Lecture8-02-waves.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Waves in coastal zone
Waves in coastal zone
 Rocky shorelines like this one in Oregon are dominated by wave erosion and may have few sandy beaches.
Rocky shorelines like this one in Oregon are dominated by wave erosion and may have few sandy beaches.
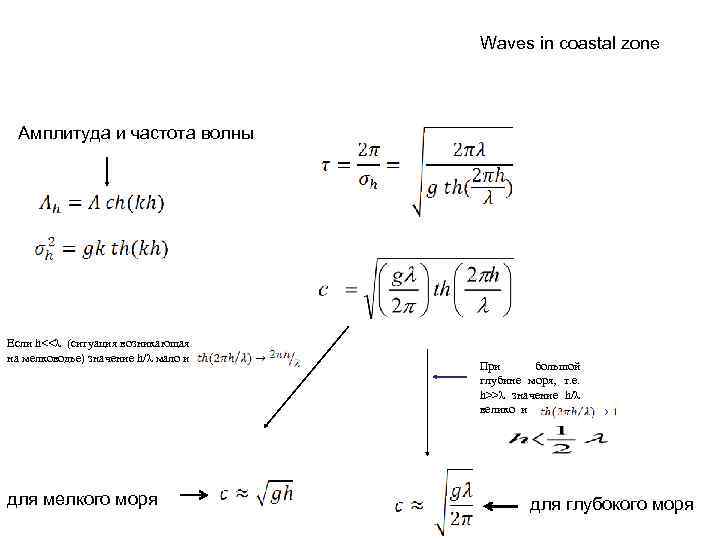 Waves in coastal zone Амплитуда и частота волны Если h<<λ (ситуация возникающая на мелководье) значение h/λ мало и для мелкого моря При большой глубине моря, т. е. h>>λ значение h/λ велико и для глубокого моря
Waves in coastal zone Амплитуда и частота волны Если h<<λ (ситуация возникающая на мелководье) значение h/λ мало и для мелкого моря При большой глубине моря, т. е. h>>λ значение h/λ велико и для глубокого моря
 Waves in coastal zone Изменение групповой скорости и длины ветровой волны Отношения групповой (V) и фазовой (c) скоростей ветровых волн при различной относительной глубине (h/λ) водоема h/λ 0, 50 0, 30 0, 20 0, 10 0, 05 0, 01 V/c 0, 50 0, 51 0, 70 0, 89 0, 97 1, 00
Waves in coastal zone Изменение групповой скорости и длины ветровой волны Отношения групповой (V) и фазовой (c) скоростей ветровых волн при различной относительной глубине (h/λ) водоема h/λ 0, 50 0, 30 0, 20 0, 10 0, 05 0, 01 V/c 0, 50 0, 51 0, 70 0, 89 0, 97 1, 00
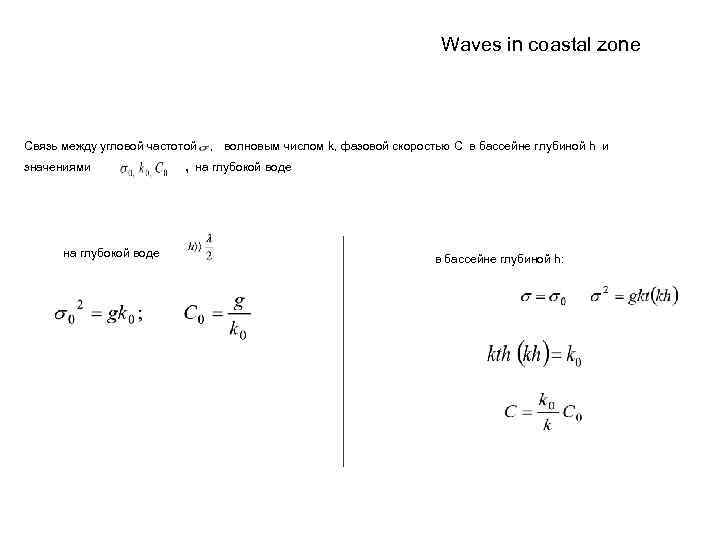 Waves in coastal zone Связь между угловой частотой значениями на глубокой воде , волновым числом k, фазовой скоростью С в бассейне глубиной h и , на глубокой воде в бассейне глубиной h:
Waves in coastal zone Связь между угловой частотой значениями на глубокой воде , волновым числом k, фазовой скоростью С в бассейне глубиной h и , на глубокой воде в бассейне глубиной h:
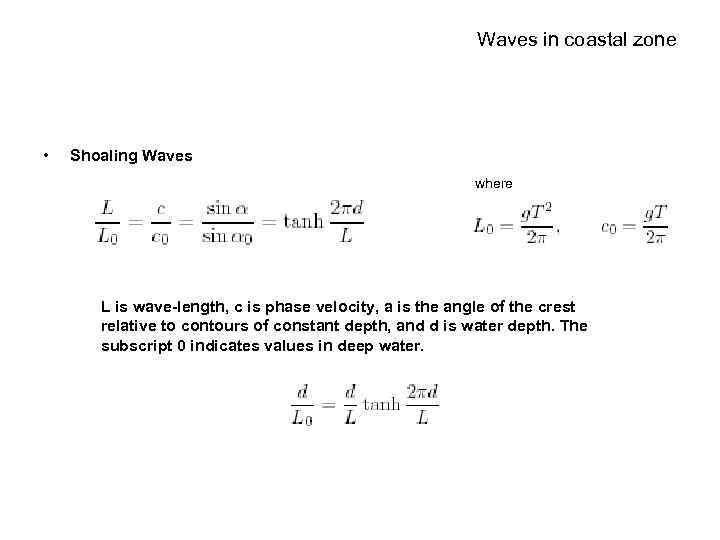 Waves in coastal zone • Shoaling Waves where L is wave-length, c is phase velocity, a is the angle of the crest relative to contours of constant depth, and d is water depth. The subscript 0 indicates values in deep water.
Waves in coastal zone • Shoaling Waves where L is wave-length, c is phase velocity, a is the angle of the crest relative to contours of constant depth, and d is water depth. The subscript 0 indicates values in deep water.
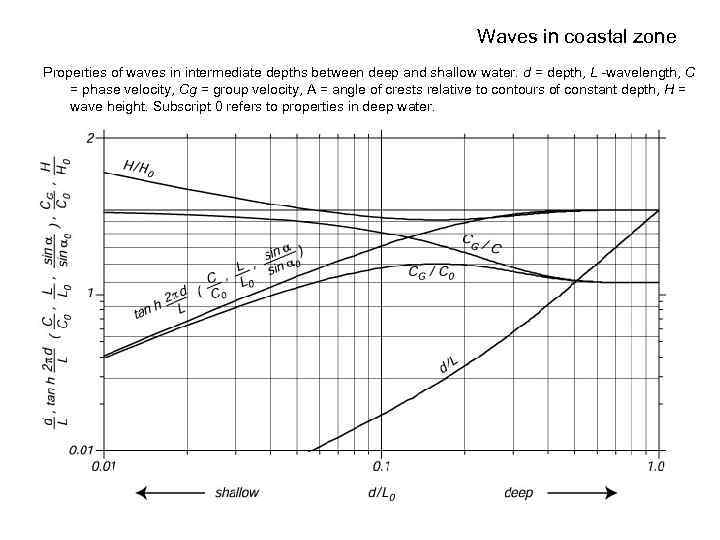 Waves in coastal zone Properties of waves in intermediate depths between deep and shallow water. d = depth, L -wavelength, C = phase velocity, Cg = group velocity, Α = angle of crests relative to contours of constant depth, H = wave height. Subscript 0 refers to properties in deep water.
Waves in coastal zone Properties of waves in intermediate depths between deep and shallow water. d = depth, L -wavelength, C = phase velocity, Cg = group velocity, Α = angle of crests relative to contours of constant depth, H = wave height. Subscript 0 refers to properties in deep water.
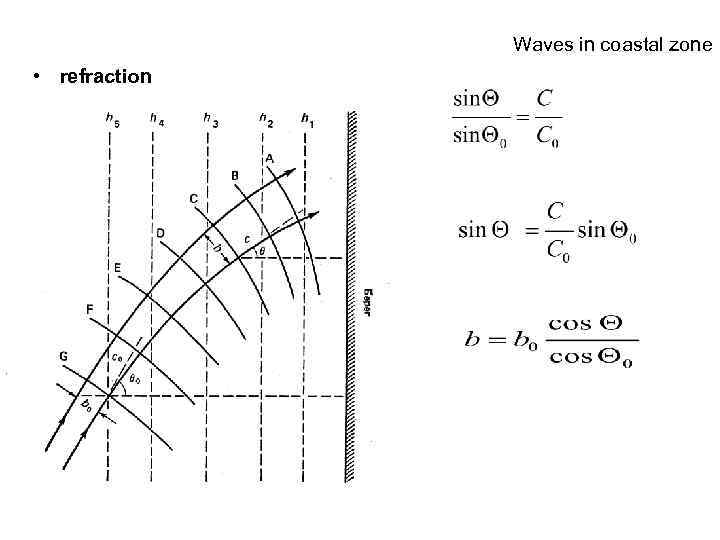 Waves in coastal zone • refraction
Waves in coastal zone • refraction
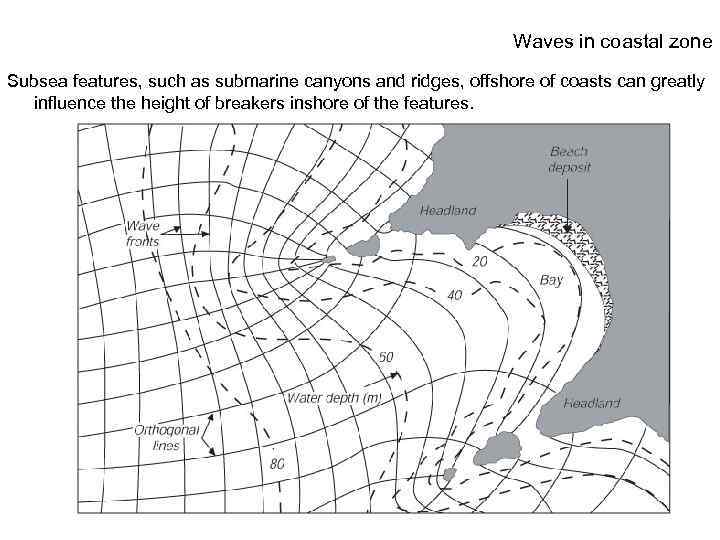 Waves in coastal zone Subsea features, such as submarine canyons and ridges, offshore of coasts can greatly influence the height of breakers inshore of the features.
Waves in coastal zone Subsea features, such as submarine canyons and ridges, offshore of coasts can greatly influence the height of breakers inshore of the features.
 Waves in coastal zone Wave refraction - Wave refraction causes wave fronts to parallel the shape of the coastline as they approach shore and encounter ground. Wave refraction causes wave energy to concentrate on headlands and preferentially erode them rather than bays.
Waves in coastal zone Wave refraction - Wave refraction causes wave fronts to parallel the shape of the coastline as they approach shore and encounter ground. Wave refraction causes wave energy to concentrate on headlands and preferentially erode them rather than bays.
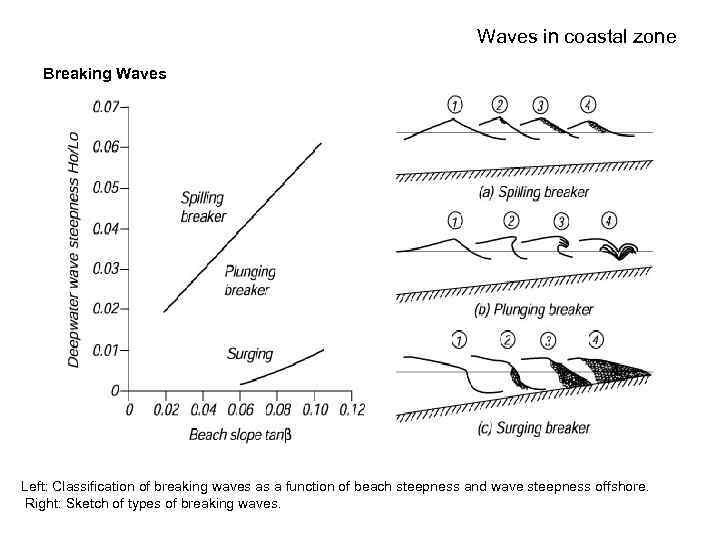 Waves in coastal zone Breaking Waves Left: Classification of breaking waves as a function of beach steepness and wave steepness offshore. Right: Sketch of types of breaking waves.
Waves in coastal zone Breaking Waves Left: Classification of breaking waves as a function of beach steepness and wave steepness offshore. Right: Sketch of types of breaking waves.
 Waves in coastal zone • 1. Steep waves tend to lose energy slowly as the waves moves into shallower water through water spilling down the front of the wave. These are spilling breakers. • 2. Less steep waves on steep beaches tend to steepen so quickly that the crest of the wave moves much faster than the trough, and the crest, racing ahead of the trough, plunges into the trough (Figure 17. 4). • 3. If the beach is sufficiently steep, the wave can surge up the face of the beach without breaking in the sense that white water is formed. Or if it is formed, it is at the leading edge of the water as it surges up the beach. An extreme example would be a wave incident on a vertical breakwater. Steep, plunging breakers are the archetypical breaker. The edge of such breakers are ideal for surfing.
Waves in coastal zone • 1. Steep waves tend to lose energy slowly as the waves moves into shallower water through water spilling down the front of the wave. These are spilling breakers. • 2. Less steep waves on steep beaches tend to steepen so quickly that the crest of the wave moves much faster than the trough, and the crest, racing ahead of the trough, plunges into the trough (Figure 17. 4). • 3. If the beach is sufficiently steep, the wave can surge up the face of the beach without breaking in the sense that white water is formed. Or if it is formed, it is at the leading edge of the water as it surges up the beach. An extreme example would be a wave incident on a vertical breakwater. Steep, plunging breakers are the archetypical breaker. The edge of such breakers are ideal for surfing.
 Waves in coastal zone Волновой нагон и его эффекты А- амплитуда волны h- глубина воды -const- зависит от наклона дна и заключена в пределах 0, 3 -0, 6. - среднее возвышение уровня относительно невозмущенного положения.
Waves in coastal zone Волновой нагон и его эффекты А- амплитуда волны h- глубина воды -const- зависит от наклона дна и заключена в пределах 0, 3 -0, 6. - среднее возвышение уровня относительно невозмущенного положения.
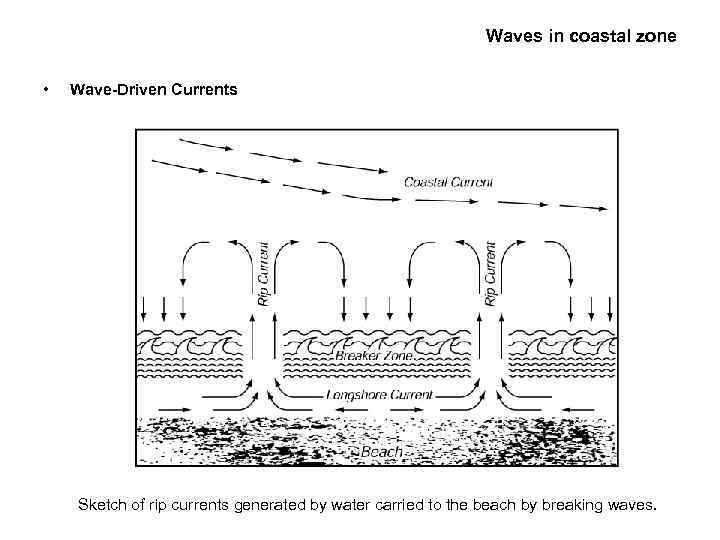 Waves in coastal zone • Wave-Driven Currents Sketch of rip currents generated by water carried to the beach by breaking waves.
Waves in coastal zone • Wave-Driven Currents Sketch of rip currents generated by water carried to the beach by breaking waves.


