e4a72eaa32b26a2133682eb685175b26.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 70

Web 2. 0的技術與應用 曾憲雄 教授 交通大學 資訊 程學系 2009/4/14

Human Intelligence vs. Machine Intelligence 在 1997 年許峰雄博士所設計的 IBM Deep Blue 打敗世界西洋棋王 Kasparov。 電腦是否已經比人腦聰明? 2

• Web 2. 0的世界 : Web 2. 0 – 網路成為 新平臺 – 內容因使用者的 參與( Participation) 而產生 • 產生 個人化(Personalization)內容 • 藉由人與人 ( P 2 P) 分享( 的 Share)。 • Web 2. 0概念 : – Tim O‘Reilly與 Media. Live國際研討會議題開始 – 一個架構在 知識上的環境 , – 人與人之間 互動 而產生出的 內容 , – 經由在 服務導向 的架構中的程式,在這個環境被 發佈,管理和使用 3 http: //www. oreillynet. com/pub/a/oreilly/tim/news/2005/09/30/what-is-web-20. html? page=3

Web 1. 0 vs. Web 2. 0 • Double. Click • Ofoto • Akamai • mp 3. com • 大英百科(Britannica Online) • 個人網站(personal websites) • evite • 網域名稱預測 (domain name speculation • 頁面瀏覽數(page views) • 螢幕擷取(screen scraping) • 發佈(publishing) • 內容管理系統 (content management systems) • 目錄(分類) (directories (taxonomy)) • Google Ad. Sense • Flickr(相片分享社群) • Bit. Torrent(P 2 P-BT下載) • Napster(P 2 P音樂下載) • 維基百科(Wikipedia) • 部落格(blogging) • upcoming. org and EVDB • 搜尋引擎優化(search engine optimization) • 每次點擊成本(cost per click) • 網路服務(web services) • 參與(participation) • 維基式管理 (wikis) • 標籤(分眾分類) (tagging ("folksonomy")) 4 • 聚合(syndication)

Turing Test是 Turing提出的一個關於 機器人 的著名判斷 原則。 此原則說:如果一個人使用任意一串問題去詢問兩個他 不能看見的對象:一個是正常 思維 的人;一個是機器, 如果經過若干詢問以後他不能得出實質的區別,則他 就可以認為該機器業已具備了人的「智能」( Intelligence)。 (取材自維基百科 ) 阿蘭 ·麥席森 ·圖靈( Alan Mathison Turing, 1912 - 1954), 英國數學家 、 邏輯學家 , 他被視為 電腦 之父。 5
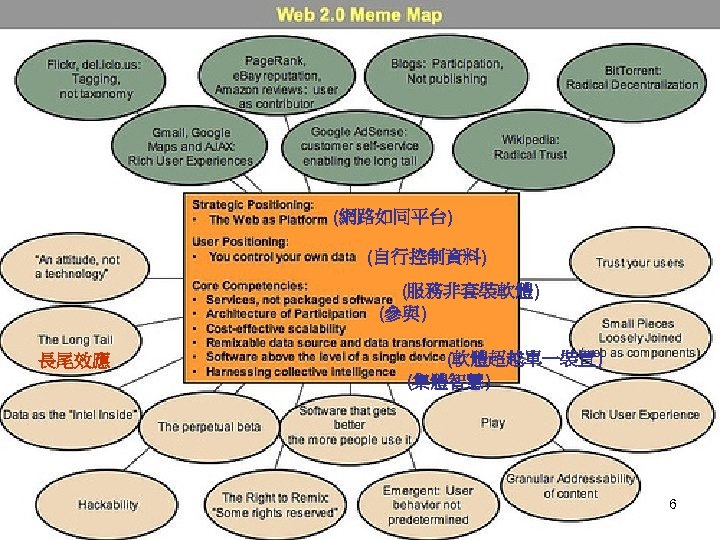
(網路如同平台) (自行控制資料) (服務非套裝軟體) (參與) 長尾效應 (軟體超越單一裝置) (集體智慧) 6

Web 2. 0原則 • 「網路應該作為平台來使用」 (The Web As Platform) • 從商業的角度看,Web 2. 0 讓泡沫的 dot com 起死 回生? – Yahoo, e-Bay, Amazon 都不是新公司。 – Google 不是第一個免費的搜索引擎。 (Alta. Vista & Overture? ) – 搜尋結果的排序 加入商業考量,正在降低公信力。 • 部落格 (Blog)的崛起 : 個人網頁每天記載的日記 形式 – 依時間前後排列方式組成 , 利用不同的遞送方式來散 佈 個人的想法與觀點 ,並且組成 價值鏈 • Web 1. 0: 7

Web 2. 0原則 • 引領群體智慧 : 超連結是網路的基礎。 – Google在搜尋領域中突圍而出 (Page. Rank ) – e. Bay的產品則是全體用戶集體活動的龐大創造物 : • 賣主提供商品,買家尋找商品 – 維基百科(Wikipedia) : • 眾多網路用戶所提供的知識為基礎,任何人皆可編輯 修改而成的線上百科全書。 – del. icio. us及 Flickr (bookmarks): • 「大眾分類」( Folksonomy)的概念 – 病毒行銷」( Viral marketing) : • 採用直接從一個用戶到另一個用戶的方式來傳播訊息 8
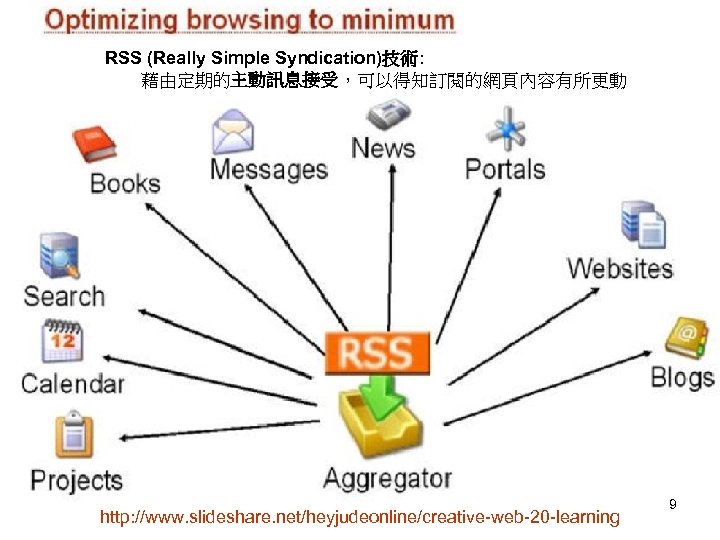
RSS (Really Simple Syndication)技術: 藉由定期的主動訊息接受,可以得知訂閱的網頁內容有所更動 http: //www. slideshare. net/heyjudeonline/creative-web-20 -learning 9

Data is the Next Intel Inside • 重要的網路應用系統,都有一個專屬資料庫 : – Google & Yahoo : 網路搜尋資料庫( web crawl) – Amazon: 產品資料庫 – e. Bay: 產品與賣家資料庫 – Google Map: 地圖資料庫 – Napster: 分散式歌曲資料庫裏 – Myspace、 Facebook: 社群資料庫 – Youtube、無名: 影音相片資料庫 ,You. Tube 的主要 內容貢獻者要求分廣告利益。 10

NEWS: 微軟擴大廣告聯盟,砸下 2. 4億美元 入 股 Facebook • Facebook: http: //www. facebook. com/ – 社交網站, – 擁有 150億美元 的身價, – (宣稱 )使用者直逼 5, 000萬 人 – 超越 My. Space: www. myspace. com WHY? ? ? 11 Source: http: //taiwan. cnet. com/news/

廣告主的天堂 • 絕佳廣告平台 : – 豐富的 個人資料 與 附加資訊 : • 誰 (Who)與他們往來,他們在 做什麼事 (What)等等。 – 個人偏好 & Social Network。 • [聚焦廣告 ](targeted advertising) : – 派送 鎖定目標 的 個人化廣告 。 – 成功案例 : Google 、 Amazon。 • 範例 : – 已訂婚 Users: • 婚紗業者 &蜜月旅遊方案 &禮餅 & etc. 。 – 地區 &年齡 &音樂喜愛 & [七月半 ]歌手樂團 : • 音樂會宣傳 – 愛吃披薩 : • 顯示出住家附近 [打不樂 ] 披薩門市的電話號碼。 Source: http: //taiwan. cnet. com/news/ 12

Web 2. 0原則 : Service • 網路時代的軟體最重要的特徵是服務 (Service),而非產品(Product): – Gmail, Google Maps, Flickr, del. icio. us, etc. • 輕巧的程式設計模式 : – 組裝式創新 (Mashup): • 整合網路上多個資料來源或功能,以創造新服 務的網路應用程式 – Google Map、 You. Tube、 Slideshare 13
信義房屋 地圖日記 14

Web 2. 0企業的核心競爭力 • 提供 服務 ,而不是套裝軟體,能以符合成本效 益的方式擴充 : – Google Mail, Map. • 控制獨特的、難以再製的資料來源,隨著越多 人使用而 累積越豐富的資料 : – Wikipedia, Facebook, 無名 • 使用者為 共同的開發者 ,善用眾人的 集體智 慧與 自助服務效能 : – Wikipedia, Myspace, Youtube • 不再侷限於個人電腦的平台之上 : – i. Pod / i. Tunes , Podcasting • 輕巧的使用者介面、開發模式、及商業模式 – Google API, Mashup : 15

1. Proposing a knowledge-based rapid prototyping approach to TM design for e-Learning grids • Traditional teaching-material design process: ADDIE model – Analysis, Design, Develop, Implement, and Evaluate • Disadvantage – Time-consuming, Expensive , Redundant effort • Alternative : Automated authoring and Reusing existing TMs • Challenges/Difficulties – Requirement elicitation – Finding useful TMs from existing ones • Minimize Development time, Development cost 16

Problem • Teaching-Material Designing Problem – For a query given by a teaching-material editor, design a teaching-material, where • the designer can interactively consult the editor to elicit the meaning of the query; • the existing materials in m LORs can be reused. – The objective is to minimize the total development time. 17

Idea • Idea: a rapid prototyping approach to designing TMs – Reuse • Using expertise to search useful TMs – Automated • KA tools are available to speed the process. • Automatically merge algorithm – Collaborative authoring • Using a Wiki-based authoring environment • Design and implementation of a searching expert system to find reusable TMs 18
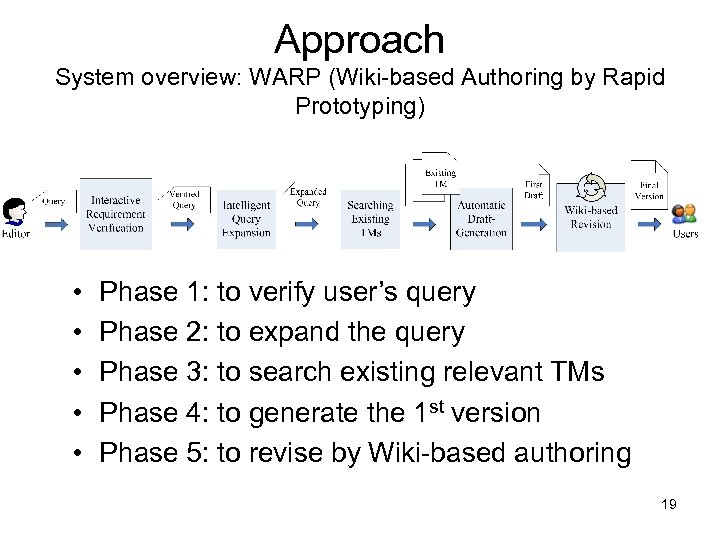
Approach System overview: WARP (Wiki-based Authoring by Rapid Prototyping) • • • Phase 1: to verify user’s query Phase 2: to expand the query Phase 3: to search existing relevant TMs Phase 4: to generate the 1 st version Phase 5: to revise by Wiki-based authoring 19
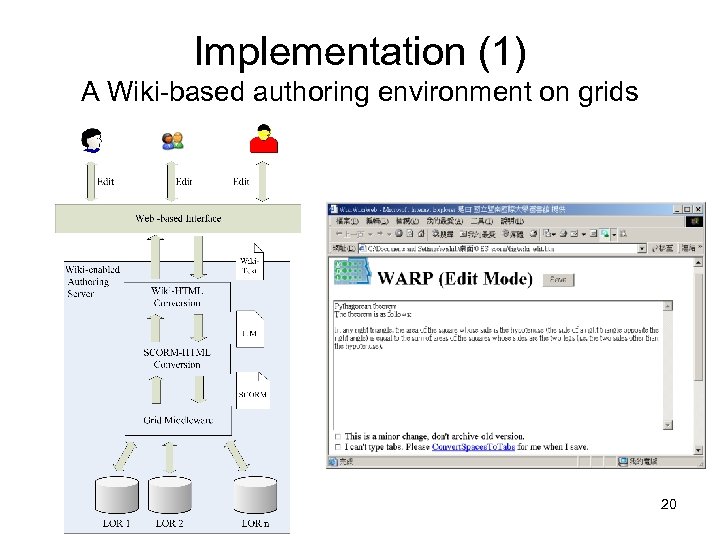
Implementation (1) A Wiki-based authoring environment on grids 20
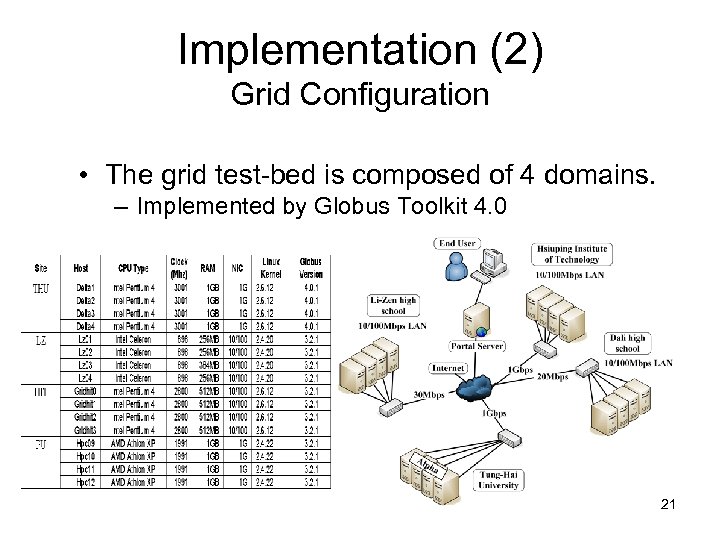
Implementation (2) Grid Configuration • The grid test-bed is composed of 4 domains. – Implemented by Globus Toolkit 4. 0 21
22
23

Web 2. 0: UGC+SNS 24 http: //www. slideshare. net/heyjudeonline/creative-web-20 -learning
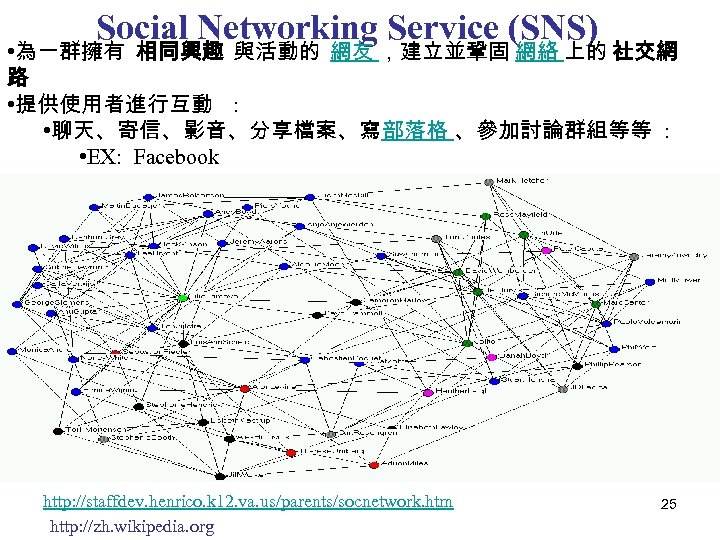
Social Networking Service (SNS) • 為一群擁有 相同興趣 與活動的 網友 ,建立並鞏固 網絡 上的 社交網 路 • 提供使用者進行互動 : • 聊天、寄信、影音、分享檔案、寫部落格 、參加討論群組等等 : • EX: Facebook http: //staffdev. henrico. k 12. va. us/parents/socnetwork. htm http: //zh. wikipedia. org 25
User-Generated Content (UGC) http: //www. linuxelectrons. com/news/general/user-generatedweb-content-will-grow-rapidly-through-2010 26
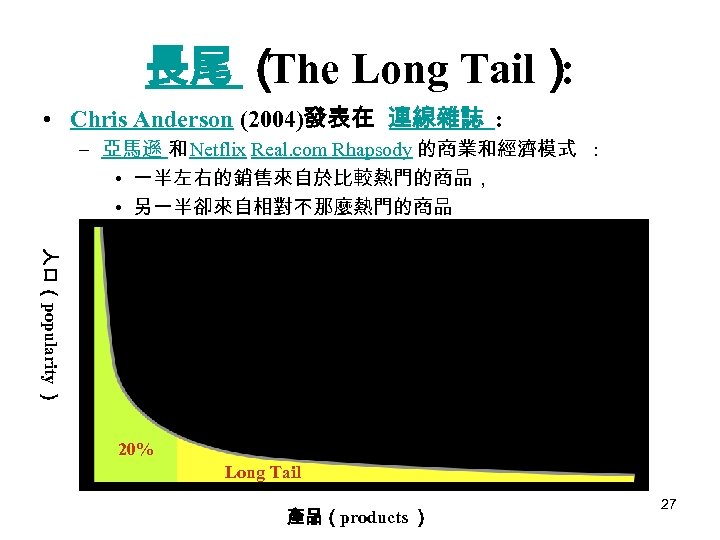
長尾 ( Long Tail) The : • Chris Anderson (2004)發表在 連線雜誌 : – 亞馬遜 和 Netflix Real. com Rhapsody 的商業和經濟模式 : • 一半左右的銷售來自於比較熱門的商品, • 另一半卻來自相對不那麼熱門的商品 人口(popularity ) 20% Long Tail 產品(products ) 27

長尾 ( The Long Tail) : • 20 -80法則 : – 企業界 80%的業績來自 20%的產品 • 長尾 (The Long Tail): – Web 2. 0興起後,改變 20 -80法則的新理論 – Internet讓 99%的產品都有機會銷售 : • 長尾特性商品將具有增長企業營利空間的價值。 • 長尾商品總值甚至可與暢銷商品抗衡。 – 「長尾」的總合也未必超越幾個暢銷品,更何況不只一家 Web 2. 0 在分一條長尾。 • 28

2. Folksonomy-based Indexing for Location-aware Retrieval of Learning Contents • An example scenario of location-aware u-learning – The “identification of plants” unit of the Nature Science course in an elementary school – Place: campus Ø System: Can you identify the type of the plant in front of you? Ø Student: No. Ø System: What is the color of the flower? Ø Student: red. Ø… – The system is aware of the location of the student, and the nearby plants, by sensor technologies and maps. 29
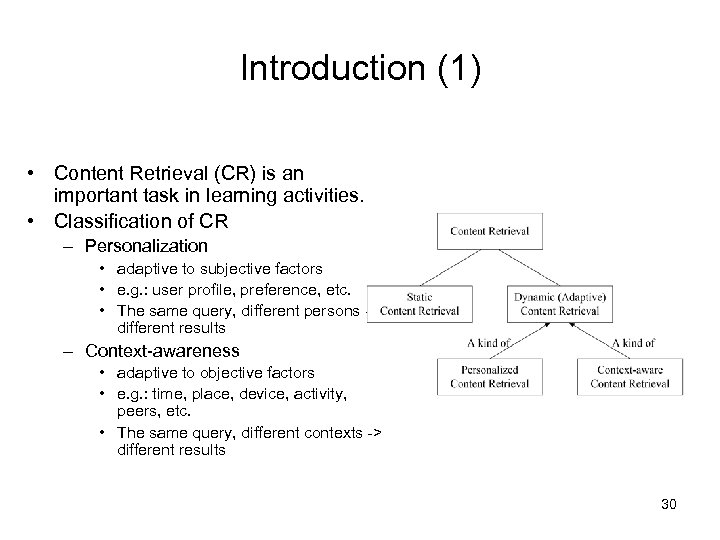
Introduction (1) • Content Retrieval (CR) is an important task in learning activities. • Classification of CR – Personalization • adaptive to subjective factors • e. g. : user profile, preference, etc. • The same query, different persons -> different results – Context-awareness • adaptive to objective factors • e. g. : time, place, device, activity, peers, etc. • The same query, different contexts -> different results 30
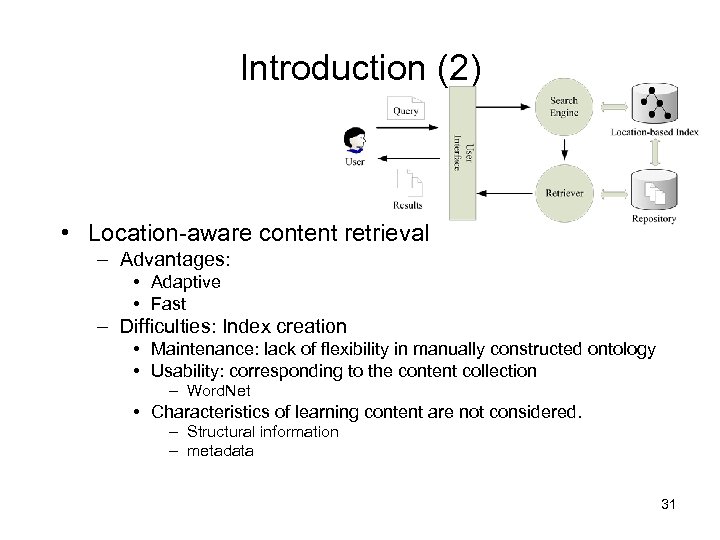
Introduction (2) • Location-aware content retrieval – Advantages: • Adaptive • Fast – Difficulties: Index creation • Maintenance: lack of flexibility in manually constructed ontology • Usability: corresponding to the content collection – Word. Net • Characteristics of learning content are not considered. – Structural information – metadata 31
Preliminaries (1) • Folksonomy: One of Web 2. 0 features – Collaborative categorization using freely chosen keywords – To allow users to describe a set of shared items • Bookmarks: del. icio. us • Photos: Flickr • Scientific publications: Cite. ULike 32

Preliminaries (2) • Example: http: //del. icio. us – To store your bookmarks online – To use tags to organize and remember your bookmarks – To see the interesting links that your friends and other people bookmark, and share links with them in return. – You can search del. icio. us to discover cool and useful bookmarks that everyone else has saved • Limitations – Informal: • the set of keywords is not fixed • Semantic ambiguity – Single-layer structure – Limited sharing scope: not crossing the boundaries of a single website 33
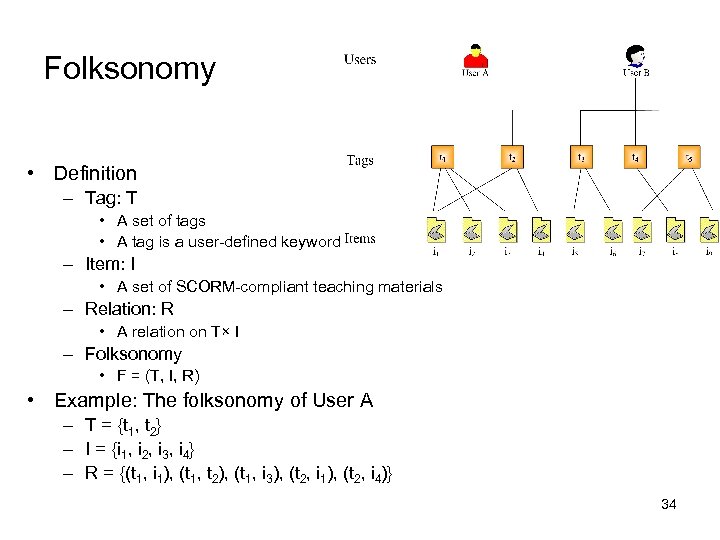
Folksonomy • Definition – Tag: T • A set of tags • A tag is a user-defined keyword – Item: I • A set of SCORM-compliant teaching materials – Relation: R • A relation on T× I – Folksonomy • F = (T, I, R) • Example: The folksonomy of User A – T = {t 1, t 2} – I = {i 1, i 2, i 3, i 4} – R = {(t 1, i 1), (t 1, t 2), (t 1, i 3), (t 2, i 1), (t 2, i 4)} 34
Problem • Definition: Index (a rooted tree ) – The nodes represent concepts in the domain, and the edges represent relations between nodes. – A node is a specialization of its parent node. – Each node is associated with a feature vector, which characterizes the semantic meaning of this concept. • Folksonomy-based Index Creation Problem – propose a folksonomy-based method to automatically construct location-based indices. The built ontology can be applied to organization and retrieval of learning contents. Given a collection of learning contents and corresponding folksonomies, construct an Index for the collection. – Precision and recall of retrieval using the built index 35

36 http: //www. slideshare. net/heyjudeonline/creative-web-20 -learning

網路世代 (N-gen) • 吸收資訊快,資訊多元. • 反應速度快. • 需求為主 (on-demand)地使用媒體 : – 喜歡在持續與朋友通訊 ( MSN、 QQ、 Skype) • 喜歡自行創作與分享 37
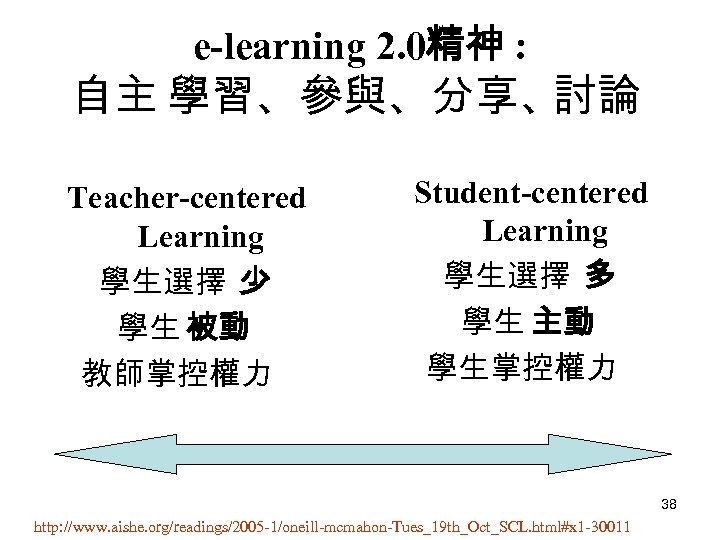
e-learning 2. 0精神 : 自主 學習、參與、分享、 討論 Teacher-centered Learning 學生選擇 少 學生 被動 教師掌控權力 Student-centered Learning 學生選擇 多 學生 主動 學生掌控權力 38 http: //www. aishe. org/readings/2005 -1/oneill-mcmahon-Tues_19 th_Oct_SCL. html#x 1 -30011

e. Learning 2. 0模式 • 基於 Web 2. 0 與 elearning新趨勢的新模式 : – 學生製作內容 (students create content) – 協同合作 (collaboration) • 利用 blogs, Wikis, discussions, RSS, etc. – 組成 學習網路 (Learning Network). – 利用 多元組成的內容 來得到 學習經驗 (learning experiences). – 利用多元 具 : • online references, courseware, • knowledge management, collaboration 與 search. 39
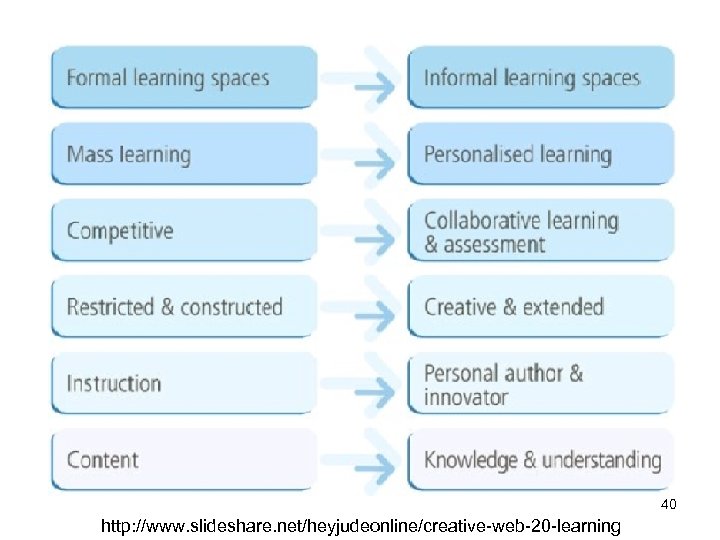
40 http: //www. slideshare. net/heyjudeonline/creative-web-20 -learning
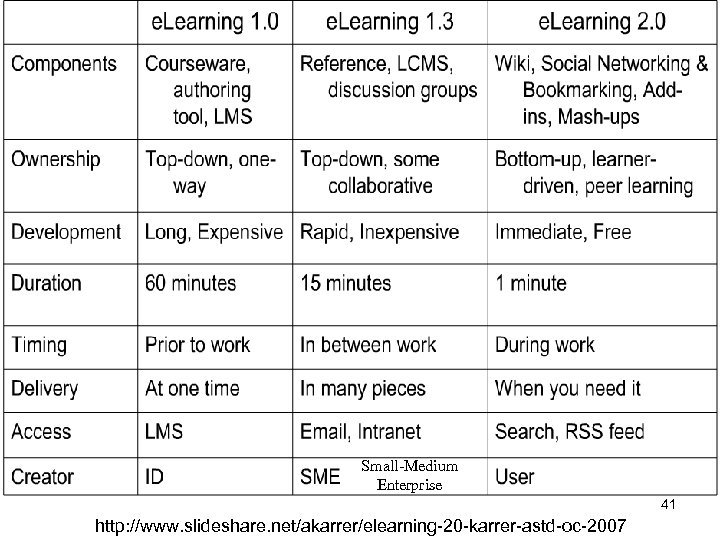
Small-Medium Enterprise 41 http: //www. slideshare. net/akarrer/elearning-20 -karrer-astd-oc-2007
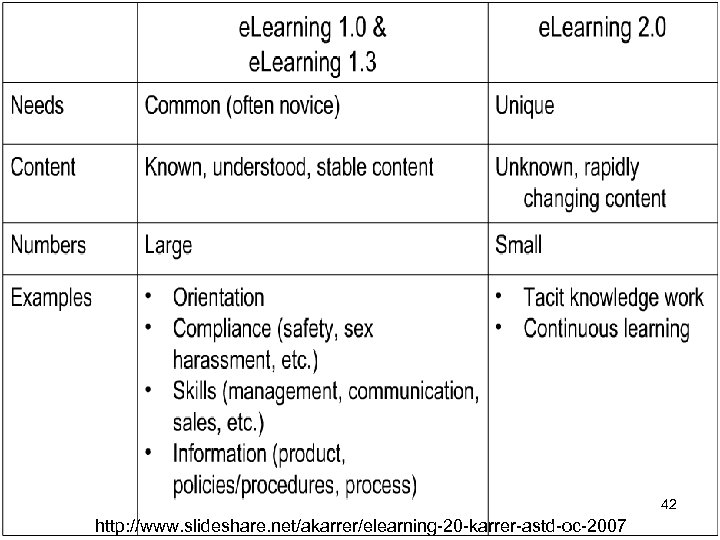
42 http: //www. slideshare. net/akarrer/elearning-20 -karrer-astd-oc-2007

Learning Community • 知識的建構 (Knowledge construction): – 最好經由 協同合作 (Collaboration)來完成. • 學生於同學間經由 供給與獲得 (give-andtake)來進行學習 : – 當學生寫下貢獻 (contributions)於討論時 : • 學生將學習到他們想說之事 • 他們所得之回應將可促進學習 43
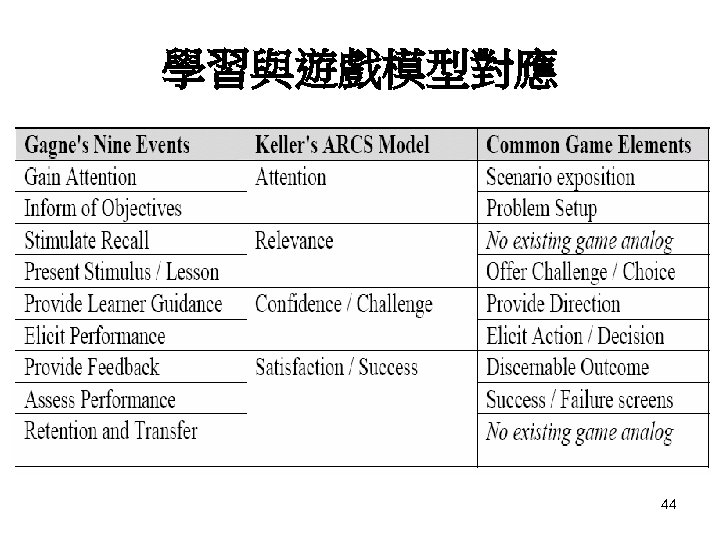
學習與遊戲模型對應 44

網路遊戲沉迷原因 • 美國羅切斯特大學研究成果 : – 因為網路遊戲滿足了人們的心理需要 – 心理上產生 成就感 和 自我支配感 : • 只有讓遊戲者與其他參與者 互動的遊戲 才能使 遊戲者更加投入,更加樂此不疲,也更容易上癮 • 讓遊戲者 自行做主 , 展示自己的能力 ,還可讓遊 戲者支配他人或得到他人的呼應和支援。 • 如果網路遊戲只是單純地向 人們提供 “樂趣 ”的 話,就不可能讓人長久著迷 。 45

Game based learning community • Web 1. 0: – 存取民主化 (Democratization of Access) • Web 2. 0 : – 參與與協同合作民主化 (Democratization of Participation and Collaboration) • Web 3 D : – 虛擬學習與共創 – (Enablement of true generative learning and cocreation distributed virtually across the world). 46

非Learning社群 47

非Learning社群 48

Second Life • 誕生於 2003年 : – 為 Real. Network前任技術長 Philip Rosedale於舊金山成立林 頓軟體公司(Linden Lab) • 社交導向的線上遊戲 : – 大規模多人線上角色扮演遊戲( MMORG)。 – 遊戲無技能點數、經驗值、等級、打怪或轉職,沒任務、解謎或組隊 • 實際經濟 : 。 – 每 1, 000個林頓元約可兌換 3. 3美元。 – 月費為 9. 95美元,會員約 90萬名,每月會費收入高達 895. 5萬美元,約 當於新台幣 2. 95億元。 • 學習應用 : – 某些大學教授會到 Second Life裡開堂授課 – 學生在裡面做實驗,也有醫生在裡面開起了診所,提供醫療諮詢服 務 – 公益人士成立支持血癌患者的團體 – Toyota及 Sun Microsystems進駐 : 增加其產品的知名度。 49 www. secondlife. com/

50

Cyber. One Classroom in Second Life 51 Source: http: //blogs. law. harvard. edu/vvvv/files/2006/09/Cyber. One_2006 -09 -21. png

Virtual Presence: Second Life Library 2. 0 52

Virtual Learning: Edu. Nation-Second Life 53

Social Network Service • Social Network Service (SNS) – Myspace, Facebook, Friendster, etc. • SNS: provide low cost social communication medium with other people • Recommend possible new friends – From your friend’s friend – Interest in the same topics • Idea: human resource hunting – e. g. Expert finding for problem solving 54

3. Trustworthy experts finding service to improve the social network for problem solving • Recommend experts to students’ for programming inquiry learning • Technical Issues – Trustworthiness – Availability – Domain expertise • Obtain the preference of experts from the behaviors on the discussion forum 55
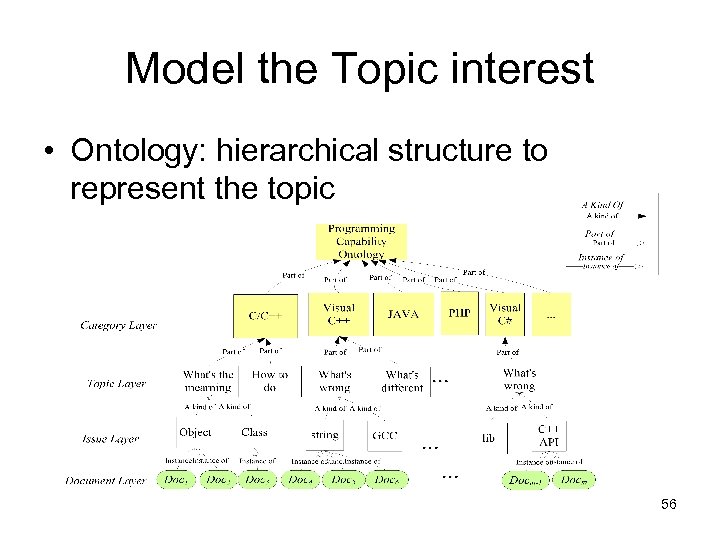
Model the Topic interest • Ontology: hierarchical structure to represent the topic 56

Trustworthy Expert Finding Service 57

Criteria • Domain expertise – Experts with similar topic interest are obtained from experts’ posting documents on the forum. • Trustworthiness – The trustworthiness values are computed by the experts’ average reputation degrees given by other community members. • Availability – The availability is heuristically obtained by the weighted average of experts’ presence frequency online. 58

Contribution • Inquiry-based learning is applied for students’ programming problem solving on Web forum. • The trustworthy experts finding service has been proposed to improve the social network for problem solving. 59

Collective Intelligence • Collective Intelligence: group intelligence that emerges from collaboration and competition of many individuals – e. g. Wikipedia • Collaborative knowledge construction – Knowledge integration – Knowledge fusion – Folksonomy-based approach 60
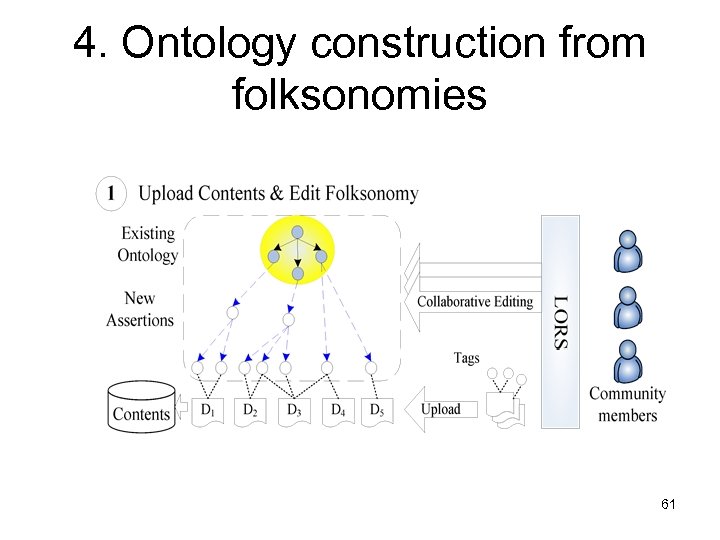
4. Ontology construction from folksonomies 61
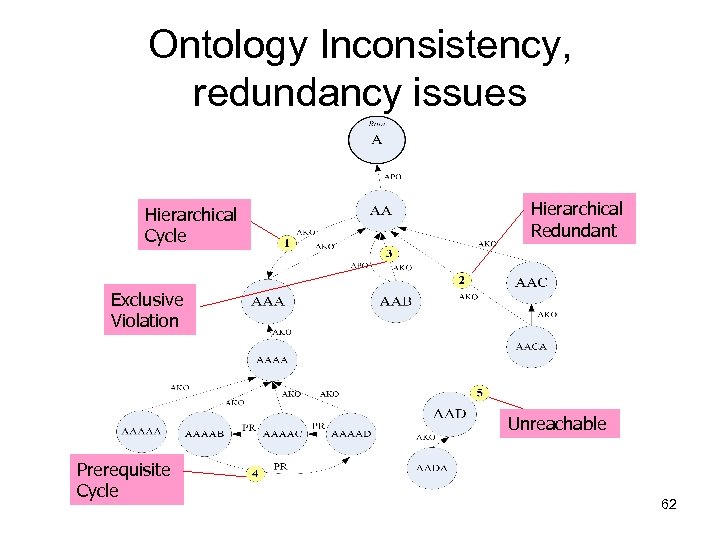
Ontology Inconsistency, redundancy issues Hierarchical Cycle Hierarchical Redundant Exclusive Violation Unreachable Prerequisite Cycle 62
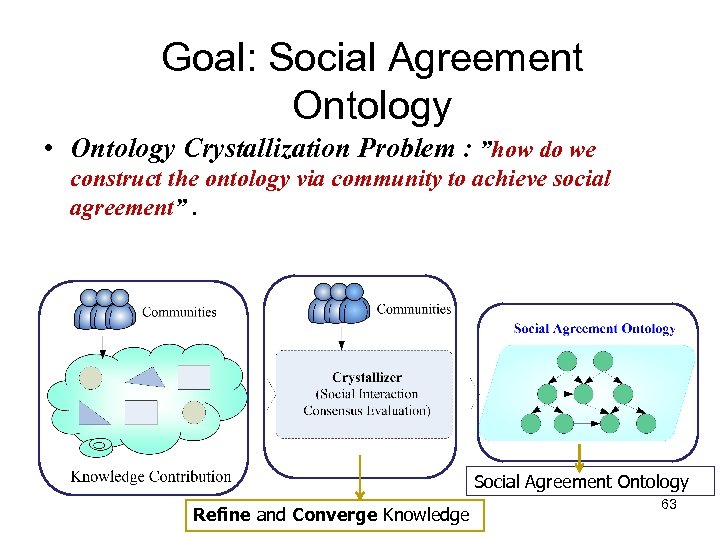
Goal: Social Agreement Ontology • Ontology Crystallization Problem : ”how do we construct the ontology via community to achieve social agreement”. Social Agreement Ontology Refine and Converge Knowledge 63
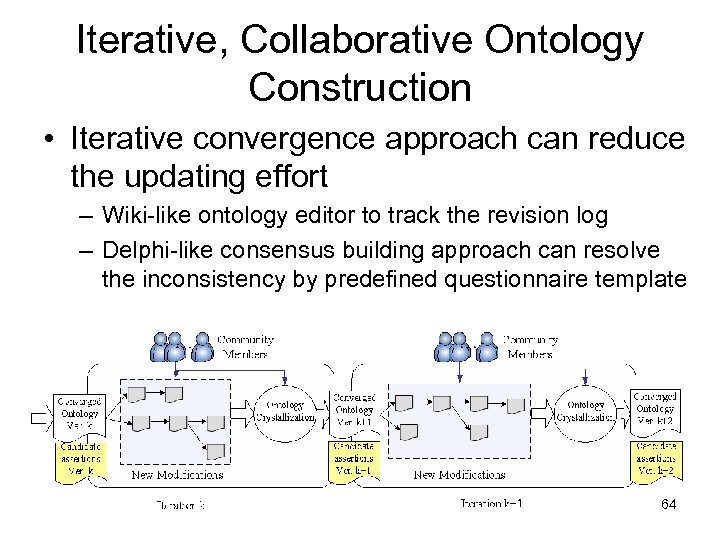
Iterative, Collaborative Ontology Construction • Iterative convergence approach can reduce the updating effort – Wiki-like ontology editor to track the revision log – Delphi-like consensus building approach can resolve the inconsistency by predefined questionnaire template 64

Questionnaire item templates to assist the inconsistency resolution Item Type Questionnaire Item Templates T 1: Likert five-point scales Do you agree or disagree with this relationship? Concept (Ci) Relation (rm) Concept (Cj) (1)Strongly Agree (2)Agree (3)Not Agree and Not Disagree (4)Disagree (5)Strongly Disagree T 2: True/False Do you agree or disagree with this relationship? Concept (Ci) Relation (rm) Concept (Cj) (1)Agree (2)Disagree T 3: Multiple concepts What is your opinion about which following Concept (CX) is the selection most suitable for Concept (CX/Ci) Relation (rm) Concept (Cj/Cx) ? (1)Concept 1 (2)Concept 2 (3)…(n) Conceptn (n+1) Not Above All (, where n≦ 5) T 4: Multiple relation selection What is your opinion about which following Relation (rm) that is the most suitable to describe the relationship between Concept (Ci) and Concept (Cj) ? (1)Relation 1 (2)Relation 2 (3)…(n) Relation n (n+1) Not Above All (, 65 where n≦ 5)

System implementation Questionnaire Wiki-like Ontology Editor 66
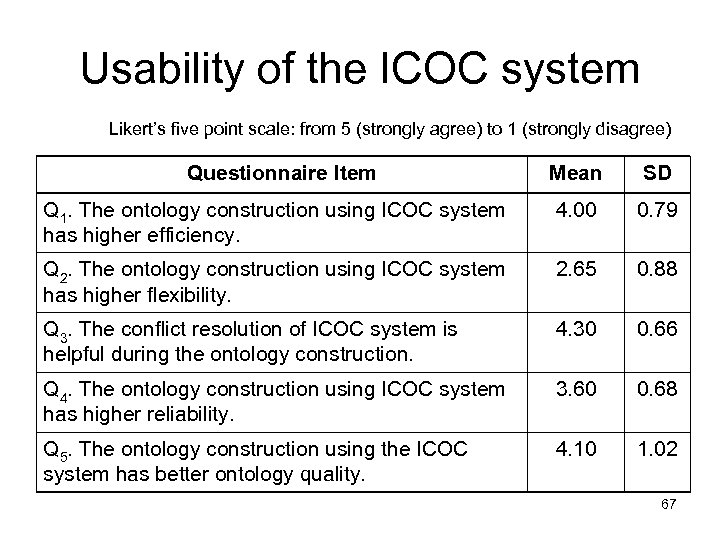
Usability of the ICOC system Likert’s five point scale: from 5 (strongly agree) to 1 (strongly disagree) Questionnaire Item Mean SD Q 1. The ontology construction using ICOC system has higher efficiency. 4. 00 0. 79 Q 2. The ontology construction using ICOC system has higher flexibility. 2. 65 0. 88 Q 3. The conflict resolution of ICOC system is helpful during the ontology construction. 4. 30 0. 66 Q 4. The ontology construction using ICOC system has higher reliability. 3. 60 0. 68 Q 5. The ontology construction using the ICOC system has better ontology quality. 4. 10 1. 02 67

Contribution • The inconsistency and redundancy of folksonomy-based approach was modeled as Ontology Crystallization Problem • The iterative, collaborative convergence process was proposed • The experimental result shows the ICOC system is feasible and effective. 68

結論 • 「長尾理論」也無法否認 20%的網站正在 吸引 80%目光的事實。 • Web 2. 0 : 網路上資訊分享的現象與環境 – 把 Web 2. 0 做為商業手段時,正在使 dot com 夢想成真,但並不保證是一個獲利模式。 – UGC+SNS這個現象,正在改變許多科學研究 的方法。 69

The END
e4a72eaa32b26a2133682eb685175b26.ppt