65c43532483b6cd12500c57530af5b3a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 144
 Welcome to: August 12, 2008 We want your questions, feedback, and suggestions. But, there may not be enough time to take them all during the presentation. Please write and submit them at the presentation end. Thanks!
Welcome to: August 12, 2008 We want your questions, feedback, and suggestions. But, there may not be enough time to take them all during the presentation. Please write and submit them at the presentation end. Thanks!
 Presenters (in order of presentation): • Psychological Services: Tracy Schatzberg • School Psychologist: Etta Rahming • Guidance Counselor: Bonnie Anzalone • Social Worker: Alex Smith 2
Presenters (in order of presentation): • Psychological Services: Tracy Schatzberg • School Psychologist: Etta Rahming • Guidance Counselor: Bonnie Anzalone • Social Worker: Alex Smith 2
 Handouts • We are promoting “paperless” communication to save district funds and the environment. • “Handouts” are available online as a Powerpoint presentation and PDF document. (The website address appears later. ) • You may edit the Powerpoint presentation for training purposes at your school. 3
Handouts • We are promoting “paperless” communication to save district funds and the environment. • “Handouts” are available online as a Powerpoint presentation and PDF document. (The website address appears later. ) • You may edit the Powerpoint presentation for training purposes at your school. 3
 The little red star… • Our time for completing this presentation is limited. • In some parts, we can only highlight the key points. • Additional details are provided throughout the presentation. 4
The little red star… • Our time for completing this presentation is limited. • In some parts, we can only highlight the key points. • Additional details are provided throughout the presentation. 4
 The little red star… • Our time for completing this presentation is limited. • In some parts, we can only highlight the key points. • Additional details are provided throughout the presentation. • Frames with a red star in the upper right corner include details for later study. 5
The little red star… • Our time for completing this presentation is limited. • In some parts, we can only highlight the key points. • Additional details are provided throughout the presentation. • Frames with a red star in the upper right corner include details for later study. 5
 Broad Goals • Explore methods to work more efficiently on Functional Behavior Assessments (FBA) and Behavior Intervention Plans (BIP) • Remove barriers and build the infrastructure • Assure compliance with laws and related rules • Provide high quality services to all students 6 with behavior challenges
Broad Goals • Explore methods to work more efficiently on Functional Behavior Assessments (FBA) and Behavior Intervention Plans (BIP) • Remove barriers and build the infrastructure • Assure compliance with laws and related rules • Provide high quality services to all students 6 with behavior challenges
 Objectives • Answer “Why build a FBA-BIP team? ” • Review training methods to strengthen team skills • Discover new tools • Determine when and how to seek expert support for your team • Examine how to develop and operate your team 7
Objectives • Answer “Why build a FBA-BIP team? ” • Review training methods to strengthen team skills • Discover new tools • Determine when and how to seek expert support for your team • Examine how to develop and operate your team 7
 Why Do Students and Schools Need FBAs and BIPs “It’s the right thing to do. ” Etta Rahming, School Psychologist
Why Do Students and Schools Need FBAs and BIPs “It’s the right thing to do. ” Etta Rahming, School Psychologist
 Exclusionary Disciplinary Actions • Elementary School Suspensions – 4, 135 Students 2007 -2008 - Gen. – 15, 857 Days of Suspension Ed. + ESE – 79, 285 Hours of Instruction Lost • Middle School – 13, 374 Students – 109, 981 Days of Suspension – 549, 905 Hours of Instruction Lost (OSS, ISS, ATOSS and Bus Suspension) • High School – 16, 513 Students – 110, 545 Days of Suspension – 552, 725 Hours of Instruction Lost 9
Exclusionary Disciplinary Actions • Elementary School Suspensions – 4, 135 Students 2007 -2008 - Gen. – 15, 857 Days of Suspension Ed. + ESE – 79, 285 Hours of Instruction Lost • Middle School – 13, 374 Students – 109, 981 Days of Suspension – 549, 905 Hours of Instruction Lost (OSS, ISS, ATOSS and Bus Suspension) • High School – 16, 513 Students – 110, 545 Days of Suspension – 552, 725 Hours of Instruction Lost 9
 Suspensions 2007 -2008 - Gen. Ed. + ESE • Alternative Education (OSS, ISS, ATOSS – 591 Students and Bus Suspension) – 11, 691 Days of Suspension – 58, 455 Hours of Instruction Lost • Career Centers – 486 Students – 2, 925 Days of Suspension – 14, 625 Hours of Instruction Lost 10
Suspensions 2007 -2008 - Gen. Ed. + ESE • Alternative Education (OSS, ISS, ATOSS – 591 Students and Bus Suspension) – 11, 691 Days of Suspension – 58, 455 Hours of Instruction Lost • Career Centers – 486 Students – 2, 925 Days of Suspension – 14, 625 Hours of Instruction Lost 10
 Suspensions 2007 -2008 - Gen. Ed. + ESE • ESE Centers (OSS, ISS, ATOSS and Bus Suspension) – 299 Students – 2, 778 Days of Suspension – 13, 890 Hours of Instruction Lost • Youth Services – 12 Students – 86 Days of Suspension – 430 Hours of Instruction Lost 11
Suspensions 2007 -2008 - Gen. Ed. + ESE • ESE Centers (OSS, ISS, ATOSS and Bus Suspension) – 299 Students – 2, 778 Days of Suspension – 13, 890 Hours of Instruction Lost • Youth Services – 12 Students – 86 Days of Suspension – 430 Hours of Instruction Lost 11
 Suspension Totals • 35, 410 Students (Duplicated Count) • 253, 863 Days of Suspension • 1, 269, 315 Hours of Instruction Lost instructional hours compound problems with academic frustration and failure, exacerbate behavior challenges, and thereby increase the student’s risk of school failure, dropout, and/or exclusion. 12
Suspension Totals • 35, 410 Students (Duplicated Count) • 253, 863 Days of Suspension • 1, 269, 315 Hours of Instruction Lost instructional hours compound problems with academic frustration and failure, exacerbate behavior challenges, and thereby increase the student’s risk of school failure, dropout, and/or exclusion. 12
 Exclusionary disciplinary actions Are used disproportionately for students with Emotional/Behavioral Disabilities (EBD): 333 ESE Student Change of Placements (2007 -08) For students with EBD, (whose disability is most likely to be manifested behaviorally), the analysis is: 7% Total Students With Disabilities 40% Students whose actions resulted in a 13 Change of Placement
Exclusionary disciplinary actions Are used disproportionately for students with Emotional/Behavioral Disabilities (EBD): 333 ESE Student Change of Placements (2007 -08) For students with EBD, (whose disability is most likely to be manifested behaviorally), the analysis is: 7% Total Students With Disabilities 40% Students whose actions resulted in a 13 Change of Placement
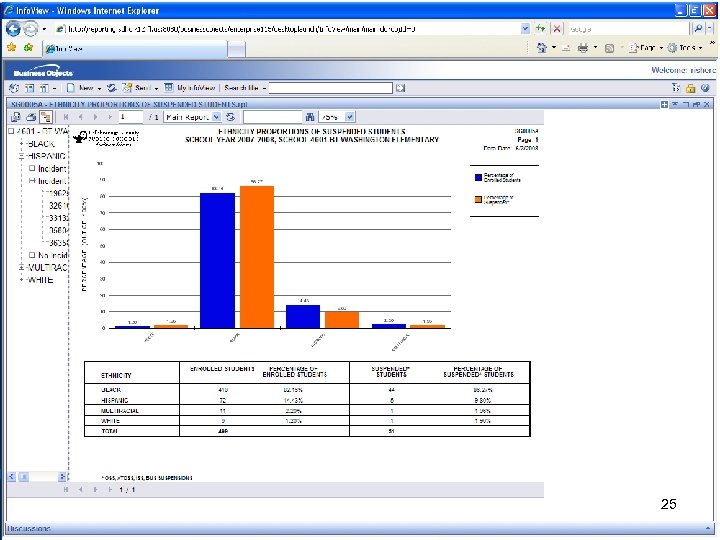
 Exclusionary disciplinary actions Are used disproportionately for some minority students: Average Ethnicity Proportions of Suspended Gen. Ed. + ESE Students (2007 -08) ENROLLED • • • Indian Multiracial Hispanic Asian White Black SUSPENDED 1% 5% 27% 3% 42% 22% 1% 5% 26% 1% 29% 38% 14
Exclusionary disciplinary actions Are used disproportionately for some minority students: Average Ethnicity Proportions of Suspended Gen. Ed. + ESE Students (2007 -08) ENROLLED • • • Indian Multiracial Hispanic Asian White Black SUSPENDED 1% 5% 27% 3% 42% 22% 1% 5% 26% 1% 29% 38% 14
 Exclusionary disciplinary actions: • May inadvertently increase the frequency, duration, and intensity of some student behaviors. Examples: – Out-of-School Suspensions may reinforce problem behaviors by: • allowing the student to avoid or escape schoolwork. • allowing the student to access high potency reinforcers (video games, sex, alcohol, drugs) in the community. • Fail to teach alternative behaviors • May appear to be coercive and result in student counter-control behaviors, severe aggression, harm to self, or other serious behavior changes • Could be reduced by early and effective FBAs 15 and behavioral interventions
Exclusionary disciplinary actions: • May inadvertently increase the frequency, duration, and intensity of some student behaviors. Examples: – Out-of-School Suspensions may reinforce problem behaviors by: • allowing the student to avoid or escape schoolwork. • allowing the student to access high potency reinforcers (video games, sex, alcohol, drugs) in the community. • Fail to teach alternative behaviors • May appear to be coercive and result in student counter-control behaviors, severe aggression, harm to self, or other serious behavior changes • Could be reduced by early and effective FBAs 15 and behavioral interventions
 What Are the Potential Negative Outcomes? The risks of failure in school are severe. Students who receive ineffective interventions and drop out, or are excluded, from school can experience: • Functional illiteracy • Fewer paths of opportunity after school • Adult life of poverty • Dependence on social welfare systems • Incarceration • Substance abuse • Health insurance gaps, health problems, early death 16 What are the costs to society? Or, our schools?
What Are the Potential Negative Outcomes? The risks of failure in school are severe. Students who receive ineffective interventions and drop out, or are excluded, from school can experience: • Functional illiteracy • Fewer paths of opportunity after school • Adult life of poverty • Dependence on social welfare systems • Incarceration • Substance abuse • Health insurance gaps, health problems, early death 16 What are the costs to society? Or, our schools?
 Reasons for Building FBA-BIP Teams To assure that students who are at risk of, or who have experienced, exclusionary disciplinary actions have received: • Adequate FBAs • BIPs that contain scientific, research-based interventions • BIPs that were implemented for a reasonable time period • Data that demonstrates the BIP was implemented • Data that demonstrates intervention integrity 17
Reasons for Building FBA-BIP Teams To assure that students who are at risk of, or who have experienced, exclusionary disciplinary actions have received: • Adequate FBAs • BIPs that contain scientific, research-based interventions • BIPs that were implemented for a reasonable time period • Data that demonstrates the BIP was implemented • Data that demonstrates intervention integrity 17
 Reasons for Building FBA-BIP Teams To meet the behavioral intervention needs of General Education and Special Education students: • reduce ineffective disciplinary actions • provide better universal and targeted group interventions • provide better individualized FBAs and BIPs, when warranted 18
Reasons for Building FBA-BIP Teams To meet the behavioral intervention needs of General Education and Special Education students: • reduce ineffective disciplinary actions • provide better universal and targeted group interventions • provide better individualized FBAs and BIPs, when warranted 18
 Reasons for Building FBA-BIP Teams To meet the behavioral intervention needs of General Education and Special Education students: • prevent the severe negative outcomes associated with school failure and dropping out 19
Reasons for Building FBA-BIP Teams To meet the behavioral intervention needs of General Education and Special Education students: • prevent the severe negative outcomes associated with school failure and dropping out 19
 Is There A Better Way To Identify Students Who May Need FBA-BIPs? Tracy Schatzberg, Psychological Services
Is There A Better Way To Identify Students Who May Need FBA-BIPs? Tracy Schatzberg, Psychological Services
 Early identification of students who may need FBA-BIPs • New online district discipline data system (known as “Crystal Enterprises” or “Business Objects”) • Permits better Tier 1 Universal Screening • School access to their current site information on demand • Can print the reports or export to other formats such as PDF or Excel 21
Early identification of students who may need FBA-BIPs • New online district discipline data system (known as “Crystal Enterprises” or “Business Objects”) • Permits better Tier 1 Universal Screening • School access to their current site information on demand • Can print the reports or export to other formats such as PDF or Excel 21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 Early identification of students who may need FBA-BIPs June-July 2008 - Orientation of Administrators August 2008 – Schools form Behavior (or Performance) Leadership Teams with Student Support Staff August–December 2008 - Area-Based Team Training: • Team Member Skills & Roles • Streamlining Data Entry & Online Data Access • 3 -Tier Problem Solving Models • Interventions (Selection and Implementation) • Problem-Solving & Data-based decision making (RTI) with STAT & the Professional Learning Community • School Improvement Plans 26 Proposed: Online discipline data collection system
Early identification of students who may need FBA-BIPs June-July 2008 - Orientation of Administrators August 2008 – Schools form Behavior (or Performance) Leadership Teams with Student Support Staff August–December 2008 - Area-Based Team Training: • Team Member Skills & Roles • Streamlining Data Entry & Online Data Access • 3 -Tier Problem Solving Models • Interventions (Selection and Implementation) • Problem-Solving & Data-based decision making (RTI) with STAT & the Professional Learning Community • School Improvement Plans 26 Proposed: Online discipline data collection system
 What Are The Laws and Rules Impacting FBAs and BIPs? “Besides being the right thing to do, it’s the law. ”
What Are The Laws and Rules Impacting FBAs and BIPs? “Besides being the right thing to do, it’s the law. ”
 Remember… • Frames with a red star in the upper right corner include details for later study. 28
Remember… • Frames with a red star in the upper right corner include details for later study. 28
 IDEA 2004: FBAs and BIPs for ESE students • Part E: Procedural Safeguards • Discipline Procedures • § 300. 530 Authority of school personnel. (Excerpts) • Complete text: http: //www. wrightslaw. com/idea/index. htm 29
IDEA 2004: FBAs and BIPs for ESE students • Part E: Procedural Safeguards • Discipline Procedures • § 300. 530 Authority of school personnel. (Excerpts) • Complete text: http: //www. wrightslaw. com/idea/index. htm 29
 (d) Services. (1) A child with a disability who is removed from the child’s current placement pursuant to paragraphs (c), or (g) of this section must- • (ii) Receive, as appropriate, a functional behavioral assessment, and behavioral intervention services and modifications, that are designed to address the behavior violation so that it does not recur. 30
(d) Services. (1) A child with a disability who is removed from the child’s current placement pursuant to paragraphs (c), or (g) of this section must- • (ii) Receive, as appropriate, a functional behavioral assessment, and behavioral intervention services and modifications, that are designed to address the behavior violation so that it does not recur. 30
 (e) Manifestation determination. (1) Within 10 school days of any decision to change the placement of a child with a disability because of a violation of a code of student conduct, … (f) If the LEA, the parent, and relevant members of the IEP Team make the determination that the conduct was a manifestation of the child’s disability, the IEP Team must(1) Either-– • (i) Conduct a functional behavioral assessment, • unless the LEA had conducted a functional behavioral assessment before the behavior that resulted in the change of placement occurred, and implement a behavioral intervention plan for the child; or (ii) If a behavioral intervention plan already has been developed, review the behavioral intervention plan, and modify it, as necessary, to address the behavior; … 31
(e) Manifestation determination. (1) Within 10 school days of any decision to change the placement of a child with a disability because of a violation of a code of student conduct, … (f) If the LEA, the parent, and relevant members of the IEP Team make the determination that the conduct was a manifestation of the child’s disability, the IEP Team must(1) Either-– • (i) Conduct a functional behavioral assessment, • unless the LEA had conducted a functional behavioral assessment before the behavior that resulted in the change of placement occurred, and implement a behavioral intervention plan for the child; or (ii) If a behavioral intervention plan already has been developed, review the behavioral intervention plan, and modify it, as necessary, to address the behavior; … 31
 EBD Technical Assistance Paper • TAP #: K 12: 2008 -53 • New from Florida DOE May 9, 2008 • Complete text: http: //www. fldoe. org/ese/pub-home. asp 32
EBD Technical Assistance Paper • TAP #: K 12: 2008 -53 • New from Florida DOE May 9, 2008 • Complete text: http: //www. fldoe. org/ese/pub-home. asp 32
 Purposes of State Board of Education rule To ensure that students with emotional/behavioral disabilities (E/BD): • receive appropriate interventions in general education settings • are identified in a responsive manner; • and, when necessary, receive special education services in the least restrictive setting. 33
Purposes of State Board of Education rule To ensure that students with emotional/behavioral disabilities (E/BD): • receive appropriate interventions in general education settings • are identified in a responsive manner; • and, when necessary, receive special education services in the least restrictive setting. 33
 Key features • School-based intervention teams apply a problem-solving process to develop evidence -based interventions of sufficient intensity to match the student’s needs. – In HCPS, these teams are STAT and the problem-solving process is a multi-tier RTI approach to providing instruction and intervention, at increasing levels of intensity, based on student response to each intervention. – FBA is a comprehensive problem-solving 34 process to develop an intervention.
Key features • School-based intervention teams apply a problem-solving process to develop evidence -based interventions of sufficient intensity to match the student’s needs. – In HCPS, these teams are STAT and the problem-solving process is a multi-tier RTI approach to providing instruction and intervention, at increasing levels of intensity, based on student response to each intervention. – FBA is a comprehensive problem-solving 34 process to develop an intervention.
 Key features Before implementing individual interventions (e. g. , FBA and BIP), there should be evidence that: • school, • classroom, and • small group interventions are effective with the majority of students - In HCPS, this is an area for ongoing emphasis. 35
Key features Before implementing individual interventions (e. g. , FBA and BIP), there should be evidence that: • school, • classroom, and • small group interventions are effective with the majority of students - In HCPS, this is an area for ongoing emphasis. 35
 Key features Interventions should be implemented: • for a reasonable period of time* – (as determined by the local problem-solving team on a case -by-case basis, dependent on the nature of the problem(s), the nature and intensity of interventions, frequency of progress monitoring, and ability to evaluate trends. ) • and with a level of intensity • that matches the student’s needs. - In HCPS, this is an area for ongoing emphasis. 36
Key features Interventions should be implemented: • for a reasonable period of time* – (as determined by the local problem-solving team on a case -by-case basis, dependent on the nature of the problem(s), the nature and intensity of interventions, frequency of progress monitoring, and ability to evaluate trends. ) • and with a level of intensity • that matches the student’s needs. - In HCPS, this is an area for ongoing emphasis. 36
 Key features For students requiring individual interventions, • a Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA) should be conducted, and • individual interventions should be developed and implemented based on the FBA. - In HCPS, this is an area for ongoing emphasis. 37
Key features For students requiring individual interventions, • a Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA) should be conducted, and • individual interventions should be developed and implemented based on the FBA. - In HCPS, this is an area for ongoing emphasis. 37
 Key features • Data are used: – for ongoing student progress monitoring and data analysis – to evaluate intervention effectiveness and fidelity – and inform decisions about the focus and intensity of interventions. • Most students with behavioral or emotional challenges will respond to interventions developed, implemented, and evaluated in the above manner. • However, some students may need specially designed instruction and related services beyond general education resources and supports to sustain adequate progress in the learning environment. 38
Key features • Data are used: – for ongoing student progress monitoring and data analysis – to evaluate intervention effectiveness and fidelity – and inform decisions about the focus and intensity of interventions. • Most students with behavioral or emotional challenges will respond to interventions developed, implemented, and evaluated in the above manner. • However, some students may need specially designed instruction and related services beyond general education resources and supports to sustain adequate progress in the learning environment. 38
 Key features • Appropriate data will contribute to more appropriate referrals for evaluation. • Prior to referring for an evaluation, there should be documentation that interventions have been implemented as designed. • RTI references in the E/BD rule: – “persistent” emotional/ behavioral responses – “not sufficiently responsive to evidence-based interventions” 39
Key features • Appropriate data will contribute to more appropriate referrals for evaluation. • Prior to referring for an evaluation, there should be documentation that interventions have been implemented as designed. • RTI references in the E/BD rule: – “persistent” emotional/ behavioral responses – “not sufficiently responsive to evidence-based interventions” 39
 Extraordinary circumstances • Some students may have an acute onset of emotional/behavioral characteristics where the severity of the emotional/behavioral manifestations requires immediate ESE services. • An example could be a student coming from a residential hospital facility with a significant mental health diagnosis and a history of intensive support services in restrictive settings. • The need for such immediate ESE services should be infrequent and closely monitored. - Even under extraordinary circumstances, a FBA is still warranted so that a behavioral intervention can 40 be developed and implemented.
Extraordinary circumstances • Some students may have an acute onset of emotional/behavioral characteristics where the severity of the emotional/behavioral manifestations requires immediate ESE services. • An example could be a student coming from a residential hospital facility with a significant mental health diagnosis and a history of intensive support services in restrictive settings. • The need for such immediate ESE services should be infrequent and closely monitored. - Even under extraordinary circumstances, a FBA is still warranted so that a behavioral intervention can 40 be developed and implemented.
 Florida DOE Monitoring of District Implementation of E/BD Rule To monitor for rule compliance, staff will look for evidence that data were analyzed when making the eligibility decision. Non-example: checklists with initiation and duration dates of interventions are not sufficient evidence. Example: Sufficient evidence of intervention effectiveness includes: – clearly documented FBAs – graphs – summary descriptions of conferences – intervention team meetings, and – observations of the student 41
Florida DOE Monitoring of District Implementation of E/BD Rule To monitor for rule compliance, staff will look for evidence that data were analyzed when making the eligibility decision. Non-example: checklists with initiation and duration dates of interventions are not sufficient evidence. Example: Sufficient evidence of intervention effectiveness includes: – clearly documented FBAs – graphs – summary descriptions of conferences – intervention team meetings, and – observations of the student 41
 Components of EBD Evaluation • Functional Behavioral Assessment – The FBA should be initiated as part of general education interventions Team responsibilities: – Review the existing FBA – If needed, Revise the FBA – If it is incomplete or missing, Complete the FBA 42
Components of EBD Evaluation • Functional Behavioral Assessment – The FBA should be initiated as part of general education interventions Team responsibilities: – Review the existing FBA – If needed, Revise the FBA – If it is incomplete or missing, Complete the FBA 42
 Components of EBD Evaluation • Functional Behavioral Assessment – Initiated as part of general education interventions • Psychological evaluation (including “a review of evidence-based interventions that have already been implemented, the student’s response to those interventions, and the criteria used to evaluate their success”) • Social-developmental history compiled from a structured interview • Educational evaluation • Medical evaluation when determined necessary by ESE Director or designee 43
Components of EBD Evaluation • Functional Behavioral Assessment – Initiated as part of general education interventions • Psychological evaluation (including “a review of evidence-based interventions that have already been implemented, the student’s response to those interventions, and the criteria used to evaluate their success”) • Social-developmental history compiled from a structured interview • Educational evaluation • Medical evaluation when determined necessary by ESE Director or designee 43
 Reasons for Building FBA-BIP Teams To learn and support systems (e. g. , online discipline data) that identify students with emerging behavior challenges and provide timely interventions. To assure that relevant laws and rules are understood by teachers, administrators, and other educational professionals. To provide oversight and assistance in complying with relevant laws and rules. 44
Reasons for Building FBA-BIP Teams To learn and support systems (e. g. , online discipline data) that identify students with emerging behavior challenges and provide timely interventions. To assure that relevant laws and rules are understood by teachers, administrators, and other educational professionals. To provide oversight and assistance in complying with relevant laws and rules. 44
 How Does Our Team Get Training, Tools, and Support? Bonnie Anzalone, Guidance Counselor
How Does Our Team Get Training, Tools, and Support? Bonnie Anzalone, Guidance Counselor
 Training • Thanks to everybody who completed the 6 -hour FDLRS “FBA and More” course – Special thanks to Shelley Cedola-Hayes and her FDLRS co-trainers! – Special thanks to the FACT members for arranging and providing Area-based training • Encourage others from your school to attend the “FBA and More” course – Training dates: to be announced pending the hiring of Shelley’s replacement (now Area 5 ESE DRT) • Plan Area-based “FBA and More” courses • New course sequence to be announced soon: Online & traditional classroom training to expand skills and knowledge beyond the “FBA and More” 46 course.
Training • Thanks to everybody who completed the 6 -hour FDLRS “FBA and More” course – Special thanks to Shelley Cedola-Hayes and her FDLRS co-trainers! – Special thanks to the FACT members for arranging and providing Area-based training • Encourage others from your school to attend the “FBA and More” course – Training dates: to be announced pending the hiring of Shelley’s replacement (now Area 5 ESE DRT) • Plan Area-based “FBA and More” courses • New course sequence to be announced soon: Online & traditional classroom training to expand skills and knowledge beyond the “FBA and More” 46 course.
 Related Professional Development STAT (revised manual now available) Training dates to be announced: • 3 -Tier Problem Solving • Tier 1 Schoolwide Behavioral Interventions • Tier 2 Targeted Group and Classroom Behavioral Interventions • • Data Collection Data Graphing & Interpretation Data-Based Decision-Making Eligibility Decisions (based on RTI) 47
Related Professional Development STAT (revised manual now available) Training dates to be announced: • 3 -Tier Problem Solving • Tier 1 Schoolwide Behavioral Interventions • Tier 2 Targeted Group and Classroom Behavioral Interventions • • Data Collection Data Graphing & Interpretation Data-Based Decision-Making Eligibility Decisions (based on RTI) 47
 Web-based Tools • Write this address in your notes: • http: //interventioncentral. mysdhc. org/ – Handouts for this presentation! – Structured interviews for FBA – Direct observation forms to support pattern analysis – Data forms and Measurement tools (electronic and mechanical tally counters, etc. ) – Graph templates – Professional references to review and cite to increase the credibility of the written document – And more! 48
Web-based Tools • Write this address in your notes: • http: //interventioncentral. mysdhc. org/ – Handouts for this presentation! – Structured interviews for FBA – Direct observation forms to support pattern analysis – Data forms and Measurement tools (electronic and mechanical tally counters, etc. ) – Graph templates – Professional references to review and cite to increase the credibility of the written document – And more! 48
 When and how to seek expert support • To learn, to enhance services, and to comply with ethical rules • Practical guidelines • Available supports: - ESE Area offices - Area Team supports (e. g. , consultations at School Psychologist Area Team meetings) - Local expertise (refer to Area directories of certified district staff - BCBA, BCABA, CBA, and CABA) - Functional Assessment Consultant Team (FACT) Please refer to the directory on the website. 49
When and how to seek expert support • To learn, to enhance services, and to comply with ethical rules • Practical guidelines • Available supports: - ESE Area offices - Area Team supports (e. g. , consultations at School Psychologist Area Team meetings) - Local expertise (refer to Area directories of certified district staff - BCBA, BCABA, CBA, and CABA) - Functional Assessment Consultant Team (FACT) Please refer to the directory on the website. 49
 How Does Our Team Build a Strong Foundation and Proceed with Development?
How Does Our Team Build a Strong Foundation and Proceed with Development?
 Building a Strong Foundation • A FBA-BIP team cannot succeed if critical systems are not in place. • The following frames describe activities necessary to assure the success of your FBA-BIP Team. • As noted, the FBA-BIP Team must collaborate with other school teams to assure these critical systems are in place. 51
Building a Strong Foundation • A FBA-BIP team cannot succeed if critical systems are not in place. • The following frames describe activities necessary to assure the success of your FBA-BIP Team. • As noted, the FBA-BIP Team must collaborate with other school teams to assure these critical systems are in place. 51
 Tie FBA-BIPs to STAT, 3 Tier Problem-solving and RTI • The next frame depicts the 3 Tier Model as a Pyramid. • Tier 1 includes universal, school-wide behavioral interventions. • Tier 1 behavioral interventions emphasize proactive environmental and teaching strategies, plus reinforcement-based methods. • The emphasis is NOT on disciplinary procedures. 52
Tie FBA-BIPs to STAT, 3 Tier Problem-solving and RTI • The next frame depicts the 3 Tier Model as a Pyramid. • Tier 1 includes universal, school-wide behavioral interventions. • Tier 1 behavioral interventions emphasize proactive environmental and teaching strategies, plus reinforcement-based methods. • The emphasis is NOT on disciplinary procedures. 52
 Problem Identification Evaluate Response to Intervention (Rt. I) Problem Analysis Implement Plan 53
Problem Identification Evaluate Response to Intervention (Rt. I) Problem Analysis Implement Plan 53
 Tier 1 Behavioral Interventions Collaborate with other school teams to assure: • All school staff are connected with all students – Everybody takes responsibility to ensure that each and every student succeeds. • Behavioral expectations are clearly defined and posted for all schoolwide and classroom settings – Students receive instruction, rehearsal, reviews, and reinforcers for improved performance and meeting expectations (i. e. , following rules) • Discipline referrals are systematically used as universal screening tools for early identification of students who may need intensive interventions 54
Tier 1 Behavioral Interventions Collaborate with other school teams to assure: • All school staff are connected with all students – Everybody takes responsibility to ensure that each and every student succeeds. • Behavioral expectations are clearly defined and posted for all schoolwide and classroom settings – Students receive instruction, rehearsal, reviews, and reinforcers for improved performance and meeting expectations (i. e. , following rules) • Discipline referrals are systematically used as universal screening tools for early identification of students who may need intensive interventions 54
 Tier 2 Behavioral Interventions • Universal (Tier 1) interventions will NOT be “universally” effective. (However, they should meet the needs of at least 75% of the students. ) • Targeted-group (Tier 2) behavioral interventions are needed for some students. • Tier 2 behavioral interventions also emphasize proactive environmental and teaching strategies, plus reinforcementbased methods, delivered in smaller group settings. 55
Tier 2 Behavioral Interventions • Universal (Tier 1) interventions will NOT be “universally” effective. (However, they should meet the needs of at least 75% of the students. ) • Targeted-group (Tier 2) behavioral interventions are needed for some students. • Tier 2 behavioral interventions also emphasize proactive environmental and teaching strategies, plus reinforcementbased methods, delivered in smaller group settings. 55
 Problem Identification Evaluate Response to Intervention (Rt. I) Problem Analysis Implement Plan 56
Problem Identification Evaluate Response to Intervention (Rt. I) Problem Analysis Implement Plan 56
 Remember… • Frames with a red star in the upper right corner include details for later study. 57
Remember… • Frames with a red star in the upper right corner include details for later study. 57
 Tier 2 Behavioral Interventions Collaborate with other school teams to assure Tier 2 behavioral services are effectively implemented. Questions for your team to address: • How, and how often, are students identified as needing Tier 2 services? • How are prior and current Tier 1 behavioral interventions documented? What aspects of the Tier 1 interventions were not sufficient? Why? • How are academic variables addressed regarding their potential impact on problem behaviors (e. g. , academic frustration)? 58
Tier 2 Behavioral Interventions Collaborate with other school teams to assure Tier 2 behavioral services are effectively implemented. Questions for your team to address: • How, and how often, are students identified as needing Tier 2 services? • How are prior and current Tier 1 behavioral interventions documented? What aspects of the Tier 1 interventions were not sufficient? Why? • How are academic variables addressed regarding their potential impact on problem behaviors (e. g. , academic frustration)? 58
 Tier 2 Behavioral Interventions • How are the targeted group and classroom interventions selected to match the behavior of concern? – Are the procedures research-based best practice? – Is there sufficient focus on reinforcement-based procedures? – Are the procedures of sufficient intensity (frequency, duration)? • Are they defined and trained so that staff can implement them with fidelity? 59
Tier 2 Behavioral Interventions • How are the targeted group and classroom interventions selected to match the behavior of concern? – Are the procedures research-based best practice? – Is there sufficient focus on reinforcement-based procedures? – Are the procedures of sufficient intensity (frequency, duration)? • Are they defined and trained so that staff can implement them with fidelity? 59
 Tier 2 Behavioral Interventions • How will the team know if the intervention is (not) working? How will student progress be measured? • How and when (e. g. , how often) will the team decide when a student must receive modified or more intensive Tier 2 behavioral interventions? • How and when (e. g. , how often) will the team decide when a student should be considered for Tier 3 behavioral interventions? 60
Tier 2 Behavioral Interventions • How will the team know if the intervention is (not) working? How will student progress be measured? • How and when (e. g. , how often) will the team decide when a student must receive modified or more intensive Tier 2 behavioral interventions? • How and when (e. g. , how often) will the team decide when a student should be considered for Tier 3 behavioral interventions? 60
 Tier 3 Behavioral Interventions • Universal (Tier 1) and Targeted-group (Tier 2) behavioral interventions will NOT work with all students. (However, they should meet the needs of at least 75% of the students. ) • Individualized (Tier 3) behavioral interventions are required for some students. In some cases, these services will need to be intensive. • FBA is a comprehensive problem-solving process for developing effective interventions. 61
Tier 3 Behavioral Interventions • Universal (Tier 1) and Targeted-group (Tier 2) behavioral interventions will NOT work with all students. (However, they should meet the needs of at least 75% of the students. ) • Individualized (Tier 3) behavioral interventions are required for some students. In some cases, these services will need to be intensive. • FBA is a comprehensive problem-solving process for developing effective interventions. 61
 Problem Identification Evaluate Response to Intervention (Rt. I) Problem Analysis Implement Plan 62
Problem Identification Evaluate Response to Intervention (Rt. I) Problem Analysis Implement Plan 62
 Tier 3 Behavioral Interventions Collaborate with other school teams to assure Tier 3 behavioral services are effectively implemented: • How are prior and current Tier 1 and 2 behavioral interventions documented? What aspects of the Tier 1 and 2 interventions were not sufficient? Why? • How are academic variables addressed regarding their potential impact on problem behaviors (e. g. , academic frustration)? 63
Tier 3 Behavioral Interventions Collaborate with other school teams to assure Tier 3 behavioral services are effectively implemented: • How are prior and current Tier 1 and 2 behavioral interventions documented? What aspects of the Tier 1 and 2 interventions were not sufficient? Why? • How are academic variables addressed regarding their potential impact on problem behaviors (e. g. , academic frustration)? 63
 Tier 3 Behavioral Interventions • How are the individualized interventions selected to match the behavior of concern? – Are the procedures research-based best practice? – Is there sufficient focus on reinforcement-based procedures? – Are the procedures of sufficient intensity (frequency, duration)? • Are they defined and trained so that staff can implement them with fidelity? 64
Tier 3 Behavioral Interventions • How are the individualized interventions selected to match the behavior of concern? – Are the procedures research-based best practice? – Is there sufficient focus on reinforcement-based procedures? – Are the procedures of sufficient intensity (frequency, duration)? • Are they defined and trained so that staff can implement them with fidelity? 64
 Tier 3 Behavioral Interventions • How will the team know if the intervention is (not) working? How will student progress be measured? • How and when (e. g. , how often) will the team decide when a student must receive modified or more intensive Tier 3 behavioral interventions? • How and when (e. g. , how often) will the team decide when a student must receive behavioral interventions that require extensive resources, and/or evaluation for special education services? 65
Tier 3 Behavioral Interventions • How will the team know if the intervention is (not) working? How will student progress be measured? • How and when (e. g. , how often) will the team decide when a student must receive modified or more intensive Tier 3 behavioral interventions? • How and when (e. g. , how often) will the team decide when a student must receive behavioral interventions that require extensive resources, and/or evaluation for special education services? 65
 Tie FBA-BIPs to STAT, 3 Tier Problem-solving and RTI • Universal (Tier 1) behavioral interventions will NOT be universally effective. • Targeted-group (Tier 2) behavioral interventions will NOT work with some students. • Individualized (Tier 3) behavioral interventions may be required for some students. • Planning and documentation is the key to successful interventions at any Tier level. • Interventions must be monitored. 66
Tie FBA-BIPs to STAT, 3 Tier Problem-solving and RTI • Universal (Tier 1) behavioral interventions will NOT be universally effective. • Targeted-group (Tier 2) behavioral interventions will NOT work with some students. • Individualized (Tier 3) behavioral interventions may be required for some students. • Planning and documentation is the key to successful interventions at any Tier level. • Interventions must be monitored. 66
 Tier 3 services with a weak support base… 67
Tier 3 services with a weak support base… 67
 Tier 3 services with a weak support base… will teeter and fall 68
Tier 3 services with a weak support base… will teeter and fall 68
 Problem Identification Evaluate Response to Intervention (Rt. I) Tier 3 services (including FBA-BIP) require strong foundations at Tiers 1 & 2 Problem Analysis Implement Plan 69
Problem Identification Evaluate Response to Intervention (Rt. I) Tier 3 services (including FBA-BIP) require strong foundations at Tiers 1 & 2 Problem Analysis Implement Plan 69
 Problem Identification Evaluate Response to Intervention (Rt. I) What systems does your school have in place at each tier? Problem Analysis Implement Plan 70
Problem Identification Evaluate Response to Intervention (Rt. I) What systems does your school have in place at each tier? Problem Analysis Implement Plan 70
 Comprehensive FBA BIP (may include Behavior Contract) 1 -to-1 Replacement behavior training Services integrated with parents and community resources Example of 3 Tier System STAT problem-solving, weekly RTI monitoring at: Small group training: Replacement behaviors, Social Skills, Anger management, etc. “Behavior Clinic” Behavior Contracts & Goal Setting Parent conferences B. T. Washington Schoolwide rules are posted, rehearsed, reviewed, + reinforced “Hornets Dozen” (Principals 200 Club) Cafeteria traffic management, reports to teachers Classroom schedules + routines are posted, rehearsed, reviewed, + reinforced “Hornet Stamps” reinforcement system Daily behavior reports to parents (via agenda) Success Chains, Mystery Motivators, Good Behavior Game Student problem-solving activities + forms 71
Comprehensive FBA BIP (may include Behavior Contract) 1 -to-1 Replacement behavior training Services integrated with parents and community resources Example of 3 Tier System STAT problem-solving, weekly RTI monitoring at: Small group training: Replacement behaviors, Social Skills, Anger management, etc. “Behavior Clinic” Behavior Contracts & Goal Setting Parent conferences B. T. Washington Schoolwide rules are posted, rehearsed, reviewed, + reinforced “Hornets Dozen” (Principals 200 Club) Cafeteria traffic management, reports to teachers Classroom schedules + routines are posted, rehearsed, reviewed, + reinforced “Hornet Stamps” reinforcement system Daily behavior reports to parents (via agenda) Success Chains, Mystery Motivators, Good Behavior Game Student problem-solving activities + forms 71
 Existing or New Team? Do we really need a new team? We already have a group that does behavior… STAT RTI / Problem. Solving Team IEP Child Study Team Behavior Leadership Team Professional Learning Community FBA-Behavior Intervention Team 72
Existing or New Team? Do we really need a new team? We already have a group that does behavior… STAT RTI / Problem. Solving Team IEP Child Study Team Behavior Leadership Team Professional Learning Community FBA-Behavior Intervention Team 72
 Existing or New Team? A new team may not be necessary. For example, your STAT team may already provide excellent Tier 3 behavioral assessments and interventions. Plan with other teams to assure related services are not duplicated or conflicting. 73
Existing or New Team? A new team may not be necessary. For example, your STAT team may already provide excellent Tier 3 behavioral assessments and interventions. Plan with other teams to assure related services are not duplicated or conflicting. 73
 Existing or New Team? In some cases, a new team could be beneficial. Motivated staff with advanced training, experience, and time may be recruited for your school’s “FBA-BIP Team. ” (Create a different name for your team, if you wish. ) 74
Existing or New Team? In some cases, a new team could be beneficial. Motivated staff with advanced training, experience, and time may be recruited for your school’s “FBA-BIP Team. ” (Create a different name for your team, if you wish. ) 74
 Team Members? Ideally, the core team will include: • “intervention-friendly” teachers and successful behavior managers • members with advanced training in behavioral assessment and intervention • highly regarded staff with excellent consulting skills. 75
Team Members? Ideally, the core team will include: • “intervention-friendly” teachers and successful behavior managers • members with advanced training in behavioral assessment and intervention • highly regarded staff with excellent consulting skills. 75
 Team Members? Personnel who regularly respond to behavioral concerns are key team members. These include, but are not limited to: • • • Guidance Counselor Social Worker School Psychologist Behavior Specialists / Coach ESE Specialist and Teachers Administrator(s) 76
Team Members? Personnel who regularly respond to behavioral concerns are key team members. These include, but are not limited to: • • • Guidance Counselor Social Worker School Psychologist Behavior Specialists / Coach ESE Specialist and Teachers Administrator(s) 76
 Team Members? On a case-by-case basis, invited members to the team will include: • Teachers who interact often with the student • Parent(s) and Caretaker(s) • Student (if practical) 77
Team Members? On a case-by-case basis, invited members to the team will include: • Teachers who interact often with the student • Parent(s) and Caretaker(s) • Student (if practical) 77
 Why Is Parent Participation So Important? • Parents know the most about the child’s behavior history. • Parents are the link that exists across all school settings over the years. • Parents may have strategies that support good behavior in the home. The same strategies may work at school. • It is far better to work with parents than against! • For severe behavior, interventions must occur 78 78 across all environments including the home.
Why Is Parent Participation So Important? • Parents know the most about the child’s behavior history. • Parents are the link that exists across all school settings over the years. • Parents may have strategies that support good behavior in the home. The same strategies may work at school. • It is far better to work with parents than against! • For severe behavior, interventions must occur 78 78 across all environments including the home.
 Criteria for an acceptable FBA-BIP? • The “FBA-BIP Quick Check" form (available on the website) is recommended for: – Reviewing existing FBA-BIPs – Supporting revisions of existing FBA-BIPs – Supporting completion of new FBA-BIPS • Teachers, Administrators, or others may be resistant to feedback that an existing FBABIP is inadequate. • Rely on the team when giving related 79 feedback and offering assistance.
Criteria for an acceptable FBA-BIP? • The “FBA-BIP Quick Check" form (available on the website) is recommended for: – Reviewing existing FBA-BIPs – Supporting revisions of existing FBA-BIPs – Supporting completion of new FBA-BIPS • Teachers, Administrators, or others may be resistant to feedback that an existing FBABIP is inadequate. • Rely on the team when giving related 79 feedback and offering assistance.
 Which Students Need FBA-BIP? FBA-BIP: • Should be viewed as a proactive school-wide practice • Should not be used exclusively as a reaction to extreme or chronic behavior problems • Should be conducted when school personnel are first concerned about the behaviors of the student (i. e. , earliest disciplinary actions, before 10 days of suspension!) 80 80
Which Students Need FBA-BIP? FBA-BIP: • Should be viewed as a proactive school-wide practice • Should not be used exclusively as a reaction to extreme or chronic behavior problems • Should be conducted when school personnel are first concerned about the behaviors of the student (i. e. , earliest disciplinary actions, before 10 days of suspension!) 80 80
 Which Students Need FBA-BIP? At least one staff member tracks and informs the team of: • Discipline referrals/incidents • Suspensions or removals • Changes of placement (more restrictive) that are being considered, or have occurred • Students receiving STAT Tier 3 services with unacceptable RTI • Students whose IEP behavioral/social objectives are not being met 81
Which Students Need FBA-BIP? At least one staff member tracks and informs the team of: • Discipline referrals/incidents • Suspensions or removals • Changes of placement (more restrictive) that are being considered, or have occurred • Students receiving STAT Tier 3 services with unacceptable RTI • Students whose IEP behavioral/social objectives are not being met 81
 Which Students Need FBA-BIP? At least one staff member: • Checks student records for missing, aged, and inappropriate FBA-BIPs • Checks student records for FBAs with no evidence of BIP implementation • Start with students with EBD! 82
Which Students Need FBA-BIP? At least one staff member: • Checks student records for missing, aged, and inappropriate FBA-BIPs • Checks student records for FBAs with no evidence of BIP implementation • Start with students with EBD! 82
 What If Many Students Need FBA-BIPs? The team may: • Establish a “Triage system” for case prioritization based on: – behavior recency, history, probability of repeating – behavior severity, risks to self, others, animals, valuable property belonging to others, school, etc. – intervention restrictiveness 83
What If Many Students Need FBA-BIPs? The team may: • Establish a “Triage system” for case prioritization based on: – behavior recency, history, probability of repeating – behavior severity, risks to self, others, animals, valuable property belonging to others, school, etc. – intervention restrictiveness 83
 How do I support the team? • • • Be an active participant at all team meetings! Lead/co-lead the team, or actively support the leader Be a “high-visibility” consultant on the team Gather information for the team Train other consultants on the team Train the faculty on the 3 -tiered model of behavioral assessment and interventions to increase “buy in” • Recognize and reinforce staff responsible for successful interventions • Reinforce efforts of other team members 84 • Reinforce administrative support and attendance
How do I support the team? • • • Be an active participant at all team meetings! Lead/co-lead the team, or actively support the leader Be a “high-visibility” consultant on the team Gather information for the team Train other consultants on the team Train the faculty on the 3 -tiered model of behavioral assessment and interventions to increase “buy in” • Recognize and reinforce staff responsible for successful interventions • Reinforce efforts of other team members 84 • Reinforce administrative support and attendance
 Reasons for Building FBA-BIP Teams • Work together to reduce teacher and administrative resistance • Work together to convince Administrators that time is needed for team meetings, in-class observations, and related activities by team members. • Work together to get Administrators to attend FBA meetings • Work together to recruit excellent team members • Work together to “sell” the importance of problem solving (e. g. , STAT & FBA) and RTI via inservices, 85 book clubs-study groups, discussions, etc.
Reasons for Building FBA-BIP Teams • Work together to reduce teacher and administrative resistance • Work together to convince Administrators that time is needed for team meetings, in-class observations, and related activities by team members. • Work together to get Administrators to attend FBA meetings • Work together to recruit excellent team members • Work together to “sell” the importance of problem solving (e. g. , STAT & FBA) and RTI via inservices, 85 book clubs-study groups, discussions, etc.
 FBA/BIP Overview, Team Development, and Sample Model Alexander C. Smith School Social Worker/Behavior Analyst 86
FBA/BIP Overview, Team Development, and Sample Model Alexander C. Smith School Social Worker/Behavior Analyst 86
 All Aboard! This presentation will equip you with a plan and a map forming an FBA/BIP team at your school site. Since each school site has access to different resources and staff each site will have to ultimately devise a plan that meets the needs of the students they serve. . 87
All Aboard! This presentation will equip you with a plan and a map forming an FBA/BIP team at your school site. Since each school site has access to different resources and staff each site will have to ultimately devise a plan that meets the needs of the students they serve. . 87
 Why Work Together To Do FBAs and BIPs? 88
Why Work Together To Do FBAs and BIPs? 88
 Changes Facing Schools • • • 50 19 Gum chewing Cutting in line Not raising hand Running Writing in books 89
Changes Facing Schools • • • 50 19 Gum chewing Cutting in line Not raising hand Running Writing in books 89
 Changes Facing Schools 1990 » Assault » Weapons » Drugs • Bullying /intimidation • Self-mutilation As the problems in schools change and increase in severity, our interventions (FBA/BIP) need to reflect the intense level of need. 90
Changes Facing Schools 1990 » Assault » Weapons » Drugs • Bullying /intimidation • Self-mutilation As the problems in schools change and increase in severity, our interventions (FBA/BIP) need to reflect the intense level of need. 90
 More reasons to Work Together To Do FBA/BIPs: 1. ) Ken, Tracy, and Rhonda will yell at us if we don’t (just kidding). 2. ) It is required by local and federal law. 3. ) Help reduce teacher ‘stress’. When teachers leave the field after serving less than 3 years, they often cite problematic student behavior/class disruption as a main reason. (They also cite low pay but student support staff can’t help ‘em on that one. ) 4. ) Improve student achievement by reducing problem behavior(s). 5. ) By teaching and reinforcing the replacement behaviors (the good ones we want ‘em to show us!!) we are teaching social skills, along with the 3 R’s. Students with ‘good’ social skills and an education are more likely to find gainful employment. This means the little buggers will have jobs that pay well enough 91 to keep social security going for when we all retire!!!!!
More reasons to Work Together To Do FBA/BIPs: 1. ) Ken, Tracy, and Rhonda will yell at us if we don’t (just kidding). 2. ) It is required by local and federal law. 3. ) Help reduce teacher ‘stress’. When teachers leave the field after serving less than 3 years, they often cite problematic student behavior/class disruption as a main reason. (They also cite low pay but student support staff can’t help ‘em on that one. ) 4. ) Improve student achievement by reducing problem behavior(s). 5. ) By teaching and reinforcing the replacement behaviors (the good ones we want ‘em to show us!!) we are teaching social skills, along with the 3 R’s. Students with ‘good’ social skills and an education are more likely to find gainful employment. This means the little buggers will have jobs that pay well enough 91 to keep social security going for when we all retire!!!!!
 What does this mean for me and my school/team? Is there PAPERWORK involved? !? FBA BIP 92
What does this mean for me and my school/team? Is there PAPERWORK involved? !? FBA BIP 92
 Surprise, Surprise……YES, I’m afraid so. But it will not be so bad. Besides the end result is worth it. And did I mention it was the law and we gotta do it? 93
Surprise, Surprise……YES, I’m afraid so. But it will not be so bad. Besides the end result is worth it. And did I mention it was the law and we gotta do it? 93
 Steps involved 1. ) Educate your school and help create or reinforce an existing culture that supports ‘positive’ behavior. One way to do this is help dispel certain myths or misunderstandings that other school staff may have about behavior in general. 2. ) Support the teachers and other school staff. Offer to assist them with things that may be a bit out of their area of expertise. (Just imagine if one day the Board told us we have to teach an algebra and chemistry!!!) 3. ) Identify the various strengths and expertise on your team. Use these to help assign the various roles. 4. ) If needed, engage other consultants who can help. 94 5. ) Ready to roll!!!
Steps involved 1. ) Educate your school and help create or reinforce an existing culture that supports ‘positive’ behavior. One way to do this is help dispel certain myths or misunderstandings that other school staff may have about behavior in general. 2. ) Support the teachers and other school staff. Offer to assist them with things that may be a bit out of their area of expertise. (Just imagine if one day the Board told us we have to teach an algebra and chemistry!!!) 3. ) Identify the various strengths and expertise on your team. Use these to help assign the various roles. 4. ) If needed, engage other consultants who can help. 94 5. ) Ready to roll!!!
 Dispel the MYTHS at Your Site • • • Problem behavior is a matter of control. Punishment changes behavior. Consequences are negative. A good Ol’ Fashioned Butt-whippin’ would fix him. A student knows why he or she misbehaves. We can use too much positive reinforcement. We can ‘punish’ by giving too many ‘rewards’. Positive reinforcement is like bribing a student. He must be possessed by demons!!! It is the parents’ fault. Can you think of more that you have heard? Uh, oh! 95
Dispel the MYTHS at Your Site • • • Problem behavior is a matter of control. Punishment changes behavior. Consequences are negative. A good Ol’ Fashioned Butt-whippin’ would fix him. A student knows why he or she misbehaves. We can use too much positive reinforcement. We can ‘punish’ by giving too many ‘rewards’. Positive reinforcement is like bribing a student. He must be possessed by demons!!! It is the parents’ fault. Can you think of more that you have heard? Uh, oh! 95
 Team Development Everyone holds a piece to the puzzle!! Adapting to various levels of personnel resources Identifying the skills of your team members Assigning roles 96
Team Development Everyone holds a piece to the puzzle!! Adapting to various levels of personnel resources Identifying the skills of your team members Assigning roles 96
 Suggested Team Roles and Functions The ‘Facilitator’ • Orchestrates activities of the team. • Receives referrals appropriate for FBA/BIP team, confirms that parent signed consent for FBA/BIP, manages/organizes paperwork. • Schedules meetings, sends notices/reminders about the meeting(s), keeps meeting minutes. • Checks/monitors progress and due dates on Case Status Report. • Assures criteria met in the FBA/BIP Quick Check form. 97
Suggested Team Roles and Functions The ‘Facilitator’ • Orchestrates activities of the team. • Receives referrals appropriate for FBA/BIP team, confirms that parent signed consent for FBA/BIP, manages/organizes paperwork. • Schedules meetings, sends notices/reminders about the meeting(s), keeps meeting minutes. • Checks/monitors progress and due dates on Case Status Report. • Assures criteria met in the FBA/BIP Quick Check form. 97
 The “Record Reviewer” • Reviews CUM folder • Requests and reviews related records from parents, other schools and community partners (other helping agencies). • Prepares list of all previously recorded behavioral concerns. • Summarizes, tags and/or copies both prior and current interventions (STAT, BIP, etc). • Summarizes supporting data (graphs, etc) as well as Response to Intervention (Rt. I) • Notes record location (where is the data kept), tags/copies information that will be useful for baseline measurement, pattern analysis, risk analysis, 98 and reinforcer survey
The “Record Reviewer” • Reviews CUM folder • Requests and reviews related records from parents, other schools and community partners (other helping agencies). • Prepares list of all previously recorded behavioral concerns. • Summarizes, tags and/or copies both prior and current interventions (STAT, BIP, etc). • Summarizes supporting data (graphs, etc) as well as Response to Intervention (Rt. I) • Notes record location (where is the data kept), tags/copies information that will be useful for baseline measurement, pattern analysis, risk analysis, 98 and reinforcer survey
 “The Interviewer” • Reviews information gathered at record review. • Interviews teachers, paras, other support staff, PARENTS, and/or other knowledgeable informants. • At each interview, discusses the broad list of behavioral concerns and uses a behavioral interviewing tool (e. g. , the Functional Analysis Assessment Tool - FAST). • Highlights information that may be useful in data gathering, pattern analysis or reinforcer survey. • NOTES PAST BEHAVIORAL INTERVENTIONS AND RESULTS. • Asks about other relevant info that may not have been included such as background, medical history and cultural. • Describes situations involving any of the following: high-risk behavior, injuries to self or others, property loss/damage, aversive/punitive procedures, physical restraint, seclusion, police activity, class removals, school/bus removal for more than 10 days, parent 99 complaints, threatened or active litigation.
“The Interviewer” • Reviews information gathered at record review. • Interviews teachers, paras, other support staff, PARENTS, and/or other knowledgeable informants. • At each interview, discusses the broad list of behavioral concerns and uses a behavioral interviewing tool (e. g. , the Functional Analysis Assessment Tool - FAST). • Highlights information that may be useful in data gathering, pattern analysis or reinforcer survey. • NOTES PAST BEHAVIORAL INTERVENTIONS AND RESULTS. • Asks about other relevant info that may not have been included such as background, medical history and cultural. • Describes situations involving any of the following: high-risk behavior, injuries to self or others, property loss/damage, aversive/punitive procedures, physical restraint, seclusion, police activity, class removals, school/bus removal for more than 10 days, parent 99 complaints, threatened or active litigation.
 “The Pinpointer” • Describes behavioral examples and non-examples alike. (eg. Throwing a baseball at your teachers head is ‘aggression’, but throwing it at your coach’s glove is not, etc. ). • Completes baseline measurement / estimation summarizing recent history of the highest priority behaviors, including the date of the last event, and the number of • Reviews info gathered during events in the last week/month. When possible makes a graph record reviews & interviews. specifying the type of measure (e. g. • Reduces broad list of frequency, duration, etc. ) or an behavioral concerns to a set estimated level using referrals, of approx. 1 -5 of the highest incidents report and anecdotal priority concerns. reports as data. • Completes a risk analysis. • Operationally defines behaviors in observable and • Describes any precursor behaviors 100 and/or behavior chains. measurable terms.
“The Pinpointer” • Describes behavioral examples and non-examples alike. (eg. Throwing a baseball at your teachers head is ‘aggression’, but throwing it at your coach’s glove is not, etc. ). • Completes baseline measurement / estimation summarizing recent history of the highest priority behaviors, including the date of the last event, and the number of • Reviews info gathered during events in the last week/month. When possible makes a graph record reviews & interviews. specifying the type of measure (e. g. • Reduces broad list of frequency, duration, etc. ) or an behavioral concerns to a set estimated level using referrals, of approx. 1 -5 of the highest incidents report and anecdotal priority concerns. reports as data. • Completes a risk analysis. • Operationally defines behaviors in observable and • Describes any precursor behaviors 100 and/or behavior chains. measurable terms.
 “The Pattern Analyst” • Reviews information gathered during the record review and interviews. • Coordinates/conducts Scatter Plot Analysis to identify activities/times of day closely associated with the behavior. • Coordinates and/or conducts multiple direct observations using an A-B-C checklist or A-B-C Anecdotal Form, etc. (see STAT manual). • Summarizes the most frequent or dominate conditions that come before the behavior and what comes after (antecedent conditions and consequences. ) 101
“The Pattern Analyst” • Reviews information gathered during the record review and interviews. • Coordinates/conducts Scatter Plot Analysis to identify activities/times of day closely associated with the behavior. • Coordinates and/or conducts multiple direct observations using an A-B-C checklist or A-B-C Anecdotal Form, etc. (see STAT manual). • Summarizes the most frequent or dominate conditions that come before the behavior and what comes after (antecedent conditions and consequences. ) 101
 “The Reinforcer Surveyor” • Makes individualized list of preferred items, events, or activities as identified by the team and student that may work as reinforcers in the intervention plan. • Good source for survey tool: http: //www. jimwrightonline. com/ php/jackpot. php 102
“The Reinforcer Surveyor” • Makes individualized list of preferred items, events, or activities as identified by the team and student that may work as reinforcers in the intervention plan. • Good source for survey tool: http: //www. jimwrightonline. com/ php/jackpot. php 102
 Scatterplots, Risk Analyses, Precursor Behaviors, and Behavior Chains, Oh My!!! • Although teams can assign roles as they chose, it can be very helpful to have a behavior analyst (BCABA, BCBA, CBA) or someone with extensive behavioral training, provide training or consultation regarding the roles of the “Pin. Pointer”, “Pattern Analyst” and “Reinforcer Surveyor. ” 103
Scatterplots, Risk Analyses, Precursor Behaviors, and Behavior Chains, Oh My!!! • Although teams can assign roles as they chose, it can be very helpful to have a behavior analyst (BCABA, BCBA, CBA) or someone with extensive behavioral training, provide training or consultation regarding the roles of the “Pin. Pointer”, “Pattern Analyst” and “Reinforcer Surveyor. ” 103
 Middle School 3 Meeting Model for FBA/BIP Prepared by: Alexander C. Smith School Social Worker/Behavior Analyst 104
Middle School 3 Meeting Model for FBA/BIP Prepared by: Alexander C. Smith School Social Worker/Behavior Analyst 104
 Before the 1 st Meeting • Before convening the FBA/BIP team for a referral, first meet as a unit to identify your team. Assign roles based on strengths and skills. • Team members should have completed the FDLRS 6 -hour “FBA and More” Training or an equivalent course. • Before the first meeting, the facilitator monitors process the ensure that the Consult / Committee level STAT process has been followed, WITHOUT adequate response to intervention and the problem behavior continues to occur at moderate to high frequency. 105
Before the 1 st Meeting • Before convening the FBA/BIP team for a referral, first meet as a unit to identify your team. Assign roles based on strengths and skills. • Team members should have completed the FDLRS 6 -hour “FBA and More” Training or an equivalent course. • Before the first meeting, the facilitator monitors process the ensure that the Consult / Committee level STAT process has been followed, WITHOUT adequate response to intervention and the problem behavior continues to occur at moderate to high frequency. 105
 1 st Meeting • Who should attend? Teacher(s), school psychologist, guidance counselor, social worker, and other linked informants. • What to accomplish? Review CUM file. Broadly define target behaviors. Set dates and times to directly observe the student, interview the teacher(s), parents and student (if appropriate). Decide who is doing what (write it down!!!) and what tools will be used. Start filling out FBA form. • Suggested/probable tools. ABC record, frequency counts, scatter plots, time by day records. • Set time to re-convene team and review accomplishment. (ideally, 2 nd meeting occurs within 2 weeks. ) **Remember to adopt a 2 client construct approach. The teacher and school needs our assistance as much as the student. ** • Estimated time. 15+ min. s • Desired Outcome(s). Teacher feels supported by team in dealing with students behavior. Teacher understands the FBA process. Behavioral targets defined. Observations, data gathering and interviews set. 106
1 st Meeting • Who should attend? Teacher(s), school psychologist, guidance counselor, social worker, and other linked informants. • What to accomplish? Review CUM file. Broadly define target behaviors. Set dates and times to directly observe the student, interview the teacher(s), parents and student (if appropriate). Decide who is doing what (write it down!!!) and what tools will be used. Start filling out FBA form. • Suggested/probable tools. ABC record, frequency counts, scatter plots, time by day records. • Set time to re-convene team and review accomplishment. (ideally, 2 nd meeting occurs within 2 weeks. ) **Remember to adopt a 2 client construct approach. The teacher and school needs our assistance as much as the student. ** • Estimated time. 15+ min. s • Desired Outcome(s). Teacher feels supported by team in dealing with students behavior. Teacher understands the FBA process. Behavioral targets defined. Observations, data gathering and interviews set. 106
 2 nd Meeting Invite the same parties that attended first meeting, especially the teacher(s) involved. • Review data collected. Facilitator to ensure appropriate data gathered, including baseline data and interviews. • Narrow list of behaviors to 1 -5 of most urgent ones. • Team to create operational definition and give examples as well as non-examples. • Team to create hypothesis about target behavior(s). • Draft BIP, based on data and hypothesis. • Schedule follow up meeting. 107
2 nd Meeting Invite the same parties that attended first meeting, especially the teacher(s) involved. • Review data collected. Facilitator to ensure appropriate data gathered, including baseline data and interviews. • Narrow list of behaviors to 1 -5 of most urgent ones. • Team to create operational definition and give examples as well as non-examples. • Team to create hypothesis about target behavior(s). • Draft BIP, based on data and hypothesis. • Schedule follow up meeting. 107
 rd Meeting 3 Note: Invite same people that attended first two meetings but for this one, include administration (AP). It is always a good idea to have the AP attend each meeting, but it is imperative that they attend this one. • BIP finished. • Introduce BIP and explain in detail who is do what and when. • Explain how Response to Intervention (Rt. I) will be measured and recorded. • Assign person and set time to observe intervention in action and record data. • Schedule FBA/BIP and Rt. I review meeting in near future. It is a good idea to make this an ongoing part of the STAT/CST meeting routine already in place at the school. 108
rd Meeting 3 Note: Invite same people that attended first two meetings but for this one, include administration (AP). It is always a good idea to have the AP attend each meeting, but it is imperative that they attend this one. • BIP finished. • Introduce BIP and explain in detail who is do what and when. • Explain how Response to Intervention (Rt. I) will be measured and recorded. • Assign person and set time to observe intervention in action and record data. • Schedule FBA/BIP and Rt. I review meeting in near future. It is a good idea to make this an ongoing part of the STAT/CST meeting routine already in place at the school. 108
 Follow up Meeting(s) • Use intervention data to determine Rt. I. • If problem behavior persists at same or greater rate, revamp FBA/BIP and tweak accordingly. (It may be a good idea to consult with a behavior analyst at this point. ) • If fidelity to the model was the ‘barrier’, determine where things went wrong and make a plan to remedy that provides support and perhaps even modeling to staff in need. Be sure to check and double check the FBA/BIP Quick Check 109 to make sure all steps completed.
Follow up Meeting(s) • Use intervention data to determine Rt. I. • If problem behavior persists at same or greater rate, revamp FBA/BIP and tweak accordingly. (It may be a good idea to consult with a behavior analyst at this point. ) • If fidelity to the model was the ‘barrier’, determine where things went wrong and make a plan to remedy that provides support and perhaps even modeling to staff in need. Be sure to check and double check the FBA/BIP Quick Check 109 to make sure all steps completed.
 Remember… • Frames with a red star in the upper right corner include details for later study. 110
Remember… • Frames with a red star in the upper right corner include details for later study. 110
 Adapted 9 -step FBA-BIP Model Thanks to Dr. Bradley Beam and Yates Elementary School
Adapted 9 -step FBA-BIP Model Thanks to Dr. Bradley Beam and Yates Elementary School
 Step 1 Teacher and Support Personnel meet to review FBA process, define behavior, and plan appropriate info gathering / data forms and times to observe. Note: Before this meeting, Consult and/or Committee level STAT process has been applied without adequate RTI. Problem behavior continues at moderate to high frequency. Personnel Involved Teacher School Psychologist Guidance Counselor Social Worker Info / Data Tools Estimated Time Desired Outcomes ABC Behavior Record Meeting = Teacher understanding of FBA process. 5 -15 minutes Frequency Counts Scatter Plots Time by Day Records Define target behaviors of concern. Selection of appropriate info gathering / data form(s), and times to observe. 112
Step 1 Teacher and Support Personnel meet to review FBA process, define behavior, and plan appropriate info gathering / data forms and times to observe. Note: Before this meeting, Consult and/or Committee level STAT process has been applied without adequate RTI. Problem behavior continues at moderate to high frequency. Personnel Involved Teacher School Psychologist Guidance Counselor Social Worker Info / Data Tools Estimated Time Desired Outcomes ABC Behavior Record Meeting = Teacher understanding of FBA process. 5 -15 minutes Frequency Counts Scatter Plots Time by Day Records Define target behaviors of concern. Selection of appropriate info gathering / data form(s), and times to observe. 112
 Step 2 Personnel Involved Info / Data Tools Direct observation Teacher by Teacher: To gather info / data School on problem behavior Psychologist in classroom. ABC Behavior Record School Psychologist monitors info gathering / data collection process: --once during 1 st 3 days --once weekly thereafter if initial check reveals proper use of tools -- fade gradually to bimonthly, then monthly if proper use of tools Scatter Plots Frequency Counts Time by Day Records Estimated Time Desired Outcomes Gather info / data for enough time to determine patterns and generate hypotheses: 1 -2 wks. for moderate-high frequency behavior (1 -5 times daily); 2 -3 wks. for low frequency behavior (1 -5 times weekly) - Prioritize target behaviors for reduction -I. D. frequency & inter-response time of problem behavior -Data reliability - I. D. possible Antecedents & Consequences - I. D. behavior chains 1 -5 minutes per Identify possible visit for monitoring functions info gathering / data collection with teacher 113
Step 2 Personnel Involved Info / Data Tools Direct observation Teacher by Teacher: To gather info / data School on problem behavior Psychologist in classroom. ABC Behavior Record School Psychologist monitors info gathering / data collection process: --once during 1 st 3 days --once weekly thereafter if initial check reveals proper use of tools -- fade gradually to bimonthly, then monthly if proper use of tools Scatter Plots Frequency Counts Time by Day Records Estimated Time Desired Outcomes Gather info / data for enough time to determine patterns and generate hypotheses: 1 -2 wks. for moderate-high frequency behavior (1 -5 times daily); 2 -3 wks. for low frequency behavior (1 -5 times weekly) - Prioritize target behaviors for reduction -I. D. frequency & inter-response time of problem behavior -Data reliability - I. D. possible Antecedents & Consequences - I. D. behavior chains 1 -5 minutes per Identify possible visit for monitoring functions info gathering / data collection with teacher 113
 Step 3 Review Cumulative Records Personnel Involved Teacher Info / Data Tools Cumulative Records Social Worker Guidance Counselor Discipline reports Report Cards STAT Documents Estimated Time Desired Outcomes 20 - 30 minutes Identify possible medical conditions, sensory conditions, or other relevant information that might serve as setting events for problem behavior. Includes a review of academic performance and attendance history 114
Step 3 Review Cumulative Records Personnel Involved Teacher Info / Data Tools Cumulative Records Social Worker Guidance Counselor Discipline reports Report Cards STAT Documents Estimated Time Desired Outcomes 20 - 30 minutes Identify possible medical conditions, sensory conditions, or other relevant information that might serve as setting events for problem behavior. Includes a review of academic performance and attendance history 114
 Step 4 Direct observation by Support Staff: Note: Prior to 1 st observation, teacher observations are reviewed to select best time for Support Personnel to observe. During initial data collection phase, there is at least 1 classroom observation. When needed, more observations are conducted to clarify existing data about patterns Personnel Involved Info / Data Tools School Psychologist ABC Behavior Record Guidance Counselor Narrative Recording Interval Recording Frequency Count Duration per occurrence Estimated Time Desired Outcomes 15 – 30 minutes Prioritize target behaviors for reduction Identify frequency & inter-response time of problem behavior Identify possible Antecedents and Consequences 115
Step 4 Direct observation by Support Staff: Note: Prior to 1 st observation, teacher observations are reviewed to select best time for Support Personnel to observe. During initial data collection phase, there is at least 1 classroom observation. When needed, more observations are conducted to clarify existing data about patterns Personnel Involved Info / Data Tools School Psychologist ABC Behavior Record Guidance Counselor Narrative Recording Interval Recording Frequency Count Duration per occurrence Estimated Time Desired Outcomes 15 – 30 minutes Prioritize target behaviors for reduction Identify frequency & inter-response time of problem behavior Identify possible Antecedents and Consequences 115
 Step 5 Personnel Involved Review of data and Teacher Structured Interview with School Teacher: Psychologist Teacher meets with Support Personnel to review and graph data, and to obtain other information via structured interview. Social Worker Info / Data Tools FAST Tool O’Neil Functional Assessment Interview Excel or other graphing program Estimated Time Desired Outcomes 15 – 30 minutes -I. D. data trends (increasing, decreasing, stability) - Confirm priority target behaviors for reduction - Identify frequency and inter-response time of problem behavior. - Identify possible Antecedents & Consequences - Identify behavior chains - Identify possible functions 116
Step 5 Personnel Involved Review of data and Teacher Structured Interview with School Teacher: Psychologist Teacher meets with Support Personnel to review and graph data, and to obtain other information via structured interview. Social Worker Info / Data Tools FAST Tool O’Neil Functional Assessment Interview Excel or other graphing program Estimated Time Desired Outcomes 15 – 30 minutes -I. D. data trends (increasing, decreasing, stability) - Confirm priority target behaviors for reduction - Identify frequency and inter-response time of problem behavior. - Identify possible Antecedents & Consequences - Identify behavior chains - Identify possible functions 116
 Step 6 Personnel Involved Info / Data Tools Structured Interview with Parent FAST Tool Social Worker Note: Much of this information may already be available from teacher records, cumulative folders, administrative conferences, etc. School Psychologist O’Neil Functional Assessment Interview Guidance Counselor Estimated Time Desired Outcomes 20 -30 minutes Identify possible medical conditions, sensory conditions, schedules and routines, or other relevant information that might serve as setting events for problem behavior. 117
Step 6 Personnel Involved Info / Data Tools Structured Interview with Parent FAST Tool Social Worker Note: Much of this information may already be available from teacher records, cumulative folders, administrative conferences, etc. School Psychologist O’Neil Functional Assessment Interview Guidance Counselor Estimated Time Desired Outcomes 20 -30 minutes Identify possible medical conditions, sensory conditions, schedules and routines, or other relevant information that might serve as setting events for problem behavior. 117
 Step 7 Team Meeting to Review FBA Personnel Involved Parent Teacher Note: Some parts of the FBA may be prepared before the meeting as drafts for team review at the meeting. However, open discussion by all participants must occur at the meeting. School Psychologist Guidance Counselor Social Worker Assistant Principal Info / Data Tools Estimated Time SDHC SB 45 - 60 Form 89040 minutes or Florida DOE FBA-BIP Form Additional documentation as necessary Desired Outcomes Present graphed data; Confirm priority target behaviors for reduction Discuss, agree upon, & write Hypotheses for Target Behaviors (i. e. , patterns of antecedents that set the occasion for inappropriate Behavior, and consequences that maintain behavior) Complete remaining parts of FBA form 118
Step 7 Team Meeting to Review FBA Personnel Involved Parent Teacher Note: Some parts of the FBA may be prepared before the meeting as drafts for team review at the meeting. However, open discussion by all participants must occur at the meeting. School Psychologist Guidance Counselor Social Worker Assistant Principal Info / Data Tools Estimated Time SDHC SB 45 - 60 Form 89040 minutes or Florida DOE FBA-BIP Form Additional documentation as necessary Desired Outcomes Present graphed data; Confirm priority target behaviors for reduction Discuss, agree upon, & write Hypotheses for Target Behaviors (i. e. , patterns of antecedents that set the occasion for inappropriate Behavior, and consequences that maintain behavior) Complete remaining parts of FBA form 118
 Step 8 Team Meeting to Develop BIP Personnel Involved Parent Teacher Note: Some parts of the BIP may be prepared before the meeting as drafts for team review at the meeting. However, open discussion by all participants must occur at the meeting. School Psychologist Guidance Counselor Social Worker Assistant Principal Info / Data Tools Estimated Time SDHC SB 45 - 60 Form 89040 minutes or Florida DOE FBA-BIP Form Additional documentation as necessary Desired Outcomes - Develop setting event and antecedent-based manipulations - Identify replacement behaviors and develop teaching strategies - Develop consequence-based manipulations - Develop progress monitoring plan Complete remaining parts of BIP form 119
Step 8 Team Meeting to Develop BIP Personnel Involved Parent Teacher Note: Some parts of the BIP may be prepared before the meeting as drafts for team review at the meeting. However, open discussion by all participants must occur at the meeting. School Psychologist Guidance Counselor Social Worker Assistant Principal Info / Data Tools Estimated Time SDHC SB 45 - 60 Form 89040 minutes or Florida DOE FBA-BIP Form Additional documentation as necessary Desired Outcomes - Develop setting event and antecedent-based manipulations - Identify replacement behaviors and develop teaching strategies - Develop consequence-based manipulations - Develop progress monitoring plan Complete remaining parts of BIP form 119
 Step 9 Student Progress Monitoring Personnel Involved Info / Data Tools Teacher ABC Record Social Worker Frequency Counts and Treatment Integrity Monitoring School Psychologist Guidance Counselor Excel or other graphing program Estimated Time Desired Outcomes Varies According to frequency & intensity of behavior, and Response to Intervention (RTI) Graph showing high levels of integrity in intervention implementation Identify trends in student data & BIP effectiveness (RTI) - Consider “power” of intervention - Consider need for revisions to intervention - Assure sufficient time in each phase of intervention Data should be graphed & reviewed at least weekly to identify changes in trends and/or Decision on EBD level evaluation referral, if 120 necessary
Step 9 Student Progress Monitoring Personnel Involved Info / Data Tools Teacher ABC Record Social Worker Frequency Counts and Treatment Integrity Monitoring School Psychologist Guidance Counselor Excel or other graphing program Estimated Time Desired Outcomes Varies According to frequency & intensity of behavior, and Response to Intervention (RTI) Graph showing high levels of integrity in intervention implementation Identify trends in student data & BIP effectiveness (RTI) - Consider “power” of intervention - Consider need for revisions to intervention - Assure sufficient time in each phase of intervention Data should be graphed & reviewed at least weekly to identify changes in trends and/or Decision on EBD level evaluation referral, if 120 necessary
 Adapted 6 -step FBA-BIP Model Thanks to Dr. Rance L. Harbor and Leto High School
Adapted 6 -step FBA-BIP Model Thanks to Dr. Rance L. Harbor and Leto High School
 Step 1 Teacher or Administrator meets with School Psychologist, Guidance Counselor, and ESE Specialist to review FBA process and discuss: • the need • the timeline, and • what data needs to obtained. • When it is needed Personnel Involved School Psychologist Measurement Tools ABC Behavior Records Discipline Referral Screen* Estimated Time Desired Outcomes Meeting approximately 15 -20 minutes. Teacher / Admin understanding of FBA process. Completing forms to have teachers complete approximately 20 minutes. Selection of appropriate data collection tools (s) and who is responsible ESE Specialist Attendance Screens* Guidance Counselor Instructional Planning tool (monitor grades) Admin 6 Week Progress Reports Student Identify possible: medical conditions, sensory conditions, family conditions, language barriers Teacher Feedback Sheets * Teacher ESE Planning Notes + Written parent permission for FBA has been obtained. Often coincides with a Reeval or 07 Consult based on if/or how recent a psych evaluation was done. Parent/Student Intake Form* Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist Any relevant information that might serve as setting events for problem behavior. Behavior Rating Scales Youth, Teacher, Parent Time by Day Records + (self-contained classrooms) ABC Behavior Record Time by Day Records Review Previous Psych/Soc/Stats and other cum records * Psych/Leto Form + ESE/Leto form Includes a review of academic performance, discipline hx, and attendance 122 history
Step 1 Teacher or Administrator meets with School Psychologist, Guidance Counselor, and ESE Specialist to review FBA process and discuss: • the need • the timeline, and • what data needs to obtained. • When it is needed Personnel Involved School Psychologist Measurement Tools ABC Behavior Records Discipline Referral Screen* Estimated Time Desired Outcomes Meeting approximately 15 -20 minutes. Teacher / Admin understanding of FBA process. Completing forms to have teachers complete approximately 20 minutes. Selection of appropriate data collection tools (s) and who is responsible ESE Specialist Attendance Screens* Guidance Counselor Instructional Planning tool (monitor grades) Admin 6 Week Progress Reports Student Identify possible: medical conditions, sensory conditions, family conditions, language barriers Teacher Feedback Sheets * Teacher ESE Planning Notes + Written parent permission for FBA has been obtained. Often coincides with a Reeval or 07 Consult based on if/or how recent a psych evaluation was done. Parent/Student Intake Form* Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist Any relevant information that might serve as setting events for problem behavior. Behavior Rating Scales Youth, Teacher, Parent Time by Day Records + (self-contained classrooms) ABC Behavior Record Time by Day Records Review Previous Psych/Soc/Stats and other cum records * Psych/Leto Form + ESE/Leto form Includes a review of academic performance, discipline hx, and attendance 122 history
 Step 2 Teacher completes Teacher Feedback Sheets, Planning Notes, and rating scales. Parent Completes Intake Sheet and Rating Scales Personnel Involved School Psychologist Measurement Tools ABC Behavior Records Discipline Referral Screen* ESE Specialist Attendance Screens* Guidance Counselor Instructional Planning tool (monitor grades) Admin 6 Week Progress Reports Student Completes Intake Sheet and Rating Scales. School Psychologist/ Intern to do clinical interview. ESE Para completes behavior management record (if applicable) School psychologist collects and monitors all data as it is received. Desired Outcomes Enough time to determine patterns and generate hypotheses re: antecedent and consequences that trigger and maintain behavior. Identify target behaviors for reduction Identify frequency and inter-response time of problem behavior. Identify trends (increasing, decreasing, stable) Student Teacher Feedback Sheets * Teacher ESE Planning Notes + Identify possible Antecedents & Consequences Parent/Student Intake Form* School Psychologist/ Intern to do classroom behavior observation. Estimated Time Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist Behavior Rating Scales Youth, Teacher, Parent Identify behavior chains - Identify functions Time by Day Records + (self-contained classrooms) ABC Behavior Record Time by Day Records Review Previous Psych/Soc/Stats and other cum records 123
Step 2 Teacher completes Teacher Feedback Sheets, Planning Notes, and rating scales. Parent Completes Intake Sheet and Rating Scales Personnel Involved School Psychologist Measurement Tools ABC Behavior Records Discipline Referral Screen* ESE Specialist Attendance Screens* Guidance Counselor Instructional Planning tool (monitor grades) Admin 6 Week Progress Reports Student Completes Intake Sheet and Rating Scales. School Psychologist/ Intern to do clinical interview. ESE Para completes behavior management record (if applicable) School psychologist collects and monitors all data as it is received. Desired Outcomes Enough time to determine patterns and generate hypotheses re: antecedent and consequences that trigger and maintain behavior. Identify target behaviors for reduction Identify frequency and inter-response time of problem behavior. Identify trends (increasing, decreasing, stable) Student Teacher Feedback Sheets * Teacher ESE Planning Notes + Identify possible Antecedents & Consequences Parent/Student Intake Form* School Psychologist/ Intern to do classroom behavior observation. Estimated Time Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist Behavior Rating Scales Youth, Teacher, Parent Identify behavior chains - Identify functions Time by Day Records + (self-contained classrooms) ABC Behavior Record Time by Day Records Review Previous Psych/Soc/Stats and other cum records 123
 Step 3 Analyze Data and Formulate Hypothesis Personnel Involved School Psychologist Measurement Tools Review data on selected tools Estimated Time 15 – 30 minutes Desired Outcomes Develop Intervention Idea and get “buy-in” ESE Specialist Guidance Counselor Admin Student Design Intervention Plans Teacher Parent Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist 124
Step 3 Analyze Data and Formulate Hypothesis Personnel Involved School Psychologist Measurement Tools Review data on selected tools Estimated Time 15 – 30 minutes Desired Outcomes Develop Intervention Idea and get “buy-in” ESE Specialist Guidance Counselor Admin Student Design Intervention Plans Teacher Parent Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist 124
 Step 4 Personnel Involved FBA Team Meeting School Psychologist (Note: some parts of the FBA may be prepared before the meeting as drafts for team review at the meeting. However, open discussion by all participants must occur at the meeting. ) Measurement Estimated Tools Time Desired Outcomes SDHC Form 89040 Selection of Target Behaviors ESE Specialist Guidance Counselor Admin Student Additional documentation as necessary 30 minutes Identify Hypotheses for Target Behaviors: patterns of antecedents that set the occasion for inappropriate behavior and consequences that maintain behavior Teacher Parent Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist 125
Step 4 Personnel Involved FBA Team Meeting School Psychologist (Note: some parts of the FBA may be prepared before the meeting as drafts for team review at the meeting. However, open discussion by all participants must occur at the meeting. ) Measurement Estimated Tools Time Desired Outcomes SDHC Form 89040 Selection of Target Behaviors ESE Specialist Guidance Counselor Admin Student Additional documentation as necessary 30 minutes Identify Hypotheses for Target Behaviors: patterns of antecedents that set the occasion for inappropriate behavior and consequences that maintain behavior Teacher Parent Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist 125
 Step 5 BIP Development Meeting Personnel Involved School Psychologist Measurement Estimated Tools Time Desired Outcomes SDHC Form 89040 (FBA-BIP form) Develop BIP: ESE Specialist (Note: some parts of the BIP may be prepared before the meeting as drafts for team review at the meeting. However, open discussion by all participants must occur at the meeting. ) Guidance Counselor Admin Student Teacher Parent Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist Additional documentation as necessary 30 minutes Develop antecedent manipulations Identify replacement behaviors Identify teaching strategies for replacement behaviors Identify consequence based manipulations Identify progress monitoring plan 126
Step 5 BIP Development Meeting Personnel Involved School Psychologist Measurement Estimated Tools Time Desired Outcomes SDHC Form 89040 (FBA-BIP form) Develop BIP: ESE Specialist (Note: some parts of the BIP may be prepared before the meeting as drafts for team review at the meeting. However, open discussion by all participants must occur at the meeting. ) Guidance Counselor Admin Student Teacher Parent Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist Additional documentation as necessary 30 minutes Develop antecedent manipulations Identify replacement behaviors Identify teaching strategies for replacement behaviors Identify consequence based manipulations Identify progress monitoring plan 126
 Step 6 Progress Monitoring Personnel Involved School Psychologist Measurement Tools ABC Behavior Records Discipline Referral Screen* ESE Specialist Attendance Screens* Guidance Counselor Instructional Planning tool (monitor grades) Admin 6 Week Progress Reports Student Teacher Feedback Sheets * Teacher ESE Planning Notes + Estimated Time Desired Outcomes Varies According to Frequency and Intensity of Behavior, and Response to Intervention Monitor integrity in intervention implementation Identify trends in data & effectiveness of BIP (RTI) Data reviewed each week, but overall plan reviewed approximately monthly based in severity. Parent/Student Intake Form* Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist Behavior Rating Scales Youth, Teacher, Parent Time by Day Records + (self-contained classrooms) ABC Behavior Record Time by Day Records Review Previous Psych/Soc/Stats and other cum records 127
Step 6 Progress Monitoring Personnel Involved School Psychologist Measurement Tools ABC Behavior Records Discipline Referral Screen* ESE Specialist Attendance Screens* Guidance Counselor Instructional Planning tool (monitor grades) Admin 6 Week Progress Reports Student Teacher Feedback Sheets * Teacher ESE Planning Notes + Estimated Time Desired Outcomes Varies According to Frequency and Intensity of Behavior, and Response to Intervention Monitor integrity in intervention implementation Identify trends in data & effectiveness of BIP (RTI) Data reviewed each week, but overall plan reviewed approximately monthly based in severity. Parent/Student Intake Form* Support Staff - Social Worker - School Nurse - S/L Therapist - ESOL Specialist Behavior Rating Scales Youth, Teacher, Parent Time by Day Records + (self-contained classrooms) ABC Behavior Record Time by Day Records Review Previous Psych/Soc/Stats and other cum records 127
 Tracking FBA / Intervention Status Student name: _____________________ Date of first request for support: _____ Date of first contact: _____ Date of this report: ____ Priority target behaviors: FBA status: Intervention status: Progress status / RTI Analysis: Important Issues To Address: Action Plan: The complete form (on the next frame) is on the website. 128
Tracking FBA / Intervention Status Student name: _____________________ Date of first request for support: _____ Date of first contact: _____ Date of this report: ____ Priority target behaviors: FBA status: Intervention status: Progress status / RTI Analysis: Important Issues To Address: Action Plan: The complete form (on the next frame) is on the website. 128
 FBA-BIP / Problem-Solving Team - Intervention Status Report CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION Student name: _____________________ Date of first request for support: ____ Date of first contact: _____ Date of this report: _____ Priority target behaviors: Case Status and Progress summary: FBA status: [ ] parent consent obtained, [ ] parent engaged in process __________ Team members assigned [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Record review [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Interviews [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Direct observations [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Behaviors pinpointed [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Pattern analysis [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Reinforcers identified [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Team meeting [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Extra support decision [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ FBA written, team agrees [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Intervention status: Measures & goals selected Procedures probed Plan written, team agrees Staff training Treatment integrity checks Plan integration [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _____________________________ [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _____________________________ [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Progress status / RTI Analysis: [ ] see attached graph(s) [ ] Goal met [ ] RTI acceptable, (improving trend/mean shift) [ ] Goal not met [ ] Data too variable or limited data to determine RTI [ ] RTI not acceptable, (no change or worsening trend/mean shift) [ ] Interview/Consult with: __________ [ ] Team meeting: ___________ [ ] Directly observe: ______________ (Re)train: _________ [ ] Revise or supplement FBA: __________ [ ] Refer for extra support [ ] Continue, [ ] Modify/intensify, [ ] Fade, [ ] Stop intervention [ ] Program for Maintenance & Generalization [ ] Other: ___________________________________ Important Issues To Address: Action Plan: 129
FBA-BIP / Problem-Solving Team - Intervention Status Report CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION Student name: _____________________ Date of first request for support: ____ Date of first contact: _____ Date of this report: _____ Priority target behaviors: Case Status and Progress summary: FBA status: [ ] parent consent obtained, [ ] parent engaged in process __________ Team members assigned [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Record review [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Interviews [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Direct observations [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Behaviors pinpointed [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Pattern analysis [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Reinforcers identified [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Team meeting [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Extra support decision [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ FBA written, team agrees [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Intervention status: Measures & goals selected Procedures probed Plan written, team agrees Staff training Treatment integrity checks Plan integration [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _____________________________ [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _____________________________ [ ] done, [ ] ongoing, [ ] pending: _______________ Progress status / RTI Analysis: [ ] see attached graph(s) [ ] Goal met [ ] RTI acceptable, (improving trend/mean shift) [ ] Goal not met [ ] Data too variable or limited data to determine RTI [ ] RTI not acceptable, (no change or worsening trend/mean shift) [ ] Interview/Consult with: __________ [ ] Team meeting: ___________ [ ] Directly observe: ______________ (Re)train: _________ [ ] Revise or supplement FBA: __________ [ ] Refer for extra support [ ] Continue, [ ] Modify/intensify, [ ] Fade, [ ] Stop intervention [ ] Program for Maintenance & Generalization [ ] Other: ___________________________________ Important Issues To Address: Action Plan: 129
 Team Meeting Efficiency Assessment The complete form is on the website. 130
Team Meeting Efficiency Assessment The complete form is on the website. 130
 • • • Sample Items On Team Efficiency Assessment: Our meeting times are announced and everyone arrives on time. An agenda with timelines is provided and followed. The goals for our meeting are announced and realistic. Our meetings are about the right duration to accomplish the goals. Our team leader keeps us focused on one topic at a time. Interruptions are minimized. 131 Off-task discussions are avoided.
• • • Sample Items On Team Efficiency Assessment: Our meeting times are announced and everyone arrives on time. An agenda with timelines is provided and followed. The goals for our meeting are announced and realistic. Our meetings are about the right duration to accomplish the goals. Our team leader keeps us focused on one topic at a time. Interruptions are minimized. 131 Off-task discussions are avoided.
 Summary of Steps Involved in the FBA/BIP Process 1. ) Problem identification. 2. ) Pinpointing/goal setting. 3. ) Information gathering (see role description. ) 4. ) Information analysis (problem analysis). 5. ) Intervention design. 6. ) Intervention implementation and explanation of who will do what, when and how often. 7. ) Intervention evaluation. 8. ) Intervention revising (if needed). 132
Summary of Steps Involved in the FBA/BIP Process 1. ) Problem identification. 2. ) Pinpointing/goal setting. 3. ) Information gathering (see role description. ) 4. ) Information analysis (problem analysis). 5. ) Intervention design. 6. ) Intervention implementation and explanation of who will do what, when and how often. 7. ) Intervention evaluation. 8. ) Intervention revising (if needed). 132
 • • • Items That May Be In Your “Tool Box” ABC Behavior records Discipline referral screen Attendance screens. Remember life is easier if 6 week progress reports. you chose the right tool Teacher feedback sheets for the job. ESE planning notes. Parent/student intake forms. Behavior rating scales. Time by Day recordings. Summary of structured interviews (FAST, MAS etc. ) • Scatterplots/graphs. • Measures of frequency and duration when appropriate. 133 • CUM file review, medical info, cultural info.
• • • Items That May Be In Your “Tool Box” ABC Behavior records Discipline referral screen Attendance screens. Remember life is easier if 6 week progress reports. you chose the right tool Teacher feedback sheets for the job. ESE planning notes. Parent/student intake forms. Behavior rating scales. Time by Day recordings. Summary of structured interviews (FAST, MAS etc. ) • Scatterplots/graphs. • Measures of frequency and duration when appropriate. 133 • CUM file review, medical info, cultural info.
 Note About Partnership • Remember to involve key stake holders during the process, especially parents!!!!!! 134
Note About Partnership • Remember to involve key stake holders during the process, especially parents!!!!!! 134
 Note About Partnership • Remember to involve key stake holders during the process, especially parents!!!!!! • We are all ‘in the same boat’ and have the same (or very similar) end goal in mind…. . better outcomes for the student and less “stress” & disruption for the teacher(s) and school. • Don’t be afraid to include/invite SRO’s, behavior intervention staff/hall monitors, specials teachers, and 135 community partners such as therapists.
Note About Partnership • Remember to involve key stake holders during the process, especially parents!!!!!! • We are all ‘in the same boat’ and have the same (or very similar) end goal in mind…. . better outcomes for the student and less “stress” & disruption for the teacher(s) and school. • Don’t be afraid to include/invite SRO’s, behavior intervention staff/hall monitors, specials teachers, and 135 community partners such as therapists.
 The Wrap-Up !!!
The Wrap-Up !!!
 Follow-up activity to start or enhance team development All site-based Guidance Counselors, Social Workers, and School Psychologists meet with other key personnel (including Administrator), and prepare your school's • FBA-BIP Team Action Plan A blank template is on the website. 137
Follow-up activity to start or enhance team development All site-based Guidance Counselors, Social Workers, and School Psychologists meet with other key personnel (including Administrator), and prepare your school's • FBA-BIP Team Action Plan A blank template is on the website. 137
 FBA-BIP Team Action Plan (template) 1. Today’s Date: 2. Team Members: 3. Our team’s areas of strength, short-term & long-term concerns/needs are: 4. Our next goals are (based on #3): 5. Our team’s action plan is: (based on #4): 6. Team Signatures (the whole team created and commits to the plan): 138
FBA-BIP Team Action Plan (template) 1. Today’s Date: 2. Team Members: 3. Our team’s areas of strength, short-term & long-term concerns/needs are: 4. Our next goals are (based on #3): 5. Our team’s action plan is: (based on #4): 6. Team Signatures (the whole team created and commits to the plan): 138
 Follow-up activity to start or enhance team development All site-based Guidance Counselors, Social Workers, and School Psychologists meet with other key personnel (including Administrator), and prepare your school's • FBA-BIP Team Action Plan • 3 tier system (pyramid model). A blank template is on the website. 139
Follow-up activity to start or enhance team development All site-based Guidance Counselors, Social Workers, and School Psychologists meet with other key personnel (including Administrator), and prepare your school's • FBA-BIP Team Action Plan • 3 tier system (pyramid model). A blank template is on the website. 139
 Comprehensive FBA BIP (may include Behavior Contract) 1 -to-1 Replacement behavior training Services integrated with parents and community resources Example of 3 Tier System STAT problem-solving, weekly RTI monitoring at: Small group training: Replacement behaviors, Social Skills, Anger management, etc. “Behavior Clinic” Behavior Contracts & Goal Setting Parent conferences B. T. Washington Schoolwide rules are posted, rehearsed, reviewed, + reinforced “Hornets Dozen” (Principals 200 Club) Cafeteria traffic management, reports to teachers Classroom schedules + routines are posted, rehearsed, reviewed, + reinforced “Hornet Stamps” reinforcement system Daily behavior reports to parents (via agenda) Success Chains, Mystery Motivators, Good Behavior Game Student problem-solving activities + forms 140
Comprehensive FBA BIP (may include Behavior Contract) 1 -to-1 Replacement behavior training Services integrated with parents and community resources Example of 3 Tier System STAT problem-solving, weekly RTI monitoring at: Small group training: Replacement behaviors, Social Skills, Anger management, etc. “Behavior Clinic” Behavior Contracts & Goal Setting Parent conferences B. T. Washington Schoolwide rules are posted, rehearsed, reviewed, + reinforced “Hornets Dozen” (Principals 200 Club) Cafeteria traffic management, reports to teachers Classroom schedules + routines are posted, rehearsed, reviewed, + reinforced “Hornet Stamps” reinforcement system Daily behavior reports to parents (via agenda) Success Chains, Mystery Motivators, Good Behavior Game Student problem-solving activities + forms 140
 Follow-up activity to start or enhance team development All site-based Guidance Counselors, Social Workers, and School Psychologists meet with other key personnel (including Administrator), and prepare your school's • FBA-BIP Team Action Plan • 3 tier system (pyramid model), and • Specific FBA-BIP Team Roles and Timelines (like the previous examples from Burnett, Yates, and Leto) 141
Follow-up activity to start or enhance team development All site-based Guidance Counselors, Social Workers, and School Psychologists meet with other key personnel (including Administrator), and prepare your school's • FBA-BIP Team Action Plan • 3 tier system (pyramid model), and • Specific FBA-BIP Team Roles and Timelines (like the previous examples from Burnett, Yates, and Leto) 141
 Follow-up activity to start or enhance team development All site-based Guidance Counselors, Social Workers, and School Psychologists meet with other key personnel (including Administrator), and prepare your school's • FBA-BIP Team Action Plan • 3 tier system (pyramid model), and • Specific FBA-BIP Team Roles, and Please submit these written descriptions to your Supervisor by September 3. 142
Follow-up activity to start or enhance team development All site-based Guidance Counselors, Social Workers, and School Psychologists meet with other key personnel (including Administrator), and prepare your school's • FBA-BIP Team Action Plan • 3 tier system (pyramid model), and • Specific FBA-BIP Team Roles, and Please submit these written descriptions to your Supervisor by September 3. 142
 Panel Discussion We want everybody’s questions, feedback, and suggestions. If we did not get to them during the presentation, please write and submit them at the presentation end, or email them to: tracy. schatzberg@sdhc. k 12. fl. us or kevin. murdock@sdhc. k 12. fl. us
Panel Discussion We want everybody’s questions, feedback, and suggestions. If we did not get to them during the presentation, please write and submit them at the presentation end, or email them to: tracy. schatzberg@sdhc. k 12. fl. us or kevin. murdock@sdhc. k 12. fl. us
 The End !!! Thanks for your participation !!!
The End !!! Thanks for your participation !!!


