0726e99b7dae271324cdecef1a6f99a3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Welcome to CMPE 003 Personal Computers: Hardware and Software Dr. Chane Fullmer Fall 2002 UC Santa Cruz October 9, 2002
Welcome to CMPE 003 Personal Computers: Hardware and Software Dr. Chane Fullmer Fall 2002 UC Santa Cruz October 9, 2002
 Class Information Midterm #1 – This Friday, October 11, 2002. – Covers Chapters 1 through 5. – Bring you Student ID. – Multiple choice • Requires Scantron #F-1712 -ERI-L (pink) • ~50 questions – No makeups after the fact October 9, 2002 2
Class Information Midterm #1 – This Friday, October 11, 2002. – Covers Chapters 1 through 5. – Bring you Student ID. – Multiple choice • Requires Scantron #F-1712 -ERI-L (pink) • ~50 questions – No makeups after the fact October 9, 2002 2
 Assignments Homework #3 – Due October 18 – Design your own Webpage – Keep in mind -- • The world at large will see your page • Don’t put private or sensitive information on your Webpage. – Details and sample – see class page – http: //www. soe. ucsc. edu/classes/cmpe 003/Fal l 02/ October 9, 2002 3
Assignments Homework #3 – Due October 18 – Design your own Webpage – Keep in mind -- • The world at large will see your page • Don’t put private or sensitive information on your Webpage. – Details and sample – see class page – http: //www. soe. ucsc. edu/classes/cmpe 003/Fal l 02/ October 9, 2002 3
 Input and Output: The User Connection Chapter 5 Part B October 9, 2002
Input and Output: The User Connection Chapter 5 Part B October 9, 2002
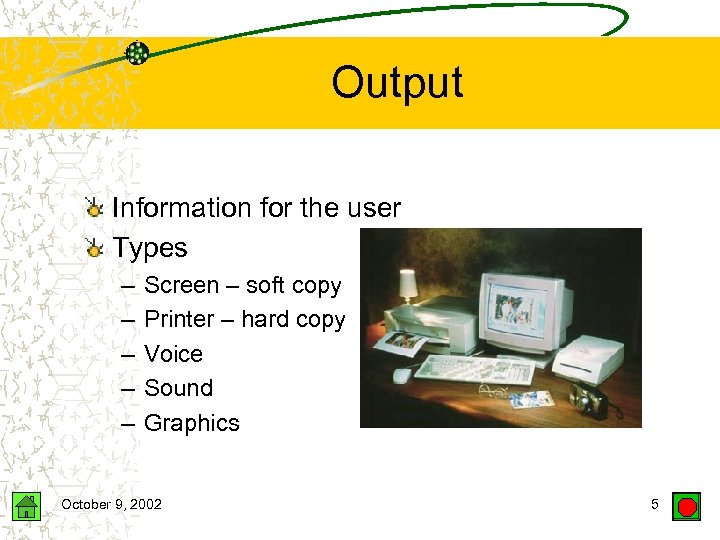 Output Information for the user Types – – – Screen – soft copy Printer – hard copy Voice Sound Graphics October 9, 2002 5
Output Information for the user Types – – – Screen – soft copy Printer – hard copy Voice Sound Graphics October 9, 2002 5
 Monitor (screen) Data that is entered appears on the screen Screen is part of the monitor October 9, 2002 6
Monitor (screen) Data that is entered appears on the screen Screen is part of the monitor October 9, 2002 6
 Monitor Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Flat panel display Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Gas Plasma Display October 9, 2002 7
Monitor Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Flat panel display Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Gas Plasma Display October 9, 2002 7
 CRT Raster scanning Sweeping electron beams across the back of the screen Phosphorous coating on back of screen Glows when hit by a beam of electrons Phosphorous loses glow and image fades and flickers Image must be continually refreshed October 9, 2002 8
CRT Raster scanning Sweeping electron beams across the back of the screen Phosphorous coating on back of screen Glows when hit by a beam of electrons Phosphorous loses glow and image fades and flickers Image must be continually refreshed October 9, 2002 8
 CRT Refresh rate / scan rate Number of times electron beams refreshes the screen Process also used for television 80 -100 times per second adequate for clear screen image – 60 Hz is problematic – Why? ? October 9, 2002 9
CRT Refresh rate / scan rate Number of times electron beams refreshes the screen Process also used for television 80 -100 times per second adequate for clear screen image – 60 Hz is problematic – Why? ? October 9, 2002 9
 CRT Interlaced vs. Non-interlaced Interlaced – – – Refresh every other line on each pass Lower refresh rate without flicker Good for fixed graphics Causes flutter with animated graphics Inexpensive Non-interlaced – Refresh every line on each pass – Typical of screens sold today October 9, 2002 10
CRT Interlaced vs. Non-interlaced Interlaced – – – Refresh every other line on each pass Lower refresh rate without flicker Good for fixed graphics Causes flutter with animated graphics Inexpensive Non-interlaced – Refresh every line on each pass – Typical of screens sold today October 9, 2002 10
 CRT Color vs. Monochrome Color – Typical monitor sold today Monochrome – Green or amber on a contrasting background – Less expensive than color – Typically used on terminals October 9, 2002 11
CRT Color vs. Monochrome Color – Typical monitor sold today Monochrome – Green or amber on a contrasting background – Less expensive than color – Typically used on terminals October 9, 2002 11
 CRT Resolution Clarity of image Pixel (Picture element) – – Dot on screen Is addressable Can be illuminated More pixels means higher resolution Dot pitch – Distance between dots – Smaller distance means better quality image October 9, 2002 12
CRT Resolution Clarity of image Pixel (Picture element) – – Dot on screen Is addressable Can be illuminated More pixels means higher resolution Dot pitch – Distance between dots – Smaller distance means better quality image October 9, 2002 12
 CRT Graphics Card/Graphics Adapter Board Plugs into expansion slot on motherboard Graphics card and monitor must be compatible for high quality image October 9, 2002 13
CRT Graphics Card/Graphics Adapter Board Plugs into expansion slot on motherboard Graphics card and monitor must be compatible for high quality image October 9, 2002 13
 CRT Size Measured diagonally Typical sizes – Office user: 15 -17 inch – High-powered graphics user: 19 inch – High-end monitors: 21 inches and up Larger size – More expensive – More space on desktop – Reduces eye strain October 9, 2002 14
CRT Size Measured diagonally Typical sizes – Office user: 15 -17 inch – High-powered graphics user: 19 inch – High-end monitors: 21 inches and up Larger size – More expensive – More space on desktop – Reduces eye strain October 9, 2002 14
 Graphics Standards Help insure that the products work together PCs Monitor Graphics boards Software October 9, 2002 15
Graphics Standards Help insure that the products work together PCs Monitor Graphics boards Software October 9, 2002 15
 Graphics Standards SVGA (Super VGA) – Resolution – 800 x 600, 1024 x 768, 1280 x 1024, 1600 x 1200 pixels – 16 million colors – Number of colors displayed simultaneously limited by amount of video memory XGA (Extended Graphics Array) – High resolution – Supports more simultaneous colors – Allows non-interlaced monitors October 9, 2002 16
Graphics Standards SVGA (Super VGA) – Resolution – 800 x 600, 1024 x 768, 1280 x 1024, 1600 x 1200 pixels – 16 million colors – Number of colors displayed simultaneously limited by amount of video memory XGA (Extended Graphics Array) – High resolution – Supports more simultaneous colors – Allows non-interlaced monitors October 9, 2002 16
 Flat-panel Screens Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Primarily on laptops Moving to desktop Skinny (depth) regardless of size October 9, 2002 17
Flat-panel Screens Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Primarily on laptops Moving to desktop Skinny (depth) regardless of size October 9, 2002 17
 Flat-panel Screens Crisp, brilliant images Easy on eyes No flicker Full dimension is useable More expensive that CRT monitors October 9, 2002 18
Flat-panel Screens Crisp, brilliant images Easy on eyes No flicker Full dimension is useable More expensive that CRT monitors October 9, 2002 18
 Flat-panel Screens Active Matrix – Thin-film transistor technology (TFT) – Transistors for each pixel – Brighter image – Viewable from an angle Passive Matrix – Fewer transistors – Cheaper – Less power – Images can appear fuzzy October 9, 2002 19
Flat-panel Screens Active Matrix – Thin-film transistor technology (TFT) – Transistors for each pixel – Brighter image – Viewable from an angle Passive Matrix – Fewer transistors – Cheaper – Less power – Images can appear fuzzy October 9, 2002 19
 Printers Produce information on paper Orientation – Portrait – Landscape Methods of printing – Impact – Nonimpact October 9, 2002 20
Printers Produce information on paper Orientation – Portrait – Landscape Methods of printing – Impact – Nonimpact October 9, 2002 20
 Impact Printers Line printer Dot-matrix printer One line at a time High volume Low quality One character at a time October 9, 2002 21
Impact Printers Line printer Dot-matrix printer One line at a time High volume Low quality One character at a time October 9, 2002 21
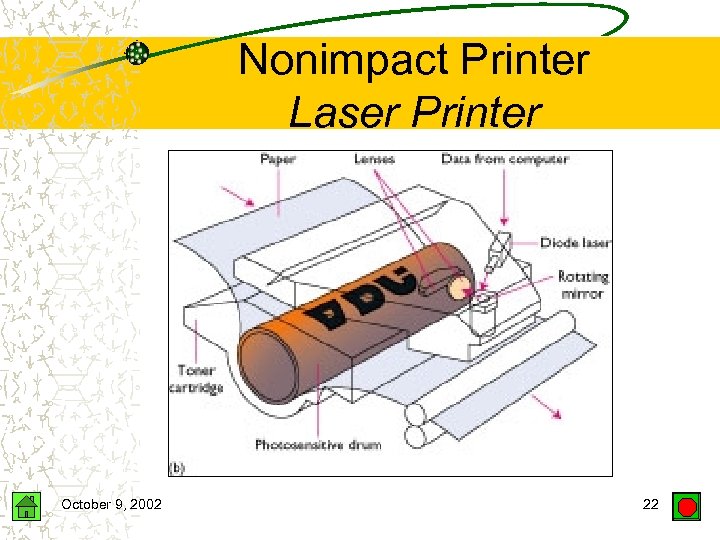 Nonimpact Printer Laser Printer October 9, 2002 22
Nonimpact Printer Laser Printer October 9, 2002 22
 Nonimpact Printer Laser Printer Transfers images to paper using a light beam Prints one page at a time 600 -1200 dpi – High quality Speed – Personal laser printers: 8 -10 ppm – Network laser printers: 35 -50 ppm – High-volume laser printers: up to 1000 ppm Black & white / Color October 9, 2002 23
Nonimpact Printer Laser Printer Transfers images to paper using a light beam Prints one page at a time 600 -1200 dpi – High quality Speed – Personal laser printers: 8 -10 ppm – Network laser printers: 35 -50 ppm – High-volume laser printers: up to 1000 ppm Black & white / Color October 9, 2002 23
 Nonimpact Printer Ink-jet Printer Spray ink at paper Black & white / Color Excellent graphics Good quality Slower than laser October 9, 2002 24
Nonimpact Printer Ink-jet Printer Spray ink at paper Black & white / Color Excellent graphics Good quality Slower than laser October 9, 2002 24
 Nonimpact Printer Choose based upon: Speed Quality Black & white vs. color Price October 9, 2002 25
Nonimpact Printer Choose based upon: Speed Quality Black & white vs. color Price October 9, 2002 25
 Sound Creates multimedia output Multiple sight and sound effects Speakers Sound card October 9, 2002 26
Sound Creates multimedia output Multiple sight and sound effects Speakers Sound card October 9, 2002 26
 Voice Output Speech Synthesis Enables machines to talk to people Types – Voice synthesizers – Voice output devices – Audio-response units Converts data in storage to vocalized sounds Synthesis by analysis – human sounds are stored and reproduced as needed Synthesis by rule – creates artificial speech October 9, 2002 27
Voice Output Speech Synthesis Enables machines to talk to people Types – Voice synthesizers – Voice output devices – Audio-response units Converts data in storage to vocalized sounds Synthesis by analysis – human sounds are stored and reproduced as needed Synthesis by rule – creates artificial speech October 9, 2002 27
 Voice Output Speech synthesis Uses Automobiles Telephone surveys Catalog order is ready Your payment is late reminder Santa Cruz Public Library – Overdue notices October 9, 2002 28
Voice Output Speech synthesis Uses Automobiles Telephone surveys Catalog order is ready Your payment is late reminder Santa Cruz Public Library – Overdue notices October 9, 2002 28
 Music and Other Sounds MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) – Communicates between MIDI devices and computer – Rules that produce and process digital music signals – MIDI information tells synthesizer • When to start and stop playing a note • Volume • Modulation Software is available for composing and editing per MIDI standard October 9, 2002 29
Music and Other Sounds MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) – Communicates between MIDI devices and computer – Rules that produce and process digital music signals – MIDI information tells synthesizer • When to start and stop playing a note • Volume • Modulation Software is available for composing and editing per MIDI standard October 9, 2002 29
 Terminals Device that provides input and output capabilities Dumb terminal – Keyboard and monitor – Connects to host for processing Intelligent terminal – Keyboard, monitor, memory, and processor – Connects with host Point-of-sale terminal (POS) – Input and output device – Captures retail data October 9, 2002 30
Terminals Device that provides input and output capabilities Dumb terminal – Keyboard and monitor – Connects to host for processing Intelligent terminal – Keyboard, monitor, memory, and processor – Connects with host Point-of-sale terminal (POS) – Input and output device – Captures retail data October 9, 2002 30
 Computer Graphics Business Education Science Sports Computer art Entertainment October 9, 2002 31
Computer Graphics Business Education Science Sports Computer art Entertainment October 9, 2002 31
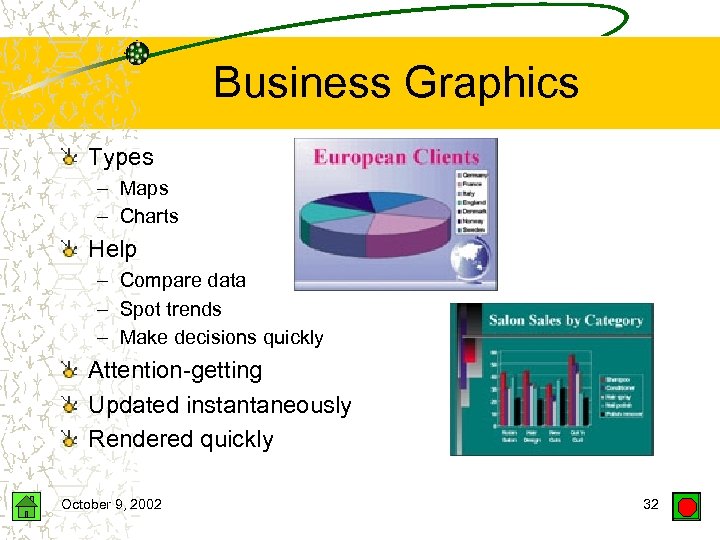 Business Graphics Types – Maps – Charts Help – Compare data – Spot trends – Make decisions quickly Attention-getting Updated instantaneously Rendered quickly October 9, 2002 32
Business Graphics Types – Maps – Charts Help – Compare data – Spot trends – Make decisions quickly Attention-getting Updated instantaneously Rendered quickly October 9, 2002 32
 Video Graphics Animated graphics Prepared one frame at a time Examples – Animated films • Monster’s Inc. (Pixar) – Commercials without humans – Arcade games October 9, 2002 33
Video Graphics Animated graphics Prepared one frame at a time Examples – Animated films • Monster’s Inc. (Pixar) – Commercials without humans – Arcade games October 9, 2002 33
 CAD/CAM Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing CAD – Computer Aided Design – Software creates 2 -D and 3 -D designs CAM – Computer Aided Manufacturing – Controls production equipment CIM (Computer Integrated Manufacturing) – Bridge between design and manufacturing – CAD/CAM integrated into manufacturing process – Provides balanced, efficient production process October 9, 2002 34
CAD/CAM Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing CAD – Computer Aided Design – Software creates 2 -D and 3 -D designs CAM – Computer Aided Manufacturing – Controls production equipment CIM (Computer Integrated Manufacturing) – Bridge between design and manufacturing – CAD/CAM integrated into manufacturing process – Provides balanced, efficient production process October 9, 2002 34
 Ethics and Data Computer data can be – Used – Sold – Altered What is legal? What can you trust? October 9, 2002 35
Ethics and Data Computer data can be – Used – Sold – Altered What is legal? What can you trust? October 9, 2002 35
 October 9, 2002 36
October 9, 2002 36


