de21fa114f18121313e26bf243231175.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
Weekly Warm Up § T or F: Solubility of solids are affected by pressure. § The solubility of a gas is affected by temperature pressure ______ AND ____. lower § The _____ the temperature of the solvent, the higher ______ the solubility of the gas. § Give an Example. Cola going flat when hot.

Chapter 22: Acids, Bases & Salts Part 1: Acids & Bases They are everywhere. . In your food In your house EVEN IN YOU!!!!! http: //www. helpteaching. com/questions/Acids_and_Bases

What is an Acid? § It comes from the Latin word acidus that means sharp sour “_____" or “____". § An acid is a solution that has an excess of hydrogen ____ ions. (H+) ___ HCl H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) § The higher the [H+], the _____ acidic the _____ more solution.

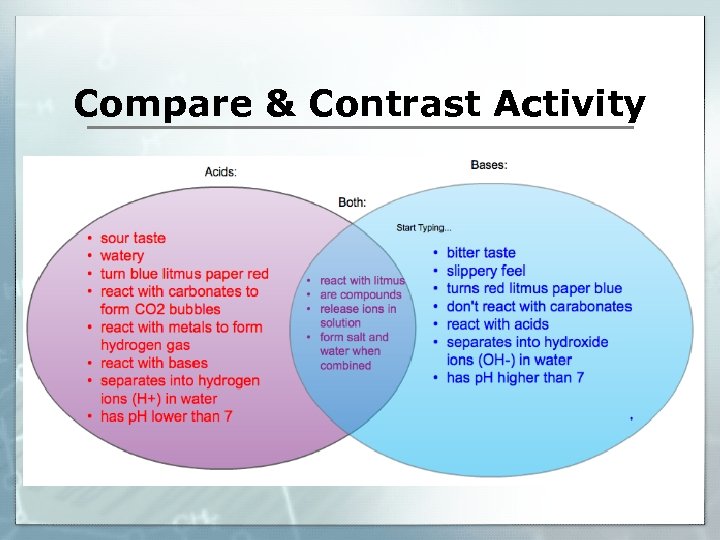
Properties of an Acid Tastes sour ____ electricity Conduct ____ Corrosive ____, which means they break down certain substances. Many acids can damage fabric, skin, and paper ______ strongly § Some acids react _______ with metals red § Turns blue litmus paper ____. § § §

Types & Uses of Acids § Acetic Acid = Vinegar § Citric Acid = Citrus: lemons, limes, & oranges. Candies: lemonhead & sour patch. § Hydrochloric Acid = gastric juices § Ascorbic Acid = Vitamin C which your body needs to function. § Sulfuric Acid = used in the production of fertilizers, steel, paints, plastics, & car batteries. § Nitric Acid = fertilizers & explosives (TNT) § Carbonic Acid = carbonated drinks, cave formation, and acid rain

What is a Base? Base § A base is a solution that has an excess of hydroxide _____ ions. (OH-) ____ Na. OH in H 2 O Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq) alkali § Another word for base is ______. ionic § Many bases are _____ compounds. § Bases are any substances that can _______ accept hydrogen ions (H+) from acids even if it doesn’t have OH. neutralize § Therefore, bases are able to _____ acids.

Properties of a Base soapy slippery Feel _____, _______ Taste _____, ______ bitter chalky Corrosive ____ electricity Can conduct ____. Alkaline (Ex: _______ batteries. ) metals § Do not react with ______. § Turns red litmus paper blue _____. § §

Uses of Bases • Na. OH-sodium hydroxide (LYE) soaps, drain cleaner, bleach, paper • Mg (OH)2 -magnesium hydroxide - antacids • Al(OH)3 -aluminum hydroxide - antacids, deodorants, water purification • NH 4 OH-ammonium hydroxide - “ammonia”, household cleaner* • Bases givesoaps ammonia and many ______, other cleaning products some of their useful properties. • Your blood is a slightly basic solution. _____ NOTE: NEVER mix Ammonia with Sodium hydroxide lung (bleach). The toxic gas produced damages _____ tissue lethal and can be ______.

What is p. H? hydrogen • p. H is an abbreviation for "power of _____" where "p" is short for the German word for power, potenz and H is the element symbol for hydrogen. acidic basic • It is used to measure how _____ or ______a solution is litmus paper is used as the p. H indicator. ______ 14 • It is a logarithmic scale that runs from zero (0) to _______ 10 • p. H scale…each step is ____ times stronger or weaker than the one next to it! neutral • A solution with a p. H of 7 is _______. • For example, a p. H of 3 is 10 times more acidic than a p. H of 4 and 100 times (10 times 10) more acidic than a p. H value of 5.
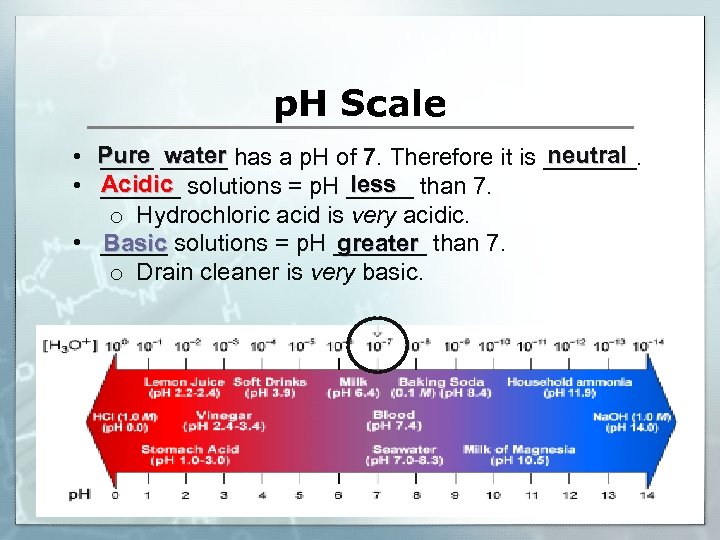
p. H Scale neutral • Pure _____ has a p. H of 7. Therefore it is _______ water Acidic less • ______ solutions = p. H _____ than 7. o Hydrochloric acid is very acidic. Basic greater • _____ solutions = p. H _______ than 7. o Drain cleaner is very basic.
Compare & Contrast Activity
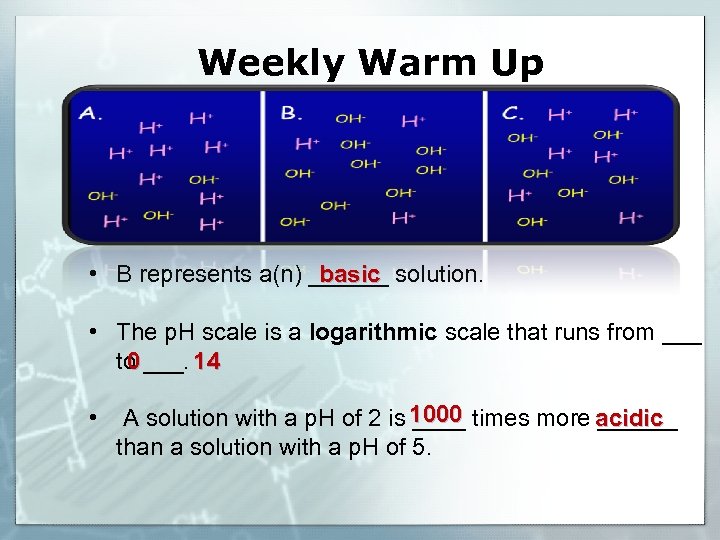
Weekly Warm Up • B represents a(n) ______ solution. basic • The p. H scale is a logarithmic scale that runs from ___ to ___. 14 0 • A solution with a p. H of 2 is 1000 times more acidic ______ than a solution with a p. H of 5.

Unit Vocabulary § Any process by which electrically neutral atoms or molecules are converted to electrically charged ionization atoms or molecules (aka. ions) is called ____. § Ions capable of conducting an electric current are electrolytes referred to as _____. § A process in which an ionic compound separates into its positive and negative ions in a solution is dissociation describes _____. Neutralization § ______ is a reaction between acid and base salt water forming a type of ____ and _____. o Na. OH + HCl Na. Cl + HOH
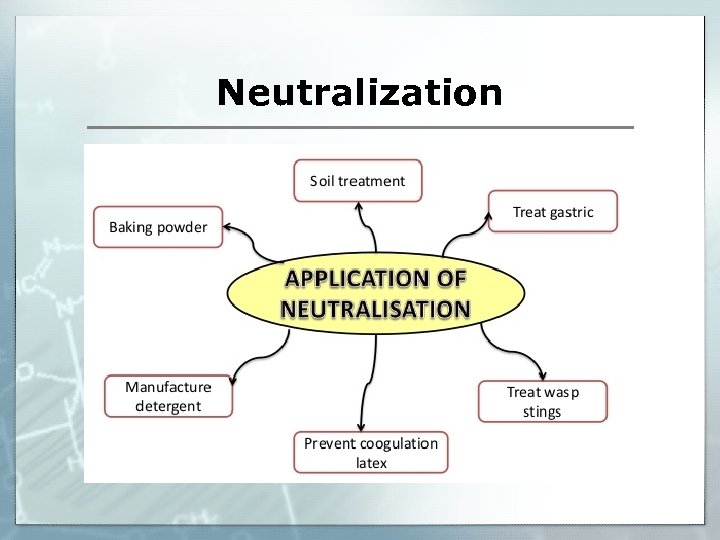
Neutralization
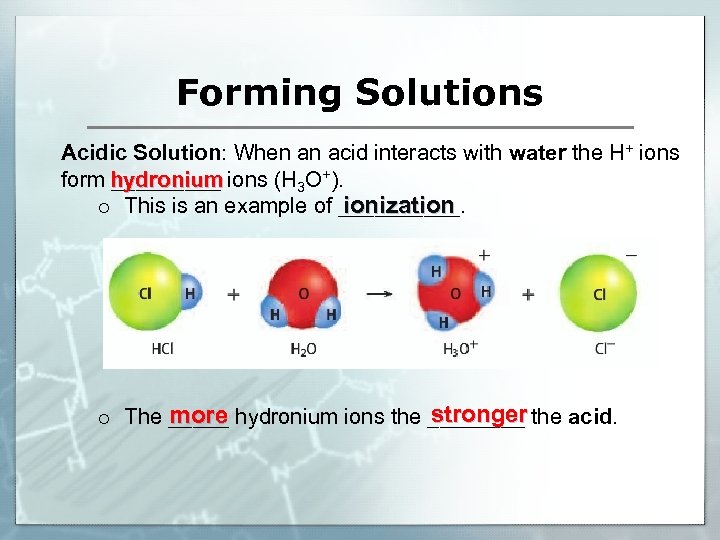
Forming Solutions Acidic Solution: When an acid interacts with water the H+ ions form hydronium ions (H 3 O+). _____ ionization o This is an example of _____. stronger more o The _____ hydronium ions the ____ the acid.
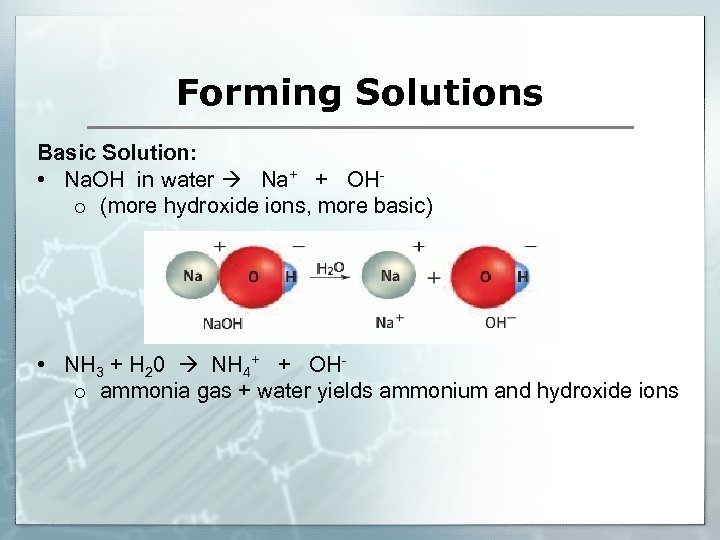
Forming Solutions Basic Solution: • Na. OH in water Na+ + OHo (more hydroxide ions, more basic) • NH 3 + H 20 NH 4+ + OHo ammonia gas + water yields ammonium and hydroxide ions

What is a Buffer? § A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable p. H. If you add acid or base to a buffered solution, its p. H will not change significantly.

Weekly Warm Up Label as either true (T) or false (F): _____ 1. Acids will not conduct electricity. F _____ 2. Bases will conduct electricity. Both conduct electricity. T F _____ 3. Acids taste bitter. Sour T _____ 4. Bases will turn red litmus paper blue. _____ 5. Acids react with some metals to produce hydrogen gas. T _____ 6. Acids will turn phenolphthalein (PHTH) indicator pink. F T _____ 7. An indicator is a substance which changes colors in acids and bases. F _____ 8. Acids have a p. H greater that 7. _____ 9. Bases feel slippery. T T _____ 10. The p. H of pure water is 7.
de21fa114f18121313e26bf243231175.ppt