a58c2c1d6f84bf7a654c245bcd1a3062.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Welcome to class of International Distribution by Dr. Satyendra Singh University of Winnipeg Canada

International Distribution • Distribution Structure – Traditional – Modern – Retail Giants • Distribution Patterns – General – Retail

Distribution Structure… • Difference Between Domestic and Foreign Structure – – • PEST Super-efficient system in the USA vs. highly complex in Japan Traditional Distribution Structure – – – – Import-oriented structure High price, small no of affluent customers Sellers market demand exceed supply Absence of cars and telephones Local monopoly of small stores Buy daily in developing country vs bi-weekly in Canada Intermediaries do not perform specific activities Import-wholesalers perform marketing function • Advertising, marketing research, warehousing, financing, storage
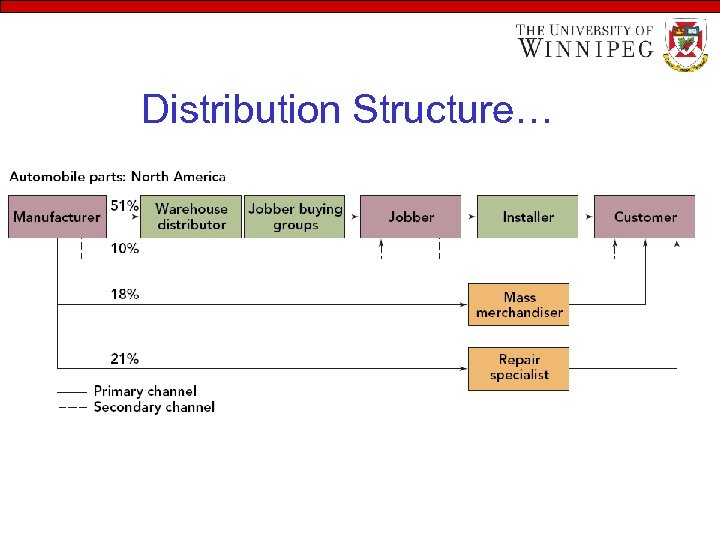
Distribution Structure…
Distribution Structure… • Japanese Channel Structure – – Small intermediaries and dealers Manufacturers control the channel Business philosophy is rooted in the unique culture Laws protect small retailers
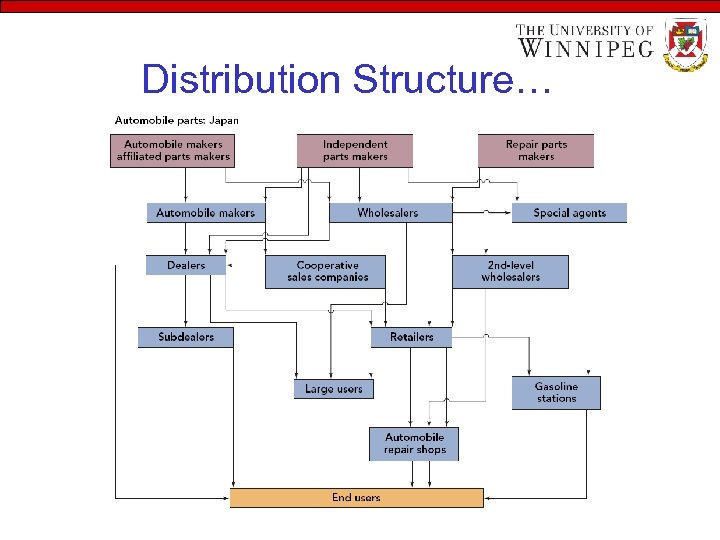
Distribution Structure…
Distribution Structure… • Modern Channel Structure – – Change in discounting, self-service, mass merchandizing, return policy… Change in direct marketing • – – – Wal-Mart, Carrefour (France), Praktikar (Germany), Ikea (Sweden) Higher margin in EU than US Internet-based system for ordering and delivering (low cost, efficient) • • – – Door-to-door selling, hypermarkets, shopping malls, catalogue, Internet GM, Ford, Nissan, Renault and Daimler. Chrysler www. covisint. com Roebuck and Carrefour www. gnx. com Brick-mortar eg. Dell, Brick-click eg Amazon, DHL, UPS Convenience store as a pickup points for web-orders

Distribution Structure • Retail Giants Structure – – – Retailers cannot export except by Internet Wal-Mart, Mc. Donald’s, Home Depot take risk in foreign markets Europeans: quick to enter foreign market, emphasis on being first, retail strategy, local needs and taste Americans: exploit domestic market first, emphasis on efficiency, standardization and value to customers International retailers have advantages over local retailers • • • World-class business processes Technology Financing Organizational capabilities Greater buying power Superior service…
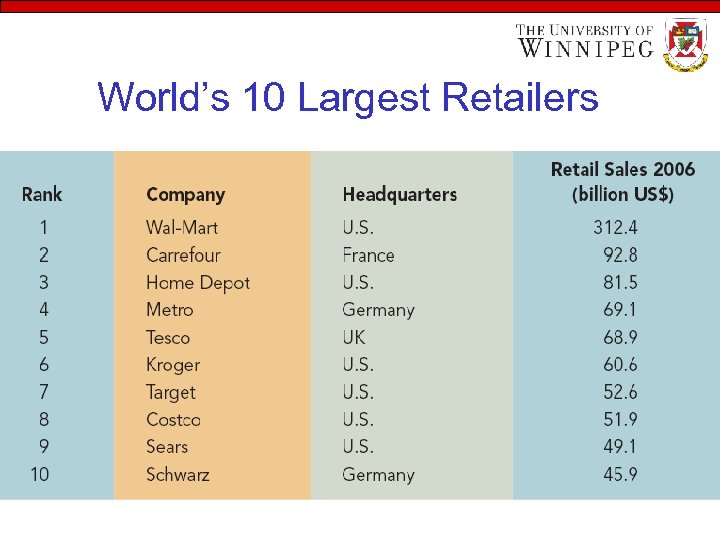
World’s 10 Largest Retailers

Distribution Pattern… • General Pattern – – Foreign channels are not the same as domestic channels Intermediary services are different • – Line breadth • • – – – – Storage and wait for customers to come and see them, India, Egypt Dealing-only narrow lines Requires government license Cost and margin Shorter channel for industrial or expensive goods Inverse relationship b/w length of channel and size of purchases Non-existent channels – selling on the roads! Blocked channels – competitors or relationships Power and competition – large whole sellers finance downstream Limited stocking – pickup from factory/distributor, if possible
Distribution Pattern • Retail Pattern – – Product lines: narrow (Italy, Morocco) vs. broad (Japan) Size pattern • • • – Direct marketing – mail, tel, door-to-door • – No of person served per retailer– higher in developed countries May be difficult to reach so many small retailers across a country Depends of economic development – single cigarette Usually best for developed economy, but Eastern European gaining popularity; e. g. , Amway Resistance to change • • Government attitude Local retailers need to compete – – – Product selection Greater convenience Customer service Liberal store hours Retailers cannot close/open stores at their wish
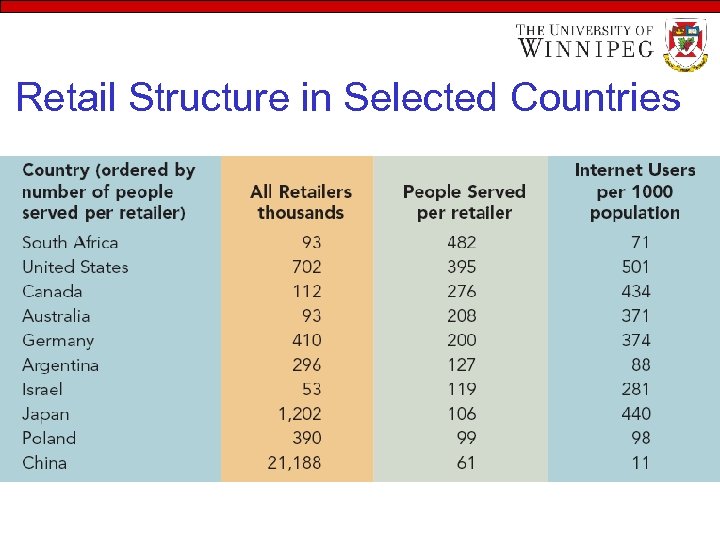
Retail Structure in Selected Countries
a58c2c1d6f84bf7a654c245bcd1a3062.ppt