147bfe2fef05c7c1b07f419f31de56d4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Water Banks in the United States Draft Report Prepared Jointly by: West. Water Research Washington Department of Ecology

Public Sector Participants

Private Sector Market Participants Water. Bank. SM Trust
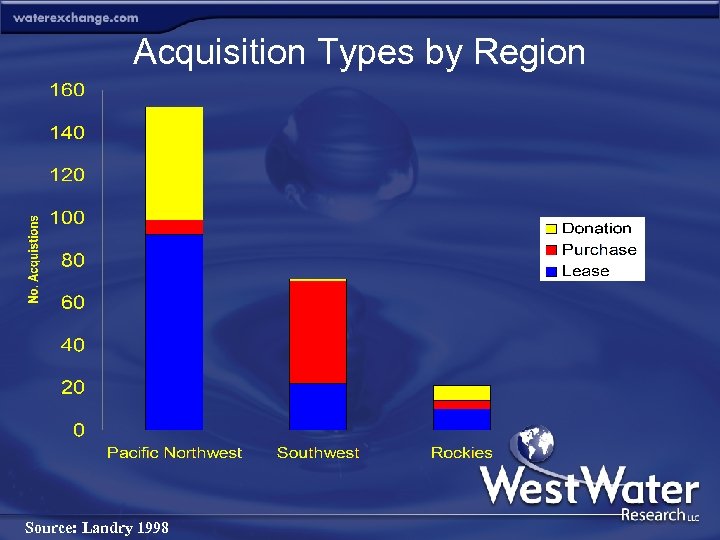
Acquisition Types by Region Source: Landry 1998

Environmental Water Acquisitions Leases, Purchases and Donations Total Quantity Acquired P. Northwest 1, 234, 57 af California 536, 323 af Southwest 306, 658 af Rockies 286, 482 af Source: Landry 1998
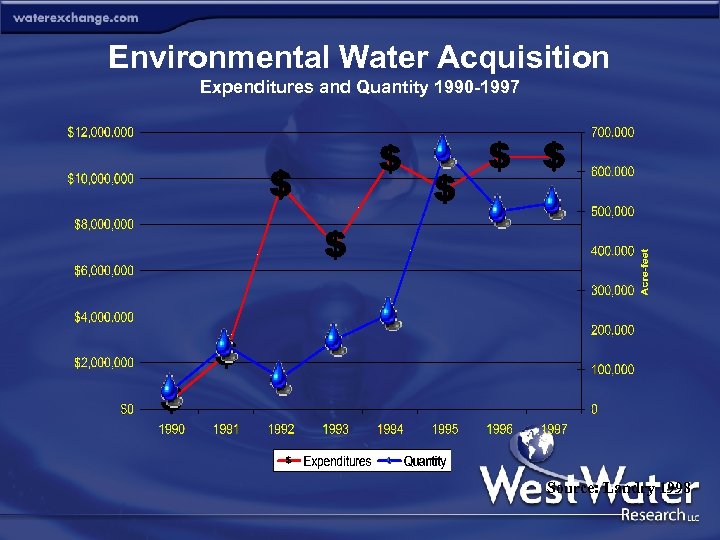
Environmental Water Acquisition Expenditures and Quantity 1990 -1997 Source: Landry 1998
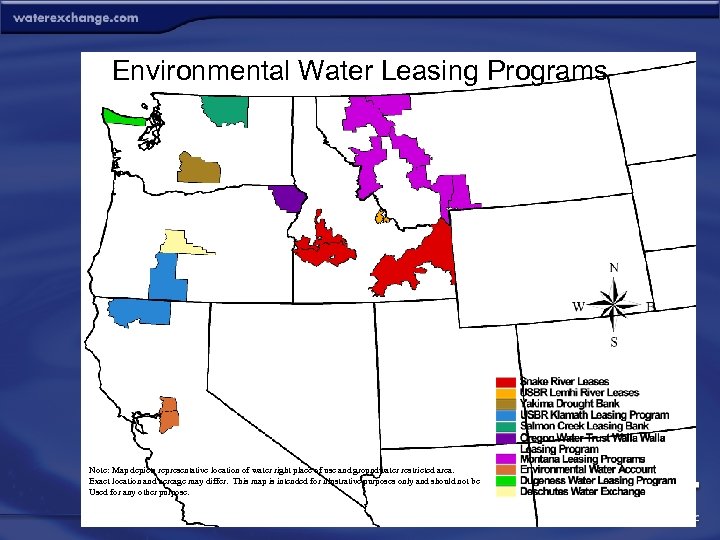
Environmental Water Leasing Programs Note: Map depicts representative location of water right place of use and groundwater restricted area. Exact location and acreage may differ. This map is intended for illustrative purposes only and should not be Used for any other purpose.
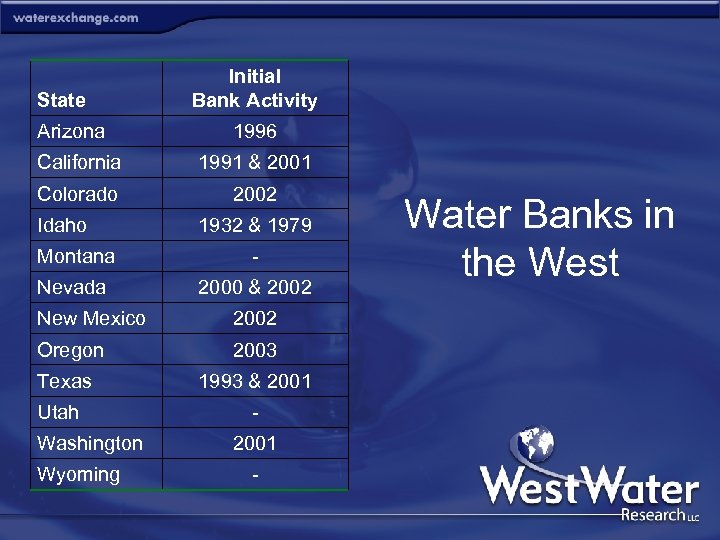
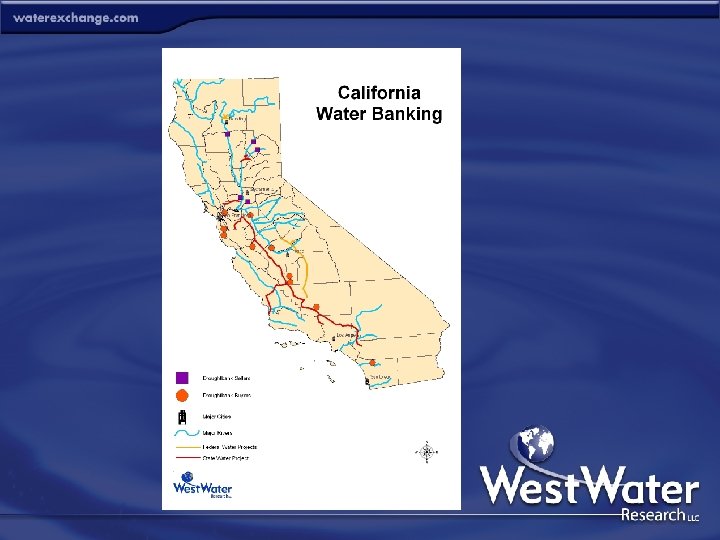
State Arizona Initial Bank Activity 1996 California 1991 & 2001 Colorado 2002 Idaho 1932 & 1979 Montana - Nevada 2000 & 2002 New Mexico 2002 Oregon 2003 Texas Utah Washington Wyoming 1993 & 2001 - Water Banks in the West
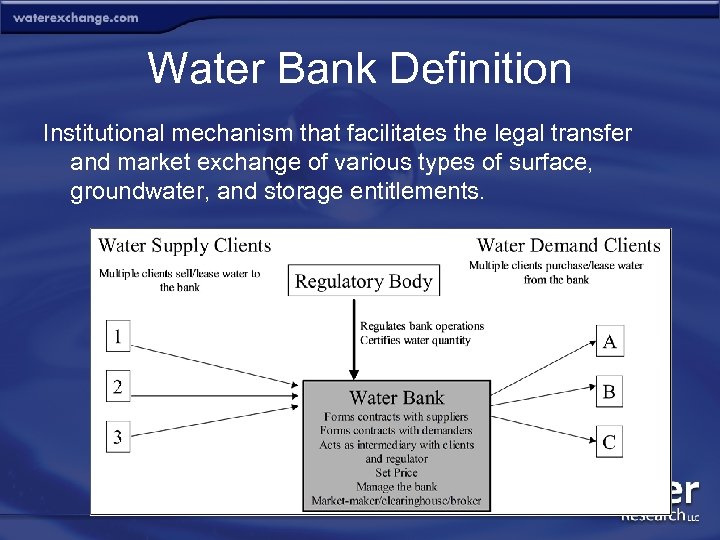
Water Bank Definition Institutional mechanism that facilitates the legal transfer and market exchange of various types of surface, groundwater, and storage entitlements.

Water Bank Formats • Water Banks are designed around specific sources or water entitlements • Common Bank Formats – Institutional Banking – Surface Storage Banking – Ground Water Banking – Conjunctive Use Banking

Purpose of Water Banking • • Creating reliability in water supply during dry years Creating seasonal water reliability Ensuring water supply for farmers Promoting water conservation by encouraging right holders to conserve and deposit rights into the bank • Acting as market mechanism • Resolving issues of inequity between groundwater and surface-water users • Ensuring compliance with intrastate agreements of instream flow

Bank Administrative Functions • • • Registry of water rights or entitlements Price setting and regulation Policies administration and daily operations Water right verification Quantifying the bankable water Specifying who can purchase or rent from the bank • Administering transfer or contract terms • Provide regulatory reporting or oversite • Resolving disputes

Market Structure of Water Banks • Clearing House – Online Bulletin Boards – Office Posting Boards • Standing or Fixed Price • Option or Contingent Markets • Auctions

California Drought Emergency Bank Profile • • • • Location: River Basin: Established: Year Active: Bank Format: Market Structure: Participation: Statewide, Primarily SWP and CVP service areas 1991, 1992, 1994 One-year leasing program Clearinghouse Supply – Northern California users; Demand – SWP and CVP contractors south of Delta Activity: High Pricing: Administrative Price Range ($/AF/YR): $68 -$175 Regulatory Oversight: Streamlined transfer process Administrator: California Department of Water Resources (DWA) Environmental Objective: Ensure minimum stream flows through the Delta
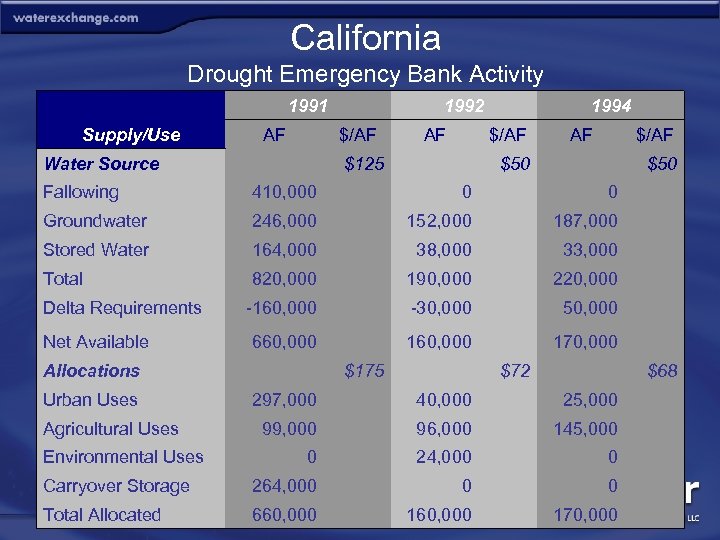
California Drought Emergency Bank Activity 1991 Supply/Use Water Source AF 1992 $/AF AF 1994 $/AF $125 AF $/AF $50 Fallowing 410, 000 Groundwater 246, 000 152, 000 187, 000 Stored Water 164, 000 38, 000 33, 000 Total 820, 000 190, 000 220, 000 -160, 000 -30, 000 50, 000 660, 000 170, 000 Delta Requirements Net Available Allocations Urban Uses Agricultural Uses 0 $50 $175 297, 000 0 $72 40, 000 $68 25, 000 99, 000 96, 000 145, 000 0 24, 000 0 Carryover Storage 264, 000 0 0 Total Allocated 660, 000 Environmental Uses 160, 000 170, 000

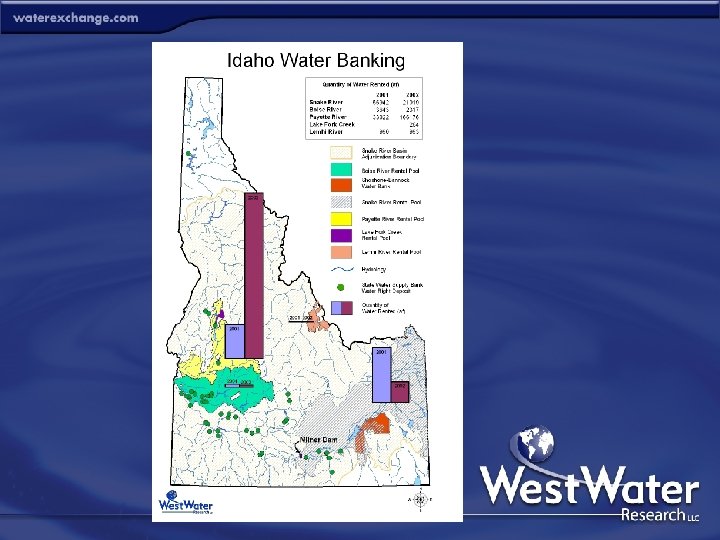
Idaho Statewide and Rental Pools Statewide Bank • • • • Location: Statewide River Basin: Statewide Year Established: 1979 Year Active: 1995 Bank Format: Institutional water bank Market Structure: Clearinghouse Participation: Supply – Open; Demand – Open Activity: Moderate Pricing: Market Based Price: $11/AF/YR Regulatory Oversight: Idaho Department of Water Resources Administrator: Idaho Department of Water Resources Environmental Objective: None Rental Pools • • • Six Established Banks Year Active: 1932 – Snake River Bank Format: Leasing stored water Market Structure: Clearinghouse Participation: Supply – Stored water; Demand – Open Activity: Low to High Pricing: Administrative Price: $3. 00 for in- basin $10. 50 out-of-basin Regulatory Oversight: State Administrator: Water District #1 Environmental Objective: None - Instream transactions encumbered by “last fill” policy
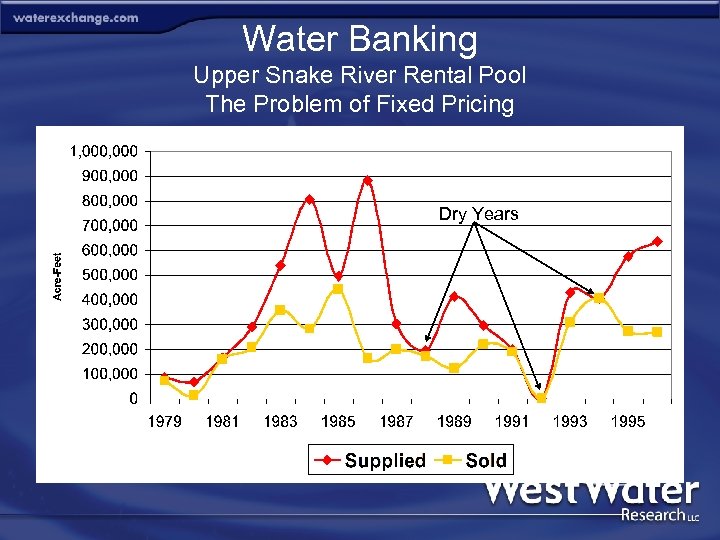
Water Banking Upper Snake River Rental Pool The Problem of Fixed Pricing Dry Years

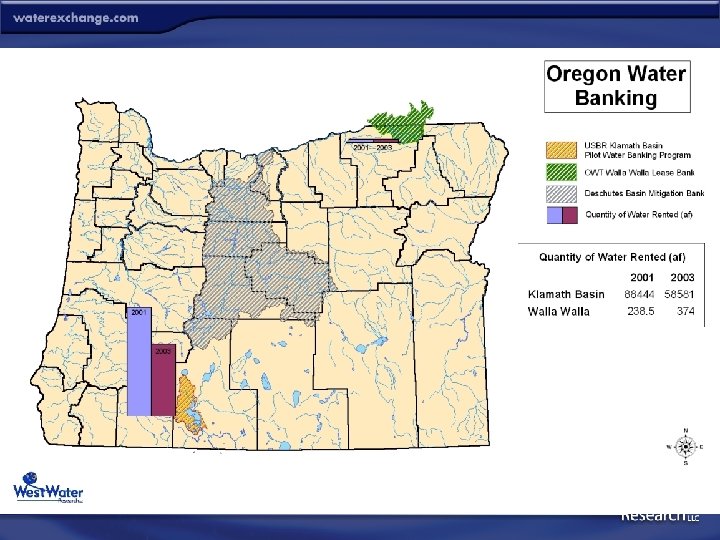
Oregon Water Banking Profile • Emerging Water Bank Programs – Klamath Basin Water Lease Bank – Walla Water Lease Bank – Deschutes Basin Groundwater Mitigation Bank • Bank Format Varies – Lease Banks are Predominate Structure – Lease Banks Operate Under Existing Regulatory Structure • Market Structure: • Participation: • • Activity: Regulatory Oversight: Administrator: Environmental: Bilateral Trades Supply – Open Demand – Bank Administrator Low to High State Federal and Nonprofit Yes

Water Banking: Six Important Considerations • What is the legal authority of the bank? – Does the bank have authority to execute trades? – Is legislation required? • What are the banks objectives and purpose? – Enhancing stream flow – Providing drought year water supplies • Who can participate in the bank? • What is the market area served by the bank? • How is water priced? – Fixed Price – Market Based • How will community acceptance and participation be encouraged?

West. Water Research Laramie Office: Houston Office: 121 Grand Avenue, Suite 222 Laramie, WY 82070 Tel: (307) 742 -3232 Fax: (307) 742 -3996 1100 Louisiana, Suite 2675 Houston, TX 77002 Tel: (713) 652 -2450 Fax: (713) 652 -2452
147bfe2fef05c7c1b07f419f31de56d4.ppt