491fd58bb4b12d32acc4b27948a716e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

website: www. Vagabond. Geology. com Ancient Pathways Ancient Peoples Week 2: into Africa Week 1: beginning in East Africa

website: SESSION 2 www. Vagabond. Geology. com - Stone Age Timeline - Ages of Human Development Week - South Africa 6: into Americas Week 5: Week 4: Week 3: Week 2: across Beringia into Asia into Europe into Africa Across Africa Week 1: beginning in East Africa
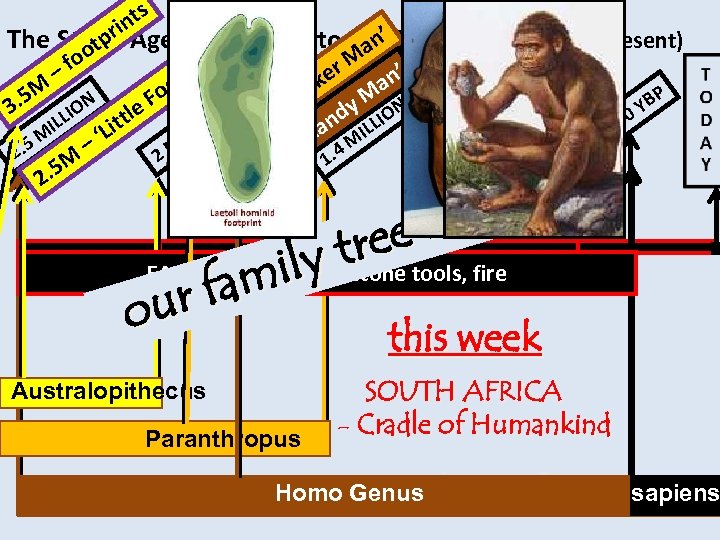
s ’ es ’ Pl The Stone Age: 2. 5 smillion to 4000 YBP (years before present) tp an o fo r M n’ , ‘M ’ – e a ot ck P M N ra Fo. 5 M ION c YB y IO 3 e N 0 ut and LL LL ttl IO I i N 00 , ‘L ILL – ‘H 4 MI 00 5 M – 3 2. 2 M 8 M 1. . 5 M 1. . 7 M 2 1 int r . . reetools, fire ly –tstone EARLY STONE i m AGE r fa ou Week 1 this week Australopithecus Paranthropus TANZANIA SOUTH AFRICA -- Laetoli Humankind Cradle of Site - Oldupai Gorge Homo Genus sapiens
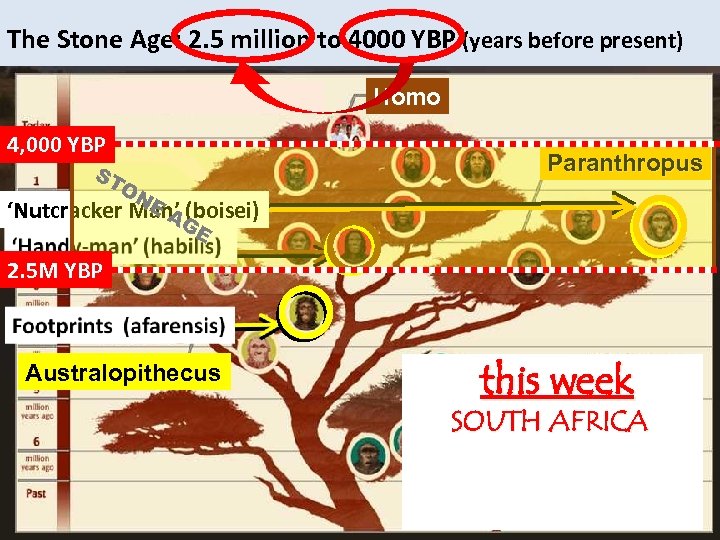
The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP (years before present) homo Homo 4, 000 YBP ST ON E Paranthropus ‘Nutcracker Man’G A (boisei) E 2. 5 M YBP Australopithecus this week Week 1 SOUTH AFRICA TANZANIA - Laetoli Site - Oldupai Gorge
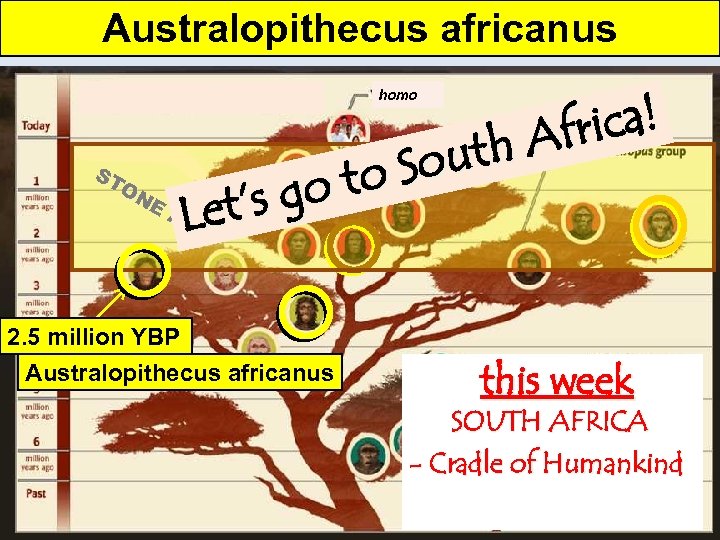
Australopithecus africanus The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP (years before present) ica! Afr uth ST o So ON ot g E AG et’s L homo E 2. 5 million YBP Australopithecus africanus this week SOUTH AFRICA - Cradle of Humankind
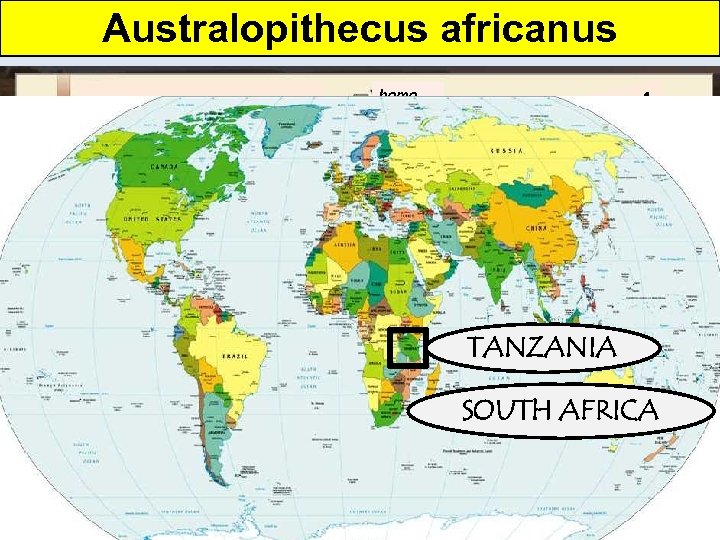
Australopithecus africanus The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP (years before present) ica! Afr uth ST o So ON ot g E AG et’s L homo E 2. 5 million YBP TANZANIA this week SOUTH AFRICA - Cradle of Humankind
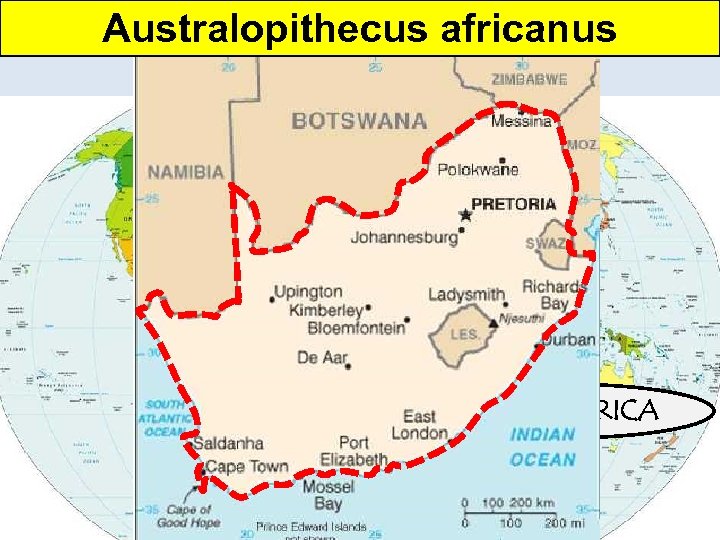
Australopithecus africanus The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP (years before present) SOUTH AFRICA
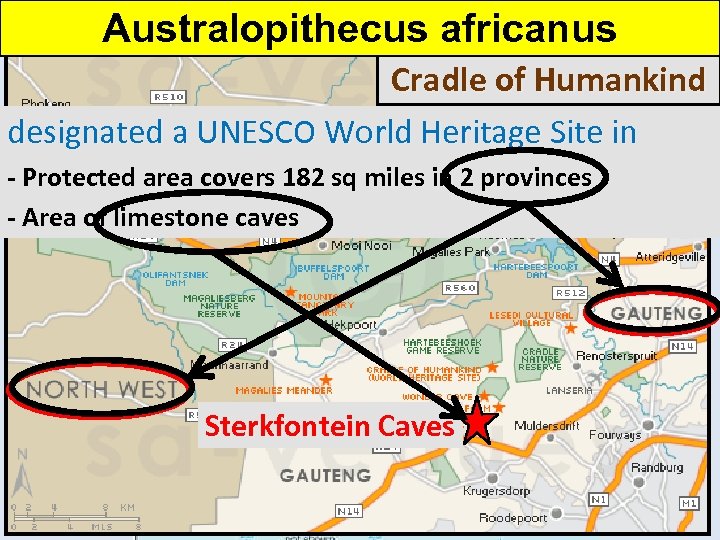
Australopithecus africanus Cradle of Humankind designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1999 - Protected area covers 182 sq miles in 2 provinces PRETORIA - Area of limestone caves Johannesburg Sterkfontein Caves
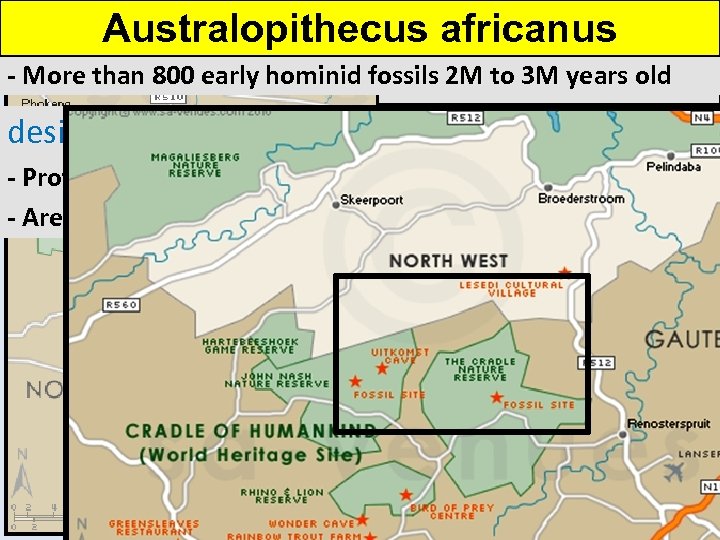
Australopithecus africanus - More than 800 early hominid fossils 2 M to 3 M years old Cradle of Humankind designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1999 - Protected area covers 182 sq miles in 2 provinces - Area of limestone caves Sterkfontein Caves
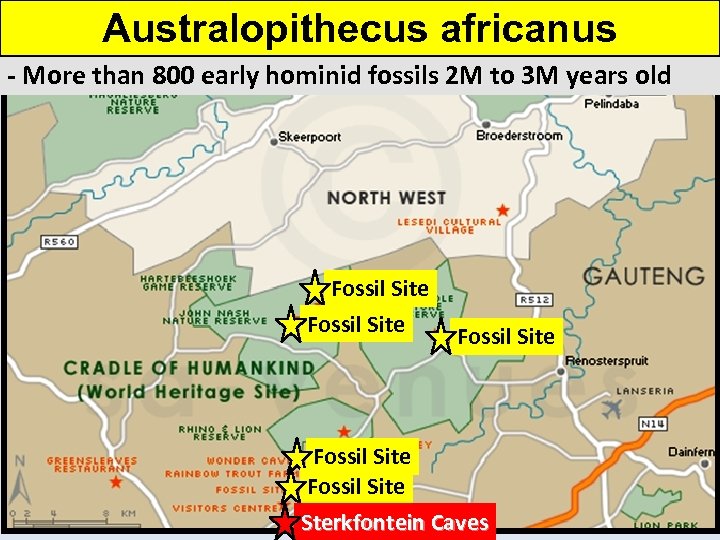
Australopithecus africanus - More than 800 early hominid fossils 2 M to 3 M years old Fossil Site Fossil Site Sterkfontein Caves

Australopithecus africanus - More than 800 early hominid fossils 2 M to 3 M years old Fossil Site Fossil Site Sterkfontain Caves

Australopithecus africanus - More than 800 early hominid fossils 2 M to 3 M years old - 1800’s: 1 st fossils unearthed by miners digging for lime - 1936: professors at U. of Witwatersrand began excavations - 1947: Dr. Robert Broom found a skull over 2 M years old

Australopithecus africanus - originally classified as ‘plesanthropus Transvaalensis’. . thus ‘Mrs. Ples’ - later reclassified as Australopithecus africanus

Australopithecus africanus - originally classified as ‘plesanthropus Transvaalensis’. . thus ‘Mrs. Ples’ - later reclassified as Australopithecus africanus

Australopithecus africanus - Dr Broom identified this fossil as an adult female based on: • body size • size of teeth cavity - later x-rays of the teeth cavities showed emerging permanent teeth at death; predicted a sub-adult male - originally classified as ‘plesanthropus Transvaalensis’ - 2012 evaluation by Stony Brook University using 3 D. . thus ‘Mrs. Ples! Ples’ ? Ms virtual reconstruction of the - later reclassified as roots of the teeth found Australopithecus africanus evidence of a adult female

Australopithecus africanus 47 years later, in 1997. . - at the Sterkfontein archives - originally classified as ‘plesanthropus Transvaalensis’. . thus ‘Mrs. Ples! Ms Ples’ - later reclassified as Australopithecus africanus

Australopithecus africanus 47 years later, in 1997. . - at the Sterkfontein archives - Dr. Ron Clarke, looking in a box of fossils, came across four foot-bone fossils - He recognized these fossils as probably from the same foot - 3 years later, in a box of monkey fossils, he came across more bones from the same body - Because of the small foot size, he called this find ‘Little Foot’
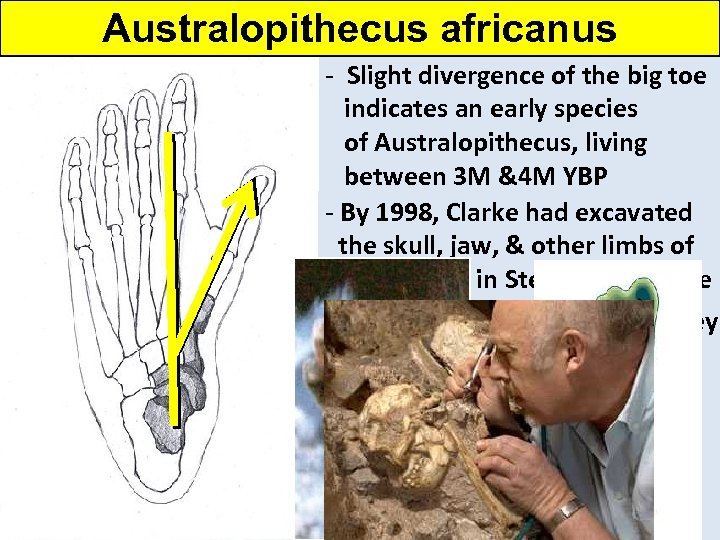
Australopithecus africanus - Slight divergence in the big toe. 47 years later, of 1997. . . - indicates an early species at the Sterkfontein archives - of Australopithecus, livinga box Dr. Ron Clarke, looking in between came across of fossils, 3 M &4 M YBPfour - By 1998, Clarke had excavated foot-bone fossils -the skull, jaw, & other limbs of He recognized these fossils ‘Little Foot’ in Sterkfontein Cave as probably from the same foot - 3 years later, in a box of monkey fossils, he came across more bones from the same body - Because of the small foot size, he called this find ‘Little Foot’

Australopithecus africanus - Slight divergence of the big toe Where was he found? species indicates an early of Australopithecus, living between 3 M &4 M YBP - By 1998, Clarke had excavated the skull, jaw, & other limbs of ‘Little Foot’ in Sterkfontein Cave ‘Little Foot’

Australopithecus africanus Where was he found?

Australopithecus africanus - 3 M YBP ‘Little Foot’ fell through a brush-covered cave shaft - falling at least 30’, he fractured many bones and died - rocks & sediments covered his body and calcified - the skeleton was preserved, embedded in rock “this almost complete skeleton is one of the earliest, most complete, & most important hominid discoveries in paleoanthropology” y? h W
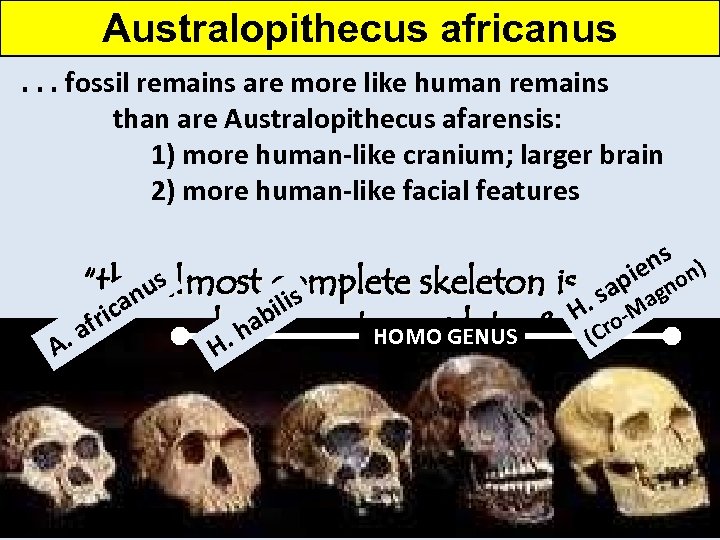
Australopithecus africanus. . . fossil remains are more like human remains than are Australopithecus afarensis: 1) more human-like cranium; larger brain 2) more human-like facial features ns n) pie o “thisus n almost complete skeleton is one agn is. sa -M ca H o bl rithe earliest, i most complete, & most a f a h HOMO GENUS (Cr. of A H. important hominid discoveries in paleoanthropology” y? h W

Australopithecus africanus. . . fossil remains are more like human remains EXTINCTION: 2 M YBP than are Australopithecus afarensis: - 1) more cooling cranium; larger brain global human-like - 2) more human-like facial features competition with Homo genus . . . may be a direct ancestor to modern humans. . A. fri a us can H ha. ilis b ns n) ie ap agno. s HOMO GENUS H o-M Cr ( W y? h
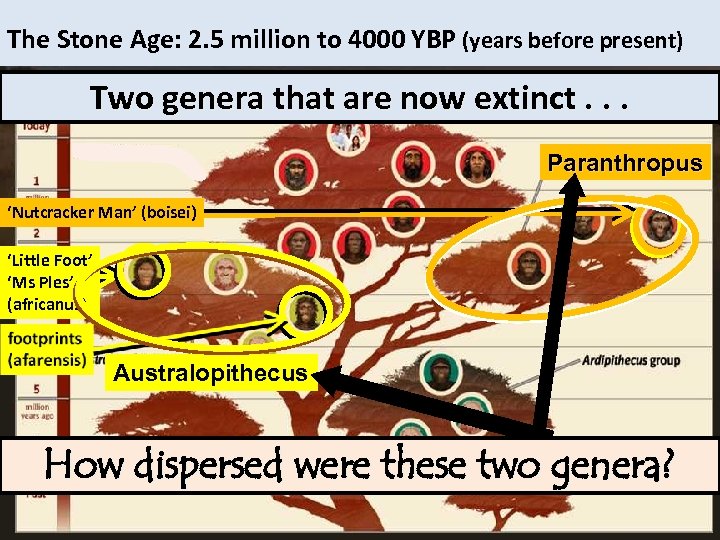
The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP (years before present) homo Two genera that are now extinct. . . Paranthropus ‘Nutcracker Man’ (boisei) ‘Little Foot’ ‘Ms Ples’ (africanus) Australopithecus How dispersed were these two genera?
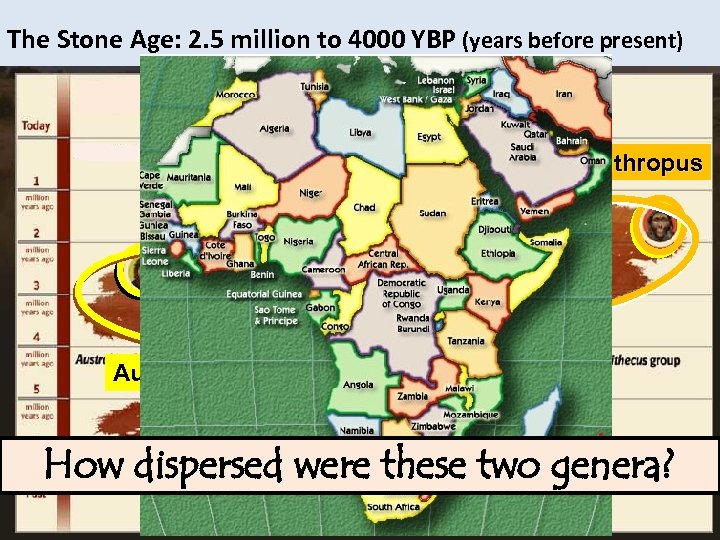
The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP (years before present) homo Paranthropus Australopithecus How dispersed were these two genera?
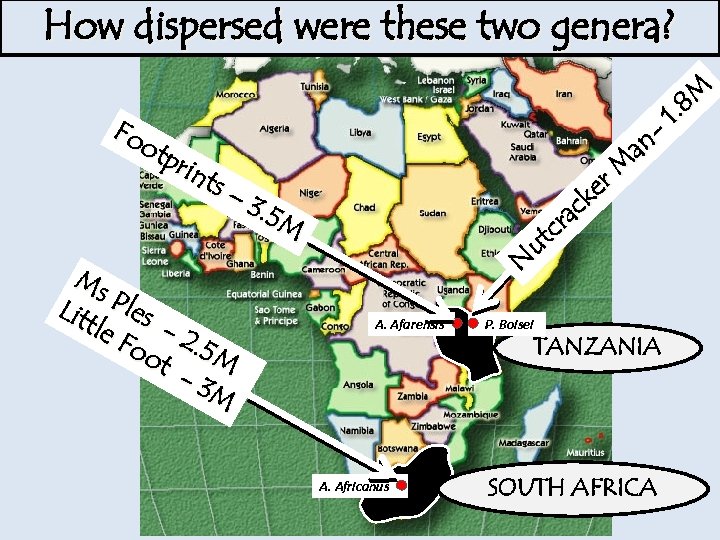
How dispersed were these two genera? Fo otp rin ts – Ms Lit Ples tle -2 Fo ot. 5 M -3 M na r. M ke ac cr ut N 3. 5 M A. Afarensis A. Africanus P. Boisei TANZANIA SOUTH AFRICA 8 M 1.
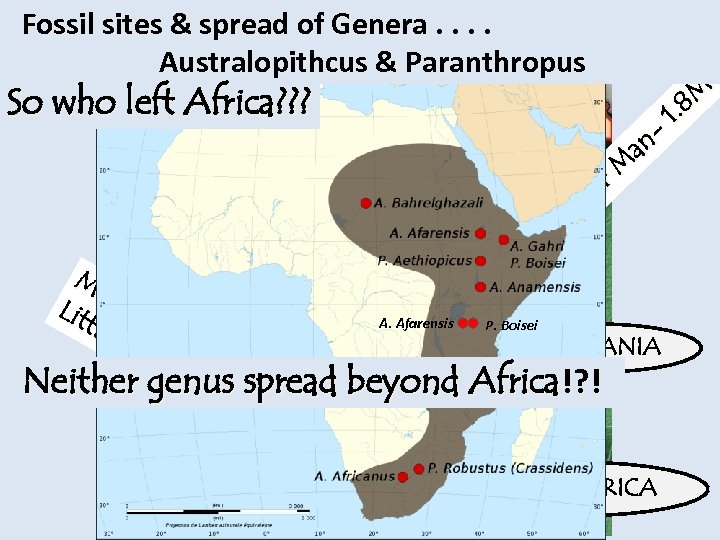
Fossil sites & spread were these. two genera? How dispersed of Genera. . . Australopithcus & Paranthropus So who left Africa? ? ? Fo otp rin ts – na r. M ke ac cr ut N 3. 5 M Ms Lit Ples A. Afarensis P. Boisei tle -2 Fo TANZANIA ot. 5 M -3 Neither genus spread beyond Africa!? ! M A. Africanus SOUTH AFRICA 8 M 1.
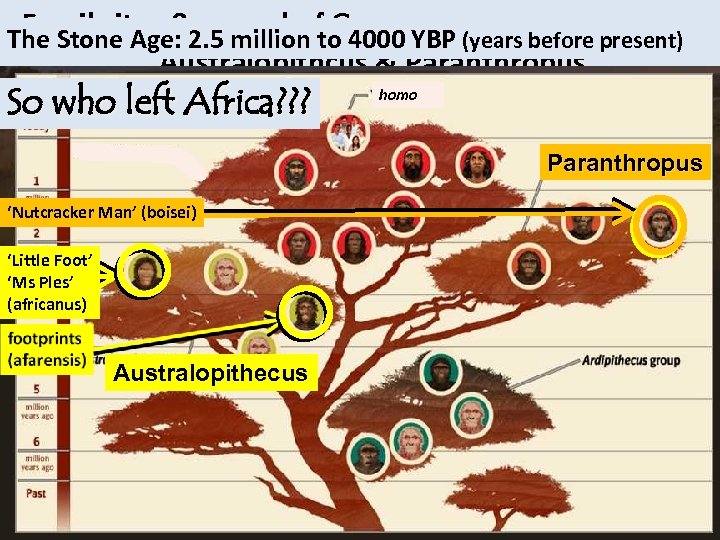
Fossil sites & spread of Genera. . Australopithcus & Paranthropus Fossil sites & spread of Genera. . . The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP. (years before present) So who left Africa? ? ? homo Paranthropus ‘Nutcracker Man’ (boisei) ‘Little Foot’ ‘Ms Ples’ (africanus) A. Afarensis P. Boisei Australopithecus Neither genus spread beyond Africa!? !
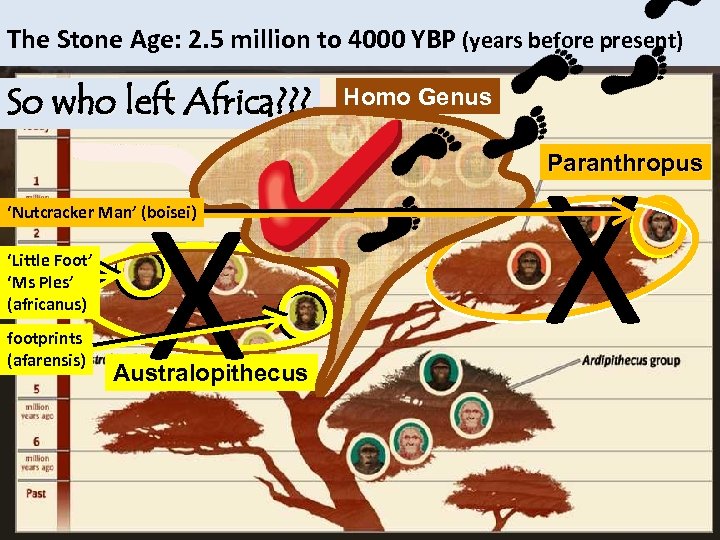
The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP (years before present) So who left Africa? ? ? X ‘Nutcracker Man’ (boisei) ‘Little Foot’ ‘Ms Ples’ (africanus) footprints (afarensis) Australopithecus homo Homo Genus X Paranthropus
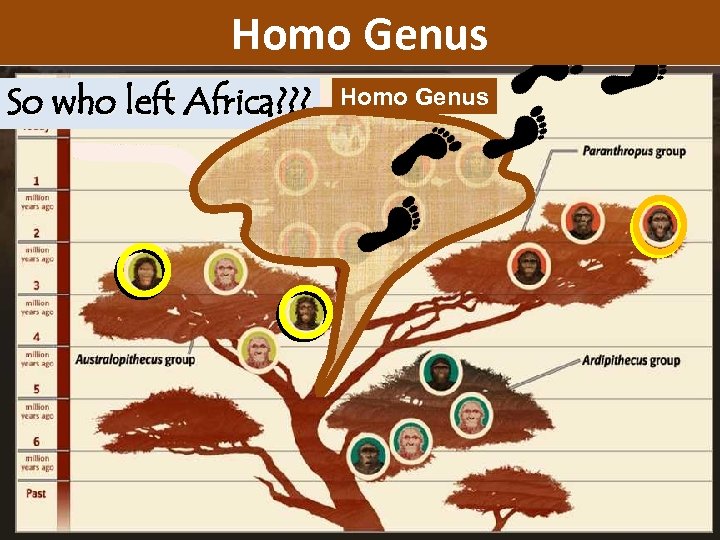
Homo Genus The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP (years before present) So who left Africa? ? ? homo Homo Genus Homo

Homo Genus 2010. . . eek? st w homo Homo er la emb Rem Until 2010, earliest known 2010. . . species of Homo Genus
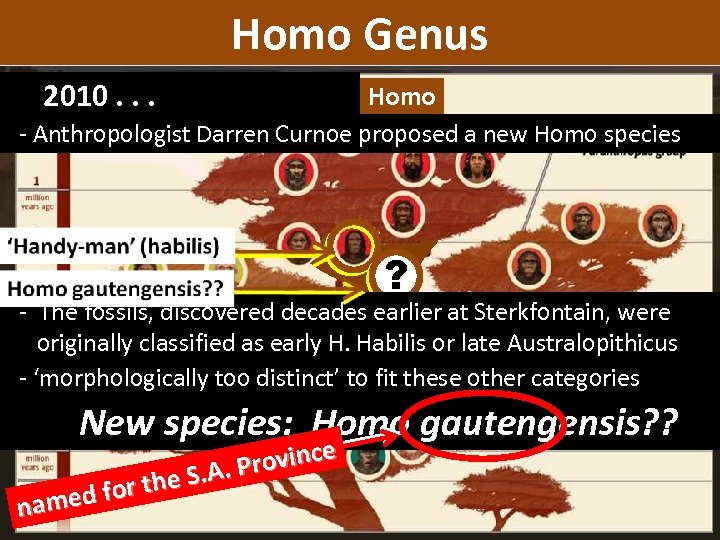
Homo Genus 2010. . . homo Homo - Anthropologist Darren Curnoe proposed a new Homo species ? - The fossils, discovered decades earlier at Sterkfontain, were originally classified as early H. Habilis or late Australopithicus - ‘morphologically too distinct’ to fit these other categories New species: Homo gautengensis? ? ovince S. A. Pr for the named
Homo Genus The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP (years before present) homo Homo ?
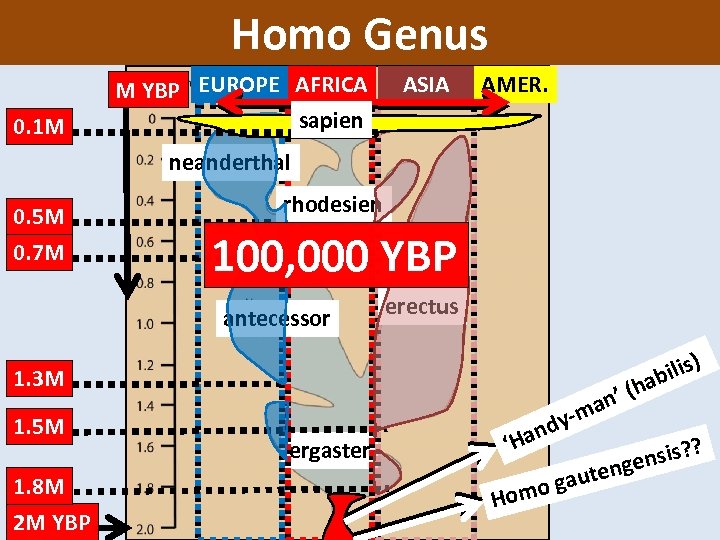
Homo Genus The Stone Age: 2. 5 million to 4000 YBP (years before present) 0. 1 M M YBP EUROPE AFRICA sapien ASIA AMER. neanderthal 0. 5 M 0. 7 M rhodesien 100, 000 YBP antecessor erectus 1. 3 M 1. 5 M 1. 8 M 2 M YBP ergaster h n’ ( a m dyan ‘H ? ? ensis teng o gau om H ilis) ab

Homo Genus NEXT WEEK. . . EUROPE AFRICA sapien ASIA AMER. Meet a French Homo sapien! 100, 000 YBP Week 3: into Europe Abri Cro-Magnon Man Week 2: into Africa Week 1: beginning in East Africa

REFERENCES http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Human_evolution http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Stone_Age http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Neolithic http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Paleolithic http: //humanorigins. si. edu/evidence/human-family-tree http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Cradle_of_Humankind http: //www. sa-venues. com/attractionsga/cradle-of-humankind. htm http: //www. sa-venues. com/maps/gauteng_cradle_of_humankind. htm http: //geology. com/world/south-africa-satellite-image. shtml http: //pubs. usgs. gov/gip/dynamic/East_Africa. html http: //www. nationsencyclopedia. com/Africa/South-Africa http: //www. sa-venues. com/maps/gauteng_magaliesberg. htm http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Mrs. _Ples http: //www. cradleofhumankind. co. za/exploretoday/Pages/_Sterkfontein. Caves. aspx http: //www. talkorigins. org/faqs/homs/rbroom. html http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Sterkfontein http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Little_Foot http: //www. panoramio. com/photo/62201978 http: //www. artlink. co. za/news_article. htm? content. ID=28164 http: //www. maropeng. co. za/index. php/exhibition_guide/sterkfontein/little_foot/ http: //popular-archaeology. com/issue/june-2011/article/ancient-nutcracker-man-had-no-taste-for-nuts http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Human_evolution http: //www. newscientist. com/article/dn 9989 -timeline-human-evolution. html http: //www. sciencedirect. com/science/article/pii/S 0018442 X 10000727 http: //www. sciencedaily. com/releases/2010/04/100408105147. htm http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Homo_gautengensis Curnoe, D. , A review of early Homo in southern Africa focusing on cranial, mandibular and dental remains, with the description of a new species (Homo gautengensis sp. Nov. ), HOMO-J. Comp. Hum. Biol. , 61: 151– 177, 2010; pp 171– 172 http: //anthro. palomar. edu/homo_1. htm http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Neanderthal

OUR TRAVEL WEBSITES TRAVEL INFORMATION WORLDWIDE HOUSING www. vrbo. com (individual owners within site) www. homeaway. com (individual owners within site) AFRICA Housing: www. villa-st-leon. co. za (private home - owner: Babel Schumacher) www. christinesbeachcottage. com (private home - owner: Dan & Christine Carter) http: //www. sa-venues. com (individual owners within site) Safari Travel: www. africa-adventure. com (US based safari company – excellent small group tours) http: //www. classicafricansafaris. com/ (Kenya: Hamish Grant -private safari guide) http: //www. arptravelgroup. com/arp/(Tanzania: Ranger Ltd- private and group safaris) www. ccafrica. com (up-scale safaris w/conservation focus) www. sanparks. org (direct booking for South Africa National Parks) CHINA www. cits. net (China International Travel Service) Guilin: http: //en. guilincits. com (agents: Christine, Shelley) FRANCE Housing: http: //www. rentapart. com (agent: Annebelle) http: //www. parisattitude. com (agent: Sylvain Guilemin) Houseboat rental: http: //alpha-croisiere. com Language Classes: OISE Paris website: www. paris. oise. com , phone: 30(0)1 -42 -22 -01 -98 SPAIN Spanish Paradors (hotels) websites: www. parador. es, http: //www. paradores-spain. com central reservations: +34 91 -516 6666, PORTUGAL parryoun@pomarv. jazznet. pt Portugal private house rental: Carole & Kenneth Parr http: //www. pousadas. pt Portuguese Posadas (hotels) : phone: +351 218 442 001 http: //www. pousadasofportugal. com/ phone: 351 -258 -82 -7151 Language Classes: Cambridge School website: www. cambridge. pt, phone: 351 -213 -124 -600
491fd58bb4b12d32acc4b27948a716e7.ppt