3f2ea11e00d65c078f073fdf5f33e0c9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Water Sector Strategic Development Plan(WSSDP, 2012 -2025) AND SDGs: ANY LINKAGES? Presentation By Ibrahim Musah , Head of Policy and Partnership Water. Aid
Water Sector Strategic Development Plan(WSSDP, 2012 -2025) AND SDGs: ANY LINKAGES? Presentation By Ibrahim Musah , Head of Policy and Partnership Water. Aid
 Introduction • Access to sustainable water and basic sanitation services is a basic human right • Water Sector Strategic Development Plan (WSSDP) provides the framework for achieving “sustainable water and basic sanitation for all by 2025. ” • Rate of population increase relative to WASH service provision! – What does this mean financially? – Do we have adequate financing mechanism in place to achieve this Vision?
Introduction • Access to sustainable water and basic sanitation services is a basic human right • Water Sector Strategic Development Plan (WSSDP) provides the framework for achieving “sustainable water and basic sanitation for all by 2025. ” • Rate of population increase relative to WASH service provision! – What does this mean financially? – Do we have adequate financing mechanism in place to achieve this Vision?
 Outline of Presentation • Introduction • WSSDP • The WASH Sector in Ghana • Cost of providing WASH services • WASH Financing • Conclusion
Outline of Presentation • Introduction • WSSDP • The WASH Sector in Ghana • Cost of providing WASH services • WASH Financing • Conclusion
 What is the WSSDP? • Water Sector Strategic Development Plan(2012 -2025) • Provides framework for implementing vision, policy objectives and targets for water and sanitation sector • It guides the water sector as a whole( state and non -state) in planning, dev’t, & Mgt of nation’s water resources in sustainable and equitable manner , and water related sanitation services • Vision : ‘‘Sustainable water and basic sanitation for all by 2025’’ • GWCL, CWSA , WRC and MMDAs are main implementing agencies
What is the WSSDP? • Water Sector Strategic Development Plan(2012 -2025) • Provides framework for implementing vision, policy objectives and targets for water and sanitation sector • It guides the water sector as a whole( state and non -state) in planning, dev’t, & Mgt of nation’s water resources in sustainable and equitable manner , and water related sanitation services • Vision : ‘‘Sustainable water and basic sanitation for all by 2025’’ • GWCL, CWSA , WRC and MMDAs are main implementing agencies
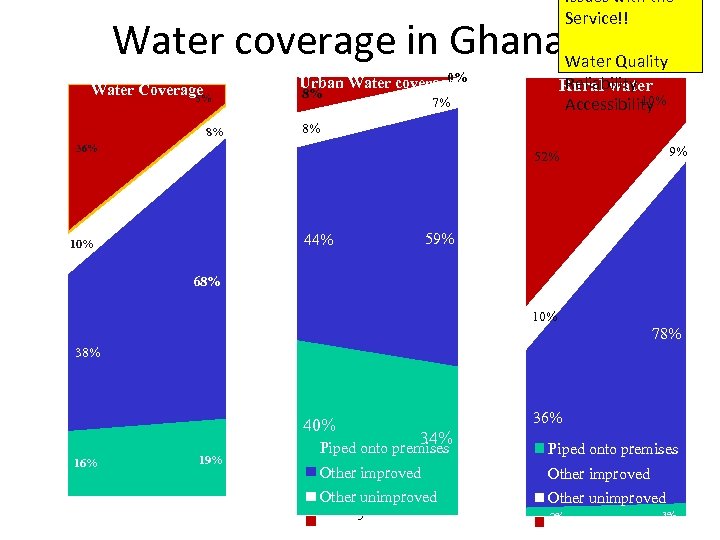 Issues with the Service!! Water coverage in Ghana. Water Quality 0% Urban Water coverage Water Coverage 5% 8% 8% Reliability Rural water 10% Accessibility 7% 8% 36% 9% 52% 59% 44% 10% 68% 10% 78% 38% 40% 36% 34% 1990 Other improved 19% 2012 1990 Piped onto premises Other improved Other unimproved 16% Piped onto premises Other unimproved 5 Surface water 2012 1990 2% Surface water 3% 2012
Issues with the Service!! Water coverage in Ghana. Water Quality 0% Urban Water coverage Water Coverage 5% 8% 8% Reliability Rural water 10% Accessibility 7% 8% 36% 9% 52% 59% 44% 10% 68% 10% 78% 38% 40% 36% 34% 1990 Other improved 19% 2012 1990 Piped onto premises Other improved Other unimproved 16% Piped onto premises Other unimproved 5 Surface water 2012 1990 2% Surface water 3% 2012
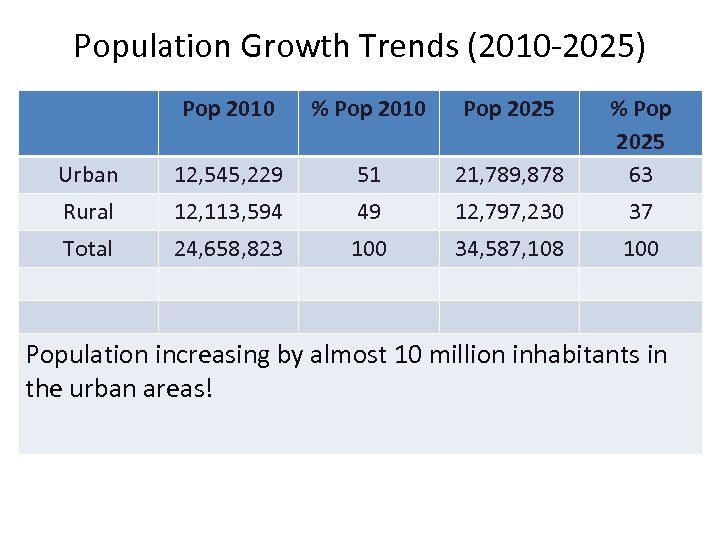 Population Growth Trends (2010 -2025) Pop 2010 % Pop 2010 Pop 2025 Urban 12, 545, 229 51 21, 789, 878 % Pop 2025 63 Rural 12, 113, 594 49 12, 797, 230 37 Total 24, 658, 823 100 34, 587, 108 100 Population increasing by almost 10 million inhabitants in the urban areas!
Population Growth Trends (2010 -2025) Pop 2010 % Pop 2010 Pop 2025 Urban 12, 545, 229 51 21, 789, 878 % Pop 2025 63 Rural 12, 113, 594 49 12, 797, 230 37 Total 24, 658, 823 100 34, 587, 108 100 Population increasing by almost 10 million inhabitants in the urban areas!
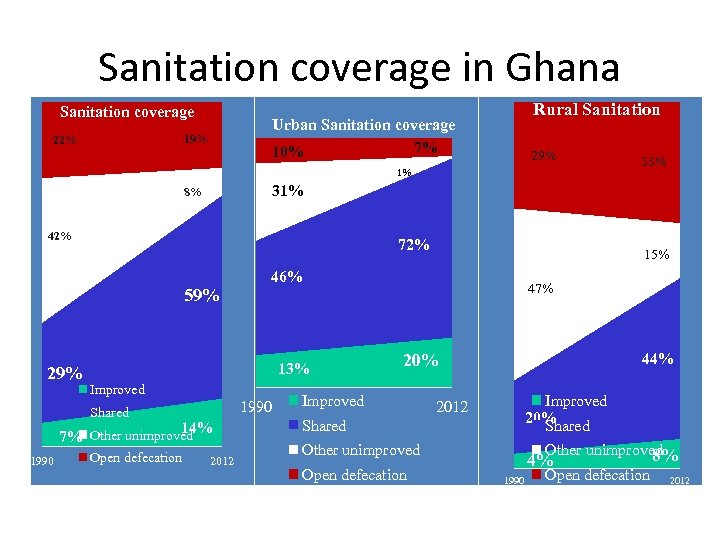 Sanitation coverage in Ghana Sanitation coverage Urban Sanitation coverage 7% 10% 19% 22% Rural Sanitation 29% 1% 31% 8% 42% 72% 59% 29% Improved 1990 14% 7% Other unimproved Open defecation 2012 15% 46% 13% Shared 1990 33% 47% 44% 20% Improved 20% Shared 2012 Shared Other unimproved Open defecation Other unimproved 8% 4% 1990 Open defecation 2012
Sanitation coverage in Ghana Sanitation coverage Urban Sanitation coverage 7% 10% 19% 22% Rural Sanitation 29% 1% 31% 8% 42% 72% 59% 29% Improved 1990 14% 7% Other unimproved Open defecation 2012 15% 46% 13% Shared 1990 33% 47% 44% 20% Improved 20% Shared 2012 Shared Other unimproved Open defecation Other unimproved 8% 4% 1990 Open defecation 2012
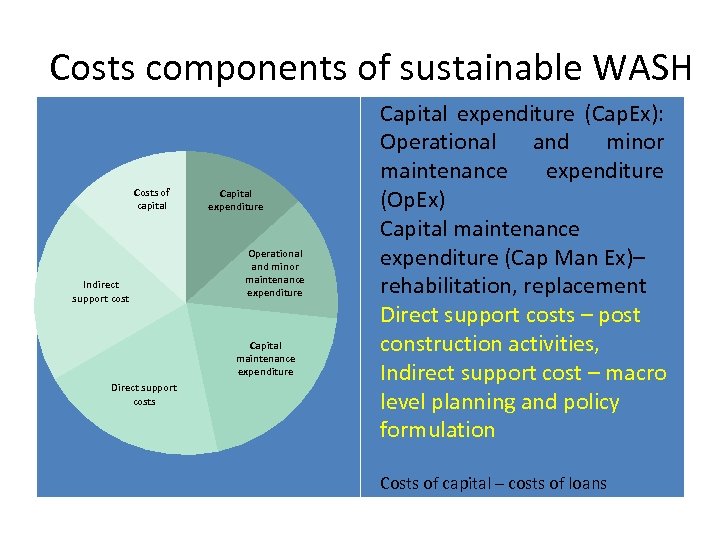 Costs components of sustainable WASH Costs of capital Indirect support cost Capital expenditure Operational and minor maintenance expenditure Capital maintenance expenditure Direct support costs Capital expenditure (Cap. Ex): Operational and minor maintenance expenditure (Op. Ex) Capital maintenance expenditure (Cap Man Ex)– rehabilitation, replacement Direct support costs – post construction activities, Indirect support cost – macro level planning and policy formulation Costs of capital – costs of loans
Costs components of sustainable WASH Costs of capital Indirect support cost Capital expenditure Operational and minor maintenance expenditure Capital maintenance expenditure Direct support costs Capital expenditure (Cap. Ex): Operational and minor maintenance expenditure (Op. Ex) Capital maintenance expenditure (Cap Man Ex)– rehabilitation, replacement Direct support costs – post construction activities, Indirect support cost – macro level planning and policy formulation Costs of capital – costs of loans
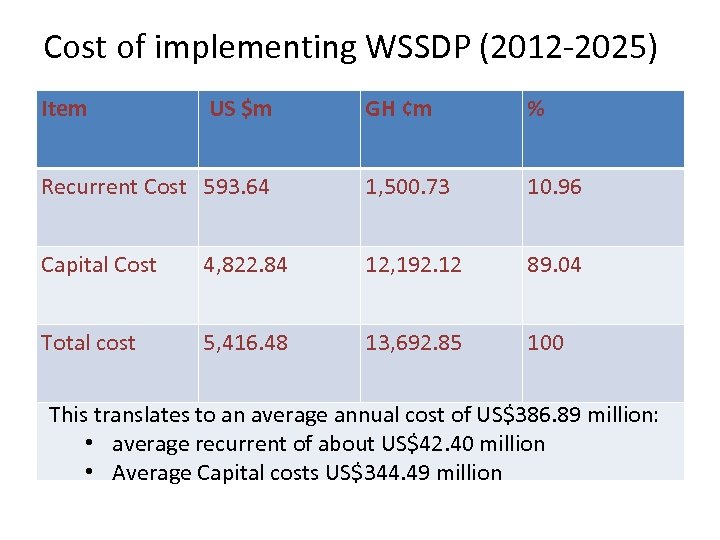 Cost of implementing WSSDP (2012 -2025) Item US $m GH ¢m % Recurrent Cost 593. 64 1, 500. 73 10. 96 Capital Cost 4, 822. 84 12, 192. 12 89. 04 Total cost 5, 416. 48 13, 692. 85 100 This translates to an average annual cost of US$386. 89 million: • average recurrent of about US$42. 40 million • Average Capital costs US$344. 49 million
Cost of implementing WSSDP (2012 -2025) Item US $m GH ¢m % Recurrent Cost 593. 64 1, 500. 73 10. 96 Capital Cost 4, 822. 84 12, 192. 12 89. 04 Total cost 5, 416. 48 13, 692. 85 100 This translates to an average annual cost of US$386. 89 million: • average recurrent of about US$42. 40 million • Average Capital costs US$344. 49 million
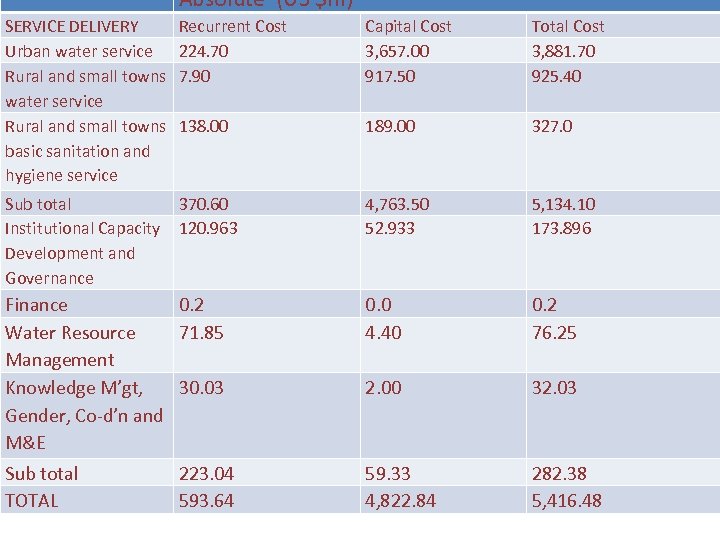 Absolute (US $m) SERVICE DELIVERY Urban water service Rural and small towns basic sanitation and hygiene service Recurrent Cost 224. 70 7. 90 Capital Cost 3, 657. 00 917. 50 Total Cost 3, 881. 70 925. 40 138. 00 189. 00 327. 0 Sub total 370. 60 Institutional Capacity 120. 963 Development and Governance 4, 763. 50 52. 933 5, 134. 10 173. 896 Finance 0. 2 Water Resource 71. 85 Management Knowledge M’gt, 30. 03 Gender, Co-d’n and M&E 0. 0 4. 40 0. 2 76. 25 2. 00 32. 03 Sub total TOTAL 59. 33 4, 822. 84 282. 38 5, 416. 48 223. 04 593. 64
Absolute (US $m) SERVICE DELIVERY Urban water service Rural and small towns basic sanitation and hygiene service Recurrent Cost 224. 70 7. 90 Capital Cost 3, 657. 00 917. 50 Total Cost 3, 881. 70 925. 40 138. 00 189. 00 327. 0 Sub total 370. 60 Institutional Capacity 120. 963 Development and Governance 4, 763. 50 52. 933 5, 134. 10 173. 896 Finance 0. 2 Water Resource 71. 85 Management Knowledge M’gt, 30. 03 Gender, Co-d’n and M&E 0. 0 4. 40 0. 2 76. 25 2. 00 32. 03 Sub total TOTAL 59. 33 4, 822. 84 282. 38 5, 416. 48 223. 04 593. 64
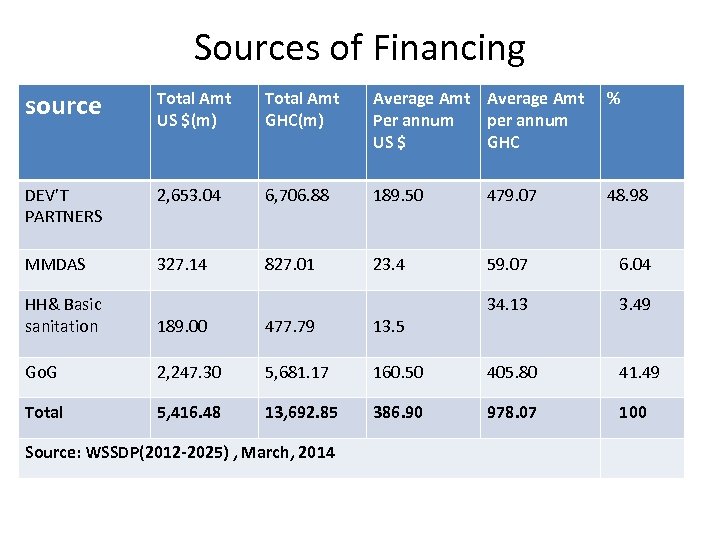 Sources of Financing source Total Amt US $(m) Total Amt GHC(m) Average Amt Per annum per annum US $ GHC % DEV’T PARTNERS 2, 653. 04 6, 706. 88 189. 50 479. 07 48. 98 MMDAS 327. 14 827. 01 23. 4 59. 07 6. 04 34. 13 3. 49 HH& Basic sanitation 189. 00 477. 79 13. 5 Go. G 2, 247. 30 5, 681. 17 160. 50 405. 80 41. 49 Total 5, 416. 48 13, 692. 85 386. 90 978. 07 100 Source: WSSDP(2012 -2025) , March, 2014
Sources of Financing source Total Amt US $(m) Total Amt GHC(m) Average Amt Per annum per annum US $ GHC % DEV’T PARTNERS 2, 653. 04 6, 706. 88 189. 50 479. 07 48. 98 MMDAS 327. 14 827. 01 23. 4 59. 07 6. 04 34. 13 3. 49 HH& Basic sanitation 189. 00 477. 79 13. 5 Go. G 2, 247. 30 5, 681. 17 160. 50 405. 80 41. 49 Total 5, 416. 48 13, 692. 85 386. 90 978. 07 100 Source: WSSDP(2012 -2025) , March, 2014
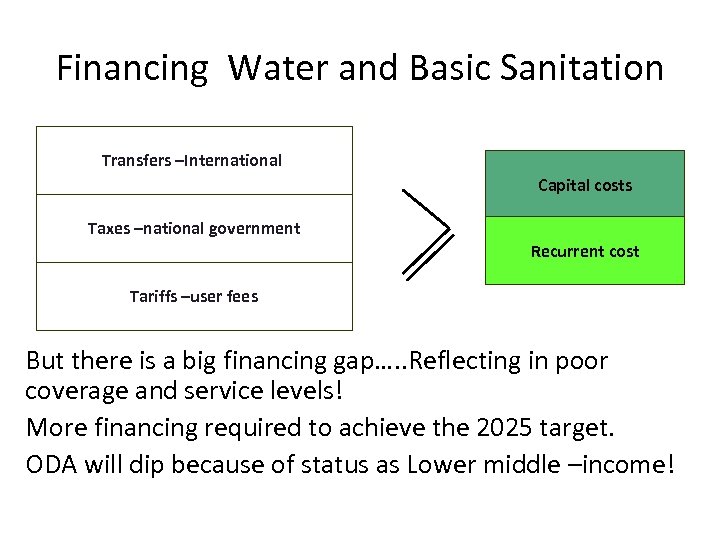 Financing Water and Basic Sanitation Transfers –International Capital costs Taxes –national government Recurrent cost Tariffs –user fees But there is a big financing gap…. . Reflecting in poor coverage and service levels! More financing required to achieve the 2025 target. ODA will dip because of status as Lower middle –income!
Financing Water and Basic Sanitation Transfers –International Capital costs Taxes –national government Recurrent cost Tariffs –user fees But there is a big financing gap…. . Reflecting in poor coverage and service levels! More financing required to achieve the 2025 target. ODA will dip because of status as Lower middle –income!
 Sustainable WASH financing • Transfers not enough! Only a small percentage of the overall financial needs to the sector. • Tariffs also not enough as focus is on the recovery of operation and maintenance costs. Under this heading are also the households own contributions to construction of their own infrastructure or paying for microcredit loans. • We need the taxes! This is the single largest source of funds for public goods and infrastructure dependent sectors like ours.
Sustainable WASH financing • Transfers not enough! Only a small percentage of the overall financial needs to the sector. • Tariffs also not enough as focus is on the recovery of operation and maintenance costs. Under this heading are also the households own contributions to construction of their own infrastructure or paying for microcredit loans. • We need the taxes! This is the single largest source of funds for public goods and infrastructure dependent sectors like ours.
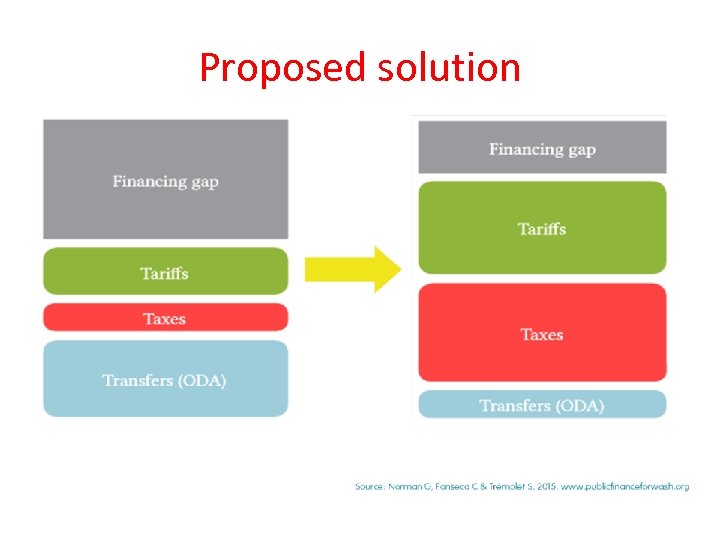 Proposed solution
Proposed solution
 GAPS IN WSSDP IN RELATION TO SDG GOAL 6 TARGETS • Pro-poor targeting is not highlighted to achieve universal and equitable access as mentioned in SDG target (6. 2) • Pollution of water bodies and sources not adequately articulated to include co-ordination across sectors( 6. 3) • Sustainability initiatives at community level • Definitive role of LGAs(service delivery authorities backed by adequate funding, M&E skills)?
GAPS IN WSSDP IN RELATION TO SDG GOAL 6 TARGETS • Pro-poor targeting is not highlighted to achieve universal and equitable access as mentioned in SDG target (6. 2) • Pollution of water bodies and sources not adequately articulated to include co-ordination across sectors( 6. 3) • Sustainability initiatives at community level • Definitive role of LGAs(service delivery authorities backed by adequate funding, M&E skills)?
 Concluding remarks What can we do about the 3 Ts? • The country’s middle income status means grants are dwindling; commercial loans or concessional loans might be available • How do we mobilise additional sources of domestic financing (increased government allocation, pension funds, insurance companies? ) • Can the sector compete for the loans? Sector needs to be better organised – well managed to ensure cost recovery. – Appropriate cost recovery policies and strategies – Efficient operations and management issues – Pooled funding for Capital Maintenance for rural water? • How can we optimise international transfers as a Middle income country? DPs?
Concluding remarks What can we do about the 3 Ts? • The country’s middle income status means grants are dwindling; commercial loans or concessional loans might be available • How do we mobilise additional sources of domestic financing (increased government allocation, pension funds, insurance companies? ) • Can the sector compete for the loans? Sector needs to be better organised – well managed to ensure cost recovery. – Appropriate cost recovery policies and strategies – Efficient operations and management issues – Pooled funding for Capital Maintenance for rural water? • How can we optimise international transfers as a Middle income country? DPs?


