ae0b8bc4fec45a50e96b66802dfa636a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

WEC-Roundtable – Augsburg – October 24 -25, 2007 „Corporate Strategies in Response to Climate Change“ Boehringer Ingelheim‘s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 1 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Is it a new topic? – Not really! 2 comics from 1979 “Mickey Mouse and Goofy explore energy” “Mickey Mouse and Goofy explore energy conservation” Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 2 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Is it a new topic? – Not really! Giveaway of ‘Chicago Tribune’ from 1980 16 -pages comic on energy conservation and energy savings Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 3 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Boehringer Ingelheim in brief Focus on Human Pharmaceuticals and Animal Health Founded in Ingelheim, Germany, in 1885 Products marketed in some 150 countries More than 38, 400 employees (2006) Net sales of almost EUR 10. 6 billion (2006) # 15 worldwide in terms of net sales (as of March 2007) Family-owned Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 4 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Boehringer Ingelheim’s caring culture We have been committed to Corporate Social Responsibility for over a century. Our caring culture embraces a broad range of activities for: • our employees and their families • our neighbours • our society • our natural environment www. boehringer-ingelheim. com/wecare Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 5 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Energy efficiency is on everyone’s lips Ø EU-Directive 2006/32/EC on energy end-use efficiency and energy services (Apr 2006) Minimum energy savings Target: 9% within 9 years (starting point: 01. 2008) Ø Energy Policy Act (USA, 2005) and National Action Plan for Energy Efficiency (NAPEE, USA 2006) Ø 1 st German ‘National Energy Efficiency Action Plan’ (EEAP, Oct 2007) • Energy savings 9% until 2017 • Detailed catalogue of measures Ø Gleneagles Plan of Action: Transforming the way we use energy (G 8 Summit, Gleneagles 2005) International Energy Agency (IEA) 1. Report (2007): “Energy efficiency requirements in building codes – energy efficiency policies for new buildings” Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 6 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Driving energy efficiency through policy Ø Research and Development create new technologies • R&D partnerships with industries Ø Standards set the floor • Codes and standards (buildings, equipment, vehicles) • Energy efficiency performance standards for utilities Ø Incentives make them viable • Market transformers (tax incentives, project (co)financing, trade-in programs with e. g. emissions credits) Ø Public education makes them widespread • Cosumer education and awareness campaigns • Labeling (e. g. US-Energy Star) Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 7 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Why energy efficiency? Ø Wide range of untapped energy efficiency potentials “Stop wasting energy (= money)!” Ø Mitigation of pollution and climate change “Negawatt/Negajoule produces no environmental (carbon) footprint!” Ø Increase of energy security position “Energy efficiency is a “homegrown” resource!” Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 8 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Management-oriented barriers to energy efficiency “Energy efficiency is one of many topics that are competing for industry’s time, resources, and leadership. Energy efficiency may be more effectively promoted not by itself, but as part of a larger agenda that is more likely to get executive attention” Frequent barriers: Ø Lack of common understanding Ø Lack of staff & management awareness Ø Lack of procedural coordination Ø Absence of energy-related accountabilities Ø Inconsistent Leadership Ø Lack of resources Ø Company’s business culture Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 9 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint What is needed for industrial energy efficiency? For a company to achieve a high level of energy efficiency, to maintain it, and continuously improve it: Ø The company needs an organizational culture that supports continuous improvement Ø The company’s management must develop methods to “hardwire” energy-efficiency into existing management practices Ø Energy efficiency becomes a “key performance indicator” for managers and workers Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 10 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint How BI is reducing its carbon footprint? ØEnergy consumption & Performance indicators ØEnergy efficiency projects ØSubstitution of fossil fuels by secondary fuels ØUse of renewable energy Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 11 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007
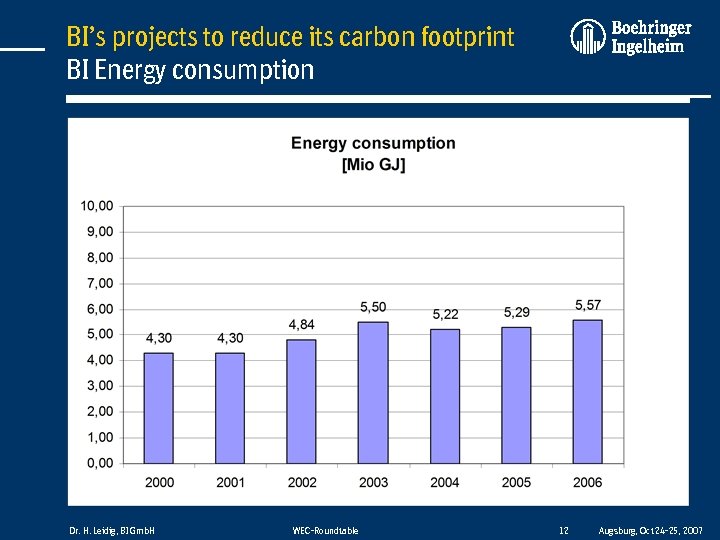
BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint BI Energy consumption Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 12 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007
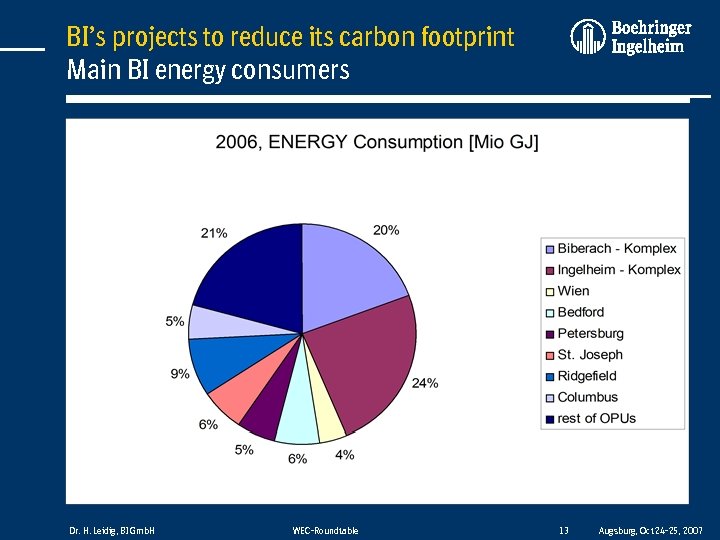
BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Main BI energy consumers Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 13 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007
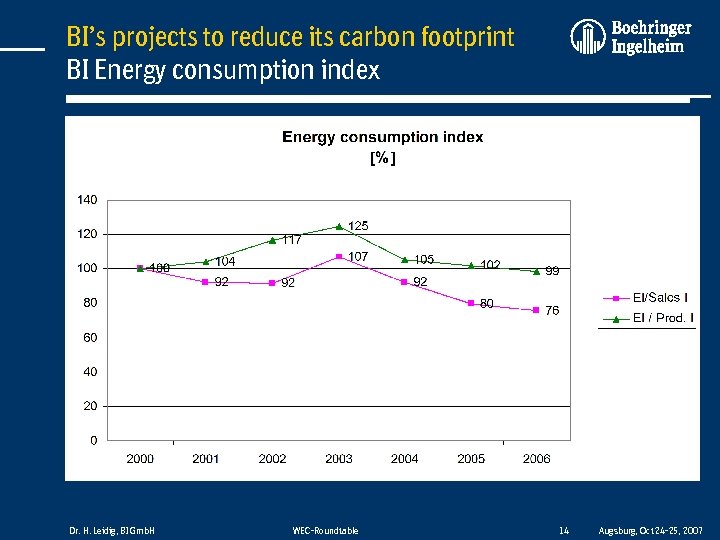
BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint BI Energy consumption index Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 14 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Environmental Key Performance Indicator Ø Environmental KPI shall be used for target-setting & performance evaluation. Therefore: composite indicators are not useful Ø Many environmental figures (water consumption, COD-load, VOC-, SO 2, NOx-emissions, hazardous/domestic waste amount) are hardly useful as KPIs Ø Energy consumption seems to be the only significant KPI – not only for Operations but also for other organizational BI-units Ø More efficient use of energy is a “hot” political & social issue and directly linked to CO 2 -reduction/climate protection Ø Rising energy costs make energy consumption a more important economic factor for BI Ø Absolute energy consumption cannot be an useful KPI – specific indicators for all organizational areas have to be developed Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 15 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007
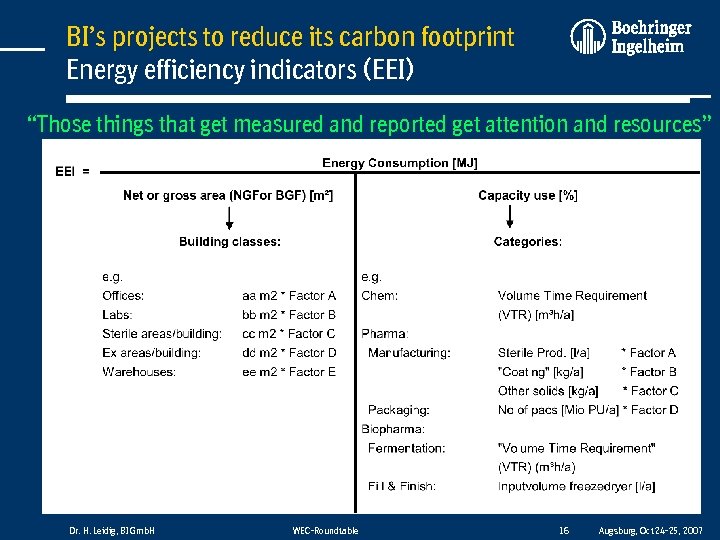
BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Energy efficiency indicators (EEI) “Those things that get measured and reported get attention and resources” Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 16 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007
BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Energy efficiency projects “Buildings are the largest end use of energy” (OECD: Residential & commercial buildings account for 35%) Ø Adequate wall & roof insulation/ A window thermal performance/shading devices Ø Efficient HVAC systems (heat recovery) B Ø Thermal energy storage (cold water) C Ø Intelligent control systems for ventilation D (No of air changes) & lighting by e. g. motion/presence sensors Ø Trigeneration (Absorption chillers) E Change of “paradigm” in capital expenditure management More emphasis on life cycle costs instead of initial investment cost Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 17 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Substitution of fossil fuels I Waste wood power plant at Ingelheim site Acting in sense of environmental policies i. e. use of renewable energies Substitution of hard coal by used wood (biomass ordinance) Increase of energy security & economics Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable Substitution of 70, 000 t/a CO ² of fossil origin Lower emissions e. g. Reduction of: Dust: 95% SO 2: 95% NOx: 50% 18 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Substitution of fossil fuels II Ø Investment for conversion of power plant: 12, 5 Mill € Ø Start-up of “waste-wood”-boiler: Sept. 2004 Ø Fuel consumption: 70. 000 t/a waste wood Ø Delivery of waste wood by trucks Ø Diesel consumption for truck transportation equals to 600 t waste wood/year (i. e. < 1% of waste wood deliveries) Ø Surplus of emission certificates due to substitution of fossil fuels Ø Further conversion of power plant planned (secondary fuels instead of heating oil) Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 19 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Use of renewable energies Ø Geothermal energy Use for heating/cooling of buildings F via heat pumps and thermal activation of constructional elements • Summer season: Reduction of room temperature: appr. 5°C • Winter season: Generation of 35 – 40% of room heating energy Ø Photovoltaics Pilot installations in Ingelheim & Biberach Currently not economical However: solar energy is the energy of the future! Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 20 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007
BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Energy management is of increasing importance as part of overall facility management! Ø Energy consumption measured online and energy data processing in central data base G Ø Energy management is part of online ecobalance system H Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 21 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint Emission trading in Germany Ø National allocation plan I (2005 -2007) Germany: 495 Mill tons CO 2/a Ø National allocation plan II (2008 -2012) Germany: 453 Mill tons CO 2/a i. e. reduced allocation of emission certificates – mainly for power plants Ø Emission trading at BI • Surplus of certificates due to waste wood power plant sold in 2005 and 2006 • Prices for CO 2 -certificates went down from 25 – 30 €/t CO 2 in 1 st quarter 2006 to less than 1 €/t CO 2 at the end of 2006 and remained there in 2007 • No certificates traded in 2007 Ø Emission trading does not function properly as supply and demand of certificates are not balanced Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 22 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

BI’s projects to reduce its carbon footprint The Carbon Neutral Challenge Ø To be carbon neutral is a real challenge and currently hardly to achieve for corporations! Ø Voluntary compensation activities: • “Planting trees” • “Buying green power” Ø HOWEVER: It has the flavour of “eco shrove-money” and “sale of indulgences” Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable I 23 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007

Thank you for your attention! Questions & Comments Dr. H. Leidig, BI Gmb. H WEC-Roundtable 24 Augsburg, Oct 24 -25, 2007
ae0b8bc4fec45a50e96b66802dfa636a.ppt