1522f7bba7594acca1d1e10e7b90f363.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53


We have contributed more than US$ 2 billion to the Chilean economy

We have created new industries for Chile, some of which are worldwide leaders

Our initiatives contribute to the development of the human capital of Chile

We have introduced the concept of innovation as a major element of competitiveness for Chile

We have created more than 75 companies

What do some relevant interest groups say about us?

“…by 1982, Fundación Chile had already implemented and was operating its first salmon farming plant. Seven years later, it was sold to a Japanese company for US$22 million” (Businessweek) “In 2004, its first year, the laboratory turned out 1. 7 m partially fattened lily bulbs, using up-to-date biotechnology. Vitro Centre is a joint venture between local investors, Fundación Chile and a Dutch firm. . . (The Economist)

Transforming Chile

Who We Are Fundación Chile is a privately owned, non-profit organization, founded in 1976 by the Chilean Government and ITT Corporation (U. S. A. ). In 2005, BHP Billiton became a co-founder. With transforming initiatives, based on the management of innovation and on high impact technology transfer, we accelerate the country’s growth so we can; “MOVE THE BOUNDARY OF POSSIBILITY”
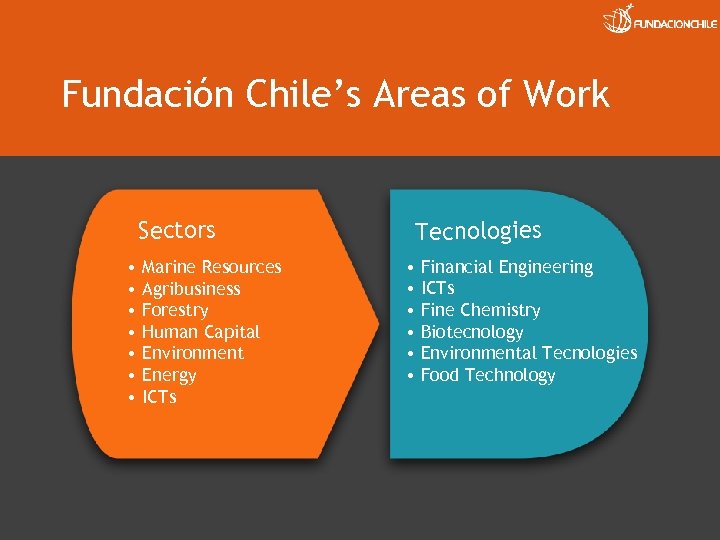
Fundación Chile’s Areas of Work Sectors • Marine Resources • Agribusiness • Forestry • Human Capital • Environment • Energy • ICTs Tecnologies • Financial Engineering • ICTs • Fine Chemistry • Biotecnology • Environmental Tecnologies • Food Technology

Fundación Chile does… o Innovative enterprises, almost always in association with companies or individuals. o Develops, adapts and sells technologies to clients in the productive and public sectors, in the country and abroad. o Fosters institutional innovations. o Captures and disseminates technologies to multiple users (as a technological antenna) through seminars, specialized magazines, internet portals, and technical assistance. o Develops standards and certification systems.
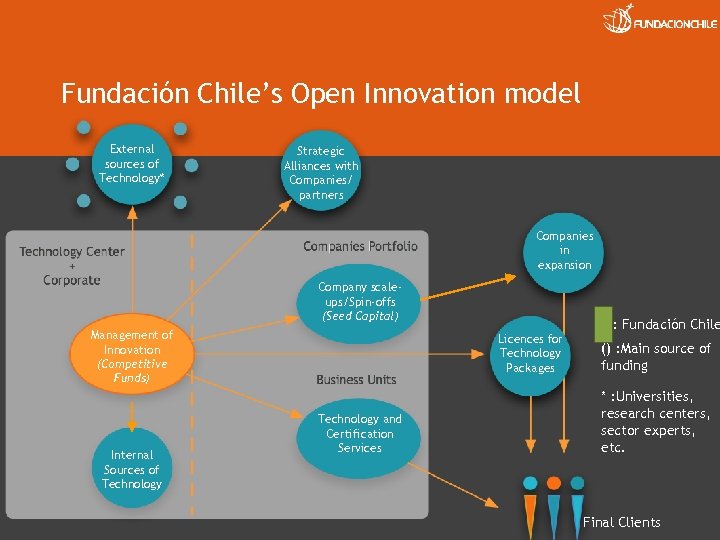
Fundación Chile’s Open Innovation model External sources of Technology* Strategic Alliances with Companies/ partners Companies in expansion Company scaleups/Spin-offs (Seed Capital) Management of Innovation (Competitive Funds) Internal Sources of Technology Licences for Technology Packages Technology and Certification Services : Fundación Chile () : Main source of funding * : Universities, research centers, sector experts, etc. Final Clients
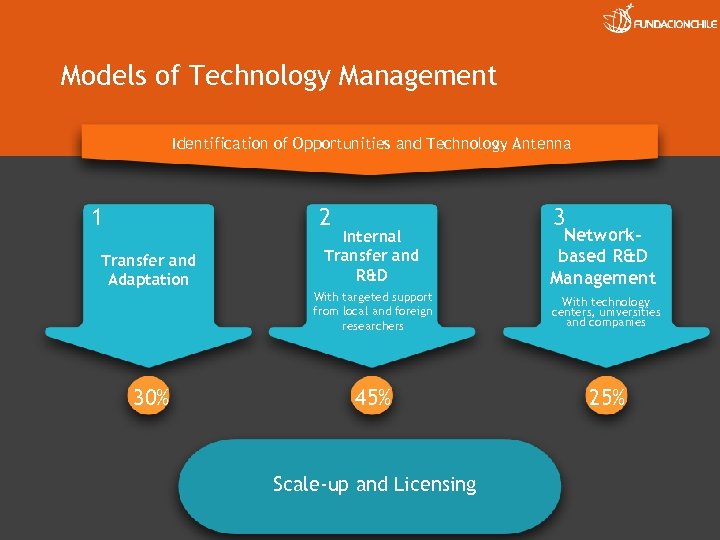
Models of Technology Management Identification of Opportunities and Technology Antenna 1 2 3 30% Networkbased R&D Management With targeted support from local and foreign researchers Transfer and Adaptation Internal Transfer and R&D With technology centers, universities and companies 45% 25% Scale-up and Licensing

Outstanding Projects Salmon farming (Region X) Processing and distribution of boxed beef (Region IX) Quality control of fruit (Central Valley) Consortium of forestry technologies (Region VIII) Clean Production Center (Metropolitan and Regions) Production of gourmet goat cheese (Metropolitan and Region IV) Production of furniture for export (Region IX) Chilean flounder and abalone hatcheries (Regions IV and V) Production of berries (Region IX) Labor Competencies Standard (All Chile) Farm and Agriculture/Cattle Chain Management (Regiones V y IX) Education (educarchile. cl) (All Chile) Forestry Securitization (Regions VI, VII and VIII) New salmon feeds (Oleotop) (Region IX)

Open Innovation Model

Obtaining Know-How and Technology; K+D All knowledge cannot be monopolized • Renewable Energy: Finland (VTT), Sweden (SWECO), Germnay (GTN, BGR), New Zealand (GNS), Israel (Weizmann Institute), Switzerland (CSEM), USA (Infinia) • Agro-Biotechnology: U. S. A. (Cornell), Spain (IRTA) • Food Value Chains: New Zealand (Waikato, dairy industry); France (Institute d’Elevage, meat), Australia (CSIRO), U. S. A. (Phytomedics, functional ingredients) • Copper and derivatives, evaluation and mitigation of risks: Australia (Austmine, AMIRA, CMR U. Queensland); U. S. A. (U. Nevada) • Environmental Technologies: U. S. A. (Batelle), Sweden (IVL) • Entrepreneurship and Corporate Ventures: U. S. A. (UCLA, UC Berkeley) • Open Innovation: U. S. A. (UC Berkeley) • Education: U. S. A. (Harvard)
Chile Global International network successful Chilean executives, interested in contributing to Chile’s development

International Dissemination of the Fundación Chile Model Fundación Jalisco (2006 – 2007) Fundación Sonora, Sagarpha (2006 -2007) Mr. Vicente Fox, former President of Mexico Sur · Sureste (2006) 2007: FCh has been contacted to assist governments in the creation of similar institutions in Peru, Panamá, El Salvador and most recently, Colombia and Uruguay

Example of Transformational projects

Biotechnology in Fruit Grapes resistant to diseases caused by fungi and viruses. Improved quality, seedless, bigger size. Stone fruit resistant to browning and mealiness

Vaccines against SRS in Salmon Recombinant vaccine against rikettsial diseases in salmon 30% mortality rate in Chilean salmon production Cost to the sector: US$150 million

Natural Pigments for Salmon Current Salmon Feed: Synthetic astaxanthin Future Salmon Feed: Natural Astaxanthin Advantages: Quality and Safety

Diversifying Aquaculture; Development of Marine Species Southern hake, Croaker, Sea bass White meat fish has 10% of the world fish trade (US$ 45 billion, not inclusing China) Technologies for raising and producing juveniles.

New Aquaculture System for Most Exposed Zones New designs and raw materials (Beginning with copper), that facilitate farming in more aggressive and exposed zones. More environmentally friendly. Shore Mid distance Off-shore

Development of Seaweed-based Products Seaweeds market is approximately US$ 5. 7 billion • In Chile, the market is about US$ 100 million; 87% is sold as dry product. Segments: • Human consumption • Functional foods and nutraceuticals • Biochemical products for cosmetics and pharamaceuticals • Extracts for agriculture and salmon farming Alliances: Departament of Ecology, UC, Biotechnology U Federico Santa María, U of Nantes (France), European Center for Seaweed Research CEVA (France)
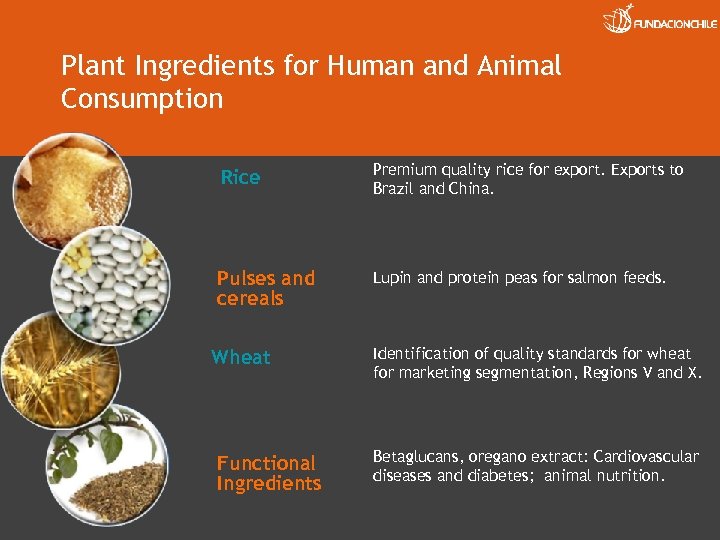
Plant Ingredients for Human and Animal Consumption Rice Premium quality rice for export. Exports to Brazil and China. Pulses and cereals Lupin and protein peas for salmon feeds. Wheat Functional Ingredients Identification of quality standards for wheat for marketing segmentation, Regions V and X. Betaglucans, oregano extract: Cardiovascular diseases and diabetes; animal nutrition.
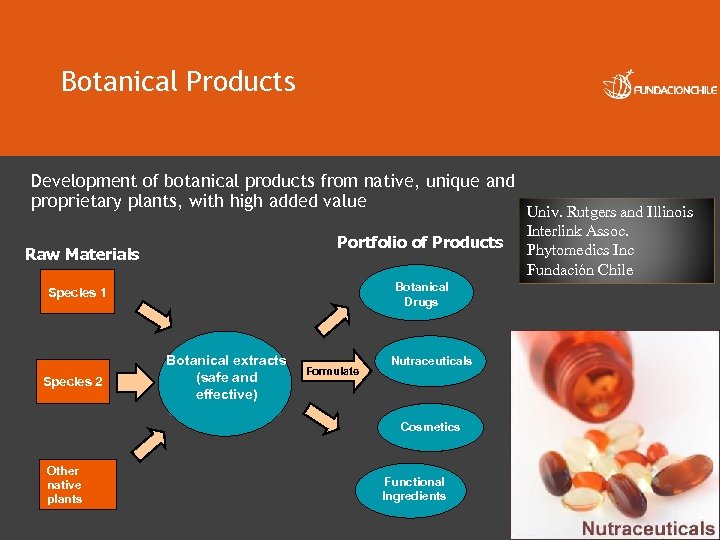
Botanical Products Development of botanical products from native, unique and proprietary plants, with high added value Portfolio of Products Raw Materials Botanical Drugs Species 1 Species 2 Botanical extracts (safe and effective) Formulate Nutraceuticals Cosmetics Other native plants Functional Ingredients Univ. Rutgers and Illinois Interlink Assoc. Phytomedics Inc Fundación Chile

Forest BIO ENERGY From pellets to revoluionizing the industrial market • Fundación Chile introduced the production of wood pellets (a solid biofuel widely accepted in Europe), with its company Eco. Pellets • Now, it is starting a new venture (Total Energy). This company offers integral services involving the sale of energy to industrial clients

Native Forest Green Business • Fundación Chile and the American NGO Forest. Ethics, created Eco. Management for the sustainable management of the native forest. • Today it manages MASISA’s natural forest patrimony. The next step; generation of energy from biomass instead of coal.

Carbon Forests Curbing climate change with business innovation • Carbon Forests; Generation of carbon credits with forestation projects, sustainable management of natural forests or retention of emissions in long lasting products. • Sale of 600 thousand tons CO 2 with Fundación Chile’s forest securitization program • Member of the Chicago Climate Exchange. Give access to the voluntary market to small and mid-sized producers.

Neosylva Increase productivity with clonal silviculture • By an agreement between Arauco, Cellfor and Fundación Chile, access was given to the somatic embryogenesis protocol for Radiata pine and to trials with more than 5 thousand clones. • Neo. Sylva will provide plants from this clonal program to the open market with 25% higher yield than the best available alternative. • The Neo. Sylva nursery in Santa Fe, with capacity for 13 million plants, becomes the biggest supplier of non integrated plants.

Passive Treatment Systems INBIOTREAT Passive systems or “wetlands”: a low cost operating system for different types of effluents (eg. acid mine waters, tailings dam clear water, organics). Technological partner:

m. Risk (Environmental Risk Assessment, Monitoring & Management): Business unit that provides specialized environmental management services. Products and services: • Evaluation of risks (exploratory and detailed) • Environmental monitoring (manual, remote sensors) • Management and visualization of data

Energy Efficiency • Promotion of ESCO Market • Demonstration cases • Financing mechanisms • Contractual plans • Job competencies • Measurement, verification and certification of savings • Mining, Agribusiness, Other industries • Labeling appliances and promotion of energy efficient technologies (refrigerators, lighting, air conditioners, motor, water pumps, etc. )

Geothermal: Exploration and Mid-low enthalpy projects • Regional studies of geothermal potential • Heat and cold storage. Modeling reservoirs • Research in drilling, reservoir stimulation • Basic and detailed engineering of small scale geothermal plants (heat/electricity) and projects involving the direct heat use • Layouts - Site supervision In alliance with

Atacama Solar Plataform Integral initiative to develop a center of activity around solar energy and its applications in the Atacama region. Mass use of solar energy applications by mining, agriculture, construction, etc. Technological innovation programs, in international networks, focused on: • Photovoltaic systems with nanoporous copper cells • Solar concentration systems (solar thermoelectricity, solar discs, concentration in photovoltaic systems) • Co-generation of energy and desalinated water

Education for Tomorrow educarchile. cl Develops educational resources that improve the quality of Chilean education available to teachers, students, principals, families and researchers. • More than 580, 000 registered users • 61% of the country’s teachers are registered in educarchile • 1, 500, 000 average visits per month • Exported to more than 17 countires (RELPE) • OAS Award for best ICT initiative • Digital Challenge Award in Chile

Education for Tomorrow School Management Educational establishments can initiate improvement processes and opt for certification from the National School Management Quality Certification Board. More than 1, 400 establishments have begun the self evaluation process 73 schools have been certified Better Schools can improve the quality of educational results, with the gradual installation of institutional management and teaching processes with integral assistance for vulnerable schools. 4 Regions 9 communities 34 schools
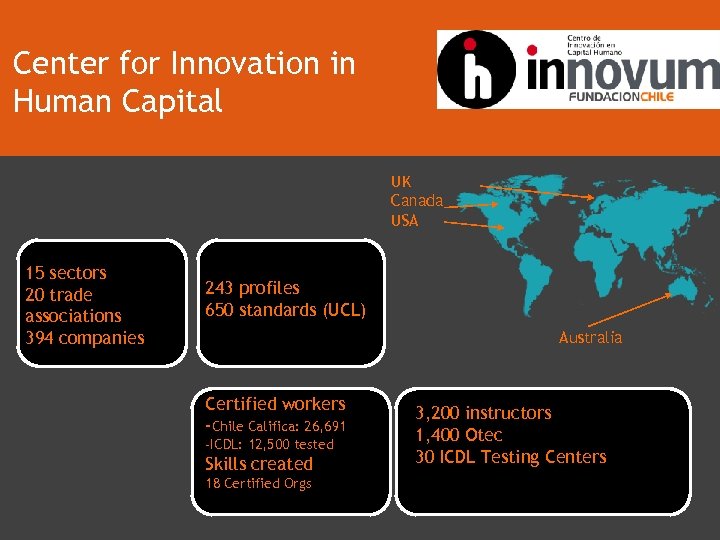
Center for Innovation in Human Capital UK Canada USA 15 sectors 20 trade associations 394 companies 243 profiles 650 standards (UCL) Australia Certified workers -Chile Califica: 26, 691 -ICDL: 12, 500 tested Skills created 18 Certified Orgs 3, 200 instructors 1, 400 Otec 30 ICDL Testing Centers

Center for Innovation in Human Capital: Our Experience Villa María Academy Codelco Education Empresa Nacional de Minería Mining Universidad del Pacífico Minería Valle Central Telefónica CTC Chile Minera Los Pelambres Telefónica Móviles m. As Ideal S. A. Clínica Santa María Tigre Chile S. A. Industry Universidad Central Services Banco Estado 24 Hrs. S. A. Electro Andina ACHS ESSBIO Banco ITAU Endesa CENCOSUD Agrosuper ENAP ESSCO Chilectra Public Instit. Contraloría Gral. De la República MIDEPLAN Biblioteca Congreso Nacional INDAP Consejo Producción Limpia Red Acuícola Coyhaique Private Networks Red Aqua. Norte Red Constru. Educa Red Minera Educa CORFO Servicio Civil Superintendencia de Salud
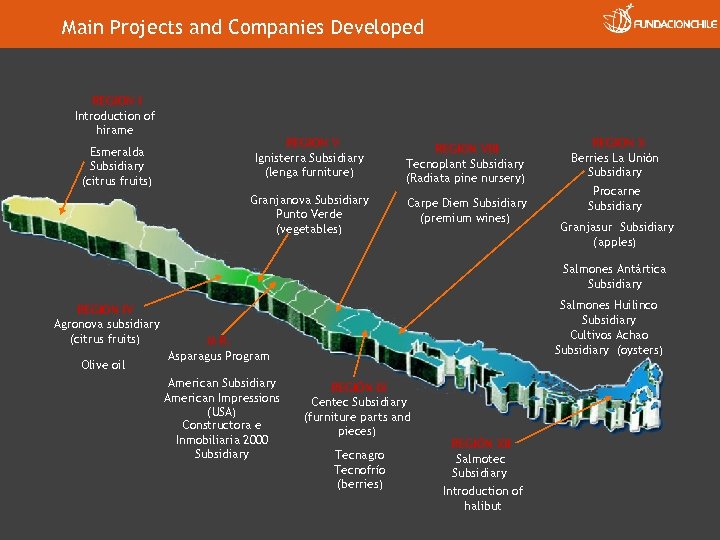
Main Projects and Companies Developed REGION I Introduction of hirame REGION V Ignisterra Subsidiary (lenga furniture) REGION VIII Tecnoplant Subsidiary (Radiata pine nursery) Granjanova Subsidiary Punto Verde (vegetables) Esmeralda Subsidiary (citrus fruits) Carpe Diem Subsidiary (premium wines) REGION X Berries La Unión Subsidiary Procarne Subsidiary Granjasur Subsidiary (apples) Salmones Antártica Subsidiary REGION IV Agronova subsidiary (citrus fruits) Olive oil Salmones Huilinco Subsidiary Cultivos Achao Subsidiary (oysters) M R. Asparagus Program American Subsidiary American Impressions (USA) Constructora e Inmobiliaria 2000 Subsidiary REGIÓN IX Centec Subsidiary (furniture parts and pieces) Tecnagro Tecnofrío (berries) REGIÓN XII Salmotec Subsidiary Introduction of halibut

Projects and Companies in Process REGION I New fruit and vegetable alternatives (kumquat) REGION III Define agricultural alternatives Job competencies Pigments for salmon farmers Restocking Chilean flounder REGION V S SRC and SPASA (abalone and turbot) Stone fruit biotevhnology Semillas Marinas Subsidiary Stone fruit and grapev ine genetics REGION II Mining Job Competencies IV REGION Cultimar subsidiary (oysters and turbot) M. R. . Subsidiary Certifica Subsidiary Vitro Chile REGIÓN VIII GCL subsidiary (quality) SIF Subsidiary Pesca Sur Trade Fair New Plant Ingredients Certfor Forest Certification REGION X Wheat Program Development of animal feed ingredients Subsidiary Genfor (forestry biotechnology) Quillaipe Experiment Center (vaccines, hake, craker) Aquasur Trade Fair Subsidiary Aquagestión Health Services Subsidiary Inacui Native Forest Management Projects Subsidiary Chevrita (gourmet goat cheese) Bioenergy Habitability Chemical Metrology Stone fruit Center biotechnology Educar Chile y Foods for children Relpe Subsidiary CCE School Chilean Management Subsidiary Sterilization Technopress Company Subsidiary Subsidiay GCL Regional Inversionistas Quality Management Businesses Innovadores and Laboratory REGION IX Animal feed ingredients development Oleotop subsidiary (rapeseed oil) REGION XII Magellans lamb development

More than 75 companies created

Current Portfolio

Strong Brand Recognition

Final Thoughts
Where is the boundary of possibility? Global Knowledge
Where is the boundary of possibility? Global Knowledge Local
Where is the boundary of possibility? Global Knowledge Local
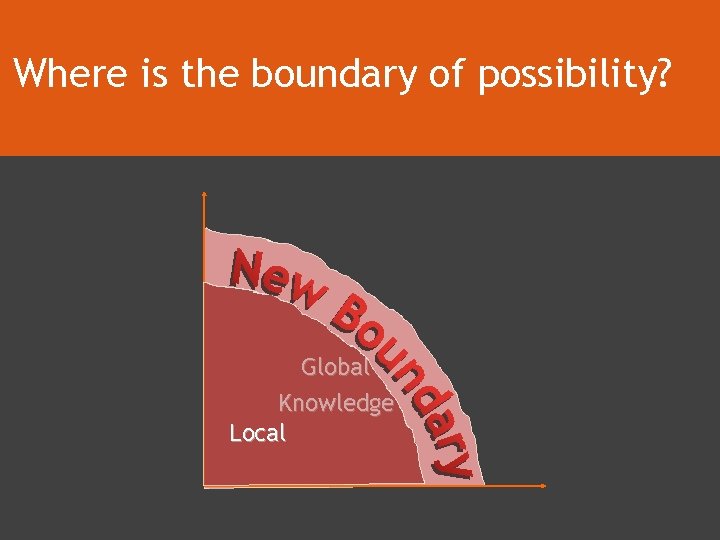
Where is the boundary of possibility? Global Knowledge Local

What is unique about the Fundación Chile model? • Public – private alliance. Privately controlled • Market oriented • Networks as basic assets for value creation and project scale-ups • Creation of companies to spread the innovation • The magic word is “Self-Financing”

1522f7bba7594acca1d1e10e7b90f363.ppt