e8a9436a5164c7d1e01d3dd668973fe4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Web Services

What are Web Services? • The concept of Web Service (WS) introduced in 1999 by Hewlett-Packard. Microsoft coined the actual term “Web Services” in June 2000 as part of the. NET initiative. • Many believe that WS is a key component of many future business-integration initiatives.

What are Web Services? • Web services are often advertised as a new wave in business process automation u Allow a seamless integration of systems and applications that communicate over the network and share data. • This technology is in its infancy. Work in progress u Unproven u Lots of hype? u

What are Web Services? • Idea of treating software as a service. u Nothing new • Evolution of many different technologies u u Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) CORBA DCOM Java RMI • What is novel? u u Overwhelming industry support Utilization of XML

Why Web Services • SUN RPC, DEC, CORBA, DCOM, Java RMI u u Not Internet-friendly Interoperability issues: standards are not always clear. Cannot be implemented in any language on any platform Software components that comprise the application are often not useful except for that application • A web service u u Can be implemented in any language on any platform Black boxes § Component-like, reusable u Based on Web standards § HTTP, XML, SOAP, WSDL, UDDI

Examples of Simple Web Services • Return the distance in miles between 2 locations • Locate entertainment, restaurants and lodging in a given area • Return the name and the postal address associated with a given phone number. • Find ATM location for a given postal code. • Return stock quotes.

Examples of Web Services • A travel agent needs to book a flight, hotel and car in a warm place. The client wants the best prices. Travel agent contacts each airline for flight information, hotel chain for hotel information and car rental agencies. u u The airlines, hotel chains and car rental agencies can be thought of as web services from the travel agent’s perspective. The travel agent’s user may think of the travel agent as a web service.

Examples of Web Services • You should note that potential reusability of each of the services described on the last two slides. • This is what has business excited. The potential to create a distributed application from different services where each service is potentially owned by a different organization. • Users of a services will often be expected to pay a fee for each use or have a service level agreement.
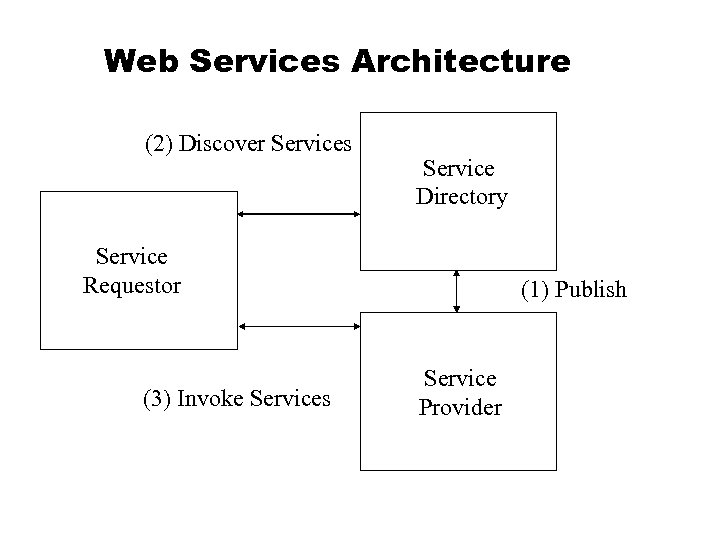
Web Services Architecture (2) Discover Services Service Directory Service Requestor (3) Invoke Services (1) Publish Service Provider

Web Services Architecture • Service Provider u Implements the Web Service and makes it available on the Internet • Service Requestor u Consumer of the Web Service • Service Directory Logically centralized directory of services u Place to publish a new web service or find existing one. u

XML • XML – Extensible Markup Language • Open standard for data exchange; for describing data which allows an infinite range of elements (tags) to be defined: Tags define content u Separation of content from presentation u

SOAP • SOAP – Simple Object Access Protocol u u Created by Microsoft and submitted to W 3 C in 1999 Multivendor support including IBM, Sun, Oracle, HP, etc; • SOAP operates as RCP mechanism with HTTP used as transport protocol. • Encodes requests and responses as XML documents. • SOAP is suppose to be simple, easy to extend and interoperable.

WSDL • WSDL – Web Services Description Language • Type of XML used to describe abilities of Web Service to its potential user. • WSLD provides the standard method of describing web services and their specific capabilities to other applications.

UDDI • UDDI – Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration • Enables the creation of searchable web service directory that allows for the registration of a service and in response to a user provide the location of a service.

Web Service Example(from SUN) • Suppose that the owner of a chain of coffee houses, called Coffee Break, wants to expand by selling coffee online. • The owner instructs the business manger to find some new coffee supplier, get their wholesale prices, and then arrange for orders to be placed as the need arises. • Coffee Break can analyze prices and decide which new coffees it wants to carry and which companies it wants to buy them from.

Web Services Example (from SUN) • Locate coffee supplier through a UDDI service directory. • The Coffee Break will issue a query to the UDDI service directory. When the search is completed, the registry will send back information on how to contact the wholesale coffee distributors that meet the criteria set out in the query.

Web Services Example • Now Coffee Break can request price lists from each of the coffee distributors returned by the UDDI Service Directory. u The Coffee Break has obtained a WSDL description for each distributor which describes the procedure to call to get prices and the URL where the request is to be sent. • Upon receiving the responses for the request for prices, Coffee Break processes the price lists. This is used to send orders.

Challenges • Standards are new and require further development as to make sure that there is true interoperability. • Lack of Security • Controversy over royalty fees (intellectual property rights to SOAP, WSDL, UDDI are held by Microsoft and IBM). • Management, monitoring, auditing • Performance: WS may be too slow for high performance applications since parsing XML takes time. • Quality of Service: Lack of standards describing quality of various web services.
e8a9436a5164c7d1e01d3dd668973fe4.ppt