b8a7edbbc7b71b20b97cdec44b7b4cd8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

We measure ordinary objects either by counting or weighing them, depending on which method is more convenient Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2 nd ed. New York: Mc. Graw-Hill. http: //weyume. com/wp-content/uploads/2011/04/rice. jpg http: //farm 1. static. flickr. com/21/90994367_5613 e 69 fd 9. jpg
Certain nouns can be used to define a collection of objects Dozen = 12 Pair = 2

The mole

The mole (n or mol) is the amount of matter that contains as many entities (atoms, molecules, ions, or other particles) as there atoms in exactly 12 g of the carbon-12 isotope (12 C) • The actual number of atoms in 12 g of carbon-12 was determined experimentally • Avogadro’s number (NA) NA = 6. 02 x 1023 Brown, , E. Le. May, and B. Bursten. 2000. Chemistry: The Central Science. 8 th ed. Phils: Pearson Education Asia Pte. Ltd. Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill.

Just as 1 dozen of oranges contains 12 oranges, 1 mole of matter contains 6. 02 x 1023 entities 1 mole 12 C atoms = 6. 02 x 1023 12 C atoms 1 mole H 2 O molecules = 6. 02 x 1023 H 2 O molecules 1 mole NO 3 - ions = 6. 02 x 1023 NO 3 - ions Brown, , E. Le. May, and B. Bursten. 2000. Chemistry: The Central Science. 8 th ed. Phils: Pearson Education Asia Pte. Ltd. Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill.

Each of these contains one mole of the substance carbon sulfur mercury copper iron Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill.

One mole (or an Avogadro’s number) is an extremely big number • One mole of softdrink cans would cover the surface of the earth to a depth of over 300 kilometers • If we were able to count the number of atoms at a rate of 10 million per second, it would take about 2 billion years to count a mole of atoms

Molar mass
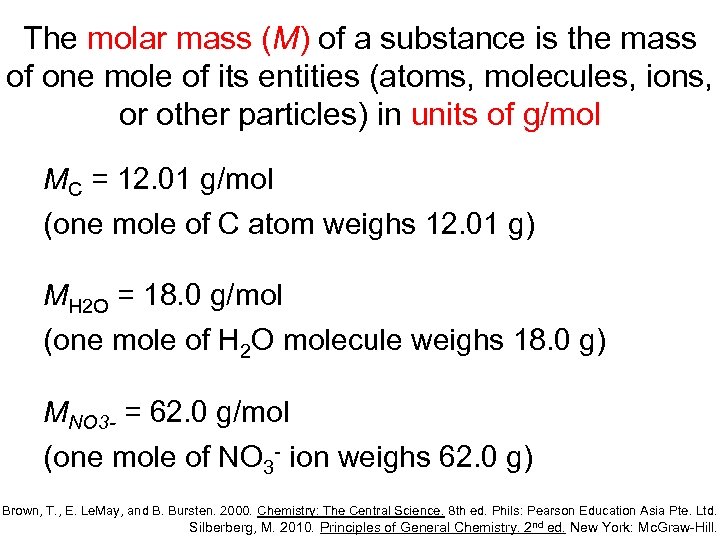
The molar mass (M) of a substance is the mass of one mole of its entities (atoms, molecules, ions, or other particles) in units of g/mol MC = 12. 01 g/mol (one mole of C atom weighs 12. 01 g) MH 2 O = 18. 0 g/mol (one mole of H 2 O molecule weighs 18. 0 g) MNO 3 - = 62. 0 g/mol (one mole of NO 3 - ion weighs 62. 0 g) Brown, T. , E. Le. May, and B. Bursten. 2000. Chemistry: The Central Science. 8 th ed. Phils: Pearson Education Asia Pte. Ltd. Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2 nd ed. New York: Mc. Graw-Hill.

The periodic table is indispensable for calculating the molar mass of a substance • Elements – M is the numerical value from the periodic table MH = 1. 008 g/mol MO = 16. 00 g/mol Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2 nd ed. New York: Mc. Graw-Hill.
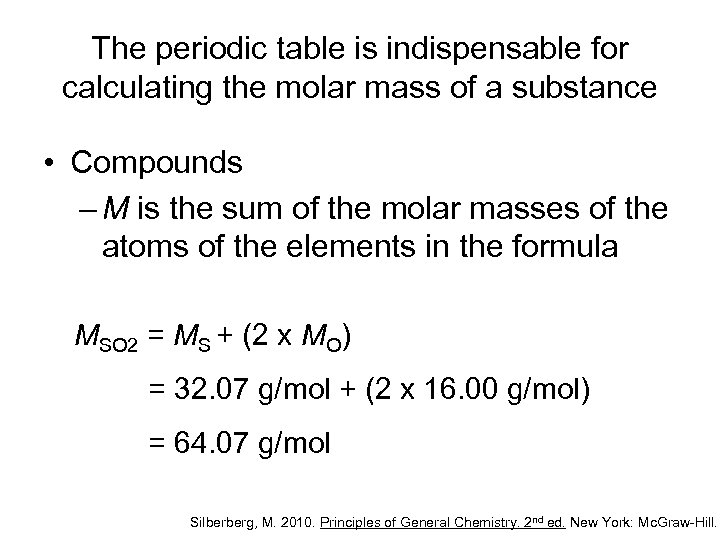
The periodic table is indispensable for calculating the molar mass of a substance • Compounds – M is the sum of the molar masses of the atoms of the elements in the formula MSO 2 = MS + (2 x MO) = 32. 07 g/mol + (2 x 16. 00 g/mol) = 64. 07 g/mol Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2 nd ed. New York: Mc. Graw-Hill.
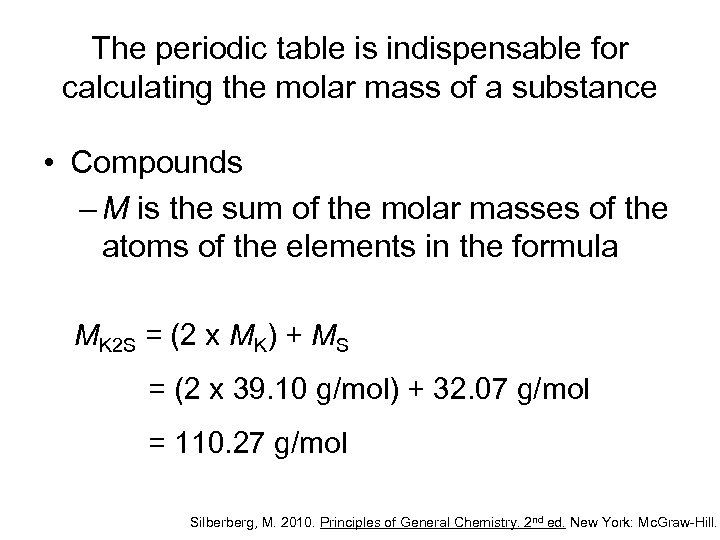
The periodic table is indispensable for calculating the molar mass of a substance • Compounds – M is the sum of the molar masses of the atoms of the elements in the formula MK 2 S = (2 x MK) + MS = (2 x 39. 10 g/mol) + 32. 07 g/mol = 110. 27 g/mol Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2 nd ed. New York: Mc. Graw-Hill.

Interconverting moles, mass, and chemical entities (atoms, molecules, ions, or other particles)

The factor-label method is used to convert from one unit to another 1 peso = 4 25 -centavos 1 peso 4 25 -centavos unit factor 4 25 -centavos 1 peso =1 =1 Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill.
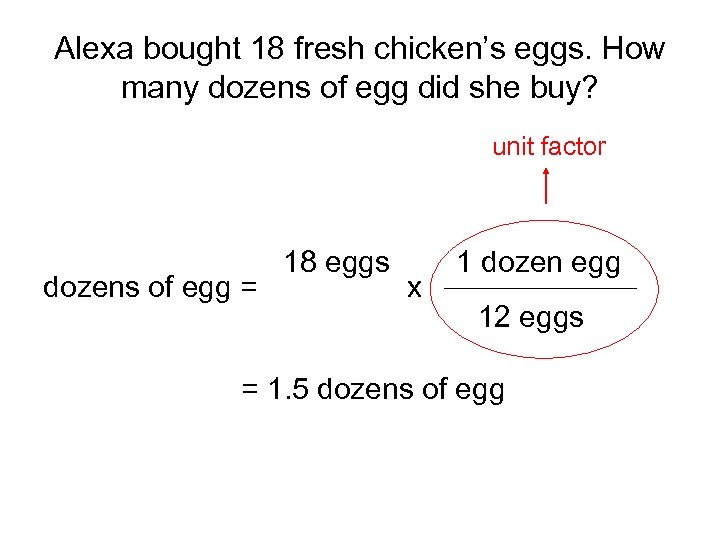
Alexa bought 18 fresh chicken’s eggs. How many dozens of egg did she buy? unit factor dozens of egg = 18 eggs x 1 dozen egg 12 eggs = 1. 5 dozens of egg
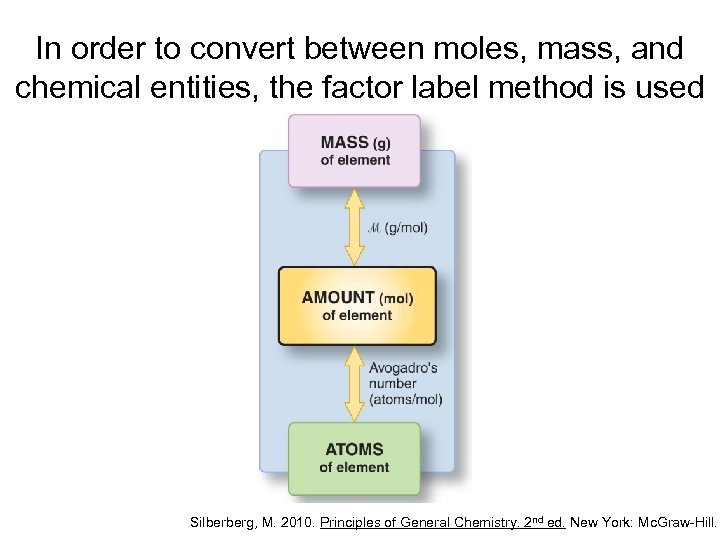
In order to convert between moles, mass, and chemical entities, the factor label method is used Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2 nd ed. New York: Mc. Graw-Hill.
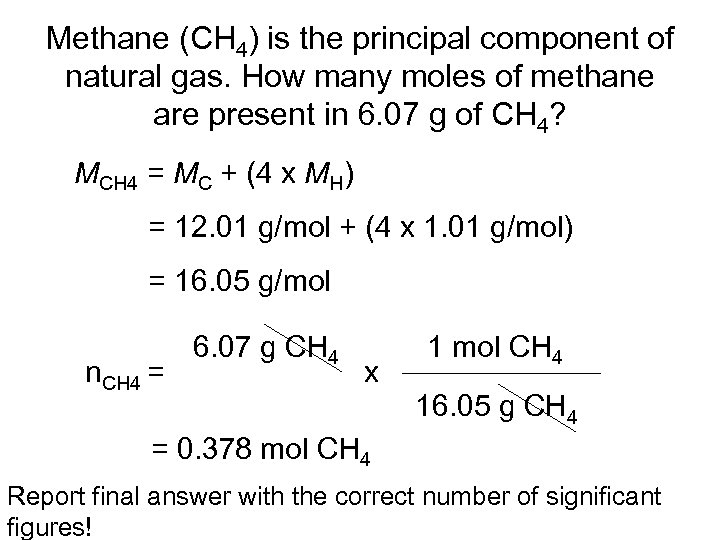
Methane (CH 4) is the principal component of natural gas. How many moles of methane are present in 6. 07 g of CH 4? MCH 4 = MC + (4 x MH) = 12. 01 g/mol + (4 x 1. 01 g/mol) = 16. 05 g/mol n. CH 4 = 6. 07 g CH 4 x 1 mol CH 4 16. 05 g CH 4 = 0. 378 mol CH 4 Report final answer with the correct number of significant figures!
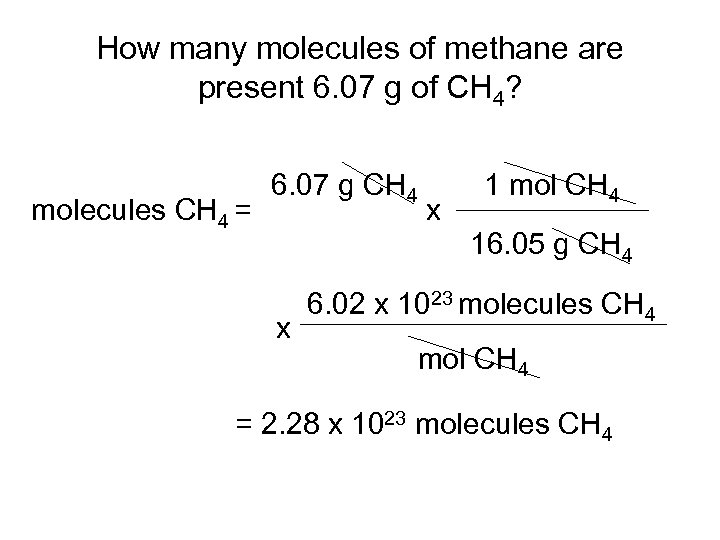
How many molecules of methane are present 6. 07 g of CH 4? molecules CH 4 = 6. 07 g CH 4 x 1 mol CH 4 16. 05 g CH 4 x 6. 02 x 1023 molecules CH 4 mol CH 4 = 2. 28 x 1023 molecules CH 4
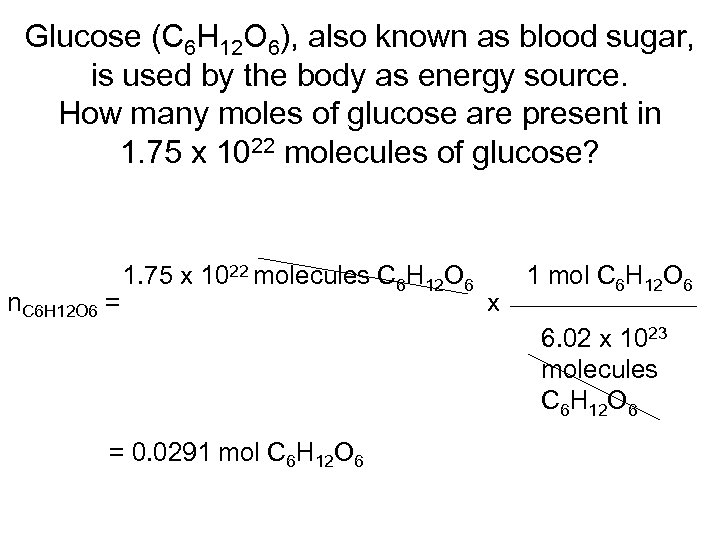
Glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6), also known as blood sugar, is used by the body as energy source. How many moles of glucose are present in 1. 75 x 1022 molecules of glucose? n. C 6 H 12 O 6 = 1. 75 x 1022 molecules C 6 H 12 O 6 x 1 mol C 6 H 12 O 6 6. 02 x 1023 molecules C 6 H 12 O 6 = 0. 0291 mol C 6 H 12 O 6

How many grams of glucose are present in 1. 75 x 1022 molecules of glucose? MC 6 H 12 O 6 = (6 x MC) + (12 x MH) + (6 x MO) = (6 x 12. 01 g/mol) + (12 x 1. 01 g/mol) + (6 x 16. 00 g/mol) = 180. 18 g/mol
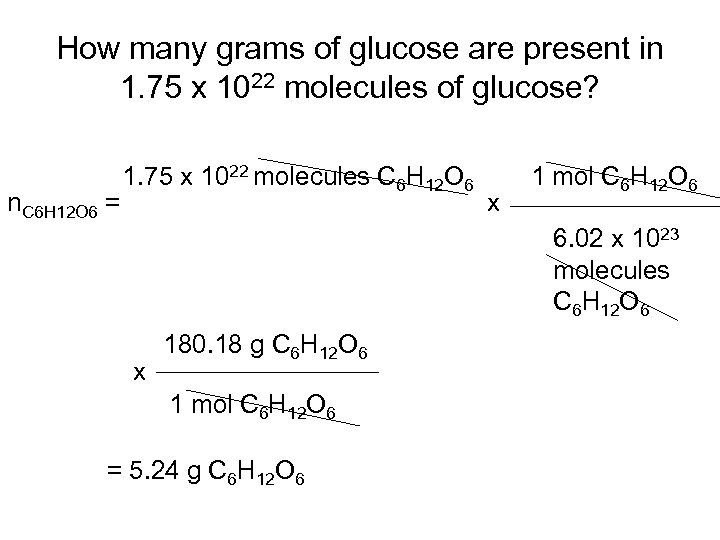
How many grams of glucose are present in 1. 75 x 1022 molecules of glucose? n. C 6 H 12 O 6 = 1. 75 x 1022 molecules C 6 H 12 O 6 x 1 mol C 6 H 12 O 6 6. 02 x 1023 molecules C 6 H 12 O 6 x 180. 18 g C 6 H 12 O 6 1 mol C 6 H 12 O 6 = 5. 24 g C 6 H 12 O 6

Chemical reactions and chemical equations
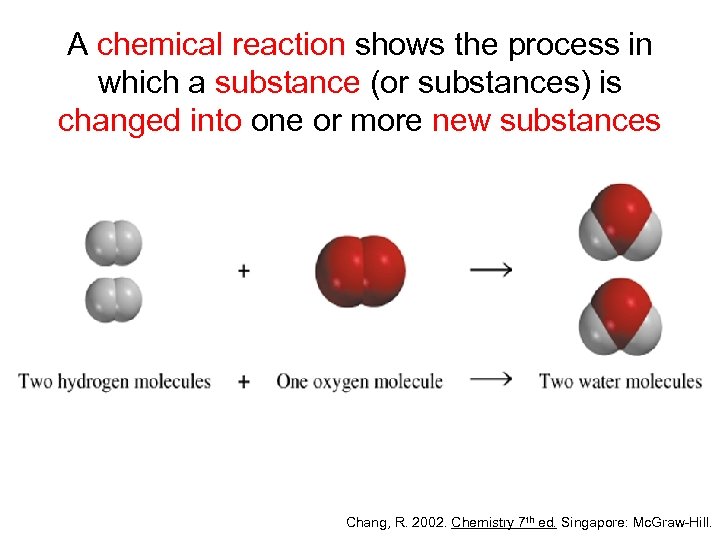
A chemical reaction shows the process in which a substance (or substances) is changed into one or more new substances Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill.
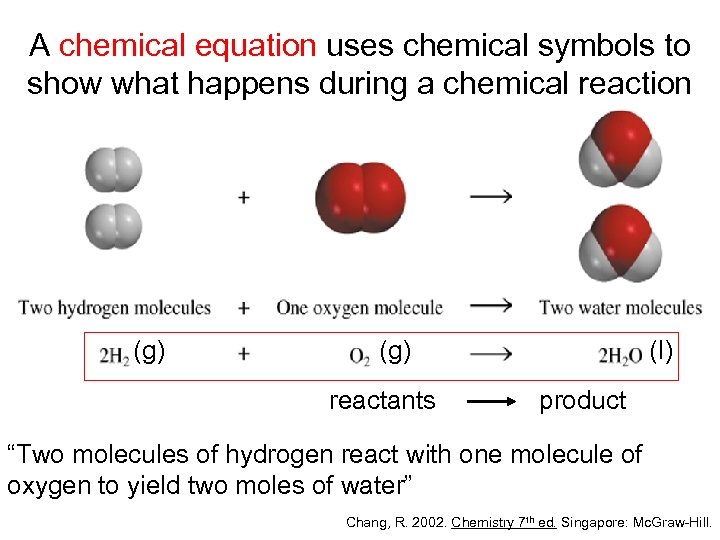
A chemical equation uses chemical symbols to show what happens during a chemical reaction (g) reactants (l) product “Two molecules of hydrogen react with one molecule of oxygen to yield two moles of water” Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill.
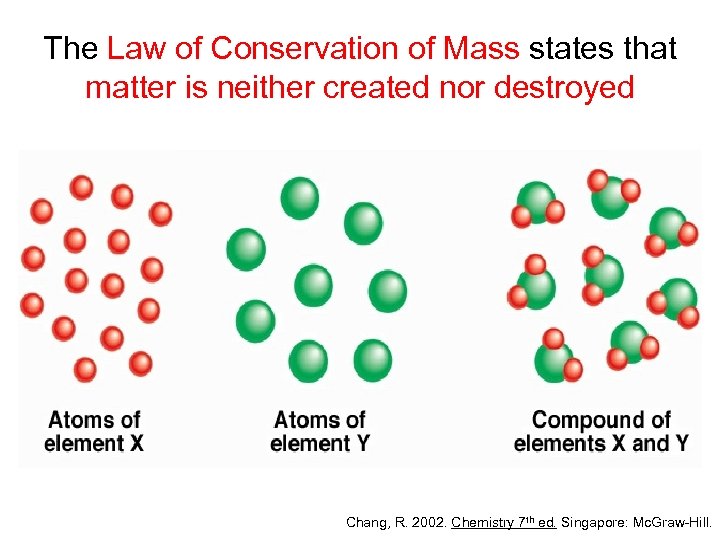
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that matter is neither created nor destroyed Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill.
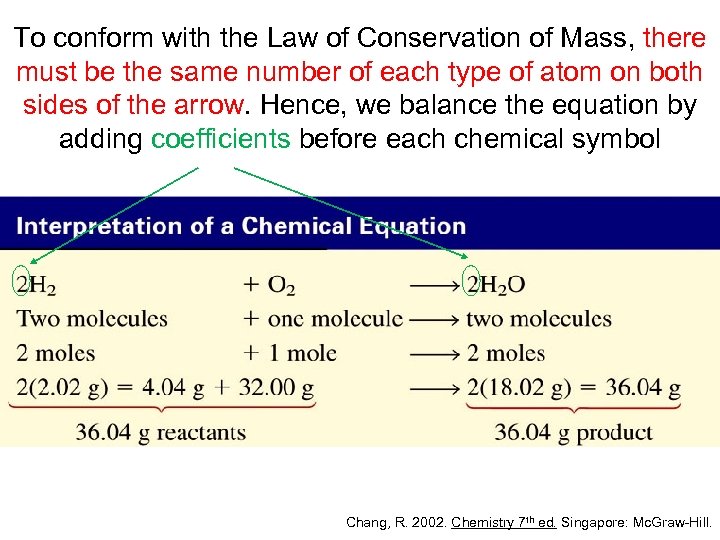
To conform with the Law of Conservation of Mass, there must be the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the arrow. Hence, we balance the equation by adding coefficients before each chemical symbol Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill.

Calculating the amounts of reactant and product

Figure on slices of bread + ham to make sandwich. Use this to relate to stoich
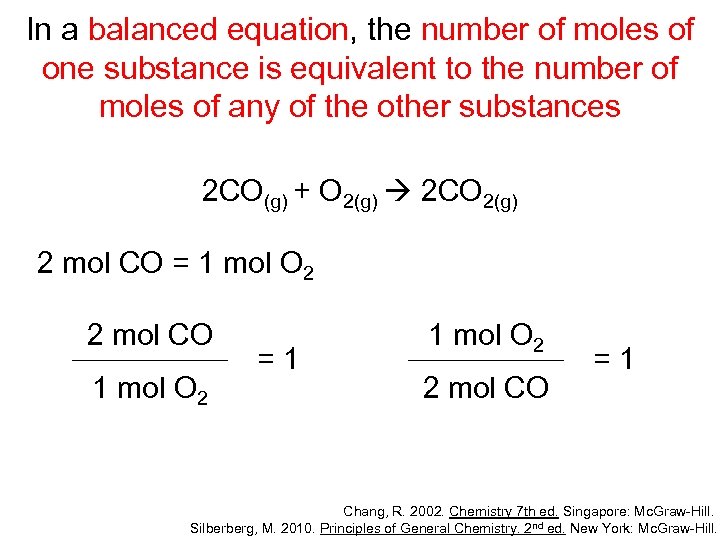
In a balanced equation, the number of moles of one substance is equivalent to the number of moles of any of the other substances 2 CO(g) + O 2(g) 2 CO 2(g) 2 mol CO = 1 mol O 2 2 mol CO 1 mol O 2 =1 1 mol O 2 2 mol CO =1 Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill. Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2 nd ed. New York: Mc. Graw-Hill.
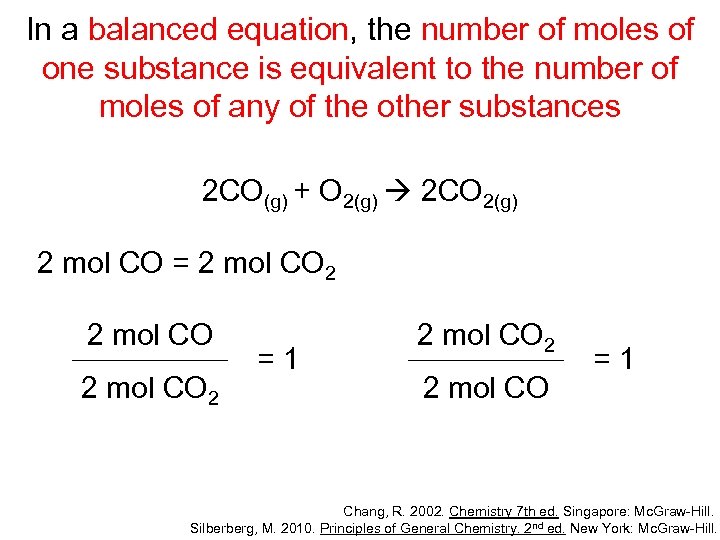
In a balanced equation, the number of moles of one substance is equivalent to the number of moles of any of the other substances 2 CO(g) + O 2(g) 2 CO 2(g) 2 mol CO = 2 mol CO 2 =1 2 mol CO 2 2 mol CO =1 Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill. Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2 nd ed. New York: Mc. Graw-Hill.
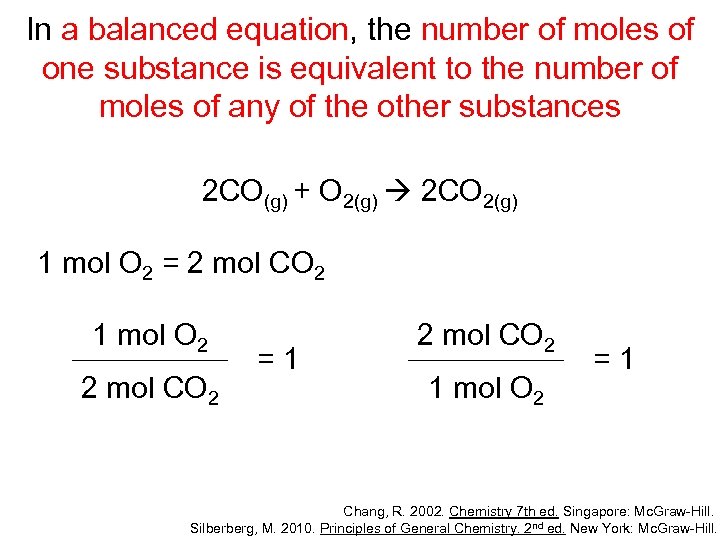
In a balanced equation, the number of moles of one substance is equivalent to the number of moles of any of the other substances 2 CO(g) + O 2(g) 2 CO 2(g) 1 mol O 2 = 2 mol CO 2 1 mol O 2 2 mol CO 2 =1 2 mol CO 2 1 mol O 2 =1 Chang, R. 2002. Chemistry 7 th ed. Singapore: Mc. Graw-Hill. Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2 nd ed. New York: Mc. Graw-Hill.

The amount of one substance in a reaction is related to that of any other Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2 nd ed. New York: Mc. Graw-Hill.
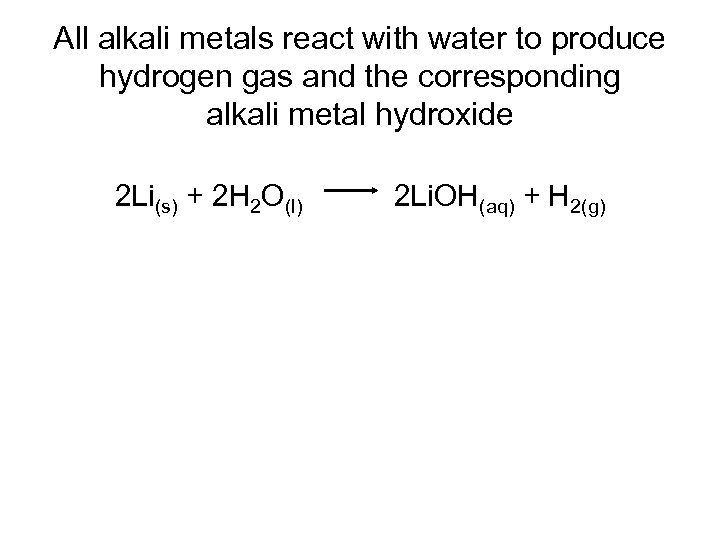
All alkali metals react with water to produce hydrogen gas and the corresponding alkali metal hydroxide 2 Li(s) + 2 H 2 O(l) 2 Li. OH(aq) + H 2(g)
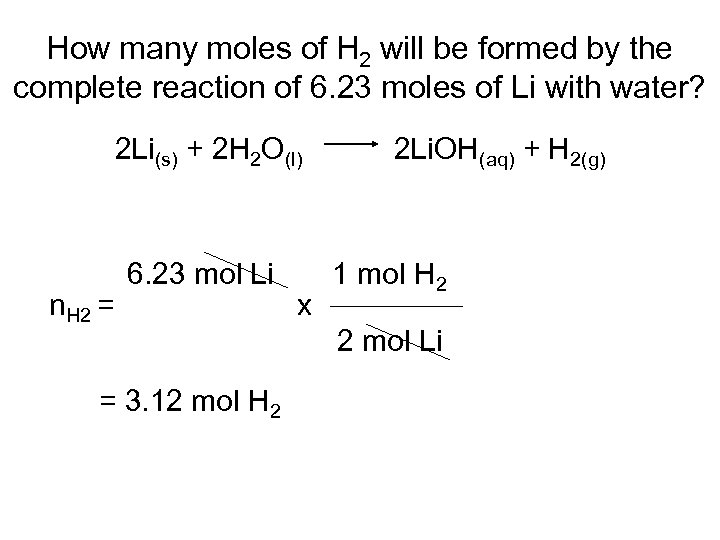
How many moles of H 2 will be formed by the complete reaction of 6. 23 moles of Li with water? 2 Li(s) + 2 H 2 O(l) n. H 2 = 6. 23 mol Li = 3. 12 mol H 2 x 2 Li. OH(aq) + H 2(g) 1 mol H 2 2 mol Li

How many grams of H 2 will be formed by the complete reaction of 80. 57 g of Li with water? 2 Li(s) + 2 H 2 O(l) m. H 2 = 80. 57 g Li x 2 Li. OH(aq) + H 2(g) 1 mol Li 6. 941 g Li x 2. 016 g H 2 1 mol H 2 = 11. 70 g H 2 x 1 mol H 2 2 mol Li

In a lifetime, the average American uses about 794 kg of copper in coins, plumbing, and wiring. Copper is obtained from sulfide ores (such as Cu 2 S) by a multistep process. After an initial grinding, the first step is to “roast” the ore (heat it strongly with O 2) to form Cu 2 O and SO 2 2 Cu 2 S(s) + 3 O 2(g) 2 Cu 2 O(s) + 2 SO 2(g)
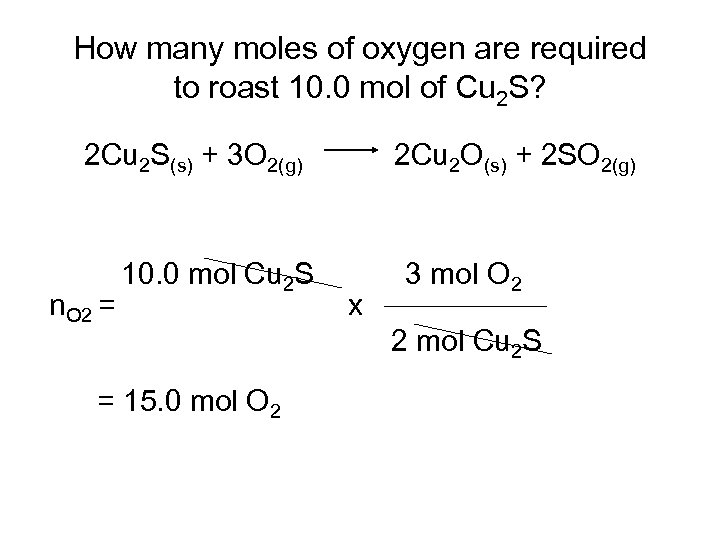
How many moles of oxygen are required to roast 10. 0 mol of Cu 2 S? 2 Cu 2 S(s) + 3 O 2(g) n. O 2 = 10. 0 mol Cu 2 S = 15. 0 mol O 2 2 Cu 2 O(s) + 2 SO 2(g) x 3 mol O 2 2 mol Cu 2 S
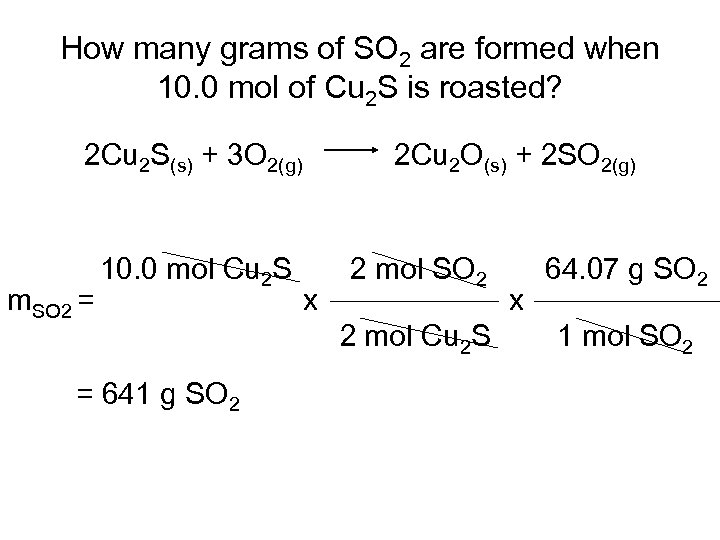
How many grams of SO 2 are formed when 10. 0 mol of Cu 2 S is roasted? 2 Cu 2 S(s) + 3 O 2(g) m. SO 2 = 10. 0 mol Cu 2 S = 641 g SO 2 2 Cu 2 O(s) + 2 SO 2(g) x 2 mol SO 2 2 mol Cu 2 S x 64. 07 g SO 2 1 mol SO 2

Ch 2 F • • No meeting this Friday Lab discussion moved to March 2 1: 30 -3: 30 pm SOM 201
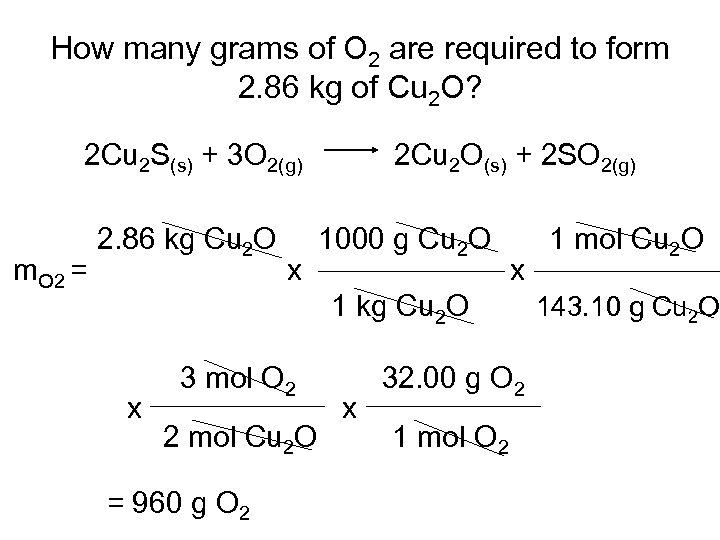
How many grams of O 2 are required to form 2. 86 kg of Cu 2 O? 2 Cu 2 S(s) + 3 O 2(g) m. O 2 = 2. 86 kg Cu 2 O x 2 Cu 2 O(s) + 2 SO 2(g) 1000 g Cu 2 O x 1 kg Cu 2 O x 3 mol O 2 2 mol Cu 2 O = 960 g O 2 x 32. 00 g O 2 1 mol Cu 2 O 143. 10 g Cu 2 O
b8a7edbbc7b71b20b97cdec44b7b4cd8.ppt