37f59200d13df799fc6c5515f4e8cacf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Web 2. 0: Technologies and Education

What is Web 2. 0? • What is Web 2. 0 ? !?

Web 2. 0 • Web 2. 0, a phrase coined by Dale Dougherty in 2003 • made famous in a paper called What is Web 2. 0: Design Patterns and Business Models for the Next Generation of Software by Tim O’Reilly • it is not a set technological standard or protocol • it is a term to describe the movement/revolution about the social connection and interaction of the web and services and technologies that sponsor and promote it. – the “second phase” of the internet – 2006 Time Person of the Year: You

Web 2. 0 • the meaning varies – Dave Winer [a software developer and entrepreneur] says: “Web 2. 0 is a marketing concept used by venture capitalists and conference promoters to try to call another bubble into existence. ” – Om Malik [a technology writer] says: “Web 2. 0 as a collection of technologies - be it Vo. IP, Digital Media, XML, RSS, Google Maps… whatever … that leverage the power of always on, high speed connections and treat broadband as a platform, and not just a pipe to connect. ” • kind of a buzz word

What was Web 1. 0? • • Web 1. 0 was about reading, Web 2. 0 is about writing Web 1. 0 was about companies, Web 2. 0 is about communities Web 1. 0 was about client-server, Web 2. 0 is about peer to peer Web 1. 0 was about HTML, Web 2. 0 is about XML Web 1. 0 was about home pages, Web 2. 0 is about blogs Web 1. 0 was about lectures, Web 2. 0 is about conversation Web 1. 0 was about advertising, Web 2. 0 is about word of mouth Web 1. 0 was about services sold over the web, Web 2. 0 is about web services • From Darren Barefoot, a technology writer • modern vs. post-modern ways of thinking

Examples of Web 2. 0 • • Blogs Wikis Tagging Multimedia Sharing RSS Podcasting Second Life

BLOGS • blog or weblog • simple webpage consisting of brief postings of opinion, information, etc. • blogosphere – a collective term encompassing all blogs and their interconnections • chronologically ordered • exchange of ideas from single author to unlimited readers • real time not journal time (ie. daily or weekly) • has links and comment fields

BLOGS • Examples of Blogs: – http: //www. insidethecbc. com/ – http: //www. engadget. com/ • Examples of Blog Sevices: – Blogger/Blogspot • https: //www. blogger. com/start • http: //canuckshockey. blogspot. com/ – Blogs. Canada • http: //www. blogscanada. ca/

WIKIS • a webpage or set of webpages that can be easily edited by anyone with access • collaborative tool – now available as an option in major software packages • has a history function to view previous versions • ease of use vs. malicious editing and vandalism – though things can be quickly corrected

WIKIS • Wikipedia – the most well-known wiki – accuracy is comparable to a regular encyclopedia • disputed though – http: //www. wikipedia. org/ • SFU related wikis: – SFU Cognitive Science • http: //www. zanyt. com/cogs_wiki/index. php? title=Welcome – LIDC • http: //wiki. lidc. sfu. ca/Home. Page

TAGGING • a tag is a keyword attached to a digital object • very often used in searches – eg. Flickr and You. Tube

TAGGING • searching Flickr for “fat” and “cat” tags will give results showing a overweight cats or other things called “fat cat”, such as the “Fat Cat” pub…

MULTIMEDIA SHARING • areas and services that facilitate the sharing and storage of digital media • eg. Flickr, You. Tube, etc. • distribution on a massive scale • productions are high quality, but on low cost digital media technology

RSS • RSS = Really Simple Syndication • allows a user to subscribe to a “feed” and gain content thru a subscription • RSS icon • up-to-date information from websites, blogs, etc. without having to go to the original source – common in news websites or other websites that are continually updated with information
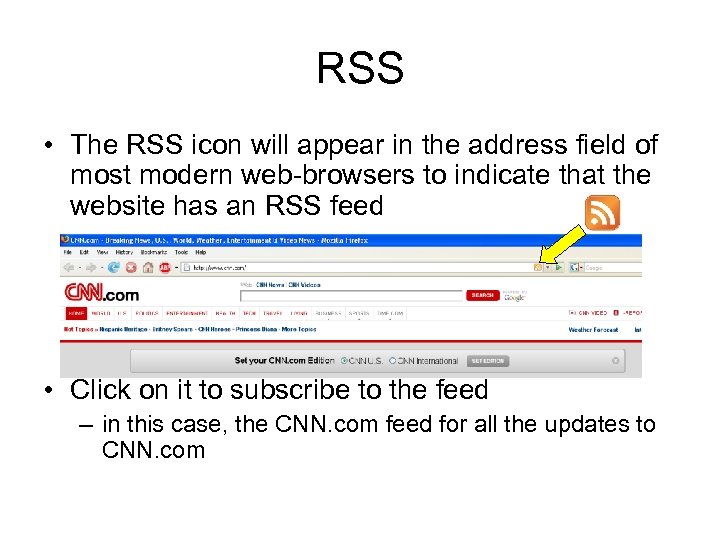
RSS • The RSS icon will appear in the address field of most modern web-browsers to indicate that the website has an RSS feed • Click on it to subscribe to the feed – in this case, the CNN. com feed for all the updates to CNN. com

PODCASTING • a podcast is an audio file uploaded to a host server and subscribed to via RSS – easy to get new, updated content • will run on more than just i. Tunes – eg. Odeo. com, My. Podcast. com, etc. • lots of potential for educational purposes • more on this later…

Second Life • a popular, virtual 3 D world where a user can construct an avatar and other 3 D environments and explore them • looks like a game, but not really a game… – venue for socializing and interacting • various agencies and entities have a presence in Second Life – including SFU and the VPD
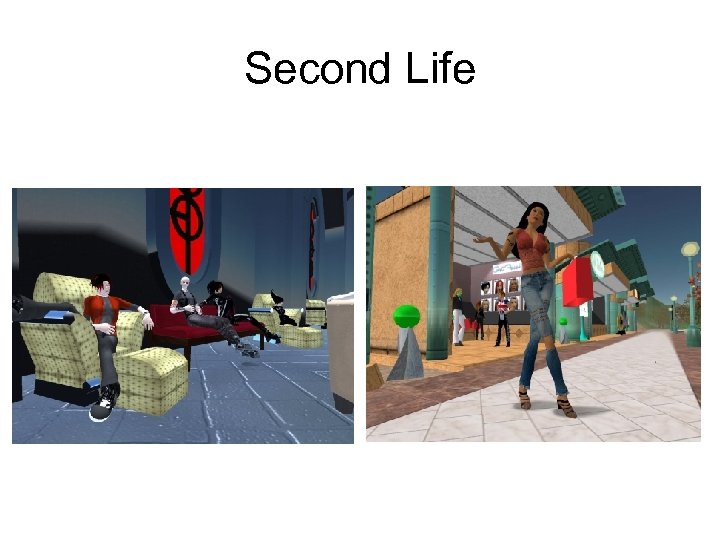

Second Life

THE SIX BIG IDEAS BEHIND WEB 2. 0 • from What is Web 2. 0? Ideas, technologies and implications for education by Paul Anderson • Individual production and User Generated Content • Harness the power of the crowd • Data on an epic scale • Architecture of Participation • Network Effects • Openness

1. Individual production and User Generated Content • content added very easily to media sites – eg. My. Space, You. Tube, etc. • content can be searched with tags • people writing blogs and contributing to wikis • user generated content – also called content self-publishing, personal publishing, self-expression. • new, cheap, accessible and quality tools lower entry bar – eg. digital cameras, mobile phones with devices, video cameras, etc. • similar to computers, printers and paper desktop publishing in early 80 s – “everybody can do it, but not anybody can do it” – talent still distinguishes

1. Individual production and User Generated Content • Cute: – Laughing Baby : • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=c. XXm 696 Ub. KY • Amusing: – Dramatic chipmunk • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=a 1 Y 73 s. PHKxw • Just Odd: – Angry German kid • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Pbcct. Wb. C 8 Q 0 • Recent: – The Tasered Student at a John Kerry Speech • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Hgr. FSHZf. D 1 o

1. Individual production and User Generated Content • existing/traditional media sources are threatened and are adapting – shows now have podcasts or can be downloaded from i. Tunes store – Radio. Head, NIN, etc. now giving away music • redefinition/reinterpretation of audience – more authors than readers • blogs that are never read… – contributors are driven by attention rather than financial motives • threats to structure and authority – traditional media sources are structured, edited and sources verified – not like the internet…

1. Individual production and User Generated Content • Remix: "Can't Tase This“ • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Xzkd_m 4 ivmc& mode=related&search=

2. Harness the power of the crowd • collective intelligence – information = intelligence (? ) • as group can be collectively more intelligent than a single individual – eg. ask the audience on who wants to be a millionaire • hazards: – “groupthink”, lack of a deep level critical thinking, etc. • “crowd sourcing” “was coined by Wired journalist Jeff Howe to conceptualize a process of Web-based out-sourcing for the procurement of media content, small tasks, even solutions to scientific problems from the crowd gathered on the Internet. ” – – eg. websites with stock materials, like shutterstock. com, istockphoto, etc. threat to existing photographic professionals content not good, but good enough eg. websites like Innocentive match scientists with R&D clients

2. Harness the power of the crowd • Folksonomy: – “Folksonomy is the result of personal free tagging of information and objects (anything with a URL) for one's own retrieval. The tagging is done in a social environment (shared and open to others). The act of tagging is done by the person consuming the information. ” Vander. Wal, 2005, blog entry. – tags are meant to connect, not categorize • tags are created in a social context with people using their own vocabulary and meanings (relative to a community) • tags are not created in formal taxonomy nor have standard meanings – remember the search for “fat” and “cat”…?

2. Harness the power of the crowd • example: – consider a search on You. Tube. com for “evan” • this can mean: – A trailer for the movie “Evan Almighty” – The “Evan” from the movie “Super. Bad” – And many more “evan”s… • each person adding a video to You. Tube. com puts an “evan” tag with it…(among other tags) • You. Tube. com does not control or categorize the content to have a standard meaning for “evan”
3. Data on an epic scale • information, data, etc. generated is staggering in its quantity with multiple sources and contributors – ‘datafication’ of the world • services exist to collect and manage this data – eg. Google • the use of these services makes these services smarter – data mining techniques – eg. the monitoring of collective buying habits to make suggestions to individual users • eg. Netflix, Amazon, etc. • data becomes a resource – privacy issues and implications – who owns this data?

4. Architecture of Participation • how a website is designed affects the participation – eg. pay vs. free – eg. classmates. com vs. facebook. com – -eg. amount of steps to register with website • a website can get better the more a person uses it – it adapts to the person • eg. recommendations from a website, or a website connecting likeminded people • open-source software – ie. the sharing of ideas and content for reuse and new combinations

5. Network Effects • “The Network Effect is a general economic term used to describe the increase in value to the existing users of a service in which there is some form of interaction with others, as more and more people start to use it” – eg. Face. Book • not all users have the same value – some are more valuable to user than other – eg. family, friends, acquaintances, co-workers, strangers, etc. • the flipside: the lock-in to technology – as more people use a certain product or service, it becomes difficult to switch to another product or service (that may be better) because there a few people to share with • eg. VHS vs. Beta • eg. Blu-ray vs HD-DVD • it shows the needs for interoperability

5. Network Effects • many things on the internet are unequal • there artificial barriers that make it easier for some and extremely difficult for others – ie. popularity, promotion, position on search engine, placement on webpage, etc. • there is a counter-movement to with the “democratization of the tools of production” as amateurs are able to flood the internet with content

6. Openness • “The development of the Web has seen a wide range of legal, regulatory, political and cultural developments surrounding the control, access and rights of digital content. ” – you don’t have to pay for stuff now! • eg. music, movies, software… • web 2. 0 stresses openness – open standards, open-source software, free data • eg. the push for Open Document Format (or ODF) – all to be used and reused freely for the common goal of open innovation • eg. Fire. Fox and its plug-ins

6. Openness • Example of copyright violation: – Robo. Cop vs. Neo • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=woq. JU 3 o. Q 4 Bg

EDUCATIONAL AND INSTRUCTIONAL ISSUES: • “In these scenarios, education is more like a conversation and learning content is something you perform some kind of operation on rather than ‘just’ reading it. “ • Problems: – – – users are in a 24/7 environment economic divide among user’s home resources differing skill levels privacy and plagiarism issues of online collaborations shared authorship and assessments • the lack of understanding about student learning modes and social aspect of the software

EDUCATIONAL AND INSTRUCTIONAL ISSUES: • eg. SFU Summer Camps used Facebook – permission form: • gave permission to create a Facebook account and to keep it active during the duration of the summer camp • permissions regarding photos – legal issues about liability and publishing photos of minors

EDUCATIONAL AND INSTRUCTIONAL ISSUES: • the redefinition of the teacher/student structure – from teacher-centered instruction to studentcentered learning/creating • how does education deal with the traditional hierarchies of knowledge and the new web 2. 0 reality?
37f59200d13df799fc6c5515f4e8cacf.ppt