2e4f99a4ca64300b17e36ba56eb3f608.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Web Spoofing Outline • Motivation • Web spoofing problem • Web spoofing attacks – works done • Web spoofing Countermeasures – works done • New Idea 1
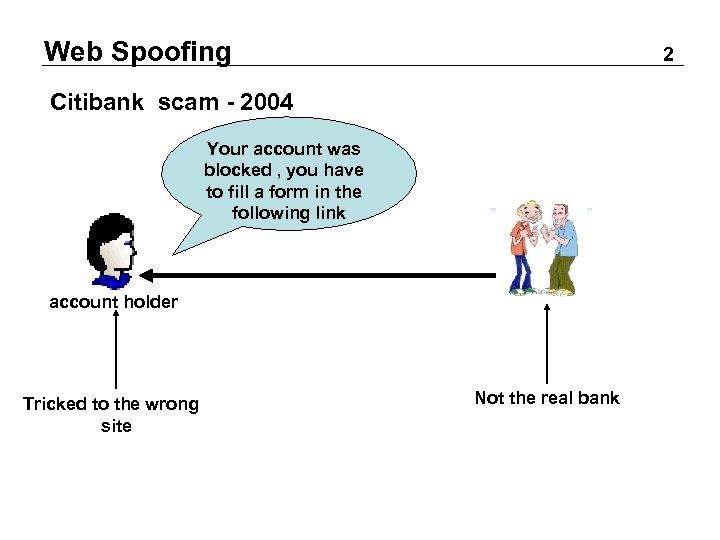
Web Spoofing 2 Citibank scam - 2004 Your account was blocked , you have to fill a form in the following link email account holder Tricked to the wrong site citibank Not the real bank
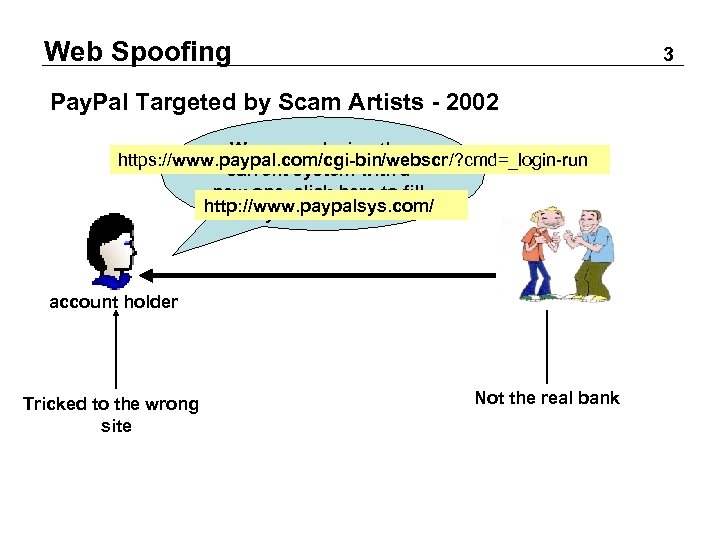
Web Spoofing 3 Pay. Pal Targeted by Scam Artists - 2002 We are replacing the https: //www. paypal. com/cgi-bin/webscr/? cmd=_login-run current system with a new one. click here to fill http: //www. paypalsys. com/ your details. email account holder Tricked to the wrong site Not the real bank
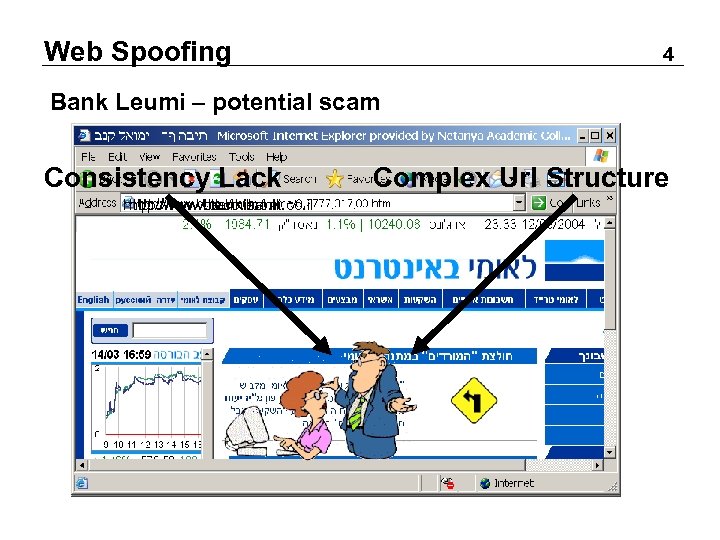
Web Spoofing 4 Bank Leumi – potential scam Consistency Lack http: //www. bll. co. il http: //www. leumibank. co. il http: //www. bankleumi. co. il http: //www. leumi. co. il Complex Url Structure
Web Spoofing 5 Our Players user server authentication is possible. Is the browser-user communication model secure enough to warrant this assumption. performs sensitive tasks.
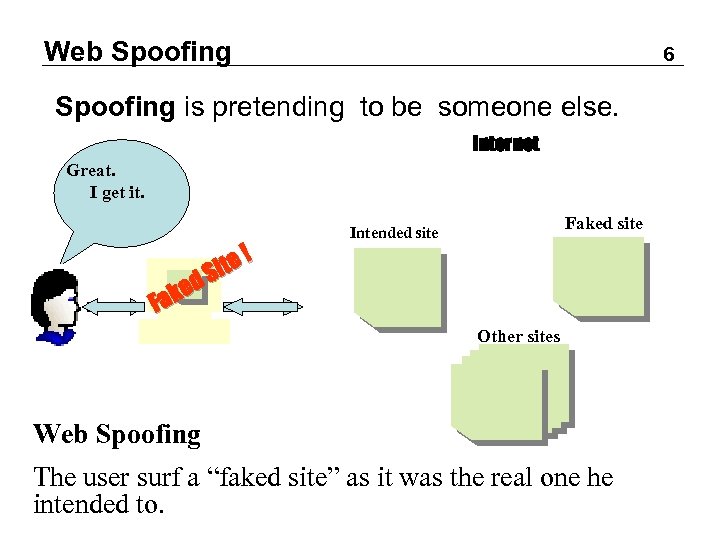
Web Spoofing 6 Spoofing is pretending to be someone else. Internet Great. He Wants I check to get it. his bank account ked Fa te ! Si Faked site Intended site Other sites Web Spoofing The user surf a “faked site” as it was the real one he intended to.

Web Spoofing 7 Faked Site • Site that imitate another one in its appearance and action for malicious purposes. • To succeed , the imitation process must take into account the level of awareness of the potential victim. Content imitation Content & Status imitation • Imitate the page sent by the server page content as content • Created by copying HTML files. the browser Status information produced by • Actions users who judge • “fine” for must be imitated sites according to their Visual • Requires Context. some programming efforts. • “fine” for sophisticated users.

Web Spoofing How the Users Get “Phished” • Normal surfing • Link in popular web page • Search engine • Web-enabled email • Sent by the attacker • Man in the middle attack • The attacker sit between the user and the real site 8

Web Spoofing 9 Works Done • Web Spoofing Revisited: SSL and Beyond – 2002 • Zishuang , Yuan and Smith. • Can users believe what their browsers tell them? attacks • Web spoofing: An Internet Con Game -1996 • Edward W. Felten and others. • spoofing entire WWW • Trust on Web Browser: Attack vs. Defence • No author given remedy • Trusted Paths for Browsers: An Open-Source Solution to Web Spoofing – 2002 • Zishuang , Yuan and Smith. • Demonstrate Open source solution
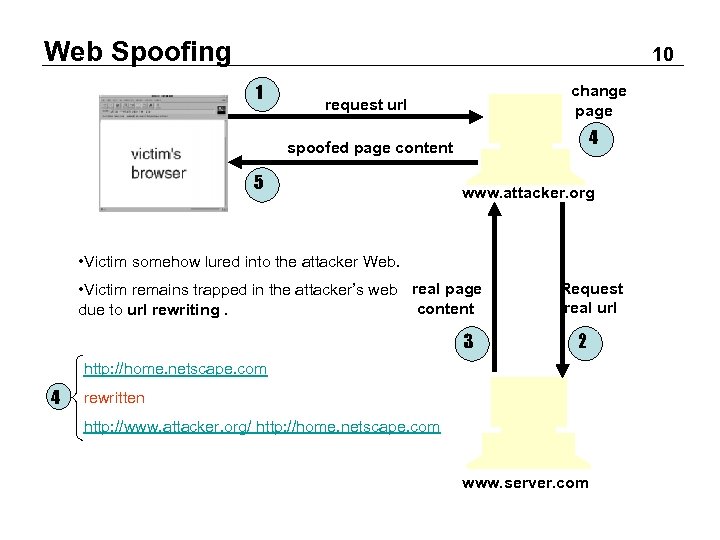
Web Spoofing 10 1 change page request url 4 spoofed page content 5 www. attacker. org • Victim somehow lured into the attacker Web. • Victim remains trapped in the attacker’s web real page content due to url rewriting. 3 Request real url 2 http: //home. netscape. com 4 rewritten http: //www. attacker. org/ http: //home. netscape. com www. server. com

Web Spoofing Complete the Illusion • Still there some evidence that may disclose the attack. • Status Line • Mouse click/move events written in javascript • Location Line • Replace the original with fake one. • Viewing Document Source • Hide the menu bar and provide another • SSL evidence do not help • The secure connection made against the attacker’s site. 11

Web Spoofing 12 • The target was Web. Blitz , a web-based e-mail system. • The language used was Javascript. • They take into account the browser type. (Netscape , IE). • Create new window with all bars turned off. • They provide a interactive fake bars instead. • The location bar get input from keyboard • A fake statusbar with lock icon to indicate SSL session. • The fake statusbar updated as needed • SSL warning windows spoofed also. • They spoof the server certificate that emerged when lock icon double clicked • Images were cached to improve load time

Web Spoofing 13 Countermeasures • Browser Configuration & recommendations • Configuring browser settings: disable javascript • Short term • Maybe selective • Make sure the location bar always visible • Make sure the url points to the server you intended to • Browser Extension • Extending functionality so the user interface is safe • Long term Good solution must prevent web spoofing and keep the browser in full functionality.

Web Spoofing 14 Abstract • suggest a solution that defend against web spoofing. • create a trusted path from the browser to the user. • implemented in Mozilla: open source browser. Design Criteria • Effectiveness • User can correctly recognize large amount of status info • Work • Cannot expect users to do a lot of work • Intrusiveness • Minimize intrusion on content

Web Spoofing 15 Rejected Approaches • Preventing the open of windows with status elements turned off. • What about pop-up warning window • What about certificate information pages • Constrict the display of server pages • User enter a “MAC phrase” at startup and browser insert it in each status element. • Adding some phrase to the title of windows.
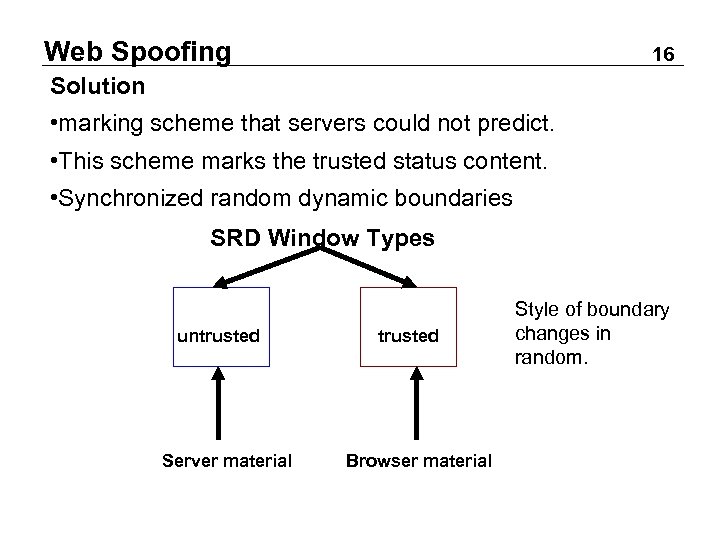
Web Spoofing 16 Solution • marking scheme that servers could not predict. • This scheme marks the trusted status content. • Synchronized random dynamic boundaries SRD Window Types untrusted Server material trusted Browser material Style of boundary changes in random.
Web Spoofing Animation of the Solution 17

Web Spoofing 18 New Idea • Creating a safe region in the top of each browser window. • It is out of loaded sites control. • Enable personal skinning. • SSL secured sites identified by a logo in this region. • Credential logos will appear in this region • Implemented in Mozilla browser.
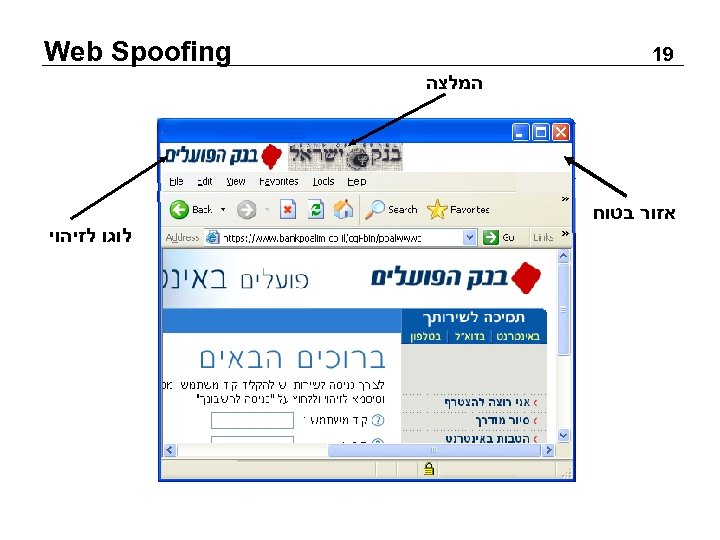
Web Spoofing 91 המלצה אזור בטוח לוגו לזיהוי
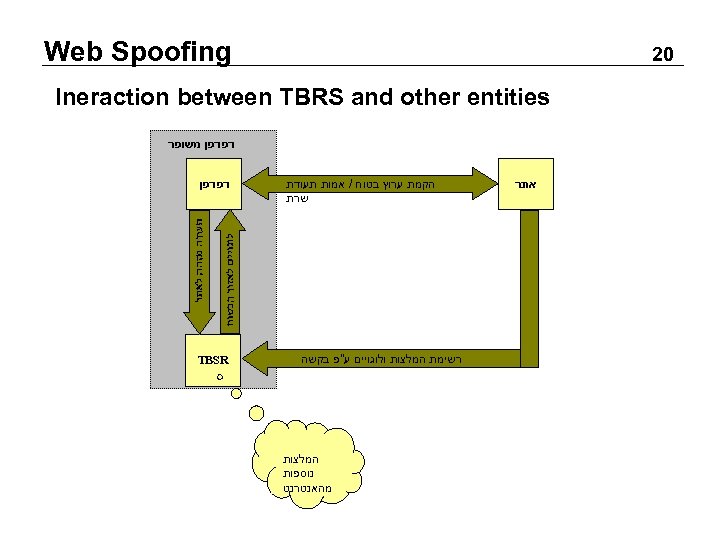
Web Spoofing 02 Ineraction between TBRS and other entities דפדפן משופר אתר הקמת ערוץ בטוח / אמות תעודת שרת רשימת המלצות ולוגויים ע"פ בקשה המלצות נוספות מהאנטרנט דפדפן TBSR
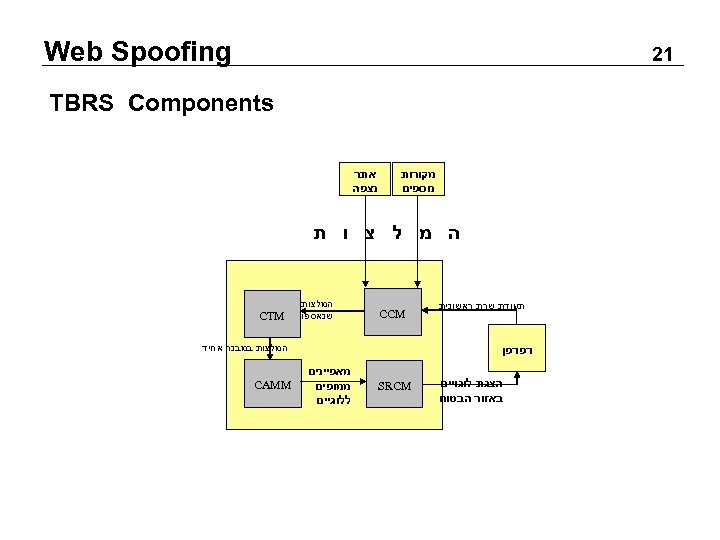
Web Spoofing 12 TBRS Components מקורות נוספים אתר נצפה ה מ ל צ ו ת תעודת שרת ראשונית CCM המלצות שנאספו המלצות במבנה אחיד דפדפן הצגת לוגויים באזור הבטוח CTM SRCM מאפיינים ממופים ללוגיים CAMM
2e4f99a4ca64300b17e36ba56eb3f608.ppt