f82e21d60d07076d8727270f49a90d86.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Web Service Modelling Ontology (WSMO) John Domingue Knowledge Media Institute, The Open University Ontolog Semantic Web Service Ontology Standard Panel, October 20 th 2005 1
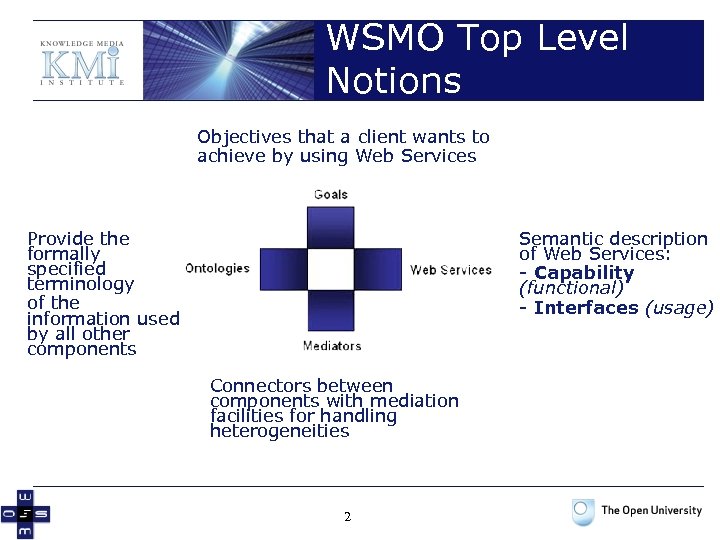
WSMO Top Level Notions Objectives that a client wants to achieve by using Web Services Provide the formally specified terminology of the information used by all other components Semantic description of Web Services: - Capability (functional) - Interfaces (usage) Connectors between components with mediation facilities for handling heterogeneities 2
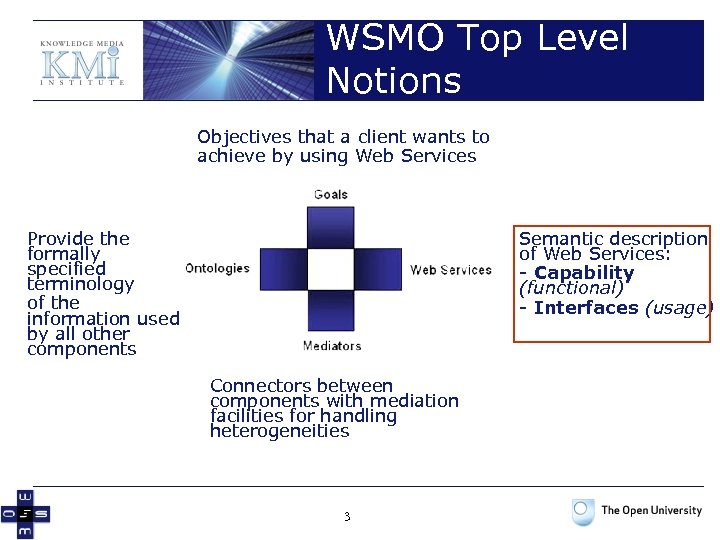
WSMO Top Level Notions Objectives that a client wants to achieve by using Web Services Provide the formally specified terminology of the information used by all other components Semantic description of Web Services: - Capability (functional) - Interfaces (usage) Connectors between components with mediation facilities for handling heterogeneities 3

Capability Specification • • • Non functional properties Imported Ontologies Used mediators • Pre-conditions What a web service expects in order to be able to provide its service. They define conditions over the input. Assumptions Conditions on the state of the world that has to hold before the Web Service can be executed Post-conditions describes the result of the Web Service in relation to the input, and conditions on it Effects Conditions on the state of the world that hold after execution of the Web Service (i. e. changes in the state of the world) • • • – OO Mediator: importing ontologies with mismatch resolution – WG Mediator: link to a Goal wherefore service is not usable a priori 4
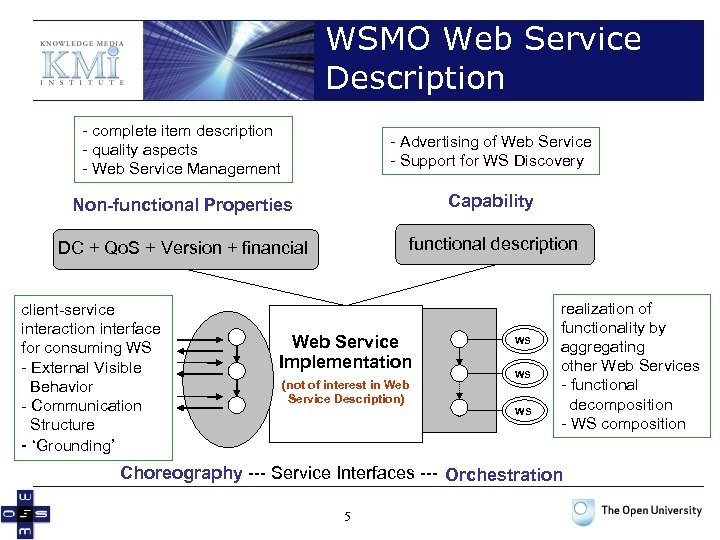
WSMO Web Service Description - complete item description - quality aspects - Web Service Management - Advertising of Web Service - Support for WS Discovery Non-functional Properties Capability DC + Qo. S + Version + financial functional description client-service interaction interface for consuming WS - External Visible Behavior - Communication Structure - ‘Grounding’ Web Service Implementation (not of interest in Web Service Description) WS WS WS realization of functionality by aggregating other Web Services - functional decomposition - WS composition Choreography --- Service Interfaces --- Orchestration 5
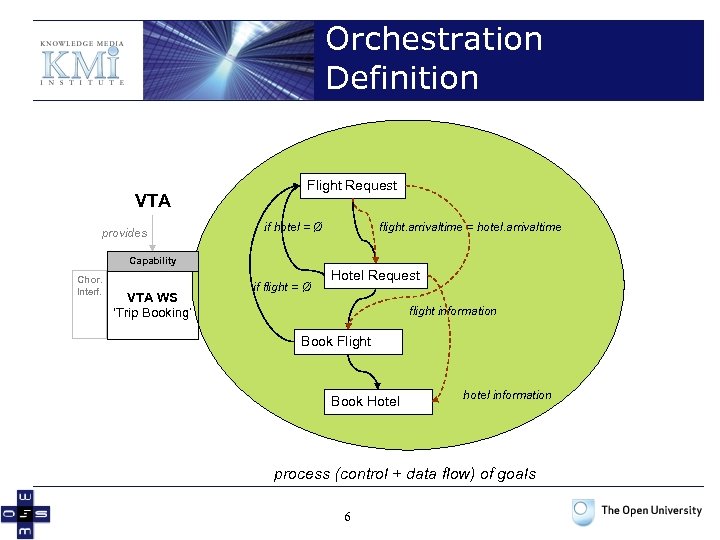
Orchestration Definition VTA provides Flight Request if hotel = Ø flight. arrivaltime = hotel. arrivaltime Capability Chor. Interf. VTA WS ‘Trip Booking’ if flight = Ø Hotel Request flight information Book Flight Book Hotel hotel information process (control + data flow) of goals 6
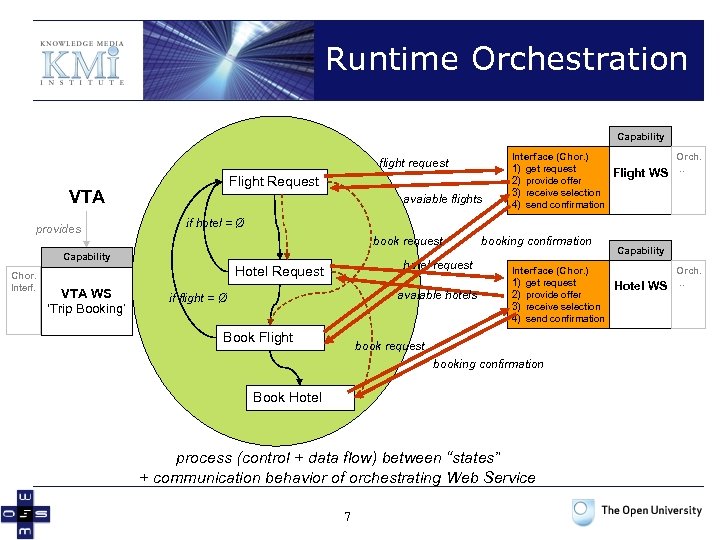
Runtime Orchestration Capability flight request Flight Request VTA provides avaiable flights book request hotel request Hotel Request VTA WS ‘Trip Booking’ Flight WS Orch. . . if hotel = Ø Capability Chor. Interface (Chor. ) 1) get request 2) provide offer 3) receive selection 4) send confirmation avaiable hotels if flight = Ø Book Flight booking confirmation Interface (Chor. ) 1) get request 2) provide offer 3) receive selection 4) send confirmation book request booking confirmation Book Hotel process (control + data flow) between “states” + communication behavior of orchestrating Web Service 7 Capability Hotel WS Orch. . .
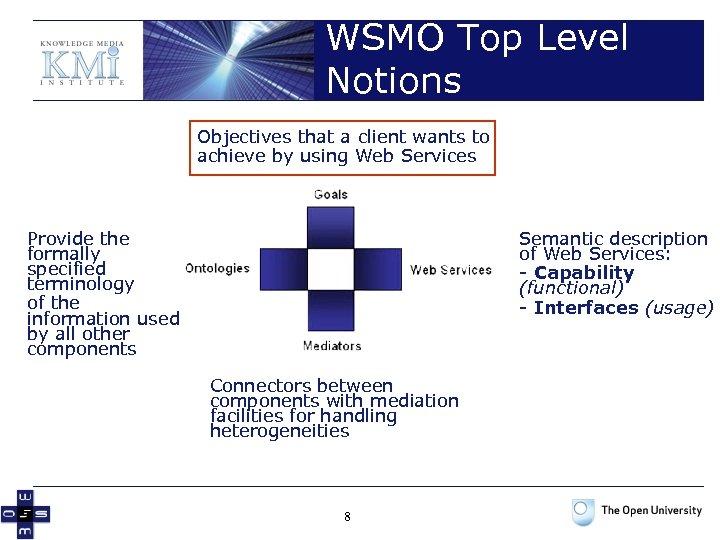
WSMO Top Level Notions Objectives that a client wants to achieve by using Web Services Provide the formally specified terminology of the information used by all other components Semantic description of Web Services: - Capability (functional) - Interfaces (usage) Connectors between components with mediation facilities for handling heterogeneities 8

Goals • Ontological De-coupling of Requester and Provider • Derived from task / problem solving methods/domain model • Structure and reuse of requests – – – Search Diagnose Classify Personalise Book a holiday • Requests may in principle not be satisfiable • Ontological relationships & mediators used to link goals to web services 9

Goal Specification • Non functional properties • Imported Ontologies • Used mediators – OO Mediators: importing ontologies with heterogeneity resolution – GG Mediator: • Goal definition by reusing an already existing goal • allows definition of Goal Ontologies • Requested Capability – describes service functionality expected to resolve the objective – defined as capability description from the requester perspective • Requested Interface – describes communication behaviour supported by the requester for consuming a Web Service (Choreography) – Restrictions / preferences on orchestrations of acceptable Web Services 10
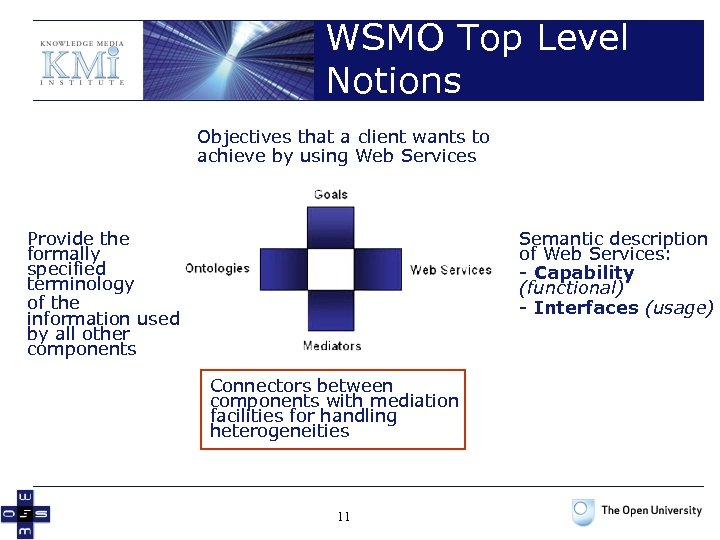
WSMO Top Level Notions Objectives that a client wants to achieve by using Web Services Provide the formally specified terminology of the information used by all other components Semantic description of Web Services: - Capability (functional) - Interfaces (usage) Connectors between components with mediation facilities for handling heterogeneities 11
Mediation • Heterogeneity … – For 1$ on programming, $5 - $9 on integration © IBM, Nelson Mattos – Mismatches on structural / semantic / conceptual / level – Assume (nearly) always necessary • Description of role – Components that resolve mismatches – Declarative description of arbitrary web service • Types of Mediation within Semantic Web Services: (1) Data: mediate heterogeneous Data Sources (2) Protocol: mediate heterogeneous Communication Patterns (3) Process: mediate heterogeneous Business Processes 12
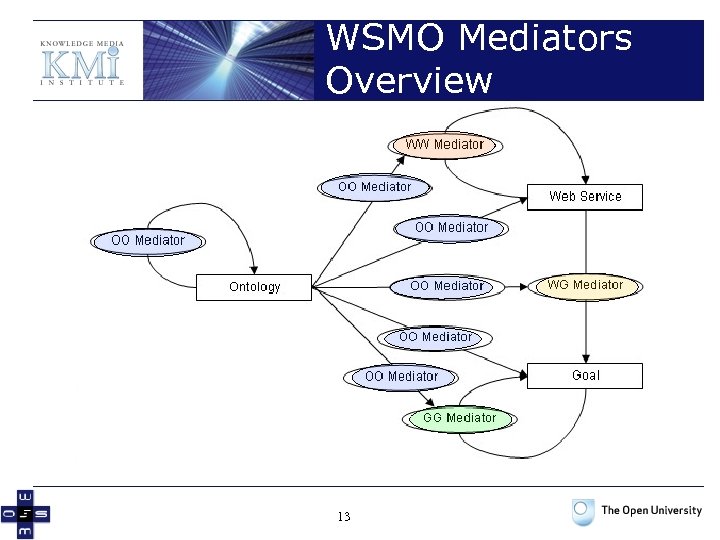
WSMO Mediators Overview 13
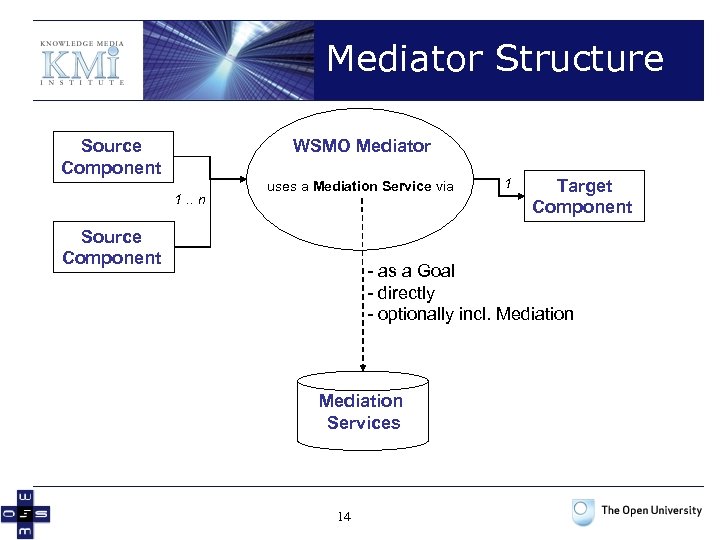
Mediator Structure Source Component WSMO Mediator 1. . n uses a Mediation Service via Source Component 1 Target Component - as a Goal - directly - optionally incl. Mediation Services 14
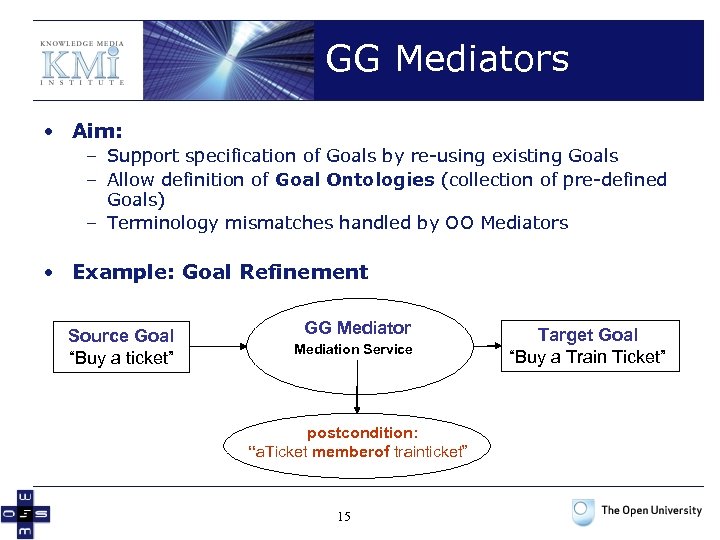
GG Mediators • Aim: – Support specification of Goals by re-using existing Goals – Allow definition of Goal Ontologies (collection of pre-defined Goals) – Terminology mismatches handled by OO Mediators • Example: Goal Refinement Source Goal “Buy a ticket” GG Mediator Mediation Service postcondition: “a. Ticket memberof trainticket” 15 Target Goal “Buy a Train Ticket”

Acknowledgements The WSMO work is funded by the European Commission under the projects DIP, Knowledge Web, SEKT, SWWS, and Esperonto; by the UK EPSRC under the AKT project; by Science Foundation Ireland under the DERI-Lion project; and by the Austrian government under the FIT-IT program. The WSMO Working Group Chairs are: Christoph Bussler, John Domingue, and Dieter Fensel 16

Relevant URLs • WSMO – http: //www. wsmo. org/ • IRS – http: //kmi. open. ac. uk/projects/irs/ • DIP – http: //dip. semanticweb. org/ 17
f82e21d60d07076d8727270f49a90d86.ppt