b5924857f9371699efa731e4793cd279.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

Week 10 Web Server Hardware and Software

Web Server Basics p Web server computer’s main job: n p respond to requests from Web client computers Web server’s main elements: n n n hardware (computers and related components) operating system software Web server software

Assignment Explore and explain different types of websites that organizations and individuals can use. Provide example of each type of website.

Web Clients and Web Servers p Web client computer n p Web server computer n p computer used to process Web client computers’ requests; have more memory and larger, faster disk drives then client computers Web browser software (Microsoft Internet Explorer, Netscape Navigator): n p used by people through their Internet connections to be part of the Web software that makes computers work as Web client, also called Web client software Web software: n platform neutral, let computers communicate with each other easily and effectively

Web Clients and Web Servers Platform neutrality? ? It Advantages? ? ? n The ability of a network to connect devices that use different operating systems is called platform neutrality. Web software lets computers to communicate with each other easily and effectively. Internet’s platform neutrality, the computers that were connected to each other using leased phone lines either had to run the same operating system software or they required translation software that allowed each computer to communicate with the other one. n Search out for more advantages of Platform Neutrality. n n
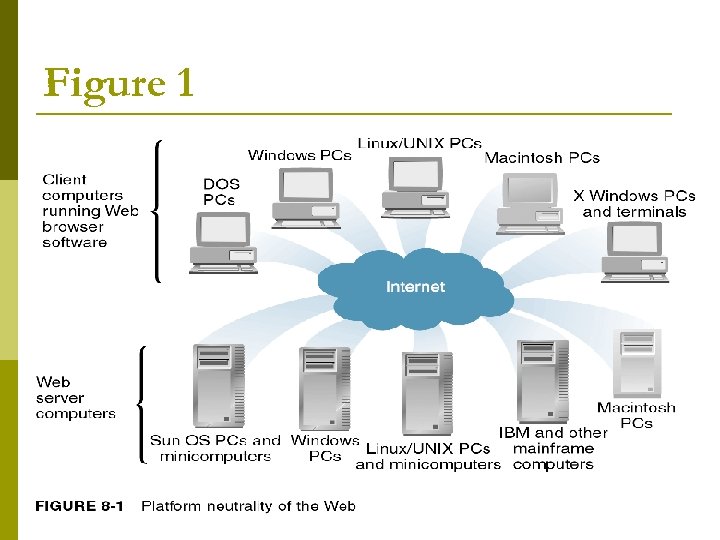
Figure 1

Dynamic Content p Two approaches are used to create dynamic Web pages. What are these and how they work? p Dynamic page: n p a Web page whose content is shaped by a program in response to user requests. Static page: n an unchanging page retrieved from disk. http: //www. fibercom. co. za/

Activity What are advantages and disadvantages of Dynamic and Static Website?

Two basic approaches to create customized pages p Server-Side Scripting/Technologies : n p slow, programs create the Web pages before sending them to the requesting Web clients as parts of response messages Dynamic Page-Generation Technologies: n server-side scripts are mixed with HTMLtagged text to create the dynamic Web page.
Various Meaning of “Server” p “Server”: n p Server: n p software that used by server computer to make files/programs available to other computers Web server: n p any computer used to make files/programs available to other computers connected to it through a network (a LAN or a WAN) Server software: n p confusedly used in many different ways computers contain document made publicly available through Internet connections Web server software: n software used by Web server

Electronic Mail
E-mail Benefits p p p First Internet Application Allows almost instant communication between two parties Attachment available such as pictures, documents, movies, worksheets etc. E-mails are also used as receipt to confirm customers orders and shipments Information update about purchases and shipment

E-mail Drawback p Time consuming p Computer Virus (businessperson spend a long time answering their e-mails) n p a program that attaches itself to another program and can cause damage when the host program is activated. Unsolicited commercial e-mails n n Waste of time and disk space Consuming large amount of Internet capacity Offensive Tremendous growth

Solutions to the Spam Problem p Individual user antispam tactics n n Limit spammers access to e-mail address Use complex e-mail address p n xq 7 yy 23@mycompany. com Control e-mail address exposure Spammer software robots search for e-mail addresses p Discussion boards, chat rooms, other online sources p n Use multiple e-mail addresses p n Switch to another if spammers use one Use filtering techniques p Based on contents
Solutions to the Spam Problem (cont’d. ) p Basic content filtering n Content-filtering techniques differ in terms of: Content elements examined p Spam indications p How strictly message classification rules applied p n n Basic content filters examine e-mail headers Filtering task software location Client-level filtering: individual users’ computers p Server-level filtering: mail server computers p
Difference between Client & Server Side Email Filtering p Most basic content filters examine the e-mail headers (From, To, Subject) and look for indications that the message might be spam. The software that performs the filtering task can be placed on individual users’ computers (called client-level filtering) or on mail server computers (called server-level filtering). p Server-level filtering can be implemented on an ISP’s mail server, an individual company’s mail server, or both. Also, many individuals that have ISP and/or company mail servers that filter their e-mail also install client-level filters on their computers.
Solutions to the Spam Problem (cont’d. ) p Basic content filtering (cont’d. ) n Black list spam filter Looks for known spammers in incoming messages’ From addresses p Requires list to be continually updated p n White list spam filter Looks for good sender From addresses in incoming messages p High false positives rate p n Used in client-level or server-level filters p Can also use approaches together with other content-filtering approaches

Solutions to the Spam Problem (cont’d. ) p Challenge-response content filtering n Compares all incoming messages to a white list If sender not on white list, automated e-mail response sent (challenge) p Challenge asks sender to reply to e-mail (response) p Reply must contain response to a challenge presented in the e-mail p n Designed so human can respond easily

Solutions to the Spam Problem (cont’d. ) p Drawbacks n n Potential abuse Doubles amount of useless e-mail messages sent 19
Solutions to the Spam Problem (cont’d. ) p Advanced content filtering n n More effective than basic content filters Looks for spam indicators in entire e-mail message p n Indicator types p n Indicator identified: message’s spam “score” raised Words, word pairs, certain HTML codes, information about where word occurs Problems p Spammers stop including defined indicators
Solutions to the Spam Problem (cont’d. ) p Technical solutions n Internet design not intended for today's needs E-mail: incidental afterthought p No mechanisms ensuring e-mail sender identity p n Internet’s polite set of rules p n Send and wait for acknowledgement (fast) Slowing down acknowledgment messages Originating computer will slow (must continue to scan for acknowledgment) p Will not send more messages until acknowledgment received p

Solutions to the Spam Problem p Legal solutions: CAN-SPAM n n n n Misleading address header information Deceptive subject headers Clear & conspicuous notice of message nature Physical postal address Mandatory provision of an opt-out mechanism Effectiveness of opt-out mechanism Transfer of e-mail address

How a challenge-response content-filtering technique works to limit spam e-mails from being delivered? p p p p One content-filtering technique uses a white list as the basis for a confirmation procedure. This technique, called challenge-response, compares all incoming messages to a white list. If the message is from a sender who is not on the white list, an automated e-mail response is sent to the sender. This message (the challenge) asks the sender to reply to the e-mail (the response). The reply must contain a response to a challenge presented in the e-mail. These challenges are designed so that a human can respond easily, but a computer would have difficulty formulating the response. This prevents a spammer from setting up a computer that receives challenges and answers them
Web Site and Internet Utility Programs

Web Site and Internet Utility Programs Finger and Ping Utilities p Tracert and other Route-Tracing Programs p Telnet and FTP Utilities p Indexing and Searching Utility Programs p Data Analysis Software p Link-Checking Utilities p Remote Server Administration p

Finger and Ping Utilities p Finger program n n n p Runs on UNIX operating systems Provides information about other network users Provides information of a list of users who are logged on to a network, or reports the last time a user logged on to the network. Ping: Packet Internet Groper n n n Tests connectivity between two Internet-connected computers Provides performance data about connection It is used to troubleshoot Internet connections. 26
Tracert and Other Route-Tracing Programs p Tracert (TRACE Rou. Te) n Sends data packets to every computer on path p n n Between one computer and another computer Provides indication of time message needs to travel from one computer to another and back Ensures remote computer online Pinpoints data traffic congestion To locate the greatest delays on the Internet. 27

Telnet and FTP Utilities p Telnet program n n n Telnet is a program that allows users to log on to a computer that is connected to the Internet. It uses the program called Telnet protocol. Useful if no Web interface Provides remote troubleshooting Web browser Telnet client p n “telnet: //” followed by remote host domain name It can be useful for running older software that does not have a Web interface. 28
Telnet and FTP Utilities (cont’d. ) p File Transfer Protocol (FTP) n n n FTP (File Transfer Protocol) can transfer files one at a time, or it can transfer many files at once. Browser protocol name (ftp: //) before remote computer domain name Useful services p p Full-privilege FTP n p Displaying remote, local computers’ directories Changing current client’s or server’s active directory Creating and removing local and remote directories FTP connection to computer (user has an account) Anonymous FTP n Guest account p p Username: “anonymous” Password: e-mail address 29

Indexing and Searching Utility Programs p Search engines (search tools) n p Browser search methods n p Search for requested documents on specific site or entire Web Compare index terms to requester’s search term Web server software contains indexing software 31


Activity p How Google indexed pages?

Data Analysis Software p Web servers capture visitor information n p Third-party Web log file analysis programs summarize information n n p Placed into Web log file (grows quickly) Query log file Return gross summary information or accumulating details Popular Web log file analysis programs n Adobe Site. Catalyst, Urchin from Google, Web. Trends 34

Link-Checking Utilities p Dead link n p Link rot n p Displays error message rather than Web page when clicked Site contains a number of links that no longer work Link checker n Examines each site page p n Identifies orphan files p n Reports broken, incorrect URLs Web site file not linked to a page Link-checking programs p Adobe Dreamweaver, Elsop Link. Scan (separate utility) 35

Remote Server Administration p Remote server administration n Web site administrator controls Web site Monitor server activity p Manipulate server p Access from any Internet-connected computer p n n Provides convenience Examples Lab. Tech Software p Net. Mechanic p 36
Server Hardware
Web Server Hardware p Server Computers n n n Web server computers have more memory, larger and faster hard disk drives, and faster processors that the typical desktop or notebook PCs. They use multiple processors. Faster processors More expensive One of the novelty is to put small server computers on a single computer board and then install many of those boards into a rack-mounted frame, called blade servers. The fundamental job of a web server is to process and respond to Web client requests that are sent using HTTP. A virtual server or virtual host is a feature that maintains more than one server on one machine.

Web Server Hardware p Web Server Performance Evaluation n n n p Hardware Operating system software Server software Connection speed User capacity Type of Web pages being delivered Speed of connection: T 3 is faster than T 1 Throughput-number of HTTP requests that a particular hardware and software combination can process in a unit of time. p Response one request time-amount of time a server requires to process
Web Server Hardware p Web Server Architecture n Centralized architecture Expensive computers p Sensitive to technical problems p n Distributed architecture (decentralized) Uses a large number of less powerful computers and divide the workload among them p Cheaper p Less sensitive p Additional cost on hubs and switches p
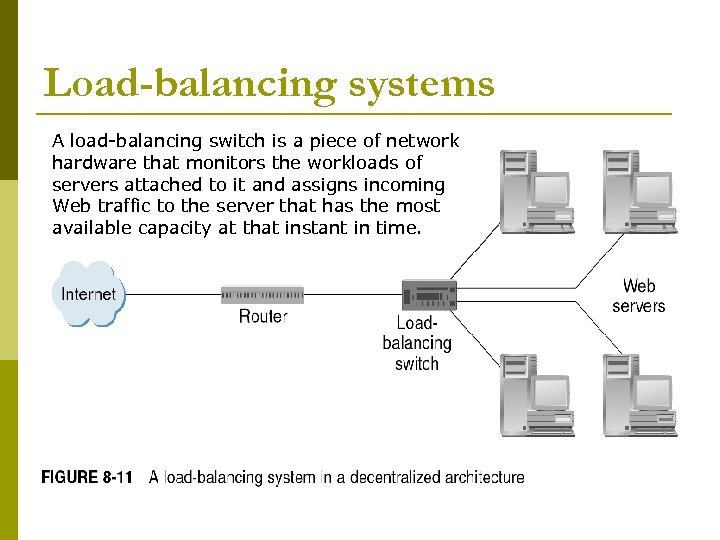
Load-balancing systems A load-balancing switch is a piece of network hardware that monitors the workloads of servers attached to it and assigns incoming Web traffic to the server that has the most available capacity at that instant in time.
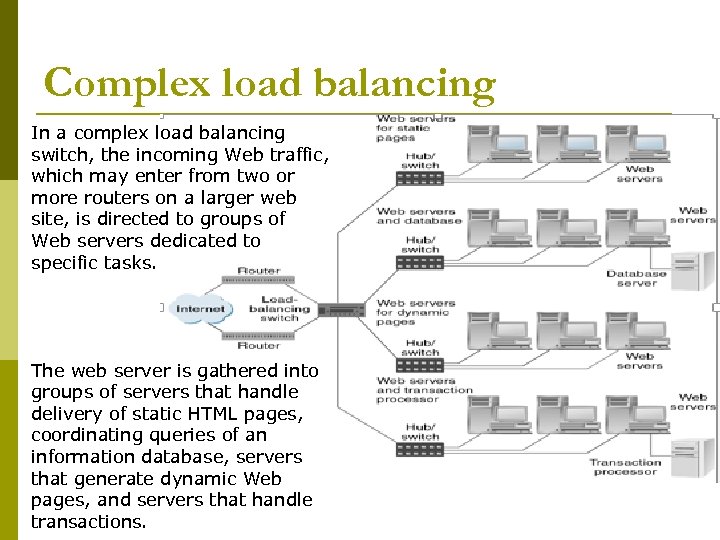
Complex load balancing In a complex load balancing switch, the incoming Web traffic, which may enter from two or more routers on a larger web site, is directed to groups of Web servers dedicated to specific tasks. The web server is gathered into groups of servers that handle delivery of static HTML pages, coordinating queries of an information database, servers that generate dynamic Web pages, and servers that handle transactions.
b5924857f9371699efa731e4793cd279.ppt