e9ab8b15116898ffc3bda9575c4a511d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78

Web Application • Web Application are programs that can be executed either on a Web server or in a Web browser. • An Online store accessed through a browser is an example of a web application.

Static and Dynamic Page • The content of a web application that consists of only HTML pages is static. It does not respond dynamically to the actions performed buy users. • To respond dynamically to user request we create Dynamic pages.
Types of Scripting • Client Side Scripting • Server Side Scripting

Client Side Scripting • Enables you to develop Web pages that can dynamically respond to user input without having to interact with a Web server.

Advantages of Client Side Scripting • Reduce network traffic • Speed up the response time

CSS Language • VB Script • Java Script

Server Side Scripting • Provides dynamic content to users based on the information stored in a remote location. • It executed on a Web Server.

SSS Language • Active Server Pages (ASP) • Java Server Pages (JSP)

ASP. Net • . Net version of ASP introduced by Microsoft. • To help developers create globally distributed software with Internet functionality. • Enable you to access information from data source. • Enables you to separate HTML design from the data retrieval mechanism.

Elements in ASP. Net • • • Web Forms Configuration Files XML Web Service Files State Management Runtime Services

Web Forms • Web forms enable you to include user interface such as Text. Box, List. Box and application logic of web applications.

Configuration File • Enable you to store the configuration settings of an ASP. Net application.

Development Environment • . Net Framework • ISS (Internet Information Services)

IIS • IIS server enables you to access the ASP. Net web application. It's work as a Web server on the network. Web server for windows platform)

Working of an ASP. Net application • Web browser send a request by URL • IIS receive and retrieves the appropriate file from the memory. • Forward it to ASP. Net script engine. • Script Engine to ISS • ISS to client

Features of ASP. Net • • Compiled Code Enriched Tool Support(WYSIWYG) Power and Flexibility Simplicity Manageability (xml) Scalability (further enhancement) Security

Programming Models in ASP. Net • Web Forms • Web Services

Check your self • What is a Web Application? • What’s the difference between Static and Dynamic pages? • What is Scripting? • How many types of Scripting Languages? • Describe about Client Side Scripting? • Describe about server Side Scripting? • What’s are the advantage of client side scripting?

• Write down some Client Side Scripting Languages? • Write down some Server Side Scripting Languages? • What’s are the advantages of ASP. Net? • What is ISS?

Web Services • Enable you to access certain functionality at the server side. • These services enable the exchange of data in a client to server or a server to server environment over the web.

Controls in ASP. Net • System. Object – System. Web. UI • System. Web. UI. Control – System. Web. UI. Web. Controls – System. Web. UI. HTMLControls

Types of Controls • • ASP. Net HTML controls ASP. Net Web controls Validation controls User controls

HTML controls • Replicas of the standard HTML tag • HTML tag are converted into HTML controls by using attributes such as ID etc. • <Input Type = Text Runat =“server” ID = “textbox 1” value = “welcome”>

Web Controls • Basic Web controls – textbox, label, button, hyperlink, radiobutton etc. • List controls – Listbox, dropdownlist, checkboxlist etc. • Rich Web controls – Calendar etc. • Data controls – Datagrid, datalist, repeater

Validation controls • Used to validate the user input. • Attached to input controls to check the values that a user enters for input controls.
Types of Validation Controls • • • Compare Validator Custum Validator Range Validator Regular Validator Required. Field Validator Validation Summary

User Controls • User Controls are ASP. Net pages that are converted into controls. • Extension is. ascx

File used in an ASP. Net Application • Assembly. Info. cs : • This file contains a set of attributes that contain general information about the assembly such as the name, description and version of the assembly.

• Global. asax: • Each web application will have one Global. asax file attached to it. It contains scripts that define the start and events of the application.

• Web. config: • This is the configuration file for your application. It is an XML file that contains configuration data.

Code Behind Feature of ASP. Net • The code behind future of ASP. Net enables you to divide an ASP. Net page in to two files. One file contains the presentation content and other file which is called the code behind file, contains all application logic. • Presentation file -. aspx • Code behind file -. cs

Automatically Generated Code • <%@ Page language =“C#” Codebehind=“Web. Form 1. aspx. cs” Auto. Event. Wireup=“false” Inherits=“Web. Application 1. Web. Form 1” • Language : Any. NET Framework supported language

Auto. Event. Wireup • Whether the page Framework calls page events and methods automatically for an ASP. Net page • Default value is set to false. • False value indicate that you must explicitly write code to bind page events.

Codebehind and Inherits • The code behind file for a page. • The class in the code behind file that a page inherits. This class can be any class derived from the Page class.

Code Inline • The practice of writing application logic in the presentation file is known as code inline.

Page Events • • Init Load Control Unload

Init and Load event • You can write the page initialization code in the Init or Load event of the Web Page. • Page_Init is the event handler for the Init event and Page_Load is the event handler for the Load event of the page.

Difference between Init and Load • There is a difference between the Init and Load event. When the Init event is fired all controls are loaded with their default values. On the other hand when the Load event is fired the controls are loaded in the memory with values that are set during the round trip.

Round Trip • A round trip is a sequence of events that a web page follows to complete the journey from a web browser to a web server.

Control Event • After the Init and Load event the page is served to user. When the user interact with the page to generate a control event such as click on a button the page is posted back to the server and the code in the control’s event handler is executed. • After processing the page is re crated and the page follow the same Init and Load events.

Is. Post. Back • Property of the Web Page • You can avoid the firing of Init and Load event by using the Is. Post. Back property of a web page. • It’s allow you to check whether the page is being requested for the first time.

Unload event • Finally when a user close the page or exits from the browser the page is unloaded from the memory and the Unload event is fired.

Code Declaration Blocks • We can add application logic or code in two different ways. One is in code behind file and another is in html code. • Mostly we prefer Code behind future. • If we write code in html then it’s known as • Code Declaration Blocks. <script language=“lan. name” runat=“server”> ----------------------</script>

ASP. Net Built in Objects • ASP. Net has a number of built in objects that run on a Web server. Built in Objects in ASP. Net are – • • • Application Request Response Server Session

Application Object • The Application object is used to store and retrieve information that can be shared among all the users of an application. • Provides access to application-wide methods and events for all sessions. • Application state is a data repository available to all classes in an ASP. NET application. • Application state is stored in memory on the server and is faster than storing and retrieving information in a database. • Application state applies to all users and all sessions. Therefore, application state is a useful place to store small amounts of often-used data that does not change from one user to another.
Request objects • Request: The request object is used to access the information sent in a request from a browser to the server.

Response object • Response : The response object is used to send information to the browser.

Server object • Server : The server object is used to access various utility functions on the server.

Session object • The session object is used to store and retrieve information about particular user sessions. • It is use to persist information throughout the user session. • ASP. Net session state enables you to store and retrieve values for a user as the user navigates the different ASP. Net pages that make up a Web application. • ASP. Net session state is enabled by default for all ASP. Net applications. • ASP. Net session-state variables are easily set and retrieved using the Session property, which stores session variable.

Required. Field Validator • You can specify that a user must provide information in a specific control on an ASP. NET Web page by adding a Required. Field. Validator control to the page and linking it to the required control. • For example, you can specify that users must fill in a Name text box before they can submit a registration form.

Properties for Required. Field Validator • Control. To. Validate – Used to specify the ID of the control that is to be validated. • Error. Messege – Message that we want to show at the time of error • Text – For showing the text when error occur.
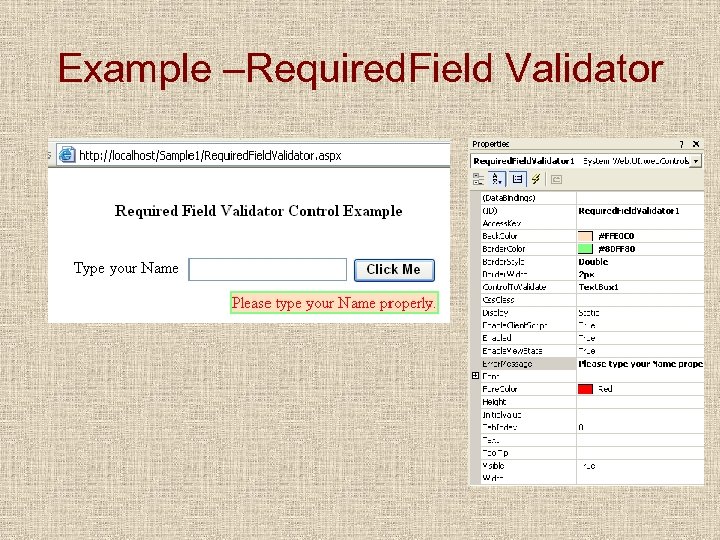
Example –Required. Field Validator

Regular. Expression. Validator • The Regular. Expression. Validator control performs its validation by comparing the data value to the regular expression pattern. • If the data value in the control does not match the regular expression the Regular. Expression. Validator control displays error.
Properties for Regular. Expression Validator • Control. To. Validate • Error. Messege • Validation. Expression – Validation condition for validate the control. By default different types of validation statements are present in it.
![Validation Expression • [] – a set of characters • Used to match any Validation Expression • [] – a set of characters • Used to match any](https://present5.com/presentation/e9ab8b15116898ffc3bda9575c4a511d/image-55.jpg)
Validation Expression • [] – a set of characters • Used to match any one of the characters with in []. we can specify a range of characters by listing the starting and ending characters separated by a dash like [a-z]. • Exa – “A[5 -9]” The above expression can be used to validate a product id that start with the letter A followed by a digit with in range of 5 to 9.

Validation Expression • {n} –Tagged expression • Used to match an expression exactly n times. Exa – “A[0 -5]{6}” The above expression can be used to validate a product id that starts with the letter A followed by six digits ranging from 0 to 5.

Validation Expression • w – Word characters • Used to match any letter, numeric and underscore character. • “w{8, 20}” • The above expression can be used to validate a password with the minimum length of 8 characters and a maximum length of 20 characters.

Validation Expression • • . – any character Used to match any one character “ 17. 09. 1983” The above expression can be used to check for date formats such as 17/09/1983, 17 -09 -1983 etc.

Validation Expression • /s – any nonwhite space character • used to match any character except spaces, tabs and line breaks. • http: //sss • The above expression can be used to check whether a valid web address has been entered such as http: //noon. com, http: //your. com etc.

Validation Expression • + - one or more character • Used to match at least one occurrence of the preceding expression • “s+@s+. s+” • The above expression can be used to validate an email id such as aaa@yahoo. com, sani@gmail. com

Validation Expression • ? - any single character • Used to match any single preceding character in an expression • “students? ” • The above expression can be used to specify that the letter s is optional. Therefore you can use the above expression to check whether a user has entered any word other than student or students.

Validation Expression • • d – any digit character Used to match any digit in the range 0 to 9. “d{6}” The above expression can be used to check for a pin code that has exactly 6 digits.

Compare Validator • use the Compare. Validator control to compare the data value entered by the user to a value in another control.

Properties for Compare Validator • Control. To. Compare – Used to specify the ID of the control that will used to compare values. • Control. To. Validate – Used to specify the ID of the control is to be validator. • Error. Messege • Value. To. Compare

Range Validator • This control is used to check whether the value of a particular control with in the minimum number and the maximum number. The minimum and maximum number values can be dates, number etc.

Properties of Range Validator • • Control to validate Error massage Maximum value Minimum value

Validation Summary • This control is used to summarize all errors and display the error list in a user specified location.

Properties of Validation Summary • Head. Text – used to set the text that will be displayed at the top of the summary. • Show. Messege. Box – Used to display the error message in a pop up message box when the value of this property is True. • Show. Summary – Used to enable or disable the summary of error messages.

Data Binding • Data Binding helps you develop such applications where controls can be bound to the values stored in a data source.

Syntax for data binding • <%# expression %> • Consider the following line of code added in the HTML view of a web form – • <asp: Text. Box id = “Name” Text = “<%# source %>” runat = “server”></asp: Text. Box>

Data Binding Expression • The portion of the code delimited with the characters <%# and %> is called Data Binding Expression. • We can only include data binding syntax expression with in it.
Data. Bind() Method • Any server control will not display data source values until we use the Data. Bind() method. • The Data. Bind() method evaluates the data binding expression and displays the evaluated expression in the server control. • We can write the following line of code in the Load event of the Web Form to evaluate all the binding expressions in the page: • Page. Data. Bind(); or Data. Bind(); • If we have just a single control for binding then we can use the Data. Bind() with that perticuler control.
Type of Data Binding • Single Value Data Binding • Multi Record Binding
Single Value Data Binding • Single value data binding involves binding controls which can display a single data value at a time. • Exa. – label control, textbox control

Multi Record Data Binding



e9ab8b15116898ffc3bda9575c4a511d.ppt