84bdfae0ab4d63ba78f7db4d22025082.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50

Web of Belief: Modeling and using Trust and Provenance in the Semantic Web Department of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering University of Maryland Baltimore County Li Ding Last updated: 3/15/2018

Outline n Introduction q n n n Research description Research plan Preliminary Work q q n n Thesis Statement The Web Of Belief Framework Evaluation Contributions to computer science Thesis Schedule

Motivation n The growing body of the Semantic Web q Observations n Information q q n More Data encoded in Semantic Web language from many sources Various dialect Ontologies Information is managed in two layer mechanism in terms of “Document, Ontology, namespace, term” q q n q Physical layer: the web of semantic web documents Logical layer: the RDF graph More Semantic Web Tools Drive forces n n Industrial: Weblog, RSS, social network websites Academic: research projects
Motivation (cont’d) n The Semantic Web has not achieved a real world “KB” q Credibility & Consistency n q Scalability n n q Facts are provided by many sources w/o guarantee Data is in vast amount Data is stored in an open and distributed context Utility n Data is fragmented q Bad URI Reference of resource & namespace in the Web of documents q Lack of associations in the RDF graph

Motivation (cont’d) n Why provenance and trust q Important concepts borrowed from human world n n q Keys to credibility assessment and justification n q Multi-discipline origins: social, epistemology, psychology The foundation of knowledge management and inference Empirical heuristics, also the complement method, in the absence of domain knowledge to direct reason over credibility. Explicit representation of justification trace. Good Heuristics to resolve inconsistency. Keys to effectiveness and efficiency n n Knowledge can be managed by Provenance besides Topic Trust reduces search complexity

Thesis Statement This dissertation shows that our Web Of Belief framework, a provenance and trust aware inference framework, is critical and effective in deriving answers with credibility assessment and justification across the open, distributed, and large scale online knowledge base provided by the Semantic Web.

Research Description
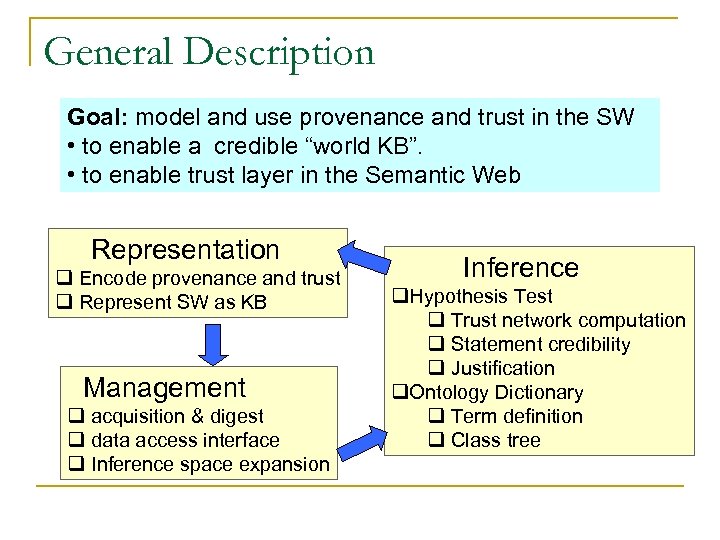
General Description Goal: model and use provenance and trust in the SW • to enable a credible “world KB”. • to enable trust layer in the Semantic Web Representation q Encode provenance and trust q Represent SW as KB Management q acquisition & digest q data access interface q Inference space expansion Inference q. Hypothesis Test q Trust network computation q Statement credibility q Justification q. Ontology Dictionary q Term definition q Class tree
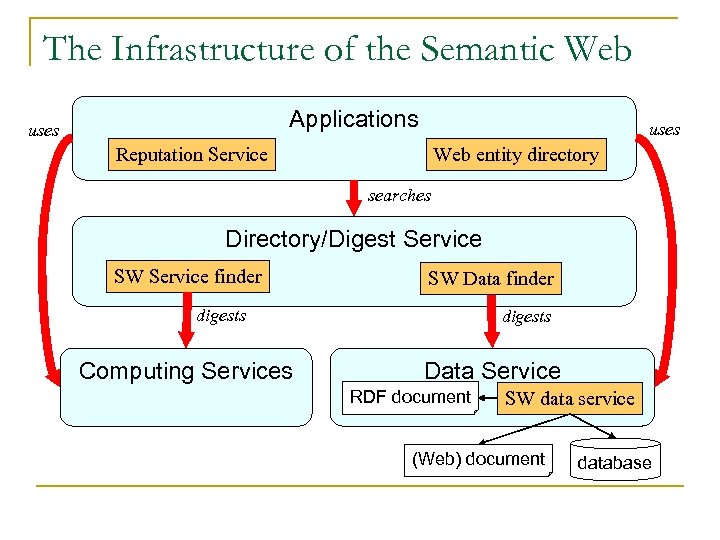
The Infrastructure of the Semantic Web Applications uses Reputation Service Web entity directory searches Directory/Digest Service SW Service finder SW Data finder digests Computing Services digests Data Service RDF document SW data service (Web) document database

Assumptions n n n Propositional knowledge (facts) Uncertain knowledge with provenance Open and distributed knowledge storage

Relationship to Other Work n Representation q q q n Data access q n Collaborative KB in open distributed context (DB) Learning q n Logical formalisms of agent model (AI) Truth theory (Epistemology) Provenance Learning agent models: knowledge and behavior (social learning & psychology) Inference q Reason over uncertain knowledge (reasoning)
Logical Formalisms n Modal Logic -- logically formalize agent q q q n Agent & action (Mc. Carthy, 1969; Kanger-Porn-Lindahl) Agent & belief and intention (Cohen, Levesque, 1990) Agent & knowledge (Epistemic logic) Agent & belief (Doxastic logic) Agent & obligation (Deontic logic ) Other logical formalisms for trust and belief q q Regan’s formal framework for belief and trust Josang’s subjective logic Abdul-Rahman’s social trust model Jones and Firozabadi’s integrated logic model of trust

Epistemology

Learning Agent models n Objects to be learned q q n Domain Trust Referral Trust Methods q q Histogram Feedback based

Reason over uncertain knowledge n Quantitative approach q Certainty factors - Mycin (Shortliffe, 1976) n q q (obsolete heuristic), similar to Fuzzy approach Possibility theory: Fuzzy logic (Zade, 1965; 1976) Dempter-Shafer theory (Dempster, 1968; Shafer 1976) q q n Subjective logic Probabilistic theory: Bayes Network (Pearl; 1982) Qualitative approach q Non-monotonic logic
Two level data access n n Datalog Logical level q RDF data access language (with provenance) n n Quads Tri. QL SPARQL Storage level q Centralized n n q triplestore Kowari Decentralized n Search engine?

Example walkthrough n Given a hypothesis/query in form of a collection of RDF statements with or w/o variables n Provenance q q n where can I find them? where are the definitions for each term? Belief( agent, fact): Who said or asserted so? Justify( fact, fact): Trust q q Can I believe them and thus use them in decision making How do I trust the other agents
Relationship to Other Work n Representation q q q n n Agent, knowledge Provenance Trust q q q n q q Pattern extraction Transitive closure RDF storage n n Probabilistic inference Scalability n Metadata RDF query language n Trust network inference Credibility n Data access q Inference Domain filter Social filter Semantic Web

Research Plan

Approach – the WOB framework n Representation q WOB ontology n n Management q q q n Model provenance and trust into the semantic web Explicit represent the semantic web Represent SW as a KB in terms of “agent, statement, association” Provenance aware data access language Social network extraction and integration Provenance and trust based knowledge base expansion Inference q Hypothesis credibility assessment n n n q Trust network inference Provenance and trust based belief evaluation Explicit justification Ontology dictionary

Research Methodology n n Identify real world problems with examples Approach problems q q n Formalize problem Position problem in literature, and find related work Find issues to be resolved Design and implement solutions Evaluation methods q q q Statistics Project application Survey
![Artifacts to be produced n n [Data] Web Of Belief Ontology [System] Swoogle metadata Artifacts to be produced n n [Data] Web Of Belief Ontology [System] Swoogle metadata](https://present5.com/presentation/84bdfae0ab4d63ba78f7db4d22025082/image-22.jpg)
Artifacts to be produced n n [Data] Web Of Belief Ontology [System] Swoogle metadata and search service q q n [System] Ontology dictionary [Data] Swoogle Statistics [System] Sem. Dis Trust layer q q [Algorithm] Trust based belief evaluation [Algorithm] Trust based knowledge expansion

Limitations n Limited in online Semantic Web documents

Preliminary Work

Web. Of. Belief Ontology n Ontology q q Entity: Document, Statement, Reference, Agent, Association n n Sub-classes: trust, belief, justification, dependency Facets q q q Provenance n n n Confidence (conditional probability) Connective (semantics) (Agent-document) Ownership/Authorship (Agent-Reference) belief (Reference-Reference) justification (doc-doc) dependency Logical Formalisms
![Web Of Belief (WOB) Conceptual Framework (v 0. 92) xsd: real [0, 1] Association. Web Of Belief (WOB) Conceptual Framework (v 0. 92) xsd: real [0, 1] Association.](https://present5.com/presentation/84bdfae0ab4d63ba78f7db4d22025082/image-26.jpg)
Web Of Belief (WOB) Conceptual Framework (v 0. 92) xsd: real [0, 1] Association. Connective confidence connective Association Dependency Justification foaf: Document Belief Reference Trust foaf: Agent selects foaf: page contains rdf: Resource dc: creator rdf: Statement source wob: imports wob: prior. Version wob: support wob: weaken wob: cause wob: imply wob: believe wob: disbelieve wob: nonbelieve wob: truthful wob: wise wob: knowledgeable wob: cooperative

Data digest service n Support data access language

Credibility Assessment n Trust Network Inference Given a trust network, how to propagate trust so as to evaluate trust between any two agents n Trust and provenance based statement evaluation n Explicit Justification

Ontology dictionary?

Social network extraction and mapping

Application n Trust based belief evaluation Trust and provenance aware inference Hypothesis testing and justification
Evaluation n n Validate derived trust relations: survey users Validate performance of WOB inference q n Compare results w or w/o trust & provenance Validate application utility: customer report
Contributions n A practical framework that makes the Semantic Web a KB q q The Web of Belief Ontology Semantic Web data digest service n n Search and browse mechanisms for SW Support of RDF data access language? q q n n Inference Judge information trustworthiness The first work in characterizing the Semantic Web trust and provenance aware distributed inference

Dissertation schedule n Measures q q n Size of data that could be handle Size of trust network Milestones q q Half-way finished

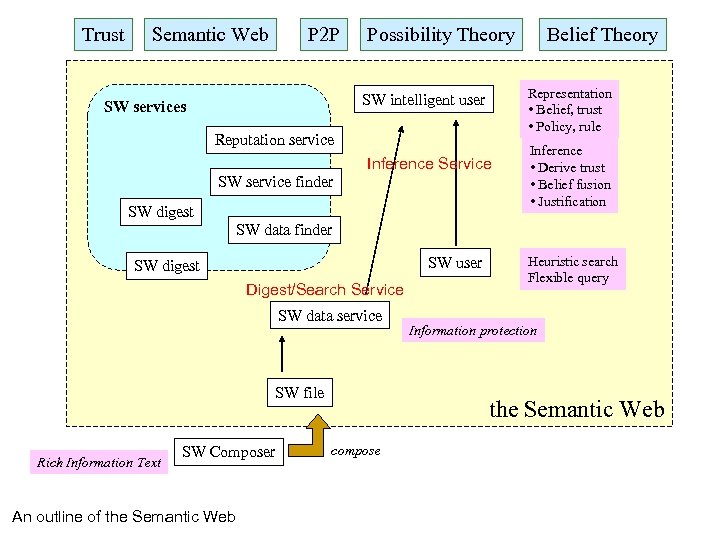
Trust Semantic Web P 2 P Possibility Theory Representation • Belief, trust • Policy, rule SW intelligent user SW services Reputation service Inference Service SW service finder SW digest Belief Theory Inference • Derive trust • Belief fusion • Justification SW data finder SW user SW digest Digest/Search Service SW data service SW file Rich Information Text SW Composer An outline of the Semantic Web Heuristic search Flexible query Information protection the Semantic Web compose
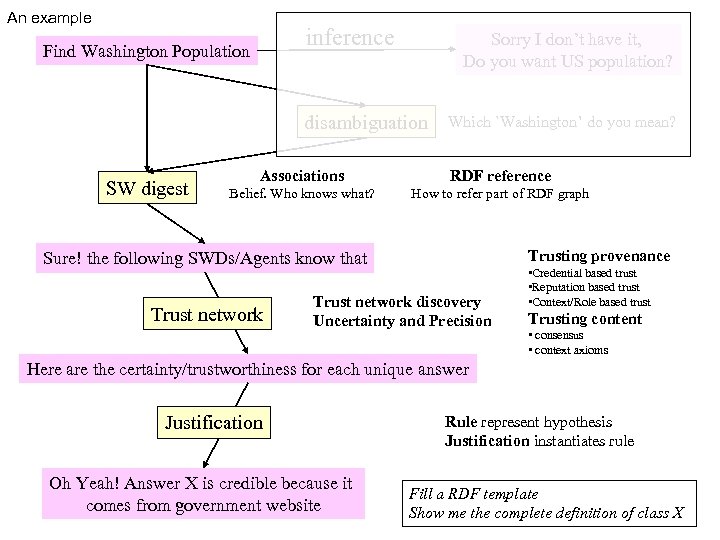
An example inference Find Washington Population Sorry I don’t have it, Do you want US population? disambiguation SW digest Which `Washington’ do you mean? Associations RDF reference Belief. Who knows what? How to refer part of RDF graph Trusting provenance Sure! the following SWDs/Agents know that Trust network discovery Uncertainty and Precision • Credential based trust • Reputation based trust • Context/Role based trust Trusting content • consensus • context axioms Here are the certainty/trustworthiness for each unique answer Justification Oh Yeah! Answer X is credible because it comes from government website Rule represent hypothesis Justification instantiates rule Fill a RDF template Show me the complete definition of class X
Expected Contributions n Framework q Features for characterize the Semantic Web q An Web of Belief ontology to connect the Semantic Web n n Association/ annotation Query language or data access language? Mechanisms q Search/browse Semantic Web Document q Judge information trustworthiness Applications q Swoogle q Semdis
1. Web of Belief – represent the SW n n Build an abstract view of the Semantic Web Select features to characterize it q q n Overall features: timeline, category Different levels: term, document, network Different classes: Entity, Association Different semantics: Meta-ontology, domainontology Build web of belief ontology for explicit representation
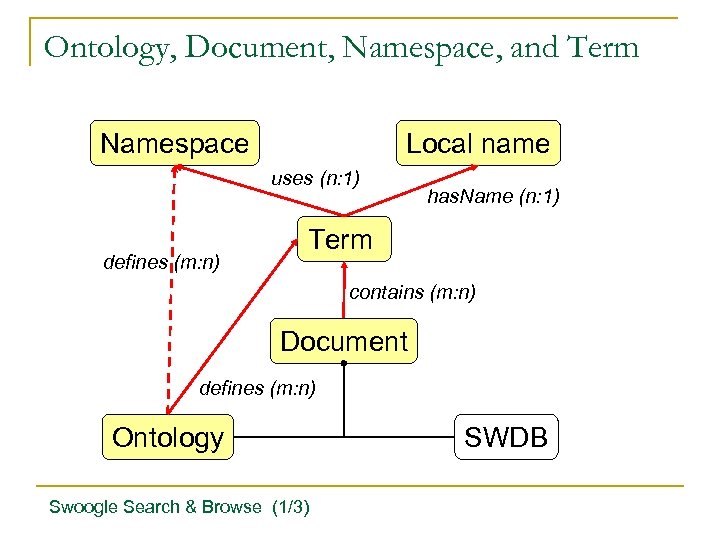
Ontology, Document, Namespace, and Term Namespace Local name uses (n: 1) defines (m: n) has. Name (n: 1) Term contains (m: n) Document defines (m: n) Ontology Swoogle Search & Browse (1/3) SWDB

n same. Local. Name
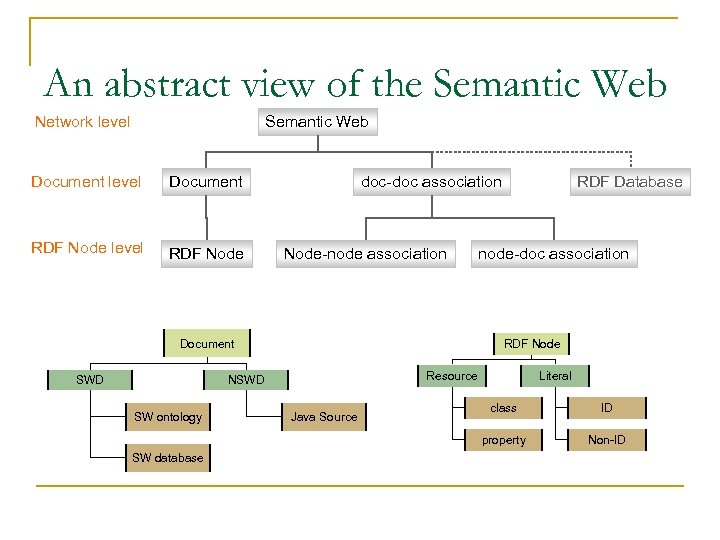
An abstract view of the Semantic Web Network level Semantic Web Document level Document RDF Node level RDF Node doc-doc association Node-node association Document SWD RDF Database node-doc association RDF Node Resource NSWD Literal SW database Java Source class ID property SW ontology Non-ID
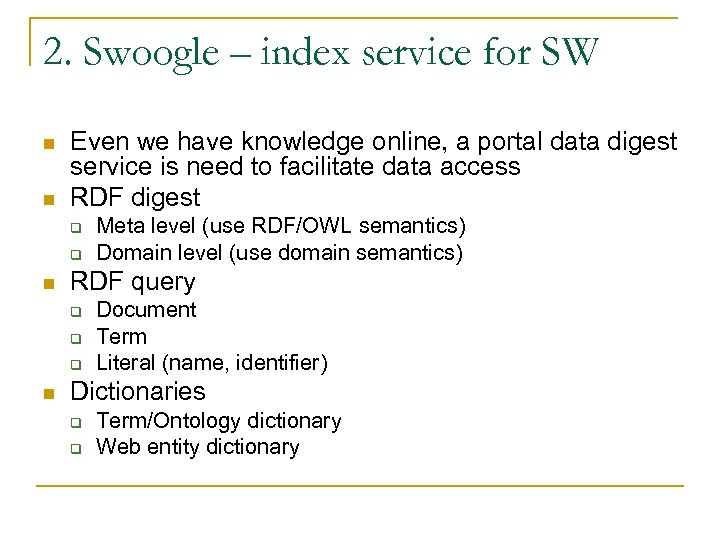
2. Swoogle – index service for SW n n Even we have knowledge online, a portal data digest service is need to facilitate data access RDF digest q q n RDF query q q q n Meta level (use RDF/OWL semantics) Domain level (use domain semantics) Document Term Literal (name, identifier) Dictionaries q q Term/Ontology dictionary Web entity dictionary
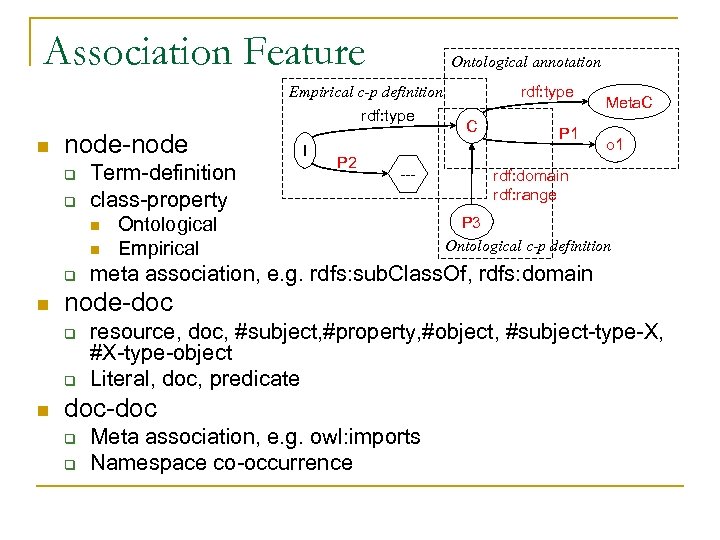
Association Feature Ontological annotation rdf: type Empirical c-p definition rdf: type n node-node q q Term-definition class-property n n q n P 2 --- Ontological Empirical P 1 o 1 rdf: domain rdf: range P 3 Ontological c-p definition meta association, e. g. rdfs: sub. Class. Of, rdfs: domain node-doc q q n I C Meta. C resource, doc, #subject, #property, #object, #subject-type-X, #X-type-object Literal, doc, predicate doc-doc q q Meta association, e. g. owl: imports Namespace co-occurrence
Story 1: Big RDF file & P 2 P n Facts q q q We found Word. Net has published its ontology in a 60 M daml file, where JENA fails to load it in memory. Most people use ontology as data exporting annotation, (Stefen Decker argues in WWW 2004 Dev day), Querying RDF should be tractable (Ian Harrock, Andy Seanbome). i. e. we need to balance the tractability and the expressiveness of a query. n q n the query result for a graph pattern (with variables) can be of three types: a subgraph, the variable binding, a max subgraph Provenance information mainly range in Agent (person, organization, website). i. e. agent’s belief Question q q q Is it appropriate to say a RDF model is a RDF file? If not, how do we describe a distributed RDF model? Will there be any very big RDF file? Why? Can we let RDF stored in small files and distributed throughout the world.

3. Sem. Dis: How to judge information trustworthiness? n Granularity q q n Association q q q n rdf: Statement SWD Information source (agent, website) Topic Social network (FOAF) Belief, Authorship (foaf: maker) Justification Trust computation q q Ranking Network Consensus

Practice of Trust n Fields q Weblog n n q n n DBLP FOAF Google n Applications q Manipulate precision n n q n FOAF RSS Online Social network n n n Disambiguation: specialize knowledge Privacy protection: generalize knowledge n Manipulate completeness – fuse knowledge Algorithms q q Trust propagation algorithm: surfer model, flow model, Belief merging algorithm n Given A new statement q Reasoning: What is its trustworthiness given opinions on it from some information sources? (subjective logic, fuzzy cognitive map) q Justification: How to find evidences to support/weaken it? (web of belief ontology for annotation) Given A question q Search: effective/efficient in open environment (rdf digest, bounded search with trust heuristic) Given Online multi-network q Social relations among information sources (FOAF) q Ontological relations among topics (subtopic) q Web entity identification and mapping Emergence model q How these can really affect the semantic web research?

Story 2: Identity n n Facts q We found a lot social network online, e. g. coauthor(dblp), knows(foaf), colleague. Different networks adopt different identities q Each of them might not well connected, or quite small, but what-if we connected them q One identity shared by multiple persons, by mistake or by nature q Identity mapping is m: n Questions q Can we determine certainty of identity q How to map identity

Story 3: Knowledge Fusion n Fact q q n We can fuse person info. From multiple FOAF file. Some statements are confirmed by a lot of people We can build a model which has multiple provenance Questions q q How to use provenance information to assure the receiver. What if Dr. Joshi want to determine his trust to the ontology created by Dr. Amit Sheth

Story 4: Justification Markup Language n Facts about distributed justification on the web (semantic web) q q The justification on the web may not always be formalized. Knowledge on the web could be objective (like database) or subjective (like joke, estimation). Knowledge on the semantic web is inherently inconsistent Determining what counts as adequate reasons is an obstacle to providing justification. This process of reason giving can be viewed as argumentation in four major forms: inductive, deductive, conclusive, and prima facie. n n Question: q q n How to represent the mixture of human inference, statistical information and logical inference Distributed justification: trust-based, case-based, logical-inference Example: I will buy a new Honda Accord because q q n Inductive and deductive justification involve evidence and logical evaluation. In a conclusive argument, reasons are analyzed by asking if another rational human would have the same belief given the same reasons. prima facie argumentation is a process of giving several reasons for believing something and choosing the most important one. (1) [inductive] it is a good car because 90% related online comments are positive ; (2) [deductive] it has better mile/gas performance; (3) [conclusive/mimic] I will buy a car since my friend (who has similar taste as me ) like to buy it. (4) [prima facie] Among all factors that make me happy, buying a new car is the most important Solution q q Formal language to express logical programming proof trace, e. g. PML We also need informative language to express human justification n Express relation between statements: support, casual, critique, Log decision process as a case for future sharing/recall/query. Cite a case/used reason as proof of new justification
84bdfae0ab4d63ba78f7db4d22025082.ppt