fa67b85fe0b358e7eaa413bec7b20804.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 “We the People”: The Constitutional Convention & Creation of the Constitution Honors U. S. History 5 th period Ms. Meghan O’Malley
“We the People”: The Constitutional Convention & Creation of the Constitution Honors U. S. History 5 th period Ms. Meghan O’Malley
 OBJECTIVES The students will: ØBe able to explain the factors that led to the Constitutional Convention and the key men involved ØInvestigate the possible reason(s) why the framers of the Constitution did not abolish slavery and the slave trade, using the inquiry instructional model ØBe able to explain the purposes, issues, compromises, elements, and ratification of the Constitution
OBJECTIVES The students will: ØBe able to explain the factors that led to the Constitutional Convention and the key men involved ØInvestigate the possible reason(s) why the framers of the Constitution did not abolish slavery and the slave trade, using the inquiry instructional model ØBe able to explain the purposes, issues, compromises, elements, and ratification of the Constitution
 Would the Civil War still have occurred if the framers of the Constitution had abolished slavery?
Would the Civil War still have occurred if the framers of the Constitution had abolished slavery?
 The End of the Revolution Ø Ø Ø October 19, 1781: CORNWALLIS surrenders to Washington at YORKTOWN September 3, 1783: TREATY OF PARIS signed December 23, 1783: WASHINGTON gives up his commission
The End of the Revolution Ø Ø Ø October 19, 1781: CORNWALLIS surrenders to Washington at YORKTOWN September 3, 1783: TREATY OF PARIS signed December 23, 1783: WASHINGTON gives up his commission
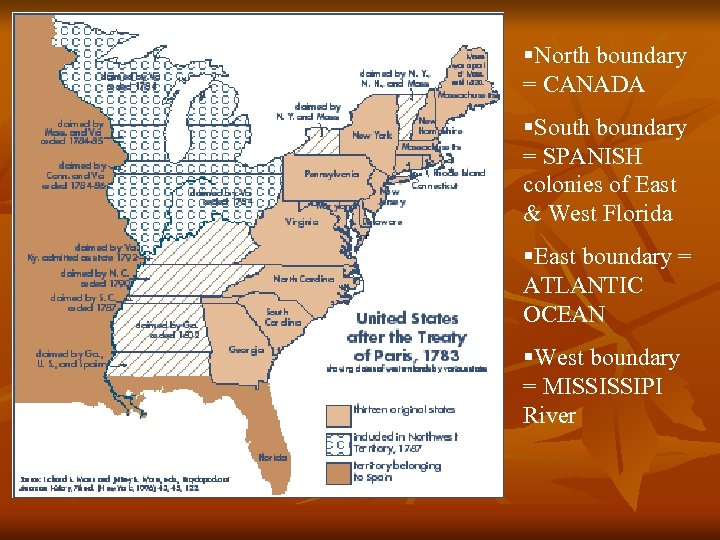 §North boundary = CANADA §South boundary = SPANISH colonies of East & West Florida §East boundary = ATLANTIC OCEAN §West boundary = MISSISSIPI River
§North boundary = CANADA §South boundary = SPANISH colonies of East & West Florida §East boundary = ATLANTIC OCEAN §West boundary = MISSISSIPI River
 Articles of Confederation Ø Ø Ø 1776 Continental Congress = LOOSE collection of DELEGATES Americans were citizens of STATES, not a NATION = “United States ARE”, not “United States IS” 1781: Continental Congress approved ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
Articles of Confederation Ø Ø Ø 1776 Continental Congress = LOOSE collection of DELEGATES Americans were citizens of STATES, not a NATION = “United States ARE”, not “United States IS” 1781: Continental Congress approved ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
 Elements of Articles Ø Ø Ø United States needed CENTRAL GOVERNMENT after breaking free from the British monarchy Established LIMITED national government ONE BRANCH = legislature made up of delegates from all the states
Elements of Articles Ø Ø Ø United States needed CENTRAL GOVERNMENT after breaking free from the British monarchy Established LIMITED national government ONE BRANCH = legislature made up of delegates from all the states
 Issues with the Articles 1. STATES were MORE POWERFUL than national government 2. No EXECUTIVE or JUDICIAL branches 3. National government LACKED POWER to TAX states 4. Any action involving MONEY had to pass with 9 of 13 votes 5. Changes needed UNANIMOUS CONSENT by states
Issues with the Articles 1. STATES were MORE POWERFUL than national government 2. No EXECUTIVE or JUDICIAL branches 3. National government LACKED POWER to TAX states 4. Any action involving MONEY had to pass with 9 of 13 votes 5. Changes needed UNANIMOUS CONSENT by states
 Problems resulting from Articles 1. Economic Ø Some state governments printed their own currency NO single NATIONAL monetary system Ø Some states taxed goods en route to other states caused CONFLICT in interstate COMMERCE Ø Congress LACKED AUTHORITY to control commerce
Problems resulting from Articles 1. Economic Ø Some state governments printed their own currency NO single NATIONAL monetary system Ø Some states taxed goods en route to other states caused CONFLICT in interstate COMMERCE Ø Congress LACKED AUTHORITY to control commerce
 Shays’ Rebellion Ø Ø Ø States passed HIGH TAXES in order to pay off debts MASSACHUSETTS supporters of the tax generally lived in eastern region of state, but farmers in western region were most affected by tax FARMERS lost possessions because of debt
Shays’ Rebellion Ø Ø Ø States passed HIGH TAXES in order to pay off debts MASSACHUSETTS supporters of the tax generally lived in eastern region of state, but farmers in western region were most affected by tax FARMERS lost possessions because of debt
 Shays’ Rebellion, cont. Ø Daniel Shays Ø Ø Ø War veteran Massachusetts farmer Led an INSURRECTION against the Massachusetts government in 1786 Congress COULD NOT send an army or force Massachusetts to intervene in the rebellion Rebellion finally ended in January 1787 when STATE GOVERNMENT sent an army
Shays’ Rebellion, cont. Ø Daniel Shays Ø Ø Ø War veteran Massachusetts farmer Led an INSURRECTION against the Massachusetts government in 1786 Congress COULD NOT send an army or force Massachusetts to intervene in the rebellion Rebellion finally ended in January 1787 when STATE GOVERNMENT sent an army
 Problems resulting from Articles 2. Political Ø Could not enforce LEGISLATION Ø EACH STATE controlled its own taxes, currency, and militia Ø National government could not force states to submit to NATIONAL obligations
Problems resulting from Articles 2. Political Ø Could not enforce LEGISLATION Ø EACH STATE controlled its own taxes, currency, and militia Ø National government could not force states to submit to NATIONAL obligations
 Problems resulting from Articles 3. Too much power given to “ordinary, ” “lesseducated citizens” Ø NATIONALISTS Ø 1786 = ANNAPOLIS Convention
Problems resulting from Articles 3. Too much power given to “ordinary, ” “lesseducated citizens” Ø NATIONALISTS Ø 1786 = ANNAPOLIS Convention
 Constitutional Convention - - May-September 1787, State House, PHILADELPHIA, PA 55 delegates from all states except RHODE ISLAND
Constitutional Convention - - May-September 1787, State House, PHILADELPHIA, PA 55 delegates from all states except RHODE ISLAND
 Purposes of the Convention 1. 2. 3. 4. AMEND the Articles of Confederation Make constitutional law the SUPREME LAW of the land Allow the states to retain some freedom to GOVERN THEMSELVES Establish LIMITS on government authority
Purposes of the Convention 1. 2. 3. 4. AMEND the Articles of Confederation Make constitutional law the SUPREME LAW of the land Allow the states to retain some freedom to GOVERN THEMSELVES Establish LIMITS on government authority
 Key delegates at Convention § George Washington Ø Unanimously elected PRESIDENT of convention Ø Presided IMPARTIALLY Ø Influenced creation of SINGLE EXECUTIVE as one of the three branches of government
Key delegates at Convention § George Washington Ø Unanimously elected PRESIDENT of convention Ø Presided IMPARTIALLY Ø Influenced creation of SINGLE EXECUTIVE as one of the three branches of government
 Key delegates at Convention, cont. James Madison Ø “FATHER of the CONSTITUTION” Ø Gained NATIONAL reputation as member of Continental Congress Ø Led many of the DEBATES, took many NOTES of the proceedings Ø Author of VIRGINIA PLAN and later the BILL OF RIGHTS n
Key delegates at Convention, cont. James Madison Ø “FATHER of the CONSTITUTION” Ø Gained NATIONAL reputation as member of Continental Congress Ø Led many of the DEBATES, took many NOTES of the proceedings Ø Author of VIRGINIA PLAN and later the BILL OF RIGHTS n
 Key delegates at Convention, cont. n Other important/famous delegates: 1) Alexander HAMILTON (NY) - Became Secretary of Treasury - Primary author of The Federalist Papers 2) Benjamin FRANKLIN (PA) - Member of colonial legislature - Commissioner to France - Signer of Declaration of Independence 3) George MASON (VA) - Author of Virginia Bill of Rights
Key delegates at Convention, cont. n Other important/famous delegates: 1) Alexander HAMILTON (NY) - Became Secretary of Treasury - Primary author of The Federalist Papers 2) Benjamin FRANKLIN (PA) - Member of colonial legislature - Commissioner to France - Signer of Declaration of Independence 3) George MASON (VA) - Author of Virginia Bill of Rights
 Preamble of the Constitution “We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promot the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America” http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=a. Nb 9 Ao. Y 5 XXE
Preamble of the Constitution “We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promot the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America” http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=a. Nb 9 Ao. Y 5 XXE
 Issues & Compromises
Issues & Compromises
 Issue #1: Amend or Abandon First major issue centered on whether to 1) AMEND the existing Articles of Confederation or 2) ABANDON the Articles and create a new government and governing document n Decision: Convention had to go BEYOND its authority in order to REPLACE the Articles with a new system n
Issue #1: Amend or Abandon First major issue centered on whether to 1) AMEND the existing Articles of Confederation or 2) ABANDON the Articles and create a new government and governing document n Decision: Convention had to go BEYOND its authority in order to REPLACE the Articles with a new system n
 Issue #2: State Representation Ø Virginia Plan Ø Elements: BI-CAMERAL (two-house) legislature Ø # of representatives IN PROPORTION to number of citizens Ø Power to TAX and regulate commerce Ø Power to VETO any act of state legislature Ø 3 BRANCHES of government: 1. LEGISLATIVE 2. EXECUTIVE, 3. JUDICIAL Ø NATIONAL government MORE POWERFUL than state government Ø
Issue #2: State Representation Ø Virginia Plan Ø Elements: BI-CAMERAL (two-house) legislature Ø # of representatives IN PROPORTION to number of citizens Ø Power to TAX and regulate commerce Ø Power to VETO any act of state legislature Ø 3 BRANCHES of government: 1. LEGISLATIVE 2. EXECUTIVE, 3. JUDICIAL Ø NATIONAL government MORE POWERFUL than state government Ø
 ØNew Jersey Plan Ø Differences from Virginia Plan Ø UNICAMERAL (onehouse) legislature Ø Every state would have ONE VOTE, regardless of population Ø Kept STATE governments MORE POWERFUL than national government
ØNew Jersey Plan Ø Differences from Virginia Plan Ø UNICAMERAL (onehouse) legislature Ø Every state would have ONE VOTE, regardless of population Ø Kept STATE governments MORE POWERFUL than national government
 Great Compromise Ø Legislative branch with TWO HOUSES (Virginia Plan) Ø SENATE = each state had same # of representatives (New Jersey Plan) Ø HOUSE of Representatives = # of representatives would be based on population (Virginia Plan) Ø This compromise BALANCED power between the LARGE and SMALL states
Great Compromise Ø Legislative branch with TWO HOUSES (Virginia Plan) Ø SENATE = each state had same # of representatives (New Jersey Plan) Ø HOUSE of Representatives = # of representatives would be based on population (Virginia Plan) Ø This compromise BALANCED power between the LARGE and SMALL states
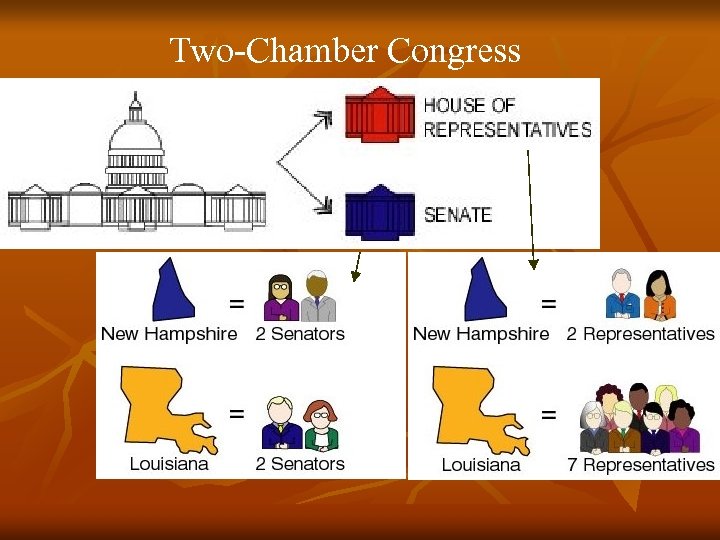 Two-Chamber Congress
Two-Chamber Congress
 Issue #3: Slaves and Population INQUIRY ACTIVITY Why did the framers of the Constitution not abolish slavery?
Issue #3: Slaves and Population INQUIRY ACTIVITY Why did the framers of the Constitution not abolish slavery?
 Issue #3: Slaves and Population n Slaves as PEOPLE: the LARGER the population = the MORE POWER in the House of Representatives for SOUTHERN states Slaves as PROPERTY: the FEDERALgovernment would get tax money from Southern states **Article 1, Section 9, Clause 1 of Constitution – slave trade could not be prohibited before 1808**
Issue #3: Slaves and Population n Slaves as PEOPLE: the LARGER the population = the MORE POWER in the House of Representatives for SOUTHERN states Slaves as PROPERTY: the FEDERALgovernment would get tax money from Southern states **Article 1, Section 9, Clause 1 of Constitution – slave trade could not be prohibited before 1808**
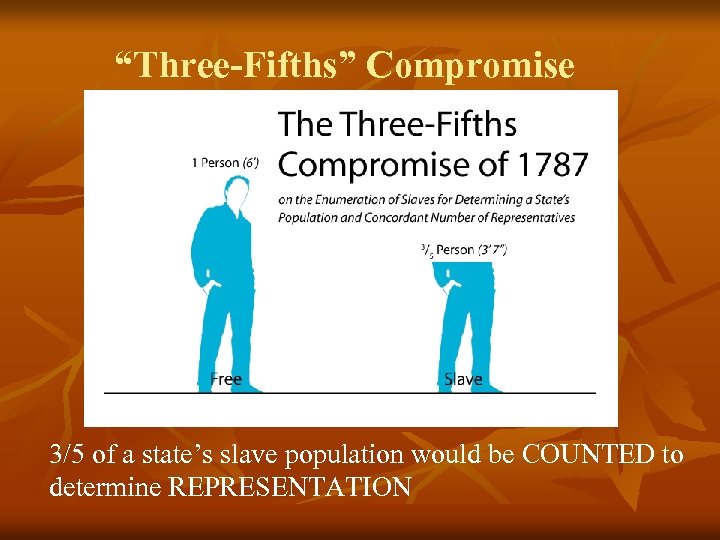 “Three-Fifths” Compromise 3/5 of a state’s slave population would be COUNTED to determine REPRESENTATION
“Three-Fifths” Compromise 3/5 of a state’s slave population would be COUNTED to determine REPRESENTATION
 Elements of the Constitution Ø Division of power in 2 ways 1. BETWEEN the federal and state governments
Elements of the Constitution Ø Division of power in 2 ways 1. BETWEEN the federal and state governments
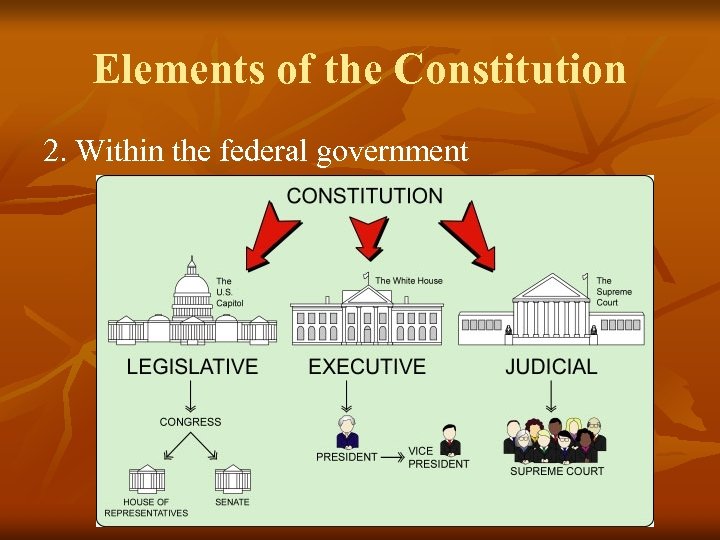 Elements of the Constitution 2. Within the federal government
Elements of the Constitution 2. Within the federal government
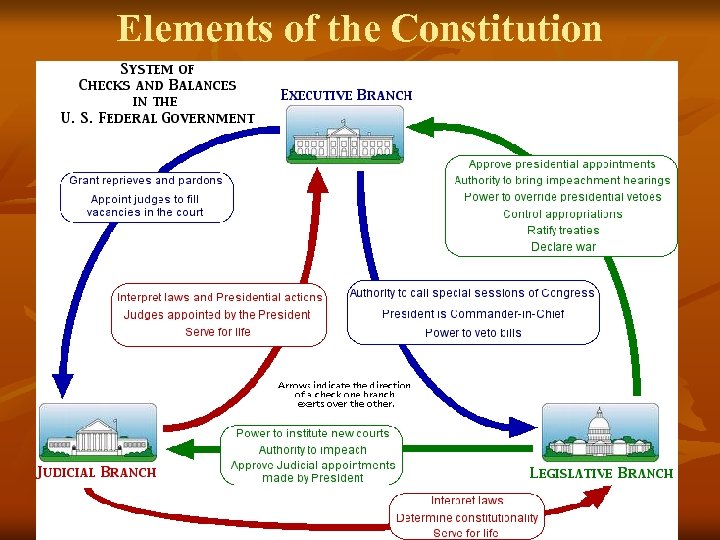 Elements of the Constitution
Elements of the Constitution
 Ratifying the Constitution n 9 of the 13 states had to RATIFY the Constitution for it to become law Special CONVENTIONS in each state voted on the ratification Conflict between the FEDERALISTS and ANTI-FEDERALISTS
Ratifying the Constitution n 9 of the 13 states had to RATIFY the Constitution for it to become law Special CONVENTIONS in each state voted on the ratification Conflict between the FEDERALISTS and ANTI-FEDERALISTS
 Federalists vs. anti-Federalists n SUPPORTED Constitution n Wanted STRONG national government n No one FACTION could dominate n Feared PEOPLE more than government n THE FEDERALIST PAPERS (written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay)
Federalists vs. anti-Federalists n SUPPORTED Constitution n Wanted STRONG national government n No one FACTION could dominate n Feared PEOPLE more than government n THE FEDERALIST PAPERS (written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay)
 Federalists vs. anti-Federalists n Anti-Federalists n OPPOSED the Constitution n Wanted strong STATE governments n Saw Constitution as BETRAYAL of what was gained through Revolution n Feared GOVERNMENT more than the people
Federalists vs. anti-Federalists n Anti-Federalists n OPPOSED the Constitution n Wanted strong STATE governments n Saw Constitution as BETRAYAL of what was gained through Revolution n Feared GOVERNMENT more than the people
 Victory for Federalists n Reasons for Federalist victory n n n Articles of Confederation were FLAWED Unified around SPECIFIC PLAN – the Constitution WELL-ORGANIZED, national group Had WASHINGTON’S support DELAWARE was the first state to ratify the Constitution; Rhode Island was the last in 1790
Victory for Federalists n Reasons for Federalist victory n n n Articles of Confederation were FLAWED Unified around SPECIFIC PLAN – the Constitution WELL-ORGANIZED, national group Had WASHINGTON’S support DELAWARE was the first state to ratify the Constitution; Rhode Island was the last in 1790
 Exit Ticket: 3, 2, 1 Answer the following prompt on the back of your data source worksheet: -What are 3 things that you learned from this lesson? - What are 2 connections you can make to other historical events or topics you have learned about? - What is 1 thing you would change about this lesson?
Exit Ticket: 3, 2, 1 Answer the following prompt on the back of your data source worksheet: -What are 3 things that you learned from this lesson? - What are 2 connections you can make to other historical events or topics you have learned about? - What is 1 thing you would change about this lesson?


