1590a7b9f4de9b10df27bb13a6f01bd2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Welcome to Cisco Academy Chapter 1

Objectives • Understand Safety Rules • Provide common knowledge base – PC Hardware • Build bridge between understanding of PC hardware and Networks similarities • Develop understanding of Boot Process • Appreciate importance of Networks • Identify network characteristics • Introduce Binary Numbering System • Appreciate importance of Bandwidth

Specific Objectives & Tasks • • • Identify four primary components of PC architecture Identify PC subsystem components Install a NIC Configure PC for different network types Develop understanding of Binary Number System Convert Decimal to Binary & Binary to Decimal Identify units of Information Be able to discuss need for Networks Be able to identify Network Devices Use analogies to understand bandwidth
PC Components • • • Transistor – amplifies or opens/closes circuit IC – does specific task; contains transistors Capacitor – stores energy in electrostatic field Connector – plugs into a port or interface LED – semiconductor device that emits light
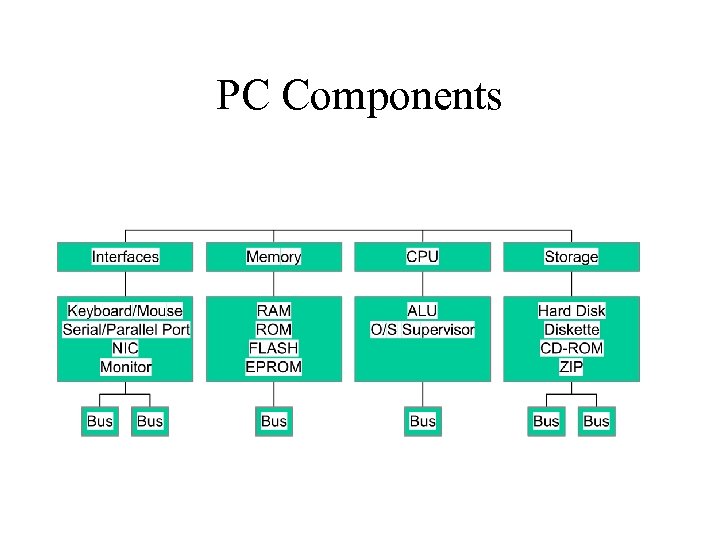
PC Components
Boot Processes • Boot Instructions – stored in ROM until used • Software Applications – stored in RAM after loading • RAM and ROM – talk to CPU through the bus • Saved Information – flows from RAM to storage device • Exported Information – flows from RAM through bus to external device such as the printer

Stop • Do Lab

NIC • Network Interface Card – printed circuit board that provides network communication capabilities to and from a personal computer • A. K. A. Lan Adapter – Can be designed for Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI (IMPORTANT) • Requires: – IRQ, I/O Address, Upper Memory address in Win 95, 98, NT
Network Card Selection Criteria • Type of Network – Ethernet, FDDI, Token Ring • Type of Media – Twisted Pair, Fiber Optic, Coaxial Cable • Type of Bus – PSI or ISA or PCMCIA (lap top) • Half duplex or full duplexing • 10 mbs or 100 mbs
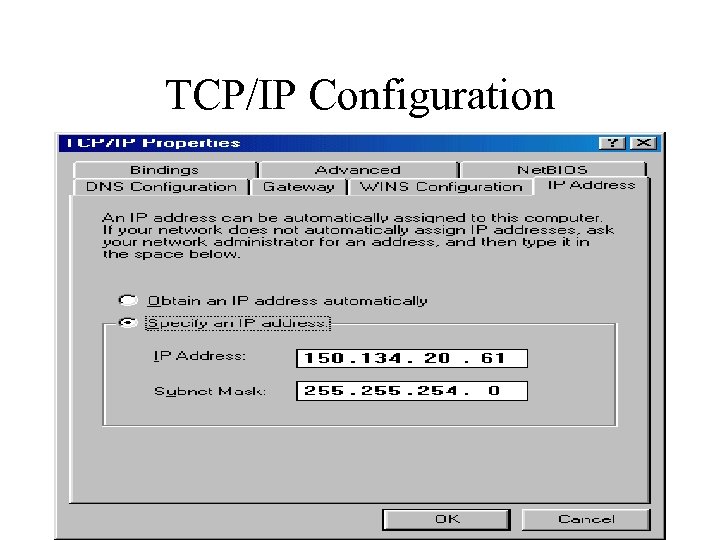
TCP/IP Configuration

Stop • Do Lab
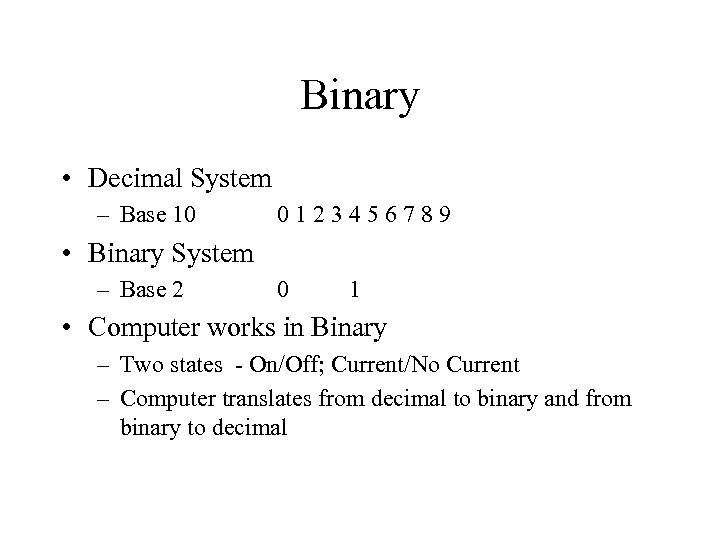
Binary • Decimal System – Base 10 0123456789 • Binary System – Base 2 0 1 • Computer works in Binary – Two states - On/Off; Current/No Current – Computer translates from decimal to binary and from binary to decimal
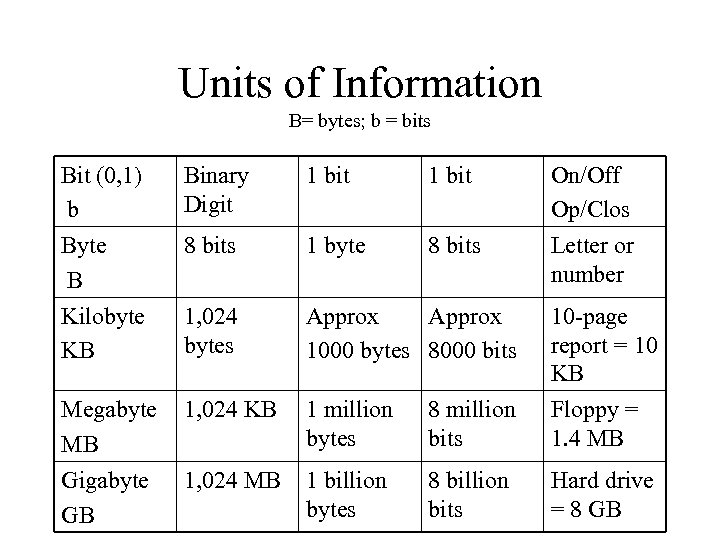
Units of Information B= bytes; b = bits Bit (0, 1) b Byte B Kilobyte KB Binary Digit 1 bit On/Off Op/Clos Letter or number 8 bits 1 byte 8 bits 1, 024 bytes Approx 1000 bytes 8000 bits 10 -page report = 10 KB Megabyte MB Gigabyte GB 1, 024 KB 1 million bytes 8 million bits Floppy = 1. 4 MB 1, 024 MB 1 billion bytes 8 billion bits Hard drive = 8 GB

Stop • Do Lab
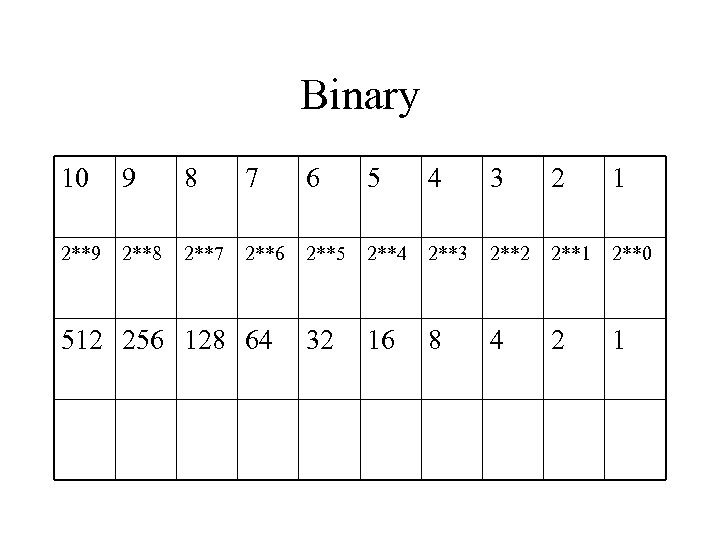
Binary 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 2**9 2**8 2**7 2**6 2**5 2**4 2**3 2**2 2**1 2**0 32 16 8 4 2 1 512 256 128 64
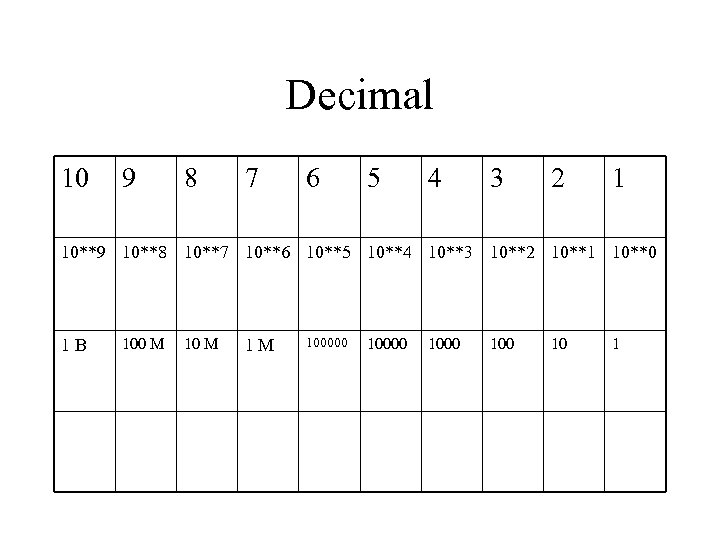
Decimal 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 10**9 10**8 10**7 10**6 10**5 10**4 10**3 10**2 10**1 10**0 1 B 100 M 1 M 100000 1000 10 1

Stop • Do Lab

IP Addressing • IP address is used to identify PC to network (at layer 3 of OSI model) • IP address is used to send traffic over WAN • IP address is usually in dotted decimal format (does not have to be) – 123. 122. 234. 255 – In binary 01111011. 0111101010. 1111 – In hex 7 B 7 A EA FF

Networks • A network is an entity - an intricately connected system of objects or people. • Networks are all around us, even inside us. • Your own nervous system and cardiovascular system are networks. • There can several types of networks • Think of some

Networks Accomplish Many Tasks • Avoid duplication of equipment and resources • Allow us to communicate efficiently • Enable us to manage computing resources • Support shared resources

Network Types • LAN – Building, Campus (group of building) • MAN – Metropolitan Area • WAN – Entire world – can even include outer space

LAN Characteristics • Operate within a limited geographic area • Allow multiple access to high bandwidth media • Control private (autonomous) networks • Provide full-time connectivity to local services • Connect physically adjacent devices

WANS • Operate over wide geographic areas • Allow access over serial interfaces operating at lower speeds • Provide full-time and part-time connectivity • Connect devices located over wide geographic areas • WANS connect LANS

Bandwidth • Measure of how much information can flow from one place to another in a given amount of time • Two types – digital and analog • Cisco course deals with digital bandwidth • Measured in BITS (b) per second

Analogies for Bandwidth • Pipe line – Bandwidth is pipes – Network devices are valves; fittings; packet is water • Highway – Bandwidth is lanes – Packets are vehicles; network devices are signals, on ramps, etc. • Audio Systems – Network devices are telephones, CD-ROMS – Packets are music
Bandwidth is Important • It is finite • It can save money • It is key measure of network design and performance • It is key to understanding Internet • The demand for it increases constantly

Throughput • The formula is Estimated Time = Size of File / Bandwidth • Throughput is always less than Bandwidth • Bandwidth is used to design networks • Throughput is used to evaluate network performance

Media • Coaxial Cable – 50 ohm and 75 ohm • Twisted Pairs – Shielded and Unshielded • Fiber Optics – Single Mode and Multi Mode (62. 5/125) • Wireless
1590a7b9f4de9b10df27bb13a6f01bd2.ppt