0f7f654b19a3713a2f6631b04e7b5756.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Weak Interacting Holographic QCD Doron Gazit Institute for Nuclear Theory University of Washington & Ho-Ung Yee ICTP, Trieste Phys. Lett. B (2008), doi: 10. 1016/j. physletb. 2008. 10. 045, ar. Xiv: 0807. 0607
Weak Interacting Holographic QCD Doron Gazit Institute for Nuclear Theory University of Washington & Ho-Ung Yee ICTP, Trieste Phys. Lett. B (2008), doi: 10. 1016/j. physletb. 2008. 10. 045, ar. Xiv: 0807. 0607
 Large N QCD has a dual classical theory in 5 -D? ! • Large N factorization of gauge invariant operators: • Implies a classical theory for gauge invariant operators (AKA master fields). • RG running survives the large N limit, thus the master field is a function of the energy scale: • The RG equations constrain flow in this scale • Holographic QCD is a gravitational theory of gauge invariant fields in 5 dimensions. • 5 th dimension corresponds roughly to the energy scale. 2 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
Large N QCD has a dual classical theory in 5 -D? ! • Large N factorization of gauge invariant operators: • Implies a classical theory for gauge invariant operators (AKA master fields). • RG running survives the large N limit, thus the master field is a function of the energy scale: • The RG equations constrain flow in this scale • Holographic QCD is a gravitational theory of gauge invariant fields in 5 dimensions. • 5 th dimension corresponds roughly to the energy scale. 2 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
 Things that we know Ad. S/CFT Duality proposal N=4 Super Yang-Mills theory in (3+1)D for Nc ∞, g. YM 0 and fixed but large is equivalent to Type IIB Supergravity in Ad. S 5×S 5 with size l¼ Mandalcena 1998 3 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
Things that we know Ad. S/CFT Duality proposal N=4 Super Yang-Mills theory in (3+1)D for Nc ∞, g. YM 0 and fixed but large is equivalent to Type IIB Supergravity in Ad. S 5×S 5 with size l¼ Mandalcena 1998 3 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
 We thus expect the dual theory of QCD… • In the UV regime: highly nonlocal, corresponding to asymptotic freedom. • In the IR regime: local, corresponding to the strongly correlated QCD. • Thus, current models of Holographic QCD model the gravitational dual as a local theory. • Properties of existing models of Holographic QCD: • Chiral symmetry. • Confinement. • Explain experimental observables to 20%. 4 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
We thus expect the dual theory of QCD… • In the UV regime: highly nonlocal, corresponding to asymptotic freedom. • In the IR regime: local, corresponding to the strongly correlated QCD. • Thus, current models of Holographic QCD model the gravitational dual as a local theory. • Properties of existing models of Holographic QCD: • Chiral symmetry. • Confinement. • Explain experimental observables to 20%. 4 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
 Motivation for Weak Interacting Holographic QCD • Many important processes include weak interaction and low-energy QCD. • Numerical calculation of observables from first principles QCD possible only using lattice calculations. • Weak interacting Holographic QCD will provide an additional tool for estimating Hadronic processes. 5 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
Motivation for Weak Interacting Holographic QCD • Many important processes include weak interaction and low-energy QCD. • Numerical calculation of observables from first principles QCD possible only using lattice calculations. • Weak interacting Holographic QCD will provide an additional tool for estimating Hadronic processes. 5 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
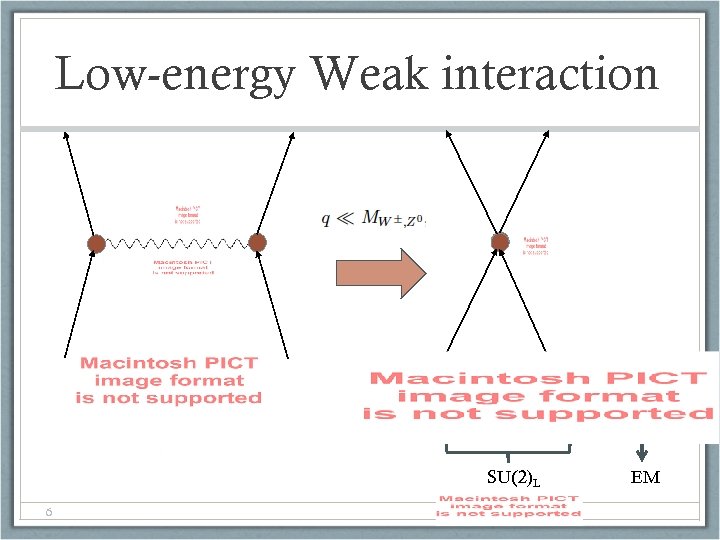 Low-energy Weak interaction SU(2)L 6 EM
Low-energy Weak interaction SU(2)L 6 EM
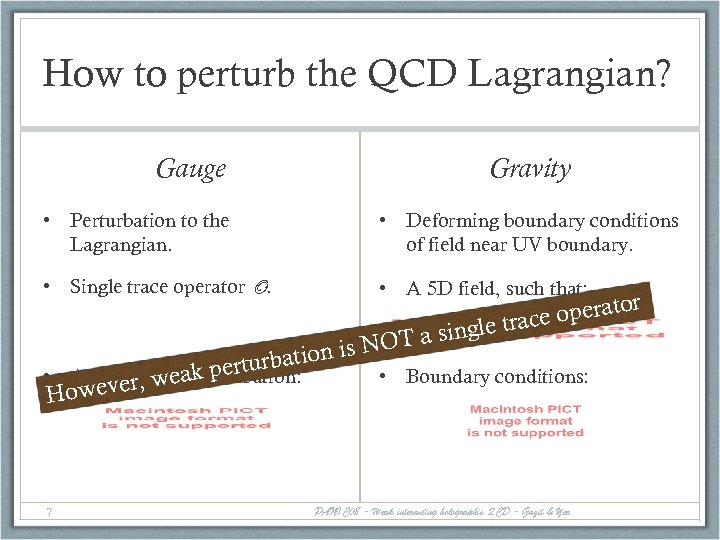 How to perturb the QCD Lagrangian? Gauge Gravity • Perturbation to the Lagrangian. • Deforming boundary conditions of field near UV boundary. • Single trace operator O. • A 5 D field, such that: urbation t • A Lagrangian k per weapertutbation: r, Howeve 7 l g OT a sin is N r to ce opera e tra • Boundary conditions: PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
How to perturb the QCD Lagrangian? Gauge Gravity • Perturbation to the Lagrangian. • Deforming boundary conditions of field near UV boundary. • Single trace operator O. • A 5 D field, such that: urbation t • A Lagrangian k per weapertutbation: r, Howeve 7 l g OT a sin is N r to ce opera e tra • Boundary conditions: PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
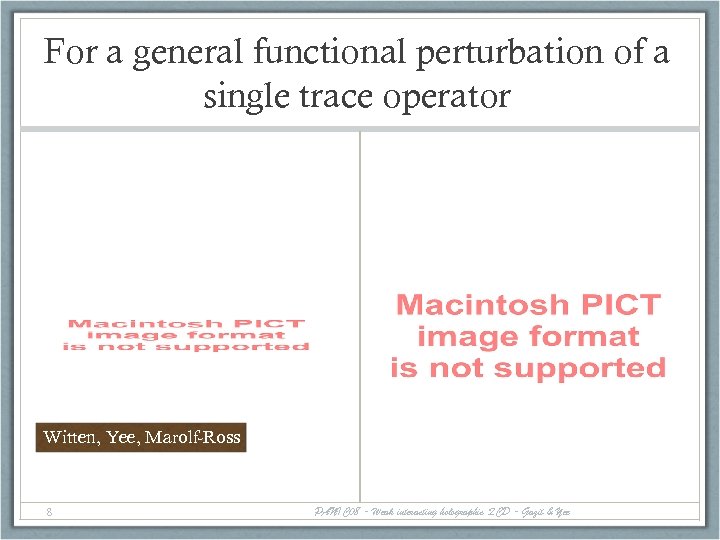 For a general functional perturbation of a single trace operator Witten, Yee, Marolf-Ross 8 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
For a general functional perturbation of a single trace operator Witten, Yee, Marolf-Ross 8 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
 Implementation The idea is general enough to implement in any Holographic Model. We demonstrated on two models: Top – Down Model: Sakai-Sugimoto Model [Sakai and Sugimoto, Witten] Bottom – Up Model: Hard/Soft Wall Model [Erlich-Katz-Son-Stephanov, Da Rold -Pomarol]. Both models lead to essentially the same results, as the 5 D gauge field includes pions and spin-1 massive bosons when we expand it in terms of 4 D modes. 9 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
Implementation The idea is general enough to implement in any Holographic Model. We demonstrated on two models: Top – Down Model: Sakai-Sugimoto Model [Sakai and Sugimoto, Witten] Bottom – Up Model: Hard/Soft Wall Model [Erlich-Katz-Son-Stephanov, Da Rold -Pomarol]. Both models lead to essentially the same results, as the 5 D gauge field includes pions and spin-1 massive bosons when we expand it in terms of 4 D modes. 9 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
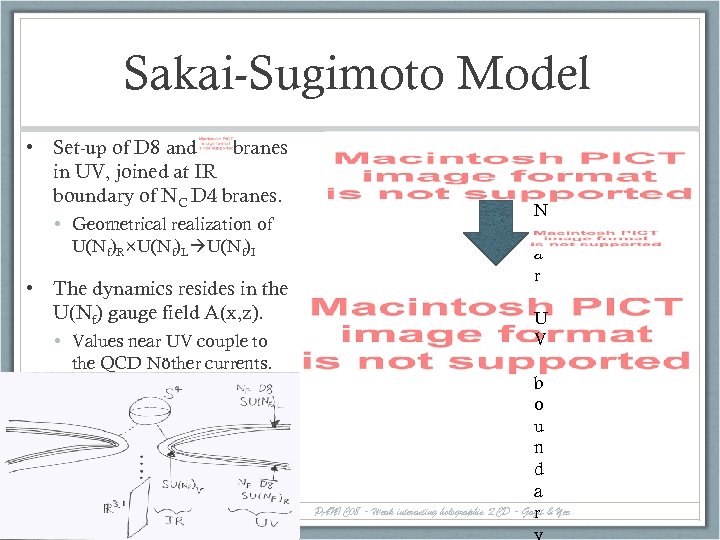 Sakai-Sugimoto Model • Set-up of D 8 and branes in UV, joined at IR boundary of NC D 4 branes. • Geometrical realization of U(Nf)R×U(Nf)L U(Nf)I • The dynamics resides in the U(Nf) gauge field A(x, z). • Values near UV couple to the QCD Nöther currents. 10 N e a r U V b o u n d a PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee r y
Sakai-Sugimoto Model • Set-up of D 8 and branes in UV, joined at IR boundary of NC D 4 branes. • Geometrical realization of U(Nf)R×U(Nf)L U(Nf)I • The dynamics resides in the U(Nf) gauge field A(x, z). • Values near UV couple to the QCD Nöther currents. 10 N e a r U V b o u n d a PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee r y
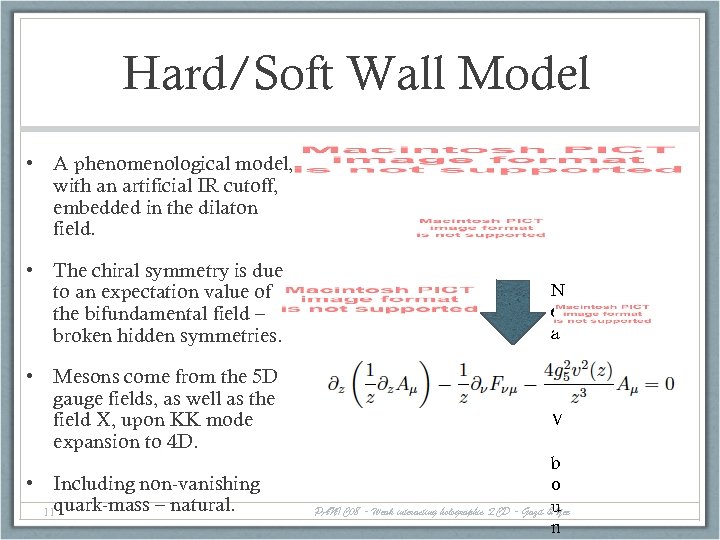 Hard/Soft Wall Model • A phenomenological model, with an artificial IR cutoff, embedded in the dilaton field. • The chiral symmetry is due to an expectation value of the bifundamental field – broken hidden symmetries. • Mesons come from the 5 D gauge fields, as well as the field X, upon KK mode expansion to 4 D. • Including non-vanishing 11 quark-mass – natural. N e a r U V b o PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit &u Yee n
Hard/Soft Wall Model • A phenomenological model, with an artificial IR cutoff, embedded in the dilaton field. • The chiral symmetry is due to an expectation value of the bifundamental field – broken hidden symmetries. • Mesons come from the 5 D gauge fields, as well as the field X, upon KK mode expansion to 4 D. • Including non-vanishing 11 quark-mass – natural. N e a r U V b o PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit &u Yee n
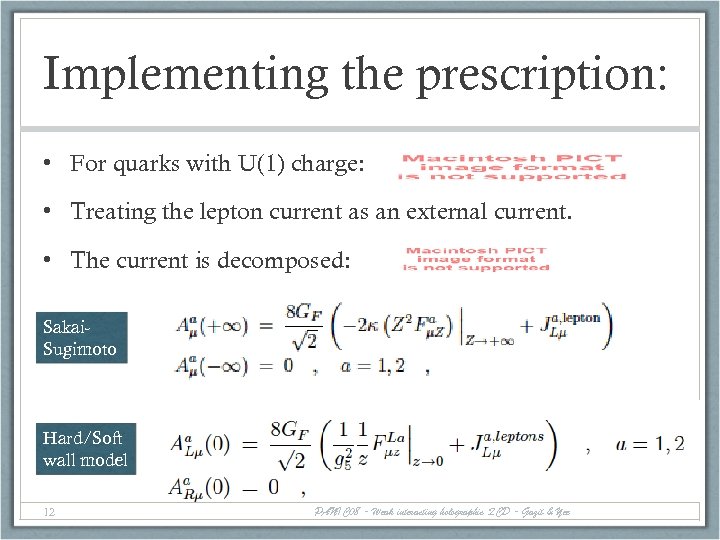 Implementing the prescription: • For quarks with U(1) charge: • Treating the lepton current as an external current. • The current is decomposed: Sakai. Sugimoto Hard/Soft wall model 12 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
Implementing the prescription: • For quarks with U(1) charge: • Treating the lepton current as an external current. • The current is decomposed: Sakai. Sugimoto Hard/Soft wall model 12 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
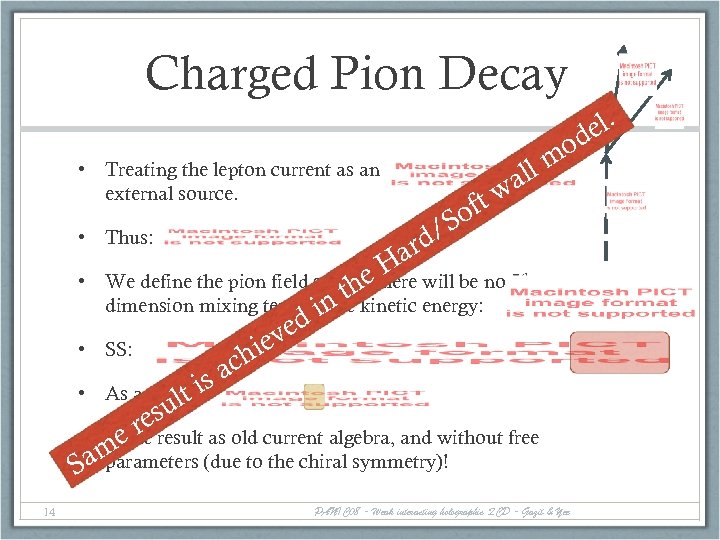 Charged Pion Decay el. d o ll m • Treating the lepton current as an external source. wa ft So / ard H • Thus: e • We define the pion field so that there will be no 5 th thkinetic energy: dimension mixing term in n i the • SS: • As a result is lt – ed iev h ac esu as old current algebra, and without free • Same result er am S parameters (due to the chiral symmetry)! 14 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
Charged Pion Decay el. d o ll m • Treating the lepton current as an external source. wa ft So / ard H • Thus: e • We define the pion field so that there will be no 5 th thkinetic energy: dimension mixing term in n i the • SS: • As a result is lt – ed iev h ac esu as old current algebra, and without free • Same result er am S parameters (due to the chiral symmetry)! 14 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
 How to calculate different reactions? • Write equation of motion for the global gauge field (i. e. the U(NF) current). • Solve it with the prescribed boundary conditions. • If you’d like pions to be involved, do it in the previous gauge fixing for Az. • For reactions that include nucleons, choose a model for baryons, and calculate baryon-pion coupling from the kinetic term, and from magnetic type of couplings: 15 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
How to calculate different reactions? • Write equation of motion for the global gauge field (i. e. the U(NF) current). • Solve it with the prescribed boundary conditions. • If you’d like pions to be involved, do it in the previous gauge fixing for Az. • For reactions that include nucleons, choose a model for baryons, and calculate baryon-pion coupling from the kinetic term, and from magnetic type of couplings: 15 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
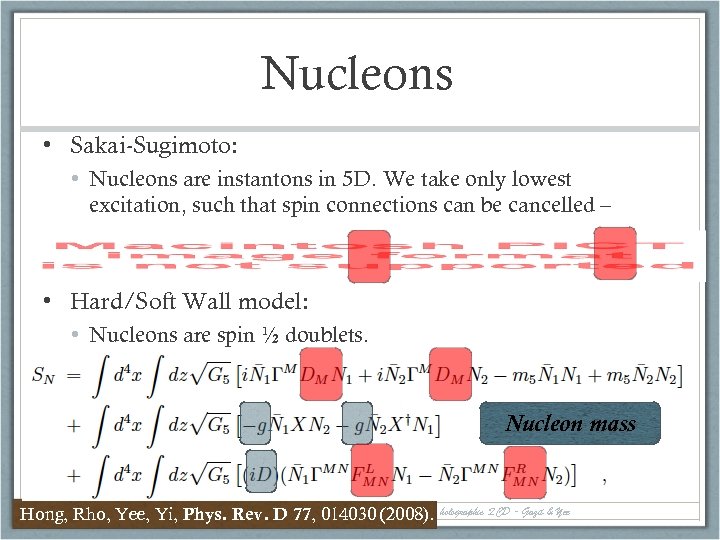 Nucleons • Sakai-Sugimoto: • Nucleons are instantons in 5 D. We take only lowest excitation, such that spin connections can be cancelled – • Hard/Soft Wall model: • Nucleons are spin ½ doublets. Nucleon mass 16 Hong, Rho, Yee, Yi, Phys. Rev. D 77, PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee 014030 (2008).
Nucleons • Sakai-Sugimoto: • Nucleons are instantons in 5 D. We take only lowest excitation, such that spin connections can be cancelled – • Hard/Soft Wall model: • Nucleons are spin ½ doublets. Nucleon mass 16 Hong, Rho, Yee, Yi, Phys. Rev. D 77, PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee 014030 (2008).
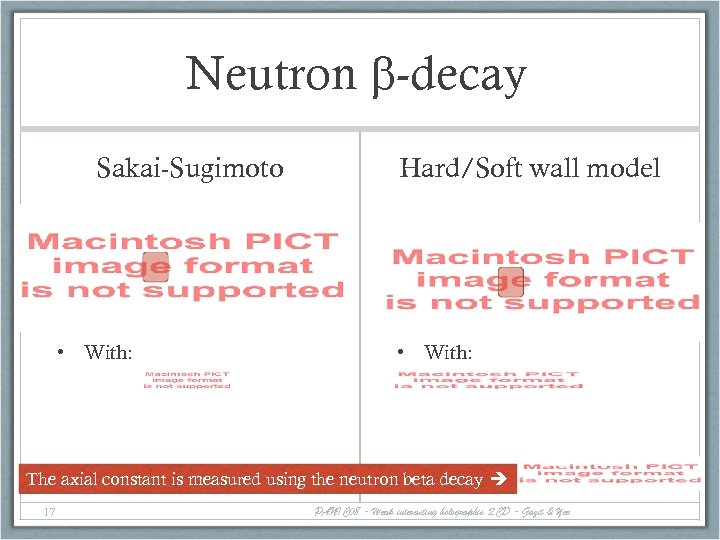 Neutron b-decay Sakai-Sugimoto • With: Hard/Soft wall model • With: The axial constant is measured using the neutron beta decay 17 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
Neutron b-decay Sakai-Sugimoto • With: Hard/Soft wall model • With: The axial constant is measured using the neutron beta decay 17 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
 Parity non-conserving pion-nucleon coupling • First example without an external source. • We are interested in parity violating couplings of mesons to the nucleons. • To this end, we consider only charged pion-nucleon coupling. • In both models, the result in the zero q limit is identical to the current algebra result: • Still, a lot to be done! 18 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
Parity non-conserving pion-nucleon coupling • First example without an external source. • We are interested in parity violating couplings of mesons to the nucleons. • To this end, we consider only charged pion-nucleon coupling. • In both models, the result in the zero q limit is identical to the current algebra result: • Still, a lot to be done! 18 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
 Conclusions • We have outlined a prescription to include weak interactions in the framework of holographic QCD. • Applicable up to energies of a few Ge. V, when strong coupling is still valid. • We have shown its strength by using Sakai-Sugimoto and Hard/Soft wall models to calculate few exemplar reactions. • The current approach, contrary to other approaches (such as c. PT), gives not only the operator structure, but the numerical coefficients, to about 20%, and valid for energies above the chiral limit. 19 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee
Conclusions • We have outlined a prescription to include weak interactions in the framework of holographic QCD. • Applicable up to energies of a few Ge. V, when strong coupling is still valid. • We have shown its strength by using Sakai-Sugimoto and Hard/Soft wall models to calculate few exemplar reactions. • The current approach, contrary to other approaches (such as c. PT), gives not only the operator structure, but the numerical coefficients, to about 20%, and valid for energies above the chiral limit. 19 PANIC 08 - Weak interacting holographic QCD - Gazit & Yee


