WEEK 1 FLOOR – PART 1 BUILDING CONSTRUCTION


WEEK 1 FLOOR – PART 1 BUILDING CONSTRUCTION II ECM 3154 Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 1 PowerPoint® Slides by Zamzarina Bt Md.Judyar

CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter brings the student through the introduction of floors that are suitable for common buildings not more than two storeys in height and explanation focus on construction of ground floor. Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 2

LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be exposed to: The types of floors The performance requirements of floors The construction process of ground floors. The advantages and disadvantages of ground floors Be familiar with the drawing plan of ground floors Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 3

LEARNING OUTCOME At the end of the lesson, students should be able to explain the requirements and construction process of ground floors. Students should also be able to read the drawing plan of ground floors. Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 4

WHAT IS SLAB??? “A flat piece of concrete, typically used as a walking surface, but may also serve as a load bearing device as in slab homes.” Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 5

FUNCTION Provide a flat surface To support load Sound, heat and fire insulator Act as a divider (privacy) for the occupants Upper slab became the ceiling for the storey below Space between slab and ceiling can be used to place building facilities Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 6
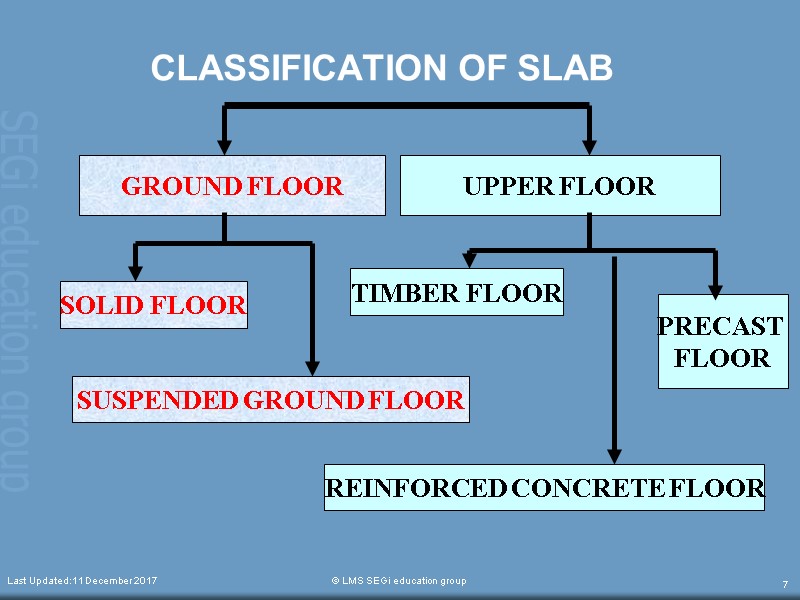
CLASSIFICATION OF SLAB Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 7 GROUND FLOOR UPPER FLOOR SOLID FLOOR SUSPENDED GROUND FLOOR TIMBER FLOOR REINFORCED CONCRETE FLOOR PRECAST FLOOR

CHARACTERISTIC OF GROUND FLOOR Simple design Load will be supported by the ground Less problem related to distance of span Choice to construct solid floor or suspended ground floor will depends on nature of the building and site condition Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 8

DESIGN CONSIDERATION Among the design function that needs to be taken in consideration for construction of ground floor slab are:- The provision of a uniform, level surface Sufficient strength and stability Exclusion of dampness from inside of building Thermal insulation Resistance to fire Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 9
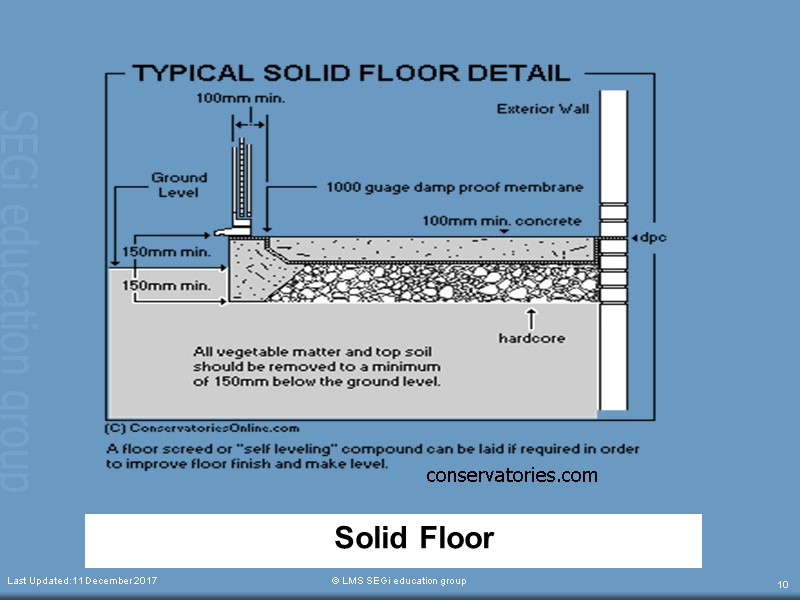
Solid Floor Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 10 conservatories.com
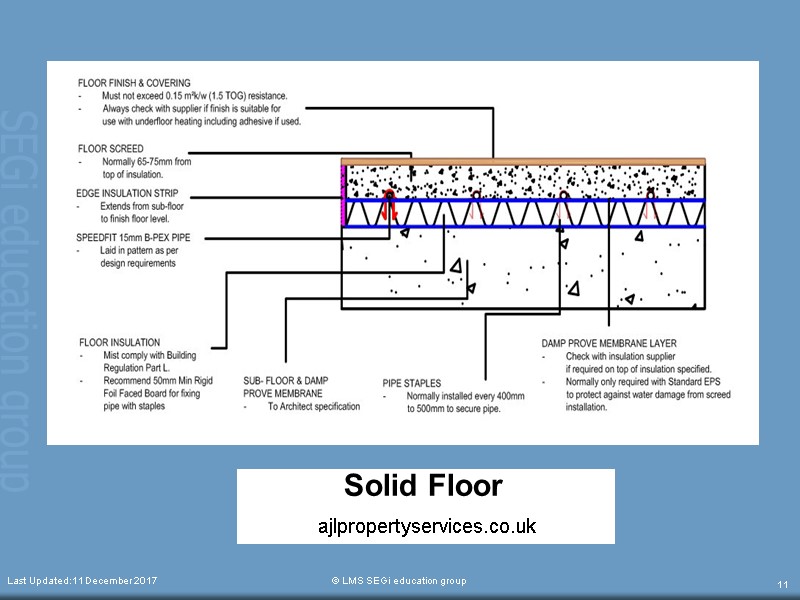
Solid Floor ajlpropertyservices.co.uk Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 11

SOLID FLOOR / NON SUSPENDED FLOOR Constructed using concrete Doesn’t use timber so there will be no decay Solid floor need other finishing Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 12

CONSTRUCTION OF SOLID FLOOR Clear the construction area Remove topsoil / unsuitable material (225 mm) Compact and level the soil Place hardcore and compact it Hardcore plays the role to fill in any small pockets that have formed during excavation in order to provide a firm base for placing concrete bed and to help spread any point loads over a greater area. Place Damp Proof Membrane Prepare formwork Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 13
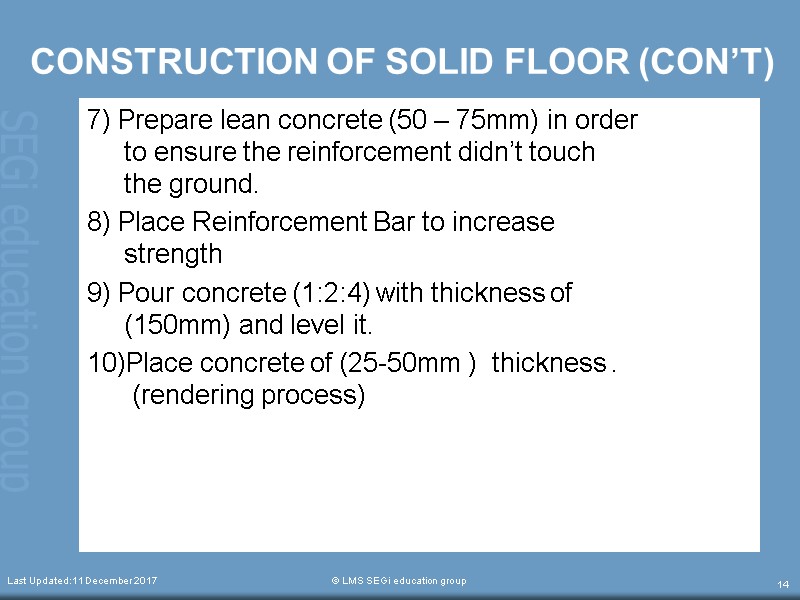
CONSTRUCTION OF SOLID FLOOR (CON’T) 7) Prepare lean concrete (50 – 75mm) in order to ensure the reinforcement didn’t touch the ground. 8) Place Reinforcement Bar to increase strength 9) Pour concrete (1:2:4) with thickness of (150mm) and level it. 10)Place concrete of (25-50mm ) thickness . (rendering process) Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 14

Topsoil is Stripped Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 15 AFTER BEFORE

Rebar Used For Slab Construction Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 16

Pouring concrete Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 17

Concrete Slab Finishing Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 18

Screeding is the process removes excess concrete and brings the top surface of the concrete to proper grade. Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 19 tipsbytom.com

SUSPENDED GROUND FLOOR A ground floor need to be suspended under the following condition: a) domestic buildings on sloping sites where more than 600mm depth of infill would be required b) where the bearing capacity and nature of the ground different from one part to another c) where the ground is shrinkable clay, expansive material or unstable soil type. Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 20
SUSPENDED GROUND FLOOR Suspended floors / slab is fixed some distance above the ground. There are 2 types of suspended ground floor such as a) Suspended timber ground floors b) Suspended precast concrete floors Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 21
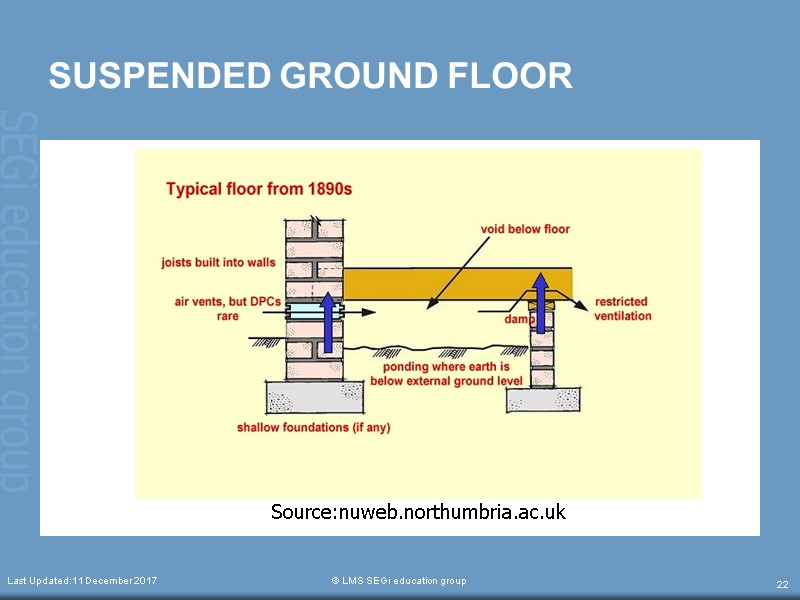
SUSPENDED GROUND FLOOR Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 22 Source:nuweb.northumbria.ac.uk
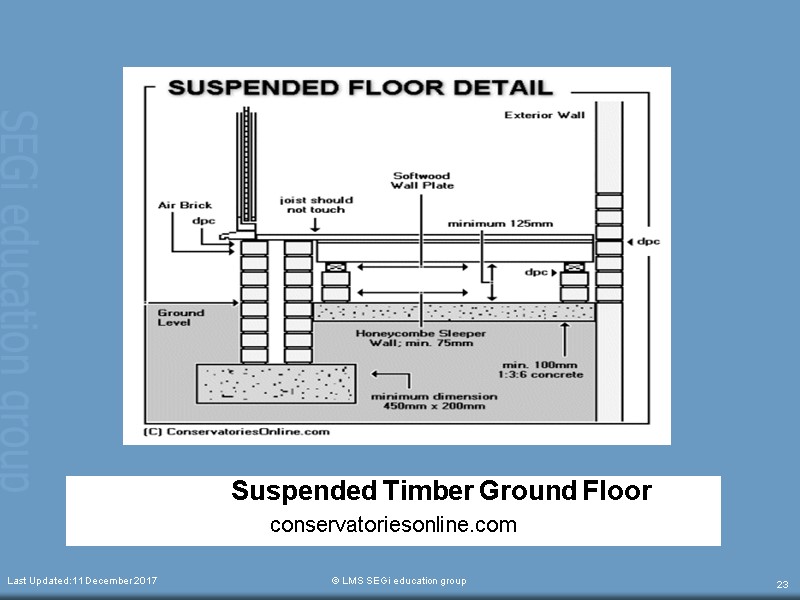
Suspended Timber Ground Floor conservatoriesonline.com Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 23

SUSPENDED TIMBER GROUND FLOOR It has some flexibility and will accept nail fixing (solid ground floor can’t use nail) Under side of ground floor must kept dry to prevent fungus attack Susceptible to dry rot and draughts but it can be avoided if the floor is designed correctly. Adequate ventilation under the floor and correct positioning of damp proof courses can keep the under floor area and timber dry. Space beneath the suspended timber floor is ideal for running electric cables, water pipes and gas pipes Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 24
SUSPENDED TIMBER GROUND FLOOR It’s more expensive form of construction than concrete floor Cheaper than pre cast concrete flooring system Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 25

QUIZZES List any Three (3) characteristics of ground floor. ………………… ………………… ………………… Determine the construction processes of solid floor. ………………. h……………. ………………. i………… ………………. J……….. ………………. ………………. ………………. ……………….. Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 26
KEY TERMS a. Damp proof membrane Definition A liquid system applied evenly to the surface of a concrete base, that adhere strongly to it even if the base contains a high level of moisture, and then sets to form a layer of controlled permeability to moisture vapour (normally less than 4g/sqm / 24 hrs). The set membrane must then allow other flooring layers to be applied b. Fire insulator Definition Insulators are materials which prevent the flow of fire Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 27

REFERENCES Chudley, Roy, Greeno, Roger (2007), ConstructionTechnology, 4th Edition, Pearson Jack Stroud Foster (2007), Structure and Fabric Part 1, 7th Edition, Pearson/ Prentice Hall Barry, R. (1998), The Construction of Building Vol 1, 7th Edition, Blackwell Science Ivor H. Seeley (1995), Building Technology, 5th Edition, Palgrave Macmillan . conservatories. COM retrieved 4th August 2011 ajlpropertyservices.co.uk retrieved 4th August 2011 tipsbytom.com retrieved 4th August 2011 Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 28

References nuweb.northumbria.ac.uk retrieved 4th August 2011 conservatoriesonline.com retrieved 4th August 2011 Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 29

Last Updated:11 December 2017 © LMS SEGi education group 30 The End
22820-bcii-week_1-floor1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

