungberg, Interactive Institute, Swedish ICT, Library Stockholm, Kista Science City and Dreamhack 20
DAC – Digital Art Center • A real place where research and innovation in technology, media, and art are created and centered around the visibility and prominence of Kista • Established in 2010 • Key players in the DAC are Stockholm University, Atrium Ljungberg, Interactive Institute, Swedish ICT, Library Stockholm, Kista Science City and Dreamhack 20
 Centre for Creation (Gestaltning) • Started in 2011 • Key players are Stockholm University, Royal Institute of Art, Stockholm Academy of Dramatic Arts, Royal College of Music in Stockholm, the City of Stockholm and Kista Theatre • Funded by City of Stockholm 21
Centre for Creation (Gestaltning) • Started in 2011 • Key players are Stockholm University, Royal Institute of Art, Stockholm Academy of Dramatic Arts, Royal College of Music in Stockholm, the City of Stockholm and Kista Theatre • Funded by City of Stockholm 21
 e. Govlab • Started in 2011 • A centre for excellence in e-Governance. • To research and develop technologies as well as methodologies and their implications for inclusive governance and citizen service delivery. 22
e. Govlab • Started in 2011 • A centre for excellence in e-Governance. • To research and develop technologies as well as methodologies and their implications for inclusive governance and citizen service delivery. 22
 Service Science and Innovation (SSI) • Established in 2010 • Research on the design of public services and service systems for more efficient public service, consequently contributing to enhanced democracy • Partners are i. a. IBM, SU Innovation and STING (Stockholm Innovation and Growth) 23
Service Science and Innovation (SSI) • Established in 2010 • Research on the design of public services and service systems for more efficient public service, consequently contributing to enhanced democracy • Partners are i. a. IBM, SU Innovation and STING (Stockholm Innovation and Growth) 23
 Cooperation with Industry • Program for Service Science and innovations (SSI) • Cooperation's with Stockholm Business Region, for instance, World Expo 2010 • Participated in Kista Science City's about 50 -100 visits to companies 2010 • Ph. D Forum • DSV Career, a thesis service for student collaborations • Collaboration with SU Innovation • Supports the DSV's alumni association DSV++ 24
Cooperation with Industry • Program for Service Science and innovations (SSI) • Cooperation's with Stockholm Business Region, for instance, World Expo 2010 • Participated in Kista Science City's about 50 -100 visits to companies 2010 • Ph. D Forum • DSV Career, a thesis service for student collaborations • Collaboration with SU Innovation • Supports the DSV's alumni association DSV++ 24
 Kista Theatre • Cooperation with Kista Theatre in projects such as: – Antigones dagbok – an ancient drama played outdoors with the audience´s mobile phones – I'm your body – a tool, a game and a game for mobile phones – Samtider 2010 – students creates their own stories – a form of personal maps – by using mobile phones and blogs as tools – Nere på jorden – in joint with DSV’s researchers, a digital platform was developed – a pedagogical tool for teachers to address the complex issues before and after the play 25
Kista Theatre • Cooperation with Kista Theatre in projects such as: – Antigones dagbok – an ancient drama played outdoors with the audience´s mobile phones – I'm your body – a tool, a game and a game for mobile phones – Samtider 2010 – students creates their own stories – a form of personal maps – by using mobile phones and blogs as tools – Nere på jorden – in joint with DSV’s researchers, a digital platform was developed – a pedagogical tool for teachers to address the complex issues before and after the play 25
 IT-ikapp • Cooperation with Kista folkhögskola in the project IT -ikapp • Goal: to reduce the digital divide and contribute to the digitally excluded groups in the community so they would be able to find the way to studies at university level • IT-ikapp has resulted in a handbook for computer use in Swedish, Arabic and Somali languages 26
IT-ikapp • Cooperation with Kista folkhögskola in the project IT -ikapp • Goal: to reduce the digital divide and contribute to the digitally excluded groups in the community so they would be able to find the way to studies at university level • IT-ikapp has resulted in a handbook for computer use in Swedish, Arabic and Somali languages 26


