4dba59573dbfc55f3fd1a20a0e4ad87a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Weatherization & Indoor Air Quality Impacts of Weatherization on Air Quality and Comfort Inside Your Home 1 1
Weatherization & Indoor Air Quality Impacts of Weatherization on Air Quality and Comfort Inside Your Home 1 1
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange What is Weatherization? • Conservation activities applied to a building that help to protect building from elements, conserve heating or cooling energy, maintain temperature and provide a safe, comfortable, and healthy living environment
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange What is Weatherization? • Conservation activities applied to a building that help to protect building from elements, conserve heating or cooling energy, maintain temperature and provide a safe, comfortable, and healthy living environment
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Typical Weatherization Components Weatherization Assessment • Determining the condition of the home • Energy Audit • Visual Inspection • Blower Door / Duct test • Other Diagnostics Weatherization Plan • Prioritized • Customized Weatherization Retrofits • Building Envelope – Sealing/Tightening – Windows & Doors • Insulation • HVAC – Heating, Cooling, Ducts • Designed Ventilation • EE Upgrades (Appliances)
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Typical Weatherization Components Weatherization Assessment • Determining the condition of the home • Energy Audit • Visual Inspection • Blower Door / Duct test • Other Diagnostics Weatherization Plan • Prioritized • Customized Weatherization Retrofits • Building Envelope – Sealing/Tightening – Windows & Doors • Insulation • HVAC – Heating, Cooling, Ducts • Designed Ventilation • EE Upgrades (Appliances)
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange The House as a “Living System” Changes made as part of a weatherization plan can impact more than energy efficiency. A Holistic approach to renovations will also address: • Comfort • Health • Safety • Durability • Sustainability
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange The House as a “Living System” Changes made as part of a weatherization plan can impact more than energy efficiency. A Holistic approach to renovations will also address: • Comfort • Health • Safety • Durability • Sustainability
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Healthy Indoor Environment Protocols Organized by Priority Issues – Alerts auditor, planner and contractor to to potential issues; recommends minimum and expanded actions • Contaminants • Building Systems – Moisture – Radon – Wood Smoke – CO, NOx, etc – Lead – Pests – Building Products – Asbestos – Other http: //www. epa. gov/iaq/homes/retrofits. html – – – HVAC Combustion Safety Source Ventilation Whole House ventilation Multi Family Ventilation
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Healthy Indoor Environment Protocols Organized by Priority Issues – Alerts auditor, planner and contractor to to potential issues; recommends minimum and expanded actions • Contaminants • Building Systems – Moisture – Radon – Wood Smoke – CO, NOx, etc – Lead – Pests – Building Products – Asbestos – Other http: //www. epa. gov/iaq/homes/retrofits. html – – – HVAC Combustion Safety Source Ventilation Whole House ventilation Multi Family Ventilation
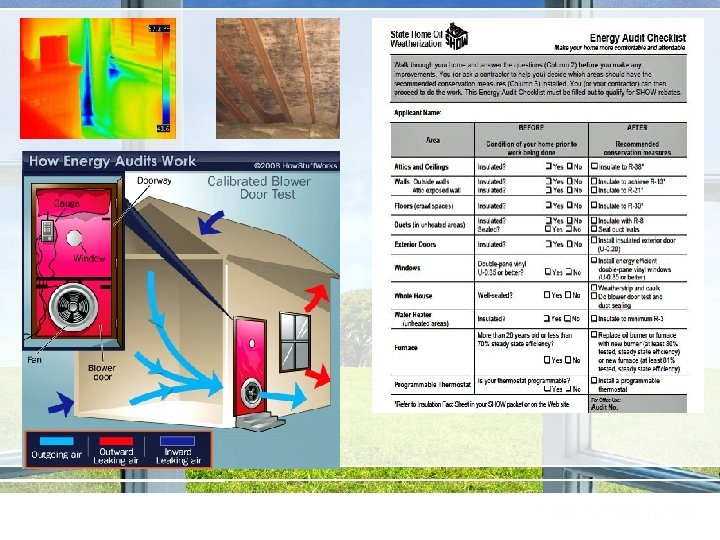
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Weatherization Assessment What’s Done? • Energy Audit – – Energy performance Base Loads • Visual inspection – – Purpose • Determine Baseline • Determine Options • Identify IAQ Concerns Overall condition Visual clues • Thermal Imaging • Blower door Test – Amount and distribution of leakage • Duct test – Loss of conditioned air • Other Diagnostics & Tests – Backdraft, CO 2, RH, http: //www. waptac. org/Weatherization-Assistant-8002 E 5. aspx
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Weatherization Assessment What’s Done? • Energy Audit – – Energy performance Base Loads • Visual inspection – – Purpose • Determine Baseline • Determine Options • Identify IAQ Concerns Overall condition Visual clues • Thermal Imaging • Blower door Test – Amount and distribution of leakage • Duct test – Loss of conditioned air • Other Diagnostics & Tests – Backdraft, CO 2, RH, http: //www. waptac. org/Weatherization-Assistant-8002 E 5. aspx
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Weatherization Plan What improvements will be performed Approach • Prioritized – Health – Cost Effectiveness • Customized – Test results – Building Specific – Occupancy & Operation Considerations • Safety • Energy • Indoor Air Quality • Comfort • Cost Effectiveness • Sustainability
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Weatherization Plan What improvements will be performed Approach • Prioritized – Health – Cost Effectiveness • Customized – Test results – Building Specific – Occupancy & Operation Considerations • Safety • Energy • Indoor Air Quality • Comfort • Cost Effectiveness • Sustainability
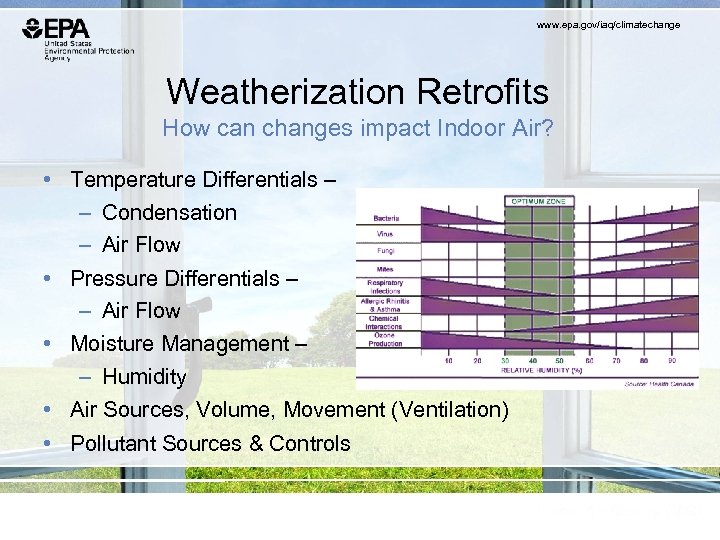 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Weatherization Retrofits How can changes impact Indoor Air? • Temperature Differentials – – Condensation – Air Flow • Pressure Differentials – – Air Flow • Moisture Management – – Humidity • Air Sources, Volume, Movement (Ventilation) • Pollutant Sources & Controls
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Weatherization Retrofits How can changes impact Indoor Air? • Temperature Differentials – – Condensation – Air Flow • Pressure Differentials – – Air Flow • Moisture Management – – Humidity • Air Sources, Volume, Movement (Ventilation) • Pollutant Sources & Controls
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Building Envelope Sealing, Tightening, Windows & Doors Weatherization Action Impact on IAQ • • • – – – • Blower Door / Duct Test based Reduce air leakage, resistance to heat transfer, thermal losses/gains Size and distribution of uncontrolled airflow Stack Effect / Source of Leakage Air Radon Reduced “Natural” Ventilation Less fresh air for occupants Increased Humidity Increased Pollutant Levels (indoor sources) – Increased Odors • Spillage / Backdrafting
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Building Envelope Sealing, Tightening, Windows & Doors Weatherization Action Impact on IAQ • • • – – – • Blower Door / Duct Test based Reduce air leakage, resistance to heat transfer, thermal losses/gains Size and distribution of uncontrolled airflow Stack Effect / Source of Leakage Air Radon Reduced “Natural” Ventilation Less fresh air for occupants Increased Humidity Increased Pollutant Levels (indoor sources) – Increased Odors • Spillage / Backdrafting
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Insulation Weatherization Action Impact on IAQ • Resistance to heat transfer, thermal losses/gains • Moves dew point surface – Shifts condensation to exterior wall • VOC – type of insulation • Loss of containment - Fibers / Particulates • Decreased Air Movement
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Insulation Weatherization Action Impact on IAQ • Resistance to heat transfer, thermal losses/gains • Moves dew point surface – Shifts condensation to exterior wall • VOC – type of insulation • Loss of containment - Fibers / Particulates • Decreased Air Movement
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Heating /Cooling / HVAC Weatherization Action • Programmable Thermostat • Ducts – – – Replacement Sealing Balancing • Furnace or A/C changeout – – Efficiency Right sizing Combustion Venting Fuel type • Wood stove changeout • Ventilation Impact on IAQ • • • Alter Pressure balance Combustion makeup air Spillage/Backdrafting Emissions Humidity
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Heating /Cooling / HVAC Weatherization Action • Programmable Thermostat • Ducts – – – Replacement Sealing Balancing • Furnace or A/C changeout – – Efficiency Right sizing Combustion Venting Fuel type • Wood stove changeout • Ventilation Impact on IAQ • • • Alter Pressure balance Combustion makeup air Spillage/Backdrafting Emissions Humidity
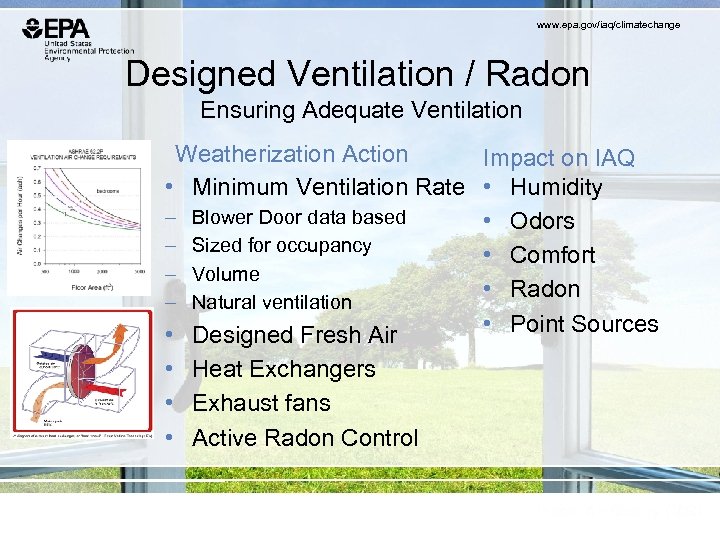 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Designed Ventilation / Radon Ensuring Adequate Ventilation Weatherization Action Impact on IAQ • Minimum Ventilation Rate • Humidity – Blower Door data based • Odors – Sized for occupancy • Comfort – Volume • Radon – Natural ventilation • Point Sources • Designed Fresh Air • Heat Exchangers • Exhaust fans • Active Radon Control
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Designed Ventilation / Radon Ensuring Adequate Ventilation Weatherization Action Impact on IAQ • Minimum Ventilation Rate • Humidity – Blower Door data based • Odors – Sized for occupancy • Comfort – Volume • Radon – Natural ventilation • Point Sources • Designed Fresh Air • Heat Exchangers • Exhaust fans • Active Radon Control
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Energy Efficient Upgrades Weatherization Action • EE Lighting • Hot water – Replacement H 2 O heater – Insulation – Reduce demand (lo flow) • Fans (attic, ceiling) • Appliances • PV/Wind Impact on IAQ • Air movement • Mixing • Emissions • Humidity
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Energy Efficient Upgrades Weatherization Action • EE Lighting • Hot water – Replacement H 2 O heater – Insulation – Reduce demand (lo flow) • Fans (attic, ceiling) • Appliances • PV/Wind Impact on IAQ • Air movement • Mixing • Emissions • Humidity
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Holistic Considerations • Landscaping shading • Water conservation
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Holistic Considerations • Landscaping shading • Water conservation
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Homeowner / Resident Education How to Effectively Operate and Maintain the Renovated House • • • Energy conservation • Maintenance • Routine Ventilation • Scheduled Humidity • In response to Sources observations Lifestyle – Don’t ignore changes that you observe – “Listen” to what your body & family are telling you
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Homeowner / Resident Education How to Effectively Operate and Maintain the Renovated House • • • Energy conservation • Maintenance • Routine Ventilation • Scheduled Humidity • In response to Sources observations Lifestyle – Don’t ignore changes that you observe – “Listen” to what your body & family are telling you
 www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Additional Resources • EPA’s Indoor Air Quality Web site: www. epa. gov/iaqq • Climate Change: www. epa. gov/climatechange// • The Inside Story: A Guide to Indoor Air Quality: www. epa. gov/iaq/pubs/insidest. html • ENERGY STAR Home Improvement: www. energystar. gov/homeimprovementt • Mold and Moisture: www. epa. gov/moldd • Weatherization Assistance Program Technical Assistance Center (WAPTAC) http: //www. waptac. org/
www. epa. gov/iaq/climatechange Additional Resources • EPA’s Indoor Air Quality Web site: www. epa. gov/iaqq • Climate Change: www. epa. gov/climatechange// • The Inside Story: A Guide to Indoor Air Quality: www. epa. gov/iaq/pubs/insidest. html • ENERGY STAR Home Improvement: www. energystar. gov/homeimprovementt • Mold and Moisture: www. epa. gov/moldd • Weatherization Assistance Program Technical Assistance Center (WAPTAC) http: //www. waptac. org/


