134ab73eefc558c0a90e8462f230dbd1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Water Safety Conference 2010 Regulatory Perspective on Development of Piped Drinking Water Safety Plan in Singapore Lam Chun Hsiang Drinking Water Unit (DWU) National Environment Agency, Singapore
Water Safety Conference 2010 Regulatory Perspective on Development of Piped Drinking Water Safety Plan in Singapore Lam Chun Hsiang Drinking Water Unit (DWU) National Environment Agency, Singapore
 Background • Singapore, Regulatory Authorities, Water Suppliers New Regulatory Framework • Objectives, Technical Committee, Regulations, Legislative Requirements Water Safety Plans • Preparation of Plans, Framework for Monitoring and Assessment Challenges and Learning Points
Background • Singapore, Regulatory Authorities, Water Suppliers New Regulatory Framework • Objectives, Technical Committee, Regulations, Legislative Requirements Water Safety Plans • Preparation of Plans, Framework for Monitoring and Assessment Challenges and Learning Points
 Background: Singapore Population: ~ 5 million Mean daily temp: ~ 26. 8 °C Mean annual rainfall: ~ 2300 mm High humidity: ~ 84%
Background: Singapore Population: ~ 5 million Mean daily temp: ~ 26. 8 °C Mean annual rainfall: ~ 2300 mm High humidity: ~ 84%
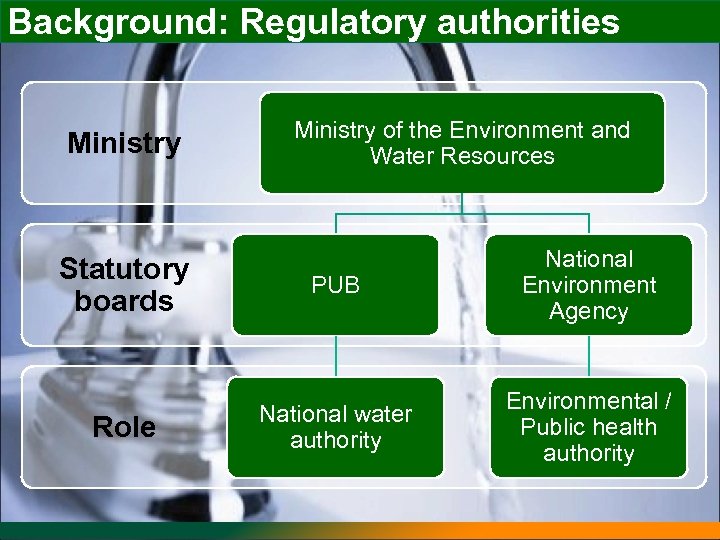 Background: Regulatory authorities Ministry of the Environment and Water Resources Statutory boards PUB National Environment Agency Role National water authority Environmental / Public health authority
Background: Regulatory authorities Ministry of the Environment and Water Resources Statutory boards PUB National Environment Agency Role National water authority Environmental / Public health authority
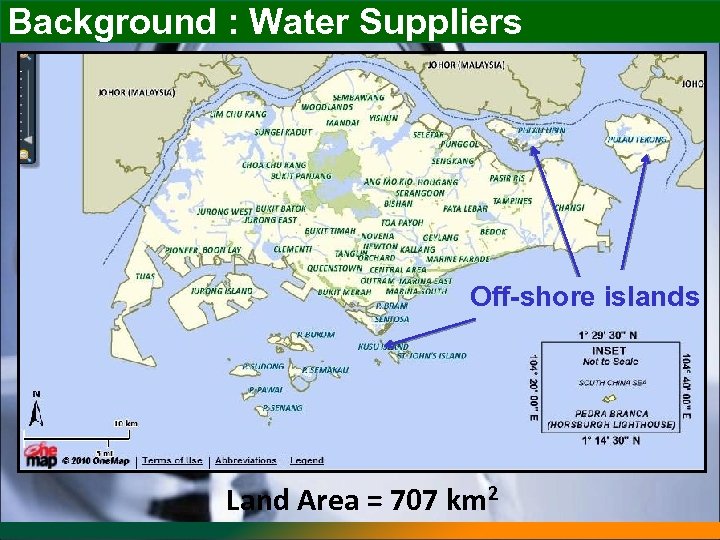 Background : Water Suppliers Off-shore islands Land Area = 707 km 2
Background : Water Suppliers Off-shore islands Land Area = 707 km 2
 Background : Water Suppliers PUB: Major supplier in Singapore Small suppliers: Usually supply < 1000 m 3 of water per day (Employ traditional or desalination technology)
Background : Water Suppliers PUB: Major supplier in Singapore Small suppliers: Usually supply < 1000 m 3 of water per day (Employ traditional or desalination technology)
 Background • Singapore, Regulatory Authorities, Water Suppliers New Regulatory Framework • Objectives, Technical Committee, Regulations, Legislative Requirements Water Safety Plans • Preparation of Plans, Framework for Monitoring and Assessment Challenges and Learning points
Background • Singapore, Regulatory Authorities, Water Suppliers New Regulatory Framework • Objectives, Technical Committee, Regulations, Legislative Requirements Water Safety Plans • Preparation of Plans, Framework for Monitoring and Assessment Challenges and Learning points
 New Regulatory Framework Objectives a) Need to establish a common set of standards for piped drinking water suppliers b)Inculcate preventive risk management practices amongst piped drinking water suppliers
New Regulatory Framework Objectives a) Need to establish a common set of standards for piped drinking water suppliers b)Inculcate preventive risk management practices amongst piped drinking water suppliers
 New Regulatory framework Technical Committee on National Drinking Water Quality Standards • Formed to advise NEA on drinking water quality standards and related issues. • Consists of 11 local and 2 overseas experts • NEA, PUB, MOH, AVA • Educational Institutions - NUS, NTU • Prof. Michael Rouse from UK • Dr. Joseph Cotruvo from USA • Expertise of committee lends credence to standards for both the industry as well as the public
New Regulatory framework Technical Committee on National Drinking Water Quality Standards • Formed to advise NEA on drinking water quality standards and related issues. • Consists of 11 local and 2 overseas experts • NEA, PUB, MOH, AVA • Educational Institutions - NUS, NTU • Prof. Michael Rouse from UK • Dr. Joseph Cotruvo from USA • Expertise of committee lends credence to standards for both the industry as well as the public
 New Regulatory Framework 8 0 0 2 Available for download from NEA’s website: www. nea. gov. sg
New Regulatory Framework 8 0 0 2 Available for download from NEA’s website: www. nea. gov. sg
 New Regulatory Framework Legislative requirements a) Compliance with the water quality standards b) Preparation of water safety and sampling plans & periodic review c) Approval of these plans by NEA d) Monitoring of water quality and submission of test results to NEA e) Calibration and maintenance of test equipment f) 24 -hour notification g) Documentation and record keeping
New Regulatory Framework Legislative requirements a) Compliance with the water quality standards b) Preparation of water safety and sampling plans & periodic review c) Approval of these plans by NEA d) Monitoring of water quality and submission of test results to NEA e) Calibration and maintenance of test equipment f) 24 -hour notification g) Documentation and record keeping
 Background • Singapore, Regulatory Authorities, Water Suppliers New Regulatory Framework • Objectives, Technical Committee, Regulations, Legislative Requirements Water Safety Plans • Preparation of Plans, Framework for Monitoring and Assessment
Background • Singapore, Regulatory Authorities, Water Suppliers New Regulatory Framework • Objectives, Technical Committee, Regulations, Legislative Requirements Water Safety Plans • Preparation of Plans, Framework for Monitoring and Assessment
 Water Safety Plans Preparation of water safety plans a) Code of Practice on Piped Drinking Water Safety and Sampling plans • Available for download from NEA’s website at: www. nea. gov. sg b) Templates for preparation of water safety plans
Water Safety Plans Preparation of water safety plans a) Code of Practice on Piped Drinking Water Safety and Sampling plans • Available for download from NEA’s website at: www. nea. gov. sg b) Templates for preparation of water safety plans
 Water Safety Plans Key components of water safety plans Based on WHO Guidelines: a) Formation of Water Safety Team b) Documentation of the system c) Hazard assessment and risk characterization d) Sanitary inspection of the raw water/supply e) Control measures and operational monitoring f) Management procedures
Water Safety Plans Key components of water safety plans Based on WHO Guidelines: a) Formation of Water Safety Team b) Documentation of the system c) Hazard assessment and risk characterization d) Sanitary inspection of the raw water/supply e) Control measures and operational monitoring f) Management procedures
 Water Safety Plans • Provides a basis for preparation of water sampling plans
Water Safety Plans • Provides a basis for preparation of water sampling plans
 Water Safety Plans Framework for monitoring and assessment Desktop Audit Water safety and sampling plans > 100, 000 test results per year Results are checked for compliance with regulatory standards and water safety and sampling plans Site Inspections Check if water safety plans are being implemented Identify risk /shortcomings and make suggestions for improvement
Water Safety Plans Framework for monitoring and assessment Desktop Audit Water safety and sampling plans > 100, 000 test results per year Results are checked for compliance with regulatory standards and water safety and sampling plans Site Inspections Check if water safety plans are being implemented Identify risk /shortcomings and make suggestions for improvement
 Background • Singapore, Regulatory Authorities, Water Suppliers New Regulatory Framework • Objectives, Technical Committee, Regulations, Legislative Requirements Water Safety Plans • Preparation of Plans, Framework for Monitoring and Assessment Challenges and Learning points
Background • Singapore, Regulatory Authorities, Water Suppliers New Regulatory Framework • Objectives, Technical Committee, Regulations, Legislative Requirements Water Safety Plans • Preparation of Plans, Framework for Monitoring and Assessment Challenges and Learning points
 Challenges and Learning Points Main challenge: To ensure that all relevant hazards are identified, and their risk characterization is carried out in a meaningful way to establish the high-risk scenarios.
Challenges and Learning Points Main challenge: To ensure that all relevant hazards are identified, and their risk characterization is carried out in a meaningful way to establish the high-risk scenarios.
 Challenges and Learning Points Challenges: a) Certain members in the water safety team may choose to have a greater flexibility in highlighting the hazard, resulting in conflict of view between members on the extent of risk. b) May make generic statements such as “All applicable parameters should be controlled to prevent the hazard”, without specifying the type of the parameters and their degree of control
Challenges and Learning Points Challenges: a) Certain members in the water safety team may choose to have a greater flexibility in highlighting the hazard, resulting in conflict of view between members on the extent of risk. b) May make generic statements such as “All applicable parameters should be controlled to prevent the hazard”, without specifying the type of the parameters and their degree of control
 Challenges and Learning Points Challenges: c) May choose not to highlight certain hazards, thinking that the regulatory agency may raise questions on the control of those hazards. d) May document inadequate or even erroneous description of the hazards, especially those who are not academically inclined.
Challenges and Learning Points Challenges: c) May choose not to highlight certain hazards, thinking that the regulatory agency may raise questions on the control of those hazards. d) May document inadequate or even erroneous description of the hazards, especially those who are not academically inclined.
 Challenges and Learning Points How various challenges were addressed: a) b) c) d) e) DWU built up the necessary expertise Reviewed the draft plans prepared by the suppliers Discussed the details with the WSP team members Conducted site audits Revised the plans where required, before seeking the management approval
Challenges and Learning Points How various challenges were addressed: a) b) c) d) e) DWU built up the necessary expertise Reviewed the draft plans prepared by the suppliers Discussed the details with the WSP team members Conducted site audits Revised the plans where required, before seeking the management approval
 Challenges and Learning Points Lessons learnt: If the requirement for preparation of water safety is not prescribed under the regulations • Suppliers may not invest their efforts and time in preparing such plans; and • even if they do, the plans may not be adequate in substance.
Challenges and Learning Points Lessons learnt: If the requirement for preparation of water safety is not prescribed under the regulations • Suppliers may not invest their efforts and time in preparing such plans; and • even if they do, the plans may not be adequate in substance.
 Challenges and Learning Points Lessons learnt: Even though water suppliers’ staff may be familiar with ISO 9001 system, they may not be able to adequately address various hazards in the WSP due to the difference in methodology used to identify and characterize the hazards.
Challenges and Learning Points Lessons learnt: Even though water suppliers’ staff may be familiar with ISO 9001 system, they may not be able to adequately address various hazards in the WSP due to the difference in methodology used to identify and characterize the hazards.
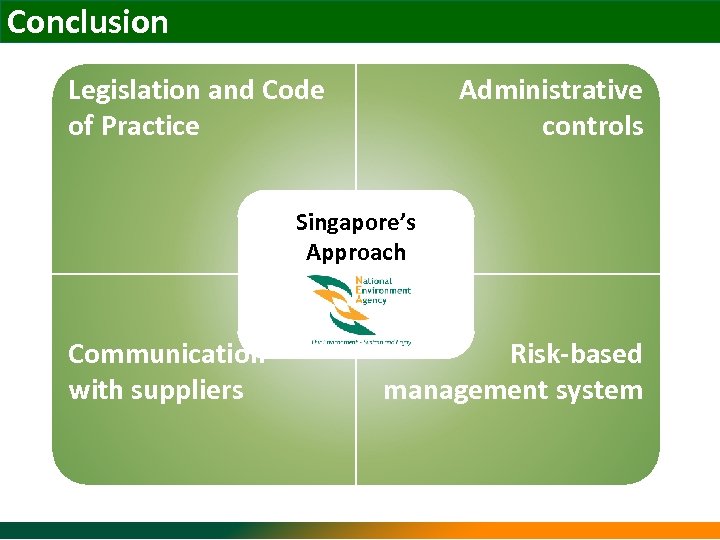 Conclusion Legislation and Code of Practice Administrative controls Singapore’s Approach Communication with suppliers Risk-based management system
Conclusion Legislation and Code of Practice Administrative controls Singapore’s Approach Communication with suppliers Risk-based management system
 “ “ With the new regulatory regime in place, Singapore’s growing population will continue to enjoy safe piped drinking water
“ “ With the new regulatory regime in place, Singapore’s growing population will continue to enjoy safe piped drinking water
 Co-authors Dr. Pranav S. Joshi Mr. Ramnath Vaidyanathan Mr. S. Satish Appoo
Co-authors Dr. Pranav S. Joshi Mr. Ramnath Vaidyanathan Mr. S. Satish Appoo
 For more details www. nea. gov. sg Topics – Drinking Water Unit E-mail Lam_chun_hsiang@nea. gov. sg
For more details www. nea. gov. sg Topics – Drinking Water Unit E-mail Lam_chun_hsiang@nea. gov. sg
 Thank you
Thank you


