cd5879cc8c9509fd68eb3cbbd6b89d2a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Welcome to class of Bottom of the Pyramid Dr. Satyendra Singh Professor, Marketing and International Business University of Winnipeg Canada s. singh@uwinnipeg. ca http: //abem. uwinnipeg. ca www. abem. ca/conference

Opportunity for growth • 7 b people • 2 b can afford good products • 5 b Bottom of Pyramid (BOP) o We need to cater BOP and develop market oriented products accordingly o Emerging markets o Developing countries o Moral responsibility to cater BOP! o Because they’re denied resources and opportunities 2
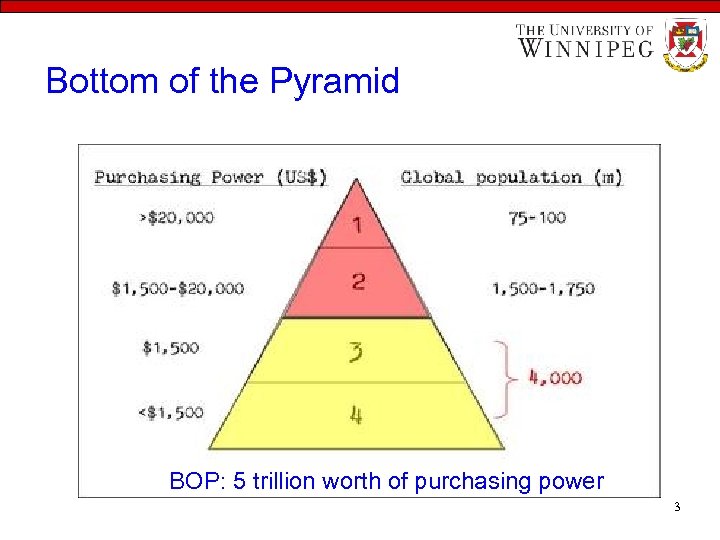
Bottom of the Pyramid BOP: 5 trillion worth of purchasing power 3

Marketing Strategies for EMs… • Need 2 strategies – Urban Global strategy is applicable • Consumers prefer global brands to local brand • Global brand equates to quality and prestige • Communicates sophistication and modernity • Admire HIG lifestyle and the products that symbolize that • Large cities have advanced distribution channels • HIG customers are less price sensitive • Serves as social distinction • Firms do not need to be based in developed countries • Concept of 3 rd world countries multinationals – E. g. Nando’s fast food from Africa 4 Now in +30 countries

Marketing Strategies for EMs • Bottom of the pyramid strategy – LIG radically different • Low price/value focused segment Tata Nano – Less features, toothbrush with no angles (i. e new design is needed) • No need to focus western markets in the beginning • Satisfy needs of the mass markets – Mahindra and Mahindra tractors, India – Ranbaxy pharmaceuticals, India – Orascom telecom, Egypt – Embraer aerospace, Brazil • These firms have learned to make a profit at prices unheard of the developed countries due to mass marketing at low $ 5

Successful firms from emerging markets • Acer • Bharti Airtel • Hailer Successful industries: Telecommunications • Lenovo Fast-moving consumer goods • LG Pharmaceuticals • QQ • Samsung • TATA move from OEM (1 -5% margin) to leadership position (+40% margin) 6

Barriers in BOP markets… • Distribution costs ↑ 7

Barriers in BOP markets… 8

Barriers in BOP markets • • Scattered villages service cost is high for durables Difficult to penetrate (+5%) remote villages Small scale growers are decentralized Uncertain cash flow BOP cannot pay upfront/poor Local knowledge and local trust Mismatched priorities clean water vs cell phone Difficult to predict demand China/child education Local knowledge and Trust microfinance Low margin and high volume difficult to achieve 9

How to ↓ distribution costs • Get local input (raw material…) • Organize the suppliers in groups • Coca-Cola in Uganda and Kenya for its juice organizes small farmers, gives them training • Wal-mart in India to make cold storage • Use technology for delivery, if possible • Use existing network of distribution post office and Western Union 10

How to ↑ cash flow • It is ok to borrow (credit) to pay western culture • University fee, car loan, house mortgages… • ↓ upfront payment • Use sachet retail strategy • Even 50 -kg fertilizer bag is sold in 5 kg, eg. • Pay-per-use Cell phone pay-as-go, irrigation pumps in India, clean drinking water in Philippines • Installment payment in India to buy gold 11

Sachet distribution in BOP markets 12

Standardization and Specialization: Successful low-Cost providers to BOP Economy of scale, very basic 13

Innovation: Reverse engineering TATA Nano: $3, 000 14

15

16

Bundling: tooth brush, paste, soap 17

Not Free in BOP Yet But Will Be Soon 18

Need to optimize value addition Commodity 1₡-2₡ Goods 5₡-25₡ Service 75₡-$1. 5 Experience $2 -$2. 50 The BOP segment may not be brand conscious yet. 19
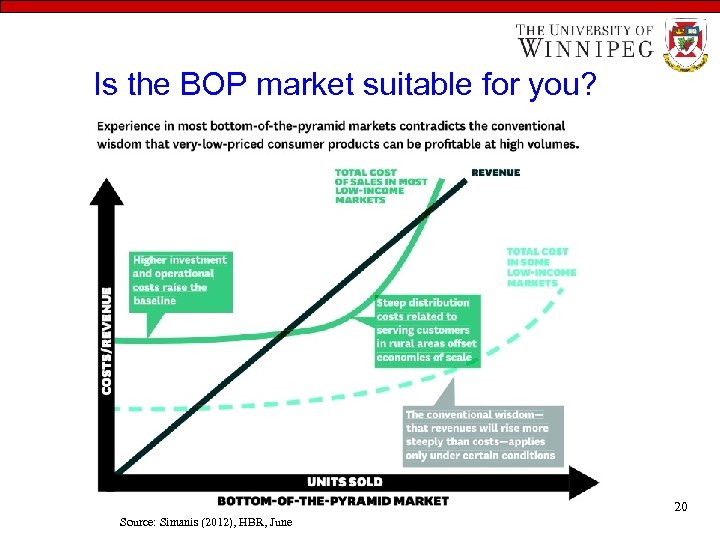
Is the BOP market suitable for you? 20 Source: Simanis (2012), HBR, June

Strategy implementation in EMs • Leadership more involved – Socioeconomic • Low formal education and high unemployment – Culture • Highly embedded and hierarchical, risk avoidance • Organizational structure – More centralized and formalized is appropriate – Small team, and group reward, collective society • Intraorganizational relations – Social and relational identities • Rank, status, self esteem, well being, relations • Top managers available physically for guidance • Learning 21

Five myths about EM! • EM are technology backwaters – I. e. Use outdated technologies; may not be true in case of cell phones • EM consumers won’t pay premium for brands – Brands affect preferences • EM cannot afford technology purchases – May not true in case of BRIC countries • Tech. from mature markets will succeed in EM – Develop new product with relevant feature – Nokia phone in India flashlight, individual call tracking for shared use of phones, multiple address book • EM consumers focus on products, not services 22

Where are Emerging Markets? Emerging Markets Trading Blocks • Asia – Association of South. East Asian Nations (ASEAN) – Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) • Africa – Economic Council of West African States (ECOWAS) – Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) • South America – Mercosur (Mercosul) 23
ASEAN: Asso. Southeast Asian Nations • Free Trade • 10 countries – Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao, Malaysia, Mayamar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam • HO: Jakarta • ASEAN scholarship • ASEAN Univ. Network 24

APEC: Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation • Eco. Growth & prosperity – Trade/invst Liberalization – Business Facilitation – Economic/tech cooperation • Important – 40% of world’s pop – 50% of world’s GDP – 40% of world’s trade • 21 countries – Australia, Brunei, Canada, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, NZ, Phil, Singapore, Thai, US, Taipei, HK, china, Mexico, PNG, Chile, Peru, USSR, Vietnam • HO: Singapore 25
ECOWAS: Economic Council West African States • Economic integration – Mutual defense, court of justice – Ecowas rail, common currency 2015 – Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Nigeria, Sierra L • 15 countries – Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde Cote d’lvoire, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea. Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Togo – Niger – suspended 2009– election problem – Guinea – suspended 2008 – coup attempt – Liberia wants to join Ecowas • HO: Abuja, Nigeria 26
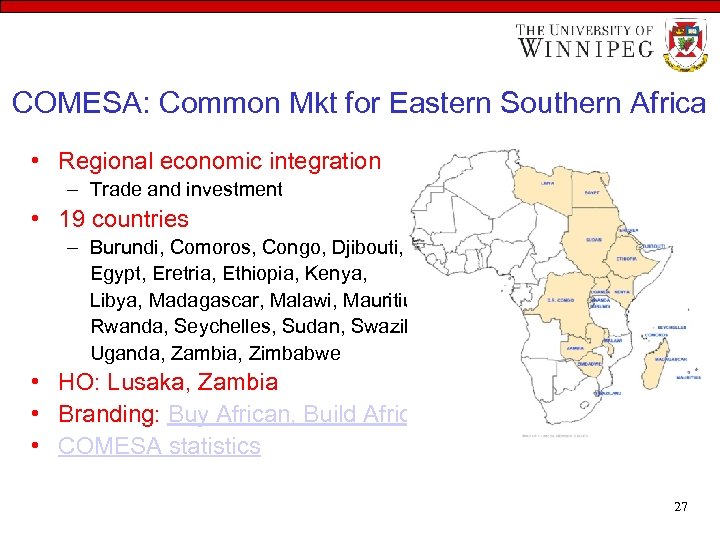
COMESA: Common Mkt for Eastern Southern Africa • Regional economic integration – Trade and investment • 19 countries – Burundi, Comoros, Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Eretria, Ethiopia, Kenya, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius Rwanda, Seychelles, Sudan, Swaziland Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe • HO: Lusaka, Zambia • Branding: Buy African, Build Africa • COMESA statistics 27

MERCOSUR • Free trade and people movement • Full member – Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay Venezuela (Paraguay to ratify) • Associate member – Bolivia, Chile, Columbia, Ecuador Peru • Observer members – Mexico – New Zealand • HO: Montevideo, Uruguay 28
cd5879cc8c9509fd68eb3cbbd6b89d2a.ppt