374eb4c050c93f60643505dbe7a7dea3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Websphere - Security Overview Jonathan Yip
Terms Websphere Application Developer(WSAD) -- It is a By-product of Eclipse -- Eclipse is an Open Source Development Tool J 2 EE 1. 2 -- It is a Platform Enables Developers to Create Different parts of their Applications as Reusable Components. Application Assembly Tool (AAT) -- A Utility to Assist the J 2 EE Provider or J 2 E Deployer with the Generation of J 2 EE-compliant Deployment Descriptors and Binding Attributes.
Security Architecture • • • J 2 EE 1. 2 compliant Java application server Security Server Security Collaborator Security Policy Security Information

Security Architecture (2) • Security server -- Authentication; Authorization; Delegation Policies • Security Collaborator -- Web Collaborator Checks the authentication if not provided Performs the authorization check Logs security tracing information – EJB (Enterprise Java. Beans) Collaborator Check authorization. Support user registries. Log security tracing information.

Security Architecture (3) • Security Policies Attributes to Record: Role and method permission Run-as mode or delegation policy Login configuration or challenge type Data protection (confidentiality and integrity) settings • Security Information -- Global security (All applications) -- Application security (Can specify on each application)
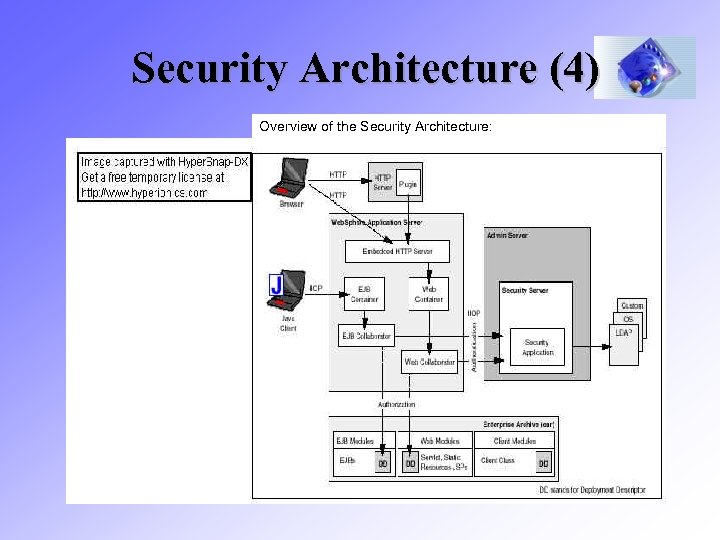
Security Architecture (4) Overview of the Security Architecture: Plug. In

Websphere Security Implementation • • How to Secure an Application The Web. Sphere Authentication Model User Registry Security Center
Securing Application Assembly Tool (AAT) • Create an Application • Create an EJB Module • Create a Web Module • Create an Application Client

Securing Application (2) 1. ) Define Business Role 2. ) Create Security Constraints for Web Resources 3. ) Define the Web Component Authentication for the Web Module 4. ) Define Security Constraints and Assign them to Roles. 5. ) Configure Delegation Role Policy 6. ) Relate Roles to Users Table Showing some Role and the Description

Websphere Authentication Model • HTTP Basic authentication -- Acquired Password from Users and Validate; Not secured. • HTTPS Client Certificate authentication -- Requres Public Key Certificate; HTTPS is Used to Transmit • Form-Based authentication -- Permits a Site-specific Login Through an HTML Page or a JSP form. The password is not encrypted and the target server is not authenticated, (SSL should be added)

User Registry • It is a Repository that Contains Users and Groups. • The Administrator can have Users or Groups Authenticated against the Local Operating System User Registry
Security Center • It is Part of the Administrator’s Console (AC) Focusing on Configuration in Security Matters
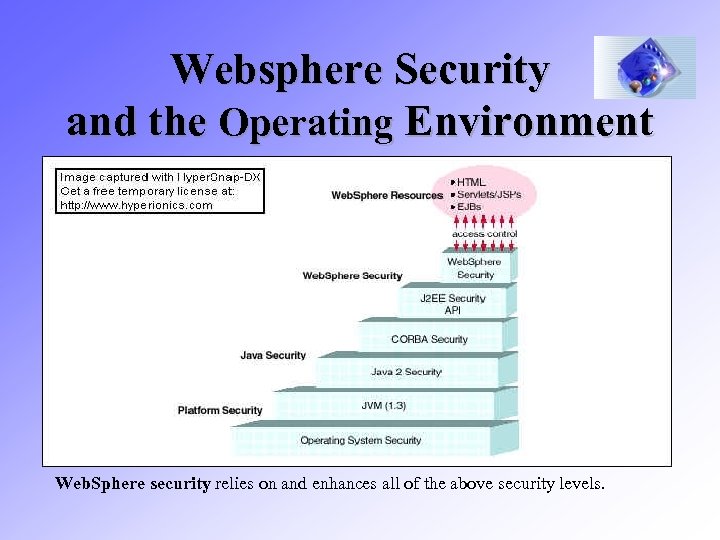
Websphere Security and the Operating Environment Web. Sphere security relies on and enhances all of the above security levels.

Other Security Features of Websphere • Encoded Passwords Web. Sphere Stores Passwords for: Accessing the Administration Repository The Administration ID to Access the Administrator’s Console Accessing Key Stores and Trust Stores • Security interoperability with z/OS -- Allows Application Servers on the UNIX or NT Side to Authenticate to the Application Server on the z/OS Side and Communicate securely.

Programmatic Security • Use to Secure Artifacts and Resources Beyond Checking the Role of an Authenticated User • Implemented by Creating a Generic Login Page Once User logs in, Form. Login. Servlet Authenticates and Place a SSO (Single Sign On) Token in a Cookie. • Advantages – Limiting the Number of Invalid Password Attempts – Checking that the User’s Subscription has not Expired – Logging Information about a User’s Visit

References: • IBM Redbook • Websphere Application Server Bible

End
374eb4c050c93f60643505dbe7a7dea3.ppt