f6576c6559c873632201de8f16d3bedd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 109
 Welcome National Dangerous Goods Training Consortium ADR Training Tanks Module 1
Welcome National Dangerous Goods Training Consortium ADR Training Tanks Module 1
 Tanks Definition • “Tank” means a tank container, portable tank, demountable tank or fixed tank • When a fixed tank with a capacity exceeding 1000 litres is attached to a vehicle or forms part of it, the vehicle becomes a tank vehicle 2
Tanks Definition • “Tank” means a tank container, portable tank, demountable tank or fixed tank • When a fixed tank with a capacity exceeding 1000 litres is attached to a vehicle or forms part of it, the vehicle becomes a tank vehicle 2
 Tanks Definition • Also includes – • Multiple element gas container(MEGC) • Mobile explosives manufacturing unit" (MEMU) • Battery vehicle 3
Tanks Definition • Also includes – • Multiple element gas container(MEGC) • Mobile explosives manufacturing unit" (MEMU) • Battery vehicle 3
 Tanks Training • An ADR driver training certificate including “tanks” is required for drivers of vehicles carrying dangerous goods in: • Fixed tanks , demountable tanks and battery vehicles exceeding 1 m 3 • Tank containers, portable tanks or MEGCs with an individual capacity exceeding 3 m 3 4
Tanks Training • An ADR driver training certificate including “tanks” is required for drivers of vehicles carrying dangerous goods in: • Fixed tanks , demountable tanks and battery vehicles exceeding 1 m 3 • Tank containers, portable tanks or MEGCs with an individual capacity exceeding 3 m 3 4
 Tanks Specific Training • This training module covers only the general requirements of ADR. • Further specific training is required by the employer regarding specific vehicles, equipment and specific loads. 5
Tanks Specific Training • This training module covers only the general requirements of ADR. • Further specific training is required by the employer regarding specific vehicles, equipment and specific loads. 5
 Inspection • Tank shells and their equipment require inspection and testing before being put into service • Periodic inspections are also required • Periodic inspections include: – External and internal inspection – Tank shell thickness – Leak proof test – Hydraulic pressure test 6
Inspection • Tank shells and their equipment require inspection and testing before being put into service • Periodic inspections are also required • Periodic inspections include: – External and internal inspection – Tank shell thickness – Leak proof test – Hydraulic pressure test 6
 Inspection • Maximum length of time between periodic inspections: Fixed Tanks (tank vehicles) Demountable tanks Battery Vehicles Tank containers MEGCs Portable tanks 6 years 5 years 7
Inspection • Maximum length of time between periodic inspections: Fixed Tanks (tank vehicles) Demountable tanks Battery Vehicles Tank containers MEGCs Portable tanks 6 years 5 years 7
 Tanks Inspection • Tanks also require intermediate inspections • Intermediate inspections include – – Leakproofness – Operation of equipment 8
Tanks Inspection • Tanks also require intermediate inspections • Intermediate inspections include – – Leakproofness – Operation of equipment 8
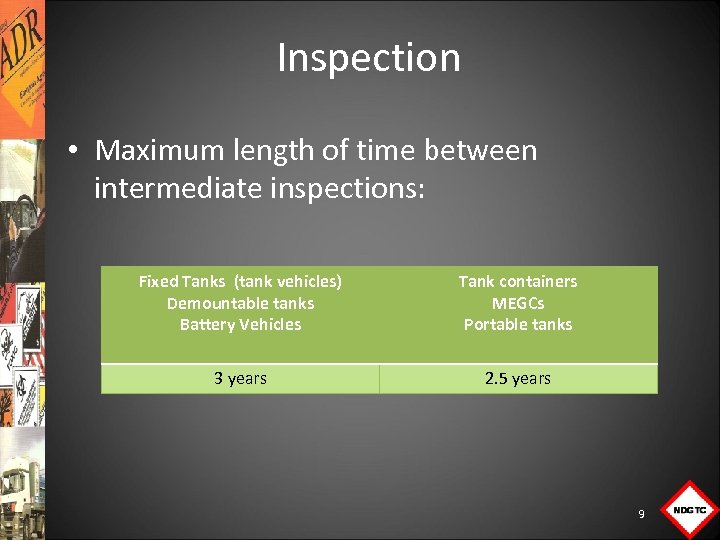 Inspection • Maximum length of time between intermediate inspections: Fixed Tanks (tank vehicles) Demountable tanks Battery Vehicles Tank containers MEGCs Portable tanks 3 years 2. 5 years 9
Inspection • Maximum length of time between intermediate inspections: Fixed Tanks (tank vehicles) Demountable tanks Battery Vehicles Tank containers MEGCs Portable tanks 3 years 2. 5 years 9
 Certification • Certificates are issued for the initial, periodic and intermediate inspections • Copies of these must be kept with the tank record of each tank • Details must also be marked on the tank plate 10
Certification • Certificates are issued for the initial, periodic and intermediate inspections • Copies of these must be kept with the tank record of each tank • Details must also be marked on the tank plate 10
 Tanks Certification • Tank vehicles , battery vehicles, MEMUs and vehicles intended for the carriage of dangerous goods in demountable tanks, tank containers, portable tanks or MEGCs, are subject to the ADR requirements concerning – – Construction – Type approval – Annual testing (Certificate of ADR approval) 11
Tanks Certification • Tank vehicles , battery vehicles, MEMUs and vehicles intended for the carriage of dangerous goods in demountable tanks, tank containers, portable tanks or MEGCs, are subject to the ADR requirements concerning – – Construction – Type approval – Annual testing (Certificate of ADR approval) 11
 Certificate of approval • Declaration of conformity from the manufacturer for new vehicles • Annual ADR test and certification (by VOSA) • Confirms continued compliance with ADR vehicle requirements • Documentation carried on vehicle • Articulated vehicles require one certificate for tractor unit and one for trailer 12
Certificate of approval • Declaration of conformity from the manufacturer for new vehicles • Annual ADR test and certification (by VOSA) • Confirms continued compliance with ADR vehicle requirements • Documentation carried on vehicle • Articulated vehicles require one certificate for tractor unit and one for trailer 12
 Certificate of approval 13
Certificate of approval 13
 Tanks Plate • Every tank is fitted with a corrosion resistant plate. • It is permanently attached to the tank • Information regarding the tank is stamped or engraved on the plate 14
Tanks Plate • Every tank is fitted with a corrosion resistant plate. • It is permanently attached to the tank • Information regarding the tank is stamped or engraved on the plate 14
 Plate • Plate information may include: – Approval number – Manufacturer – Serial number – Test pressure – Maximum working pressure – Capacity – Date and type of last inspection – Protective lining 15
Plate • Plate information may include: – Approval number – Manufacturer – Serial number – Test pressure – Maximum working pressure – Capacity – Date and type of last inspection – Protective lining 15
 Tanks Regulations • Tank is in scope of the regulations if loaded with dangerous goods or when empty but uncleaned. • CDG Regulations apply to road and rail journeys within Great Britain. • ADR applies to international road journeys in Europe • IMDG Code applies to sea journeys • RID – international rail journeys 16
Tanks Regulations • Tank is in scope of the regulations if loaded with dangerous goods or when empty but uncleaned. • CDG Regulations apply to road and rail journeys within Great Britain. • ADR applies to international road journeys in Europe • IMDG Code applies to sea journeys • RID – international rail journeys 16
 Tanks Fire Extinguishers • CDG and ADR require vehicle fire extinguishers as detailed in the core module • Driver must check before journey – Sealed – Good condition – Approved – Inspection date 17
Tanks Fire Extinguishers • CDG and ADR require vehicle fire extinguishers as detailed in the core module • Driver must check before journey – Sealed – Good condition – Approved – Inspection date 17
 Vehicle Equipment Vehicle Wheel Chock Two Warning Signs Crew Warning vest Torch Gloves Eye protection 18
Vehicle Equipment Vehicle Wheel Chock Two Warning Signs Crew Warning vest Torch Gloves Eye protection 18
 Vehicle Equipment • Additional equipment for classes 3, 4. 1, 4. 3, 8 and 9 • Vehicle Eye rinsing liquid Shovel Drain Seal Collecting Container 19
Vehicle Equipment • Additional equipment for classes 3, 4. 1, 4. 3, 8 and 9 • Vehicle Eye rinsing liquid Shovel Drain Seal Collecting Container 19
 Tanks Vehicle Equipment • Additional equipment for each member of the vehicle crew when carrying Toxic gas or toxic substances (2. 3 or 6. 1) • Respirator 20
Tanks Vehicle Equipment • Additional equipment for each member of the vehicle crew when carrying Toxic gas or toxic substances (2. 3 or 6. 1) • Respirator 20
 Documentation • • • Driver Training Certificate Photographic Identification Transport Document Instructions in Writing Declaration of conformity or Vehicle approval certificate (2 for articulated vehicles and vehicles towing trailers) 21
Documentation • • • Driver Training Certificate Photographic Identification Transport Document Instructions in Writing Declaration of conformity or Vehicle approval certificate (2 for articulated vehicles and vehicles towing trailers) 21
 Safety Precautions • During Loading – Confirm security of tank containers by checking all four twist locks are fastened – Ensure tank is suitable for load – Check tank, fittings and equipment for damage – Ensure adequate segregation of incompatible substances 22
Safety Precautions • During Loading – Confirm security of tank containers by checking all four twist locks are fastened – Ensure tank is suitable for load – Check tank, fittings and equipment for damage – Ensure adequate segregation of incompatible substances 22
 Tanks Safety Precautions • During unloading – Ensure sufficient space in receiving vessel for load – Confirm connections are correct before discharge of load – Ensure vehicle is not moved when hoses are connected – Unlock twist locks before tank containers are lifted off 23
Tanks Safety Precautions • During unloading – Ensure sufficient space in receiving vessel for load – Confirm connections are correct before discharge of load – Ensure vehicle is not moved when hoses are connected – Unlock twist locks before tank containers are lifted off 23
 UK Marking • Driver must ensure vehicle is marked correctly • Markings must be clean and unobstructed • Orange plate on front 24
UK Marking • Driver must ensure vehicle is marked correctly • Markings must be clean and unobstructed • Orange plate on front 24
 UK Marking – Single load • Orange plate each side and rear displaying Emergency Action Code at the top and UN number below 2 WE 1230 • Emergency action code indicates to the emergency services, actions to be taken during an incident 25
UK Marking – Single load • Orange plate each side and rear displaying Emergency Action Code at the top and UN number below 2 WE 1230 • Emergency action code indicates to the emergency services, actions to be taken during an incident 25
 UK Marking – Single load • Placards each side and rear 250 x 250 mm • Subsidiary placards adjacent where required • Environmentally hazardous substance mark next to placards when needed 26
UK Marking – Single load • Placards each side and rear 250 x 250 mm • Subsidiary placards adjacent where required • Environmentally hazardous substance mark next to placards when needed 26
 UK Marking – Single load • Specialist advice telephone number each side and rear • Next to orange plates 27
UK Marking – Single load • Specialist advice telephone number each side and rear • Next to orange plates 27
 UK Marking – Single load 28
UK Marking – Single load 28
 UK Marking • Information displayed by the orange plates, placards and telephone number may all be shown on hazard warning panels (UK only). • Displayed each side and rear • Placards may be reduced to 200 x 200 mm • Plain orange plate at front • Must withstand 15 minutes in a fire 29
UK Marking • Information displayed by the orange plates, placards and telephone number may all be shown on hazard warning panels (UK only). • Displayed each side and rear • Placards may be reduced to 200 x 200 mm • Plain orange plate at front • Must withstand 15 minutes in a fire 29
 UK Marking – Single load • Hazard Warning Panel 30
UK Marking – Single load • Hazard Warning Panel 30
 UK Marking – Multi load • Orange plate at front • Un number on each side of each compartment • Emergency action code each side and rear • Placards each side and rear • Telephone number each side and rear • Environmentally hazardous mark if required 31
UK Marking – Multi load • Orange plate at front • Un number on each side of each compartment • Emergency action code each side and rear • Placards each side and rear • Telephone number each side and rear • Environmentally hazardous mark if required 31
 UK Marking – Multi load 32
UK Marking – Multi load 32
 UK Marking – Multi load • Tank vehicles carrying more than one of • UN 1202 DIESEL or GAS OIL or HEATING OIL, LIGHT • UN 1203 PETROL or MOTOR SPIRIT or GASOLINE • UN 1223 KEROSENE • Need only be marked as the product with the lowest flashpoint 33
UK Marking – Multi load • Tank vehicles carrying more than one of • UN 1202 DIESEL or GAS OIL or HEATING OIL, LIGHT • UN 1203 PETROL or MOTOR SPIRIT or GASOLINE • UN 1223 KEROSENE • Need only be marked as the product with the lowest flashpoint 33
 UK Marking – Multi load Fuel 34
UK Marking – Multi load Fuel 34
 IMDG Marking • Placards • Each side and rear of tank vehicles • Each side, front and rear of tank containers and unaccompanied trailers • Must be 250 x 250 mm minimum • Subsidiary risk placards also displayed alongside main risk placards 35
IMDG Marking • Placards • Each side and rear of tank vehicles • Each side, front and rear of tank containers and unaccompanied trailers • Must be 250 x 250 mm minimum • Subsidiary risk placards also displayed alongside main risk placards 35
 IMDG Marking • UN number • Included within each main risk placard • Or in orange panel adjacent to placard 36
IMDG Marking • UN number • Included within each main risk placard • Or in orange panel adjacent to placard 36
 IMDG Marking • Proper shipping name each side METHANOL • Marine pollutants – display marine pollutant mark adjacent to placards 37
IMDG Marking • Proper shipping name each side METHANOL • Marine pollutants – display marine pollutant mark adjacent to placards 37
 IMDG Marking 38
IMDG Marking 38
 ADR Marking • Hazard Identification Number (HIN) in place of emergency action code • Single load marking – Placards each side and rear – Plain orange plates front and rear – Orange plates displaying HIN and UN Number each side 39
ADR Marking • Hazard Identification Number (HIN) in place of emergency action code • Single load marking – Placards each side and rear – Plain orange plates front and rear – Orange plates displaying HIN and UN Number each side 39
 ADR Marking 40
ADR Marking 40
 ADR Marking • Single load alternative marking – placards each side and rear – Orange plates front and rear displaying HIN and UN Number 336 1230 41
ADR Marking • Single load alternative marking – placards each side and rear – Orange plates front and rear displaying HIN and UN Number 336 1230 41
 ADR Marking 42
ADR Marking 42
 ADR Marking • Hazard Identification Numbers consist of 2 or 3 numbers meaning in general – 2 3 4 Emission of gas due to pressure or to chemical reaction Flammability of liquids (vapours) and gases or self heating liquid Flammability of solids or self heating solid 43
ADR Marking • Hazard Identification Numbers consist of 2 or 3 numbers meaning in general – 2 3 4 Emission of gas due to pressure or to chemical reaction Flammability of liquids (vapours) and gases or self heating liquid Flammability of solids or self heating solid 43
 ADR Marking 5 6 7 8 9 X Oxidizing (fire intensifying) effect Toxicity or risk of infection Radioactivity Corrosivity Risk of spontaneous violent reaction Substance reacts dangerously with water 44
ADR Marking 5 6 7 8 9 X Oxidizing (fire intensifying) effect Toxicity or risk of infection Radioactivity Corrosivity Risk of spontaneous violent reaction Substance reacts dangerously with water 44
 ADR Marking • Hazard Identification Examples– 80 Corrosive substance 88 Highly corrosive substance 86 Corrosive substance, toxic 886 Highly corrosive substance, toxic X 886 Highly corrosive substance, toxic which reacts dangerously with water 45
ADR Marking • Hazard Identification Examples– 80 Corrosive substance 88 Highly corrosive substance 86 Corrosive substance, toxic 886 Highly corrosive substance, toxic X 886 Highly corrosive substance, toxic which reacts dangerously with water 45
 ADR Marking • Hazard Identification Examples– 90 99 839 Miscellaneous substances Elevated temperature substances Corrosive, Flammable – volatile reaction 46
ADR Marking • Hazard Identification Examples– 90 99 839 Miscellaneous substances Elevated temperature substances Corrosive, Flammable – volatile reaction 46
 UK and ADR Marking • Elevated Temperature Mark • Required for liquids over 100 ⁰C • Solids over 240 ⁰C 47
UK and ADR Marking • Elevated Temperature Mark • Required for liquids over 100 ⁰C • Solids over 240 ⁰C 47
 UK and ADR Marking • Orange Plates displaying information including – Emergency Action Code – Hazard Identification Number – UN Number • Must display the information such that it is legible after 15 min engulfment in fire (tanks constructed on or after 1 st Jan 2005) 48
UK and ADR Marking • Orange Plates displaying information including – Emergency Action Code – Hazard Identification Number – UN Number • Must display the information such that it is legible after 15 min engulfment in fire (tanks constructed on or after 1 st Jan 2005) 48
 Tank Types • There are many tank types including 49
Tank Types • There are many tank types including 49
 Tank Types • LPG 50
Tank Types • LPG 50
 Tank Types • Flammable liquid 51
Tank Types • Flammable liquid 51
 Tank Types • Cryogenic 52
Tank Types • Cryogenic 52
 Tank Types • Powders and Granules 53
Tank Types • Powders and Granules 53
 Tank Types • General Purpose Chemical Tanker 54
Tank Types • General Purpose Chemical Tanker 54
 Tank Types • Waste Tank – Vacuum Tank with rear door 55
Tank Types • Waste Tank – Vacuum Tank with rear door 55
 Tank Types • Other tanks include – Heated loads – Refrigerated Loads – Foodstuffs 56
Tank Types • Other tanks include – Heated loads – Refrigerated Loads – Foodstuffs 56
 Tank Construction • Materials – Aluminium – Mild Steel – Stainless Steel – Fibre reinforced Plastic • Linings – Rubber – Plastic – Glass 57
Tank Construction • Materials – Aluminium – Mild Steel – Stainless Steel – Fibre reinforced Plastic • Linings – Rubber – Plastic – Glass 57
 Tank Construction • Atmospheric tank – Not designed to be pressurised – Discharged by gravity or pump • Pressure tank – Withstands maximum working pressure of discharge – Typically 2 bar 58
Tank Construction • Atmospheric tank – Not designed to be pressurised – Discharged by gravity or pump • Pressure tank – Withstands maximum working pressure of discharge – Typically 2 bar 58
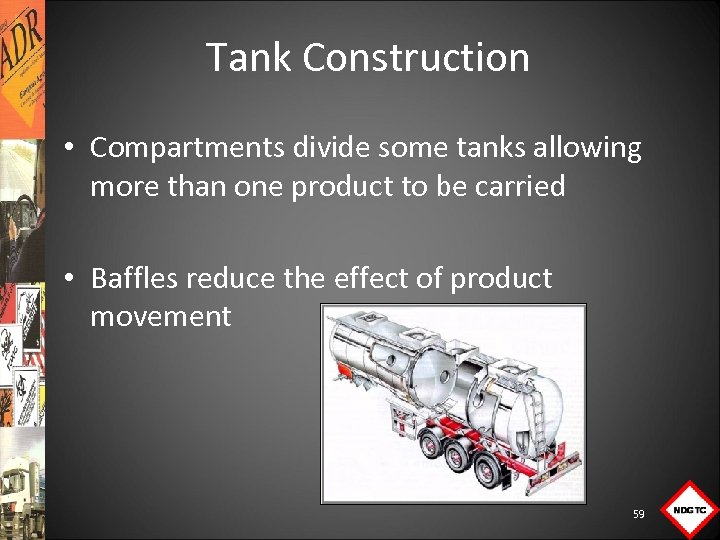 Tank Construction • Compartments divide some tanks allowing more than one product to be carried • Baffles reduce the effect of product movement 59
Tank Construction • Compartments divide some tanks allowing more than one product to be carried • Baffles reduce the effect of product movement 59
 Tank Vehicle Construction • • ADR stipulates design and construction of – Engines and fuel systems Fuel tanks Exhaust systems Electrical systems Centre of gravity Rear protection Fire resistant cabs 60
Tank Vehicle Construction • • ADR stipulates design and construction of – Engines and fuel systems Fuel tanks Exhaust systems Electrical systems Centre of gravity Rear protection Fire resistant cabs 60
 Tanks Filling Ratio • Tanks greater than 7500 ltrs with no baffles or compartments must either be filled: • More than 80% • Or less than 20% 61
Tanks Filling Ratio • Tanks greater than 7500 ltrs with no baffles or compartments must either be filled: • More than 80% • Or less than 20% 61
 Tanks Filling Ratio • Ullage – • Tanks containing liquids must leave space for liquid expansion due to an increase temperature 62
Tanks Filling Ratio • Ullage – • Tanks containing liquids must leave space for liquid expansion due to an increase temperature 62
 Tanks • Maximum allowable working pressure • Must not be exceeded during pressure discharge • Shown on tank plate 63
Tanks • Maximum allowable working pressure • Must not be exceeded during pressure discharge • Shown on tank plate 63
 Tanks • Where liquefied gases require thermally insulated tanks these may be : • Completely clad in insulating materials or • Fitted with sun shields 64
Tanks • Where liquefied gases require thermally insulated tanks these may be : • Completely clad in insulating materials or • Fitted with sun shields 64
 Tanks Equipment • Man lids • Allow access to tank for filling and cleaning 65
Tanks Equipment • Man lids • Allow access to tank for filling and cleaning 65
 Tanks Equipment • Dip Sticks • Used to ascertain quantity in tank compartment 66
Tanks Equipment • Dip Sticks • Used to ascertain quantity in tank compartment 66
 Tanks Equipment • Pressure relief, and pressure & Vacuum relief valves • Prevent excess pressure build up in tank • Also prevent excess vacuum 67
Tanks Equipment • Pressure relief, and pressure & Vacuum relief valves • Prevent excess pressure build up in tank • Also prevent excess vacuum 67
 Tanks Implosion • Excess vacuum in tank may cause implosion 68
Tanks Implosion • Excess vacuum in tank may cause implosion 68
 Tanks Equipment • Bursting discs • Prevent excess pressure in tank • Do not reseal • Require replacement once operated • Tank then requires re testing 69
Tanks Equipment • Bursting discs • Prevent excess pressure in tank • Do not reseal • Require replacement once operated • Tank then requires re testing 69
 Tanks Equipment • Pressure connections and Pressure gauges • Driver must understand correct use • MAWP must not be exceeded 70
Tanks Equipment • Pressure connections and Pressure gauges • Driver must understand correct use • MAWP must not be exceeded 70
 Tanks Equipment • Seals and bolts • Close man lid securely • Safebolts prevent lid flying open when pressure in tank • Fastened first • Unfastened last 71
Tanks Equipment • Seals and bolts • Close man lid securely • Safebolts prevent lid flying open when pressure in tank • Fastened first • Unfastened last 71
 Tanks Equipment • Emergency shut off valves • Close down whole operation when pushed 72
Tanks Equipment • Emergency shut off valves • Close down whole operation when pushed 72
 Tanks Equipment • Hose connections and blanking caps • Must be checked and in good condition 73
Tanks Equipment • Hose connections and blanking caps • Must be checked and in good condition 73
 Tanks Equipment • Outlet valves, manifolds, and valve controls 74
Tanks Equipment • Outlet valves, manifolds, and valve controls 74
 Tanks Equipment • Foot Valve • Prevents loss of product if external pipes and fittings are damaged in an accident 75
Tanks Equipment • Foot Valve • Prevents loss of product if external pipes and fittings are damaged in an accident 75
 Tanks – Equipment • Other equipment may include – Flame traps and gauzes – Temperature gauges – Fusible elements – Excess flow valves – Steam heating coils – Warm water coils 76
Tanks – Equipment • Other equipment may include – Flame traps and gauzes – Temperature gauges – Fusible elements – Excess flow valves – Steam heating coils – Warm water coils 76
 Tanks Loading • • • Obey site rules Wear appropriate PPE Report to responsible person Check location of emergency equipment Secure vehicle against accidental movement Check correct substance to be loaded 77
Tanks Loading • • • Obey site rules Wear appropriate PPE Report to responsible person Check location of emergency equipment Secure vehicle against accidental movement Check correct substance to be loaded 77
 Tanks Loading • • • Ensure sufficient capacity in tank Check adequate ullage space will be left Ensure vehicle will not be overloaded Earth vehicle before loading Control rate of filling Take precautions against fire or explosion 78
Tanks Loading • • • Ensure sufficient capacity in tank Check adequate ullage space will be left Ensure vehicle will not be overloaded Earth vehicle before loading Control rate of filling Take precautions against fire or explosion 78
 Tanks Checks During Journey Ensure Tank is sealed Hoses and other equipment are secure Blanking caps are in place Correct marks and placards are clearly displayed and are clean • All documentation is available • • • 79
Tanks Checks During Journey Ensure Tank is sealed Hoses and other equipment are secure Blanking caps are in place Correct marks and placards are clearly displayed and are clean • All documentation is available • • • 79
 Tanks Checks during journey • Ensure – There are no leaks – There is no heat build up on vehicle 80
Tanks Checks during journey • Ensure – There are no leaks – There is no heat build up on vehicle 80
 Tanks – Discharge • Obey site rules • Wear appropriate PPE • Report to responsible person where appropriate • Follow correct procedure for driver controlled delivery • Check location of emergency equipment • Secure vehicle against accidental movement 81
Tanks – Discharge • Obey site rules • Wear appropriate PPE • Report to responsible person where appropriate • Follow correct procedure for driver controlled delivery • Check location of emergency equipment • Secure vehicle against accidental movement 81
 Tanks – Discharge • Ensure – Tank/vehicle is earthed – Sufficient space in receiving tank – Hoses are connected correctly – Air or vapour is allowed back into tank during gravity or pump discharge. – Correct pump speed is maintained 82
Tanks – Discharge • Ensure – Tank/vehicle is earthed – Sufficient space in receiving tank – Hoses are connected correctly – Air or vapour is allowed back into tank during gravity or pump discharge. – Correct pump speed is maintained 82
 Tanks – Discharge • Ensure – Tank is sealed during pressure discharge – MAWP is not exceeded – Tank is depressurised after discharge – Drain and cap hoses – Clean up any spillage – Secure hoses and equipment on vehicle – Documentation states correct tank status e. g. EMPTY, UNCLEANED RETURN 83
Tanks – Discharge • Ensure – Tank is sealed during pressure discharge – MAWP is not exceeded – Tank is depressurised after discharge – Drain and cap hoses – Clean up any spillage – Secure hoses and equipment on vehicle – Documentation states correct tank status e. g. EMPTY, UNCLEANED RETURN 83
 BLEVE • • Boiling Liquid Expanding Vapour Explosion Caused by fire engulfment of tank Tank metal usually fails in the vapour space area where there is no liquid to spread heat 84
BLEVE • • Boiling Liquid Expanding Vapour Explosion Caused by fire engulfment of tank Tank metal usually fails in the vapour space area where there is no liquid to spread heat 84
 Tanks Static Electricity • Causes – Liquid flowing through pipes and hoses – Increases when liquid passes through restrictions such as filters – Splash filling (loading arm not extending to bottom of tank) – Clothing – Tools – Thunderstorms 85
Tanks Static Electricity • Causes – Liquid flowing through pipes and hoses – Increases when liquid passes through restrictions such as filters – Splash filling (loading arm not extending to bottom of tank) – Clothing – Tools – Thunderstorms 85
 Tanks Overfilling • Recall filling ratio must not be exceeded • Sufficient ullage must remain to allow for liquid expansion • Drivers must check capacity of tank/compartment and monitor quantity being loaded. 86
Tanks Overfilling • Recall filling ratio must not be exceeded • Sufficient ullage must remain to allow for liquid expansion • Drivers must check capacity of tank/compartment and monitor quantity being loaded. 86
 Tanks Overfilling • Tanks and loading sites are fitted with equipment to measure quantity being loaded • Meters • Dipsticks • Ullage bars • Sight glasses or other gauges • Weigh bridges 87
Tanks Overfilling • Tanks and loading sites are fitted with equipment to measure quantity being loaded • Meters • Dipsticks • Ullage bars • Sight glasses or other gauges • Weigh bridges 87
 Tanks • Cleaning • After cleaning tank is outside regulations • Marks and placards must be removed 88
Tanks • Cleaning • After cleaning tank is outside regulations • Marks and placards must be removed 88
 Tanks Routeing • Some areas in the UK have voluntary agreements for routes taken by dangerous goods vehicles • Elsewhere in Europe, vehicles may be banned from some routes or restricted to certain days or quantities. • Routes involving tunnels should be checked in advance for tunnel restrictions 89
Tanks Routeing • Some areas in the UK have voluntary agreements for routes taken by dangerous goods vehicles • Elsewhere in Europe, vehicles may be banned from some routes or restricted to certain days or quantities. • Routes involving tunnels should be checked in advance for tunnel restrictions 89
 Tanks – Loading and Discharge Systems • Open • Vapours escape through man lid 90
Tanks – Loading and Discharge Systems • Open • Vapours escape through man lid 90
 Tanks – Loading and Discharge Systems • Closed • No escape of vapours 91
Tanks – Loading and Discharge Systems • Closed • No escape of vapours 91
 Tanks – Loading and Discharge Systems • Gravity 92
Tanks – Loading and Discharge Systems • Gravity 92
 Tanks – Loading and Discharge Systems • Pump 93
Tanks – Loading and Discharge Systems • Pump 93
 Tanks – Loading and Discharge Systems • Pressure 94
Tanks – Loading and Discharge Systems • Pressure 94
 Tanks • Tipping tanks 95
Tanks • Tipping tanks 95
 Tanks Power Take Off • Power take off may provide power for compressors or pumps • Typically engaged by depressing clutch and operating PTO lever • Requires engine to be running at correct speed • Excessive speed can cause pump/compressor problems. 96
Tanks Power Take Off • Power take off may provide power for compressors or pumps • Typically engaged by depressing clutch and operating PTO lever • Requires engine to be running at correct speed • Excessive speed can cause pump/compressor problems. 96
 Tanks Decompression • Following pressure discharge, tank must be depressurised before leaving unloading site 97
Tanks Decompression • Following pressure discharge, tank must be depressurised before leaving unloading site 97
 Tanks Pump • Pump may require priming • Correct pump speed must be used 98
Tanks Pump • Pump may require priming • Correct pump speed must be used 98
 Tanks – Connections • Connections must be checked prior to discharge of product 99
Tanks – Connections • Connections must be checked prior to discharge of product 99
 Tanks Specific Precautions • Before working on top of a tank, guard rails or other safety measures must be in place 100
Tanks Specific Precautions • Before working on top of a tank, guard rails or other safety measures must be in place 100
 Tanks Specific Precautions • Gases – Liquid Petroleum Gas – Escape of gases creates a drop in temperature which could cause cold burns – Risk of fire or explosion – LPG’s are heavier than air and can cause asphyxiation in confined spaces – Risk of BLEVE if involved in fire 101
Tanks Specific Precautions • Gases – Liquid Petroleum Gas – Escape of gases creates a drop in temperature which could cause cold burns – Risk of fire or explosion – LPG’s are heavier than air and can cause asphyxiation in confined spaces – Risk of BLEVE if involved in fire 101
 Tanks Specific Precautions • Cryogenic Gases – Very low temperatures e. g. Nitrogen 196⁰C Helium 296⁰C – Valves should be operated slowly because of large temperature variations – Insulated gloves must be worn – Any escape can cause serious burns or internal damage to lungs – Escape can cause embrittlement of many materials including tyres and tools 102
Tanks Specific Precautions • Cryogenic Gases – Very low temperatures e. g. Nitrogen 196⁰C Helium 296⁰C – Valves should be operated slowly because of large temperature variations – Insulated gloves must be worn – Any escape can cause serious burns or internal damage to lungs – Escape can cause embrittlement of many materials including tyres and tools 102
 Tanks Specific Precautions • Wastes – Often loaded by vacuum and discharged by pressure – Tank constructed of thicker metals to cope with stresses – Driver must check tank is suitable for substance to be loaded – Most have large rear door to assist with cleaning – Waste regulations will usually apply 103
Tanks Specific Precautions • Wastes – Often loaded by vacuum and discharged by pressure – Tank constructed of thicker metals to cope with stresses – Driver must check tank is suitable for substance to be loaded – Most have large rear door to assist with cleaning – Waste regulations will usually apply 103
 Tanks • Product movement • Driver needs to anticipate surge 104
Tanks • Product movement • Driver needs to anticipate surge 104
 Tanks • Proper clutch control and careful use of the braking system can minimise product surge • Most new tank vehicles require the fitting of ABS brakes • Endurance braking systems are also required on most new tank vehicles 105
Tanks • Proper clutch control and careful use of the braking system can minimise product surge • Most new tank vehicles require the fitting of ABS brakes • Endurance braking systems are also required on most new tank vehicles 105
 Tanks • Lateral product movement changes centre of gravity • Can cause Rollover • Excessive speed can be a contributing factor 106
Tanks • Lateral product movement changes centre of gravity • Can cause Rollover • Excessive speed can be a contributing factor 106
 Tanks • Recall that • Baffles may be fitted to reduce effects of product movement • Filling ratio • Minimum of 80% if filled over 20% full 107
Tanks • Recall that • Baffles may be fitted to reduce effects of product movement • Filling ratio • Minimum of 80% if filled over 20% full 107
 Tanks • Site rules must be obeyed • PPE must be worn during loading and unloading 108
Tanks • Site rules must be obeyed • PPE must be worn during loading and unloading 108
 End of Tanks Module Questions? 109
End of Tanks Module Questions? 109


