02175f9bf73ebd3ad02fe35cee140591.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Web Developer Foundations: Using XHTML Chapter 13 E-Commerce Key Concepts 1

Learning Outcomes n In this chapter, you will learn how to: n n n n n Describe E-Commerce Identify benefits and risks of E-Commerce Describe E-Commerce business models Describe E-Commerce Security and Encryption Describe EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) Describe trends and projections for E-Commerce Describe issues related to E-Commerce Describe order and payment processing Describe E-Commerce solution options 2

What is E-Commerce? n The integration of communications, data management, and security technologies to allow individuals and organizations to exchange information related to the sale of goods and services. 3

What is E-Commerce? Major functions of E-Commerce include: the buying of goods, n the selling of goods, and n performance of financial transactions on the Internet. n 4

E-Commerce Advantages for Businesses n Reduced Costs n Increased Customer Satisfaction n More Effective Data Management n Potentially Higher Sales 5

E-Commerce Advantages for Consumers n Convenience n Easier Comparison Shopping n Access to a wider Selection of Goods 6

E-Commerce Risks for Businesses n Need for a robust, reliable web site n Fraudulent transactions n Customer reluctance to purchase online n Increased competition 7

E-Commerce Risks for Consumers n Possible Security Issues n Possible Privacy Issues n Purchasing from photos & descriptions n n Is what you see really what you get? Possible difficulty with returns 8
E-Commerce Business Models n B 2 C – Business-to-Consumer n B 2 B – Business-to-Business n C 2 C – Consumer-to-Consumer n B 2 G – Business-to-Government 9
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) n EDI is the transfer of data between different companies using networks. n This facilitates the exchange of standard business documents including purchase orders and invoices. n EDI is not new; it has been in existence since the 1960 s. 10

Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) n Organizations that exchange EDI transmissions are called trading partners. n Newer technologies such as XML and Web Services are replacing traditional EDI by allowing trading partners virtually unlimited opportunities to customize their information exchange over the Internet. 11
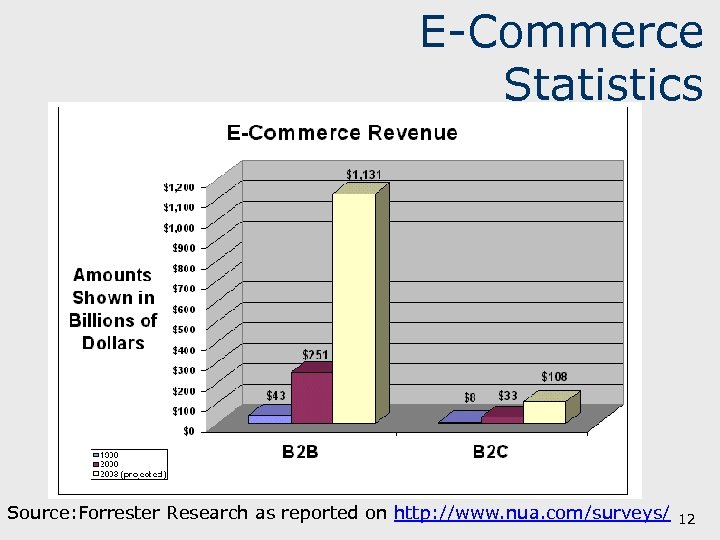
E-Commerce Statistics Source: Forrester Research as reported on http: //www. nua. com/surveys/ 12
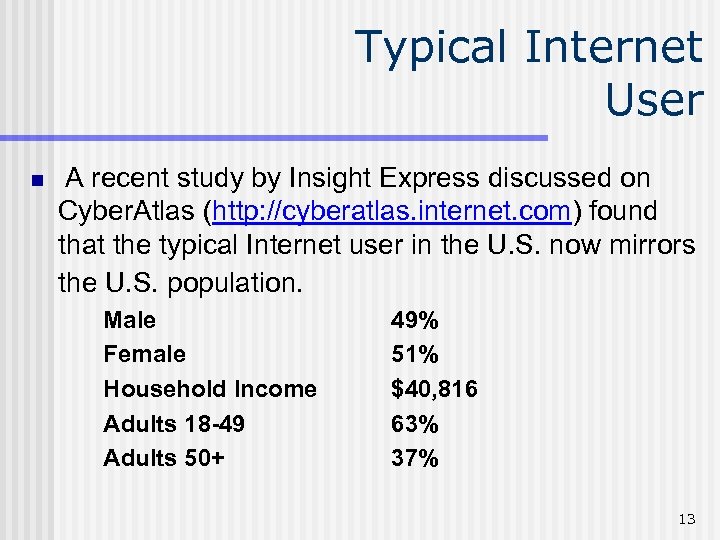
Typical Internet User n A recent study by Insight Express discussed on Cyber. Atlas (http: //cyberatlas. internet. com) found that the typical Internet user in the U. S. now mirrors the U. S. population. Male Female Household Income Adults 18 -49 Adults 50+ 49% 51% $40, 816 63% 37% 13

E-Commerce Issues n Intellectual Property n Security n Fraud n Taxation n International Commerce 14

E-Commerce Security n Encryption n Used to ensure privacy within an organization and on the Internet. n The conversion of data into an unreadable form, called a ciphertext. This ciphertext cannot be easily understood by unauthorized individuals. 15

E-Commerce Security n Decryption n n The process of converting the ciphertext back into its original form, called plaintext or cleartext, so it can be understood. The encryption/decryption process requires an algorithm and a key. 16

E-Commerce Security Encryption Types Secure E-Commerce transactions make use of the encryption technologies below: n Symmetric-key Encryption n Asymmetric-key Encryption n Hash Encryption These technologies are used as part of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) – the technology that helps to make commerce on the Internet secure. 17
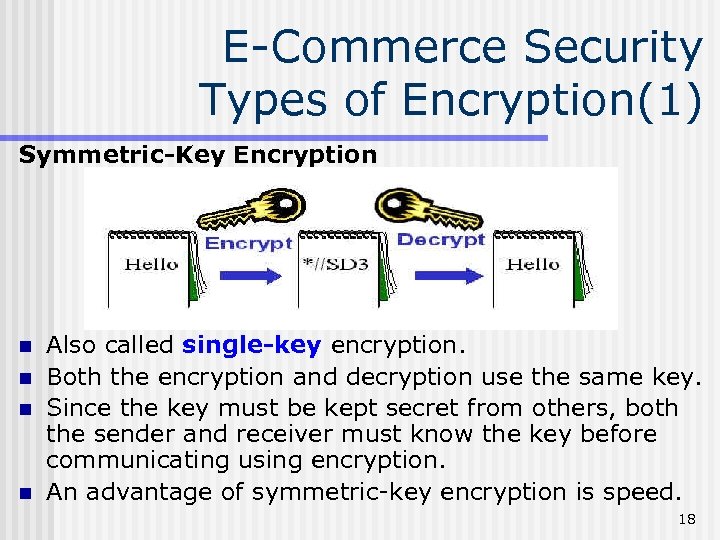
E-Commerce Security Types of Encryption(1) Symmetric-Key Encryption n n Also called single-key encryption. Both the encryption and decryption use the same key. Since the key must be kept secret from others, both the sender and receiver must know the key before communicating using encryption. An advantage of symmetric-key encryption is speed. 18
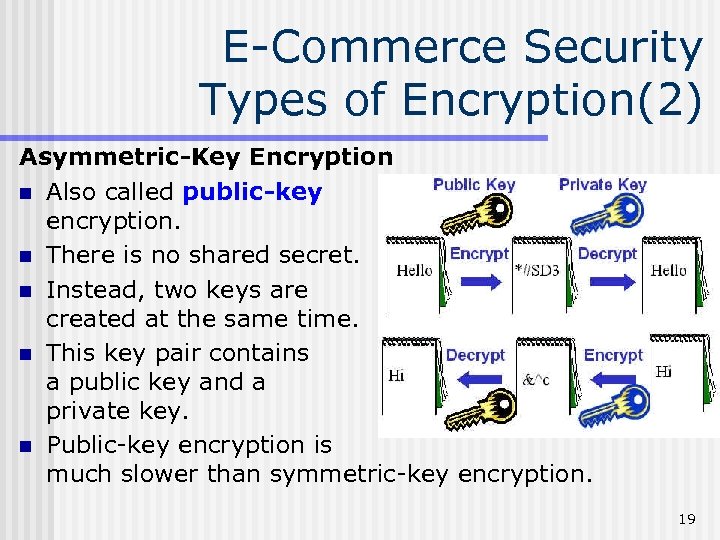
E-Commerce Security Types of Encryption(2) Asymmetric-Key Encryption n Also called public-key encryption. n There is no shared secret. n Instead, two keys are created at the same time. n This key pair contains a public key and a private key. n Public-key encryption is much slower than symmetric-key encryption. 19

E-Commerce Security Types of Encryption(3) Hash Encryption n A hash algorithm transforms a string of characters into a usually shorter fixed-length value or key that represents the original string, called a digest. n Hash encryption is one-way encryption. n Hash encryption is used for information that will not be read or decrypted. n The function of hash encryption is to verify the integrity of information. 20

Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) n SSL is a protocol that allows data to be privately exchanged over public networks. n SSL was developed by Netscape and is used to encrypt data sent between a client (usually a web browser) and a web server. n SSL utilizes both symmetric and asymmetric keys. 21
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) n SSL provides secure communication between a client and server by using: Ø Ø Server and (optionally) client digital certificates for authentication Symmetric-key cryptography using a "session key" for bulk encryption Public-key cryptography for transfer of the session key Message Digests (hash encryption) to verify the integrity of the transmission n SSL uses the “https” protocol instead of the “http” protocol n Most browsers display a “lock” icon when SSL is being used. 22
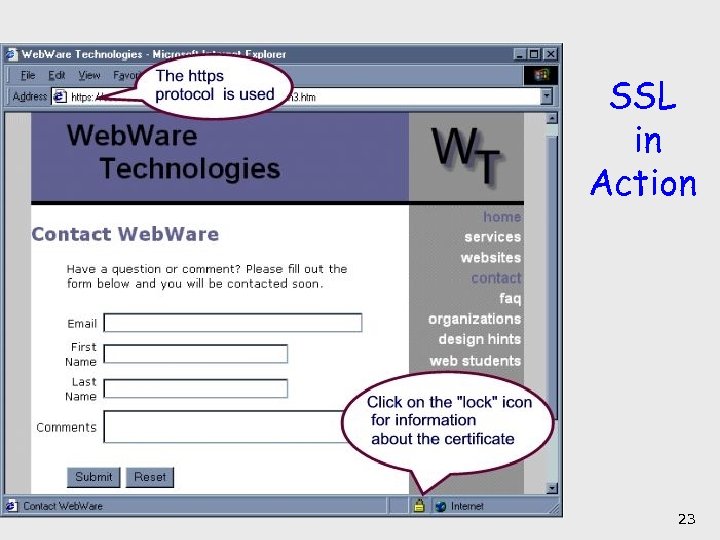
SSL in Action 23

SSL & Digital Certificate SSL enables two computers to securely communicate by using a digital certificate for authentication. n A digital certificate is a form of an asymmetric key that also contains information about the certificate, the holder of the certificate, and the issuer of the certificate. n 24
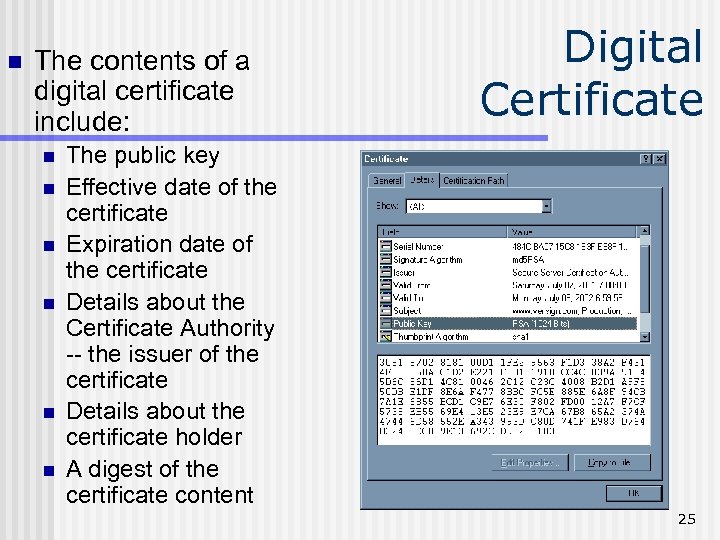
n The contents of a digital certificate include: n n n Digital Certificate The public key Effective date of the certificate Expiration date of the certificate Details about the Certificate Authority -- the issuer of the certificate Details about the certificate holder A digest of the certificate content 25

Certificate Authority A Certificate Authority is a trusted third-party organization or company that issues digital certificates. n Well-known Certificate Authorities: n n Verisign • http: //www. verisign. com n Thawte • http: //www. thawte. com 26

Obtaining a Digital Certificate n n Request a certificate from a Certificate Authority and pay the application fee. The Certificate Authority: n n n verifies your identity, issues your Certificate, and supplies you with a public/private key pair. Store the certificate in your software - such as a web server, web browser, or e-mail application. The Certificate Authority makes your certificate publicly known. 27

SSL & Digital Certificates n When you visit an e-commerce site that uses SSL, a number of steps are involved in the authentication process. n n n The web browser and web server go through initial handshaking steps using the server certificate and keys. Once trust is established, the web browser encrypts the single secret key (symmetric key) that will be used for the rest of the communication. From this point on, all data is encrypted using the secret key. 28
Order & Payment Processing n E-Commerce Payment Models: n Cash n Check n Credit n Smart Card 29
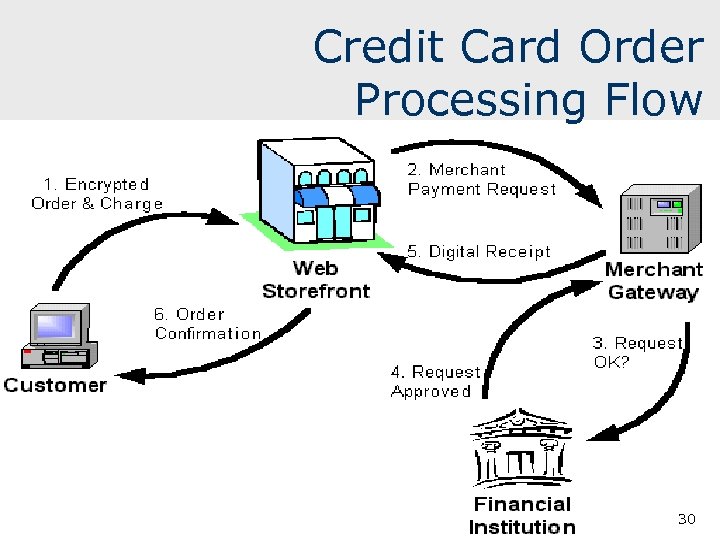
Credit Card Order Processing Flow 30

E-Commerce Storefront Solutions n Instant Online Storefront n n Yahoo!, Bigstep, Free. Merchant Off-The-Shelf Shopping Cart Software n Miva Merchant, Mercantec 31

E-Commerce Storefront Solutions n Custom Built Solution • • • n IBM's Web. Sphere Commerce Suite, Microsoft's Commerce Server Visual Studio. NET, Macromedia Dreamweaver MX, IBM’s Web. Sphere Commerce Studio Semi-Custom Built Solutions on a Budget • E-Commerce add-ons for Front. Page and Dreamweaver • Paypal order processing • Free shopping cart scripts 32

Summary n This chapter introduced you to basic ECommerce concepts and implementations. n Consider taking an E-Commerce course to continue your study of this dynamic and growing area of web development. 33
02175f9bf73ebd3ad02fe35cee140591.ppt