830c6519fce5db8efeeeeb712c78036f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Warwick Effect Polymers Ltd Innovation in Polymers Elementis Nov. 18 th, 2004
Warwick Effect Polymers Ltd Innovation in Polymers Elementis Nov. 18 th, 2004
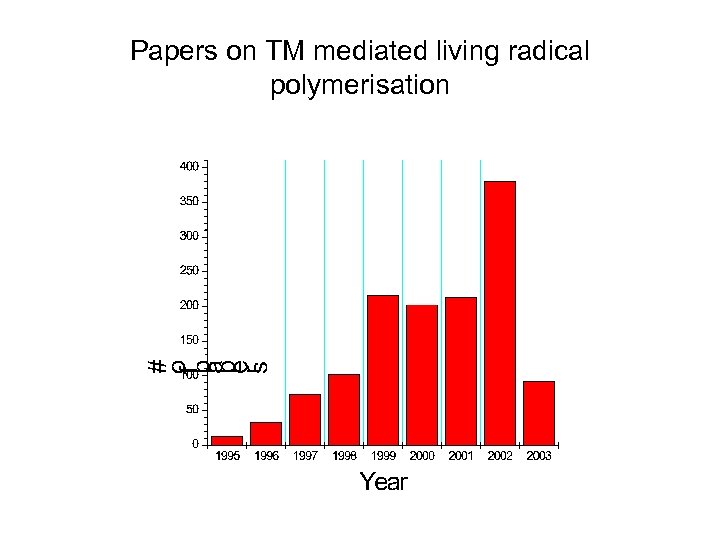 Papers on TM mediated living radical polymerisation
Papers on TM mediated living radical polymerisation
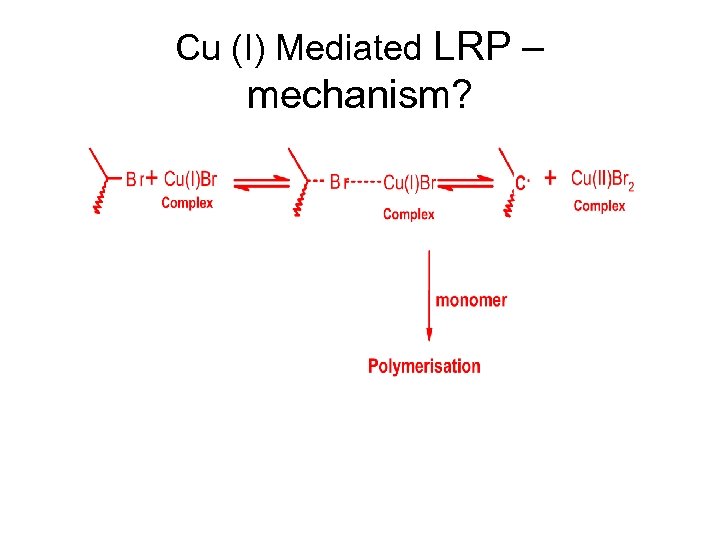 Cu (I) Mediated LRP – mechanism?
Cu (I) Mediated LRP – mechanism?
 Cu (I) Mediated LRP • Very Good Technique for control over Molecular weight • Inert to many Functional Groups • Applicable to a wide range of Monomers • Very robust Method Only really sensitive to oxygen Allowing a wide range of operating conditions L Contamination of product by Cu L Catalyst is not recycled
Cu (I) Mediated LRP • Very Good Technique for control over Molecular weight • Inert to many Functional Groups • Applicable to a wide range of Monomers • Very robust Method Only really sensitive to oxygen Allowing a wide range of operating conditions L Contamination of product by Cu L Catalyst is not recycled
 Ligands for Copper Mediated Polymerisation
Ligands for Copper Mediated Polymerisation
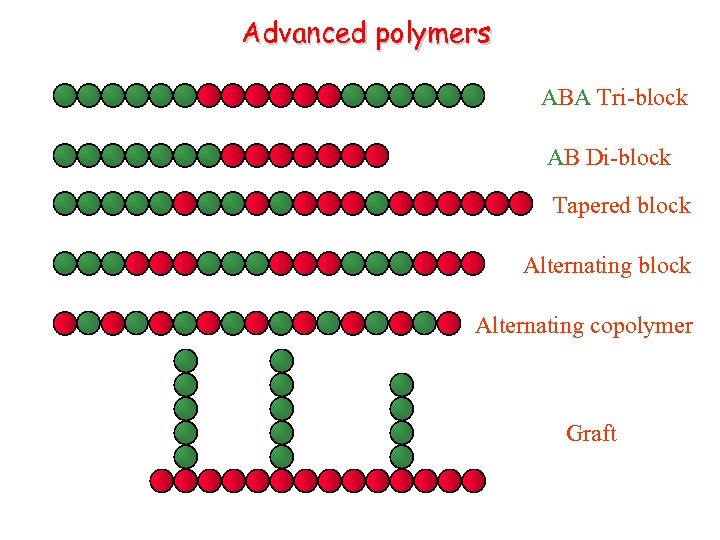 Advanced polymers ABA Tri-block AB Di-block Tapered block Alternating copolymer Graft
Advanced polymers ABA Tri-block AB Di-block Tapered block Alternating copolymer Graft
 Controlled Free Radical Polymerization and Warwick Effect Polymers • Fast-growing area of new technology • WEP has worldwide patents protecting platform/generic technology (US and Europe) • Several blue-chip customers • Significant expansion opportunities • Diverse market potential
Controlled Free Radical Polymerization and Warwick Effect Polymers • Fast-growing area of new technology • WEP has worldwide patents protecting platform/generic technology (US and Europe) • Several blue-chip customers • Significant expansion opportunities • Diverse market potential
 Management • Chairman Michael Penington • CEO Fergal O’Brien (May 2004) • CTO David Haddleton • B Dev (US) Thomas Neenan • Director Phil Stern
Management • Chairman Michael Penington • CEO Fergal O’Brien (May 2004) • CTO David Haddleton • B Dev (US) Thomas Neenan • Director Phil Stern
 Science Advisory Board • Craig Hawker, IBM, Almaden, (UCSB) • Mitsuo Sawamoto, Kyoto University • Tom Davis, University of New South Wales
Science Advisory Board • Craig Hawker, IBM, Almaden, (UCSB) • Mitsuo Sawamoto, Kyoto University • Tom Davis, University of New South Wales
 Strategy • Exploit existing IP for the development and supply of new polymers to meet specific customer needs. • Provide polymer expertise via short term contracts to develop customer base and provide revenue. • Develop new IP in polymers for healthcare.
Strategy • Exploit existing IP for the development and supply of new polymers to meet specific customer needs. • Provide polymer expertise via short term contracts to develop customer base and provide revenue. • Develop new IP in polymers for healthcare.
 Current WEP technology Partners • Company A – Hair-spray/Gel • Company B – Controlled release of Agrochemicals • Companies C, D, E …. – Poly. PEG™ for Healthcare
Current WEP technology Partners • Company A – Hair-spray/Gel • Company B – Controlled release of Agrochemicals • Companies C, D, E …. – Poly. PEG™ for Healthcare
 Scale-up • WEP able to manufacture up to 10 kg in house • Close relationship with scale up partner. • Successful scale up to 100 kg (1000 kg by Q 1 05). • WEP open to alternative scale-up options
Scale-up • WEP able to manufacture up to 10 kg in house • Close relationship with scale up partner. • Successful scale up to 100 kg (1000 kg by Q 1 05). • WEP open to alternative scale-up options
 160 kg Pilot Plant Scale up
160 kg Pilot Plant Scale up
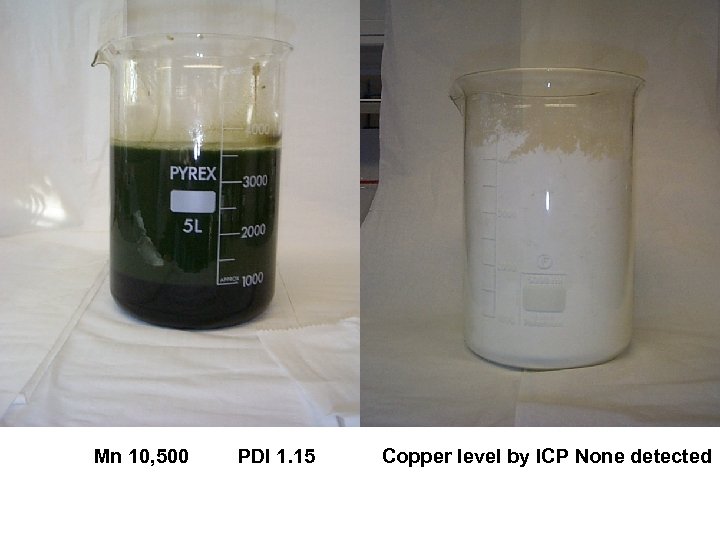 Mn 10, 500 PDI 1. 15 Copper level by ICP None detected
Mn 10, 500 PDI 1. 15 Copper level by ICP None detected
 Survey of Applications • • Solution Modifiers Surface and Fabric Modifiers Pigment and Dye Modifiers Biological – New PEG technology – Mucoadhesives – Polymers for diagnostics
Survey of Applications • • Solution Modifiers Surface and Fabric Modifiers Pigment and Dye Modifiers Biological – New PEG technology – Mucoadhesives – Polymers for diagnostics
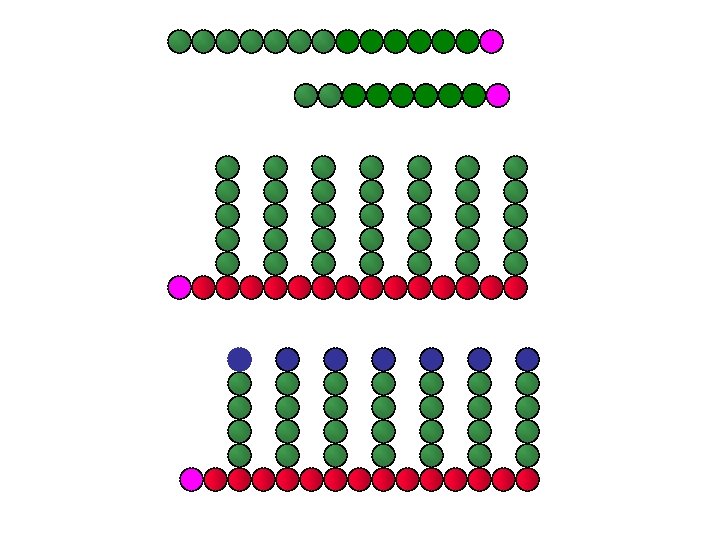
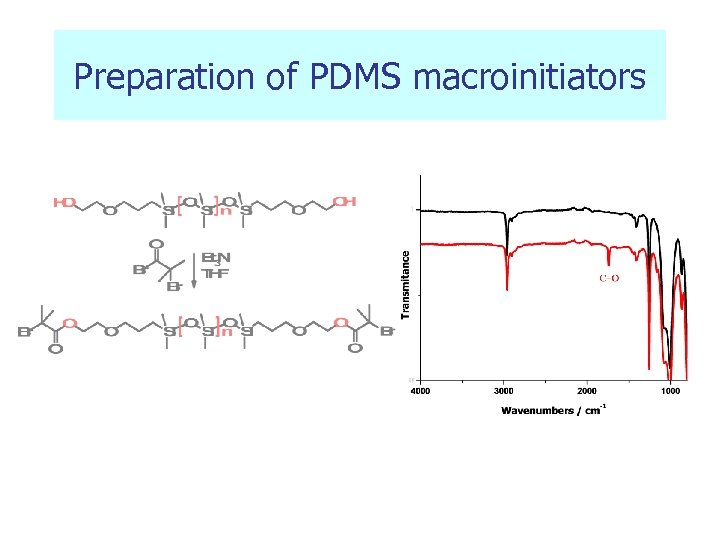 Preparation of PDMS macroinitiators
Preparation of PDMS macroinitiators
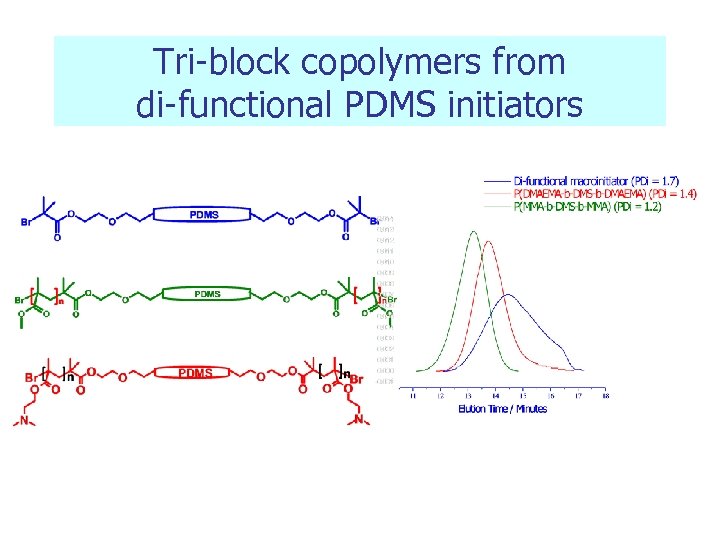 Tri-block copolymers from di-functional PDMS initiators
Tri-block copolymers from di-functional PDMS initiators
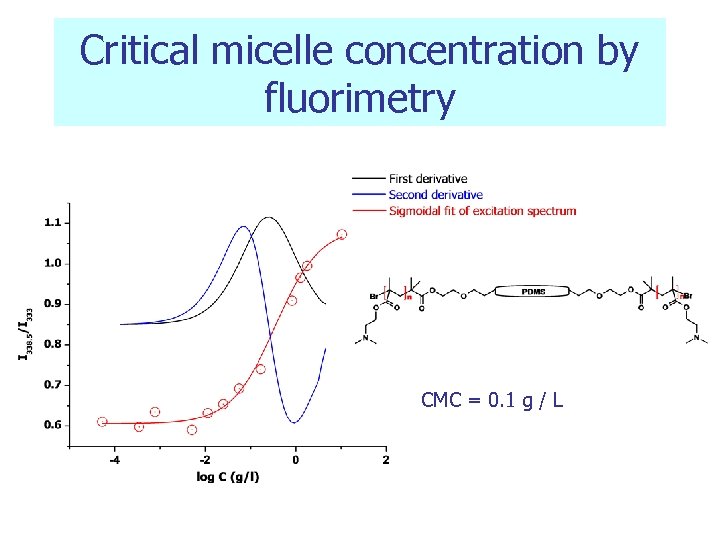 Critical micelle concentration by fluorimetry CMC = 0. 1 g / L
Critical micelle concentration by fluorimetry CMC = 0. 1 g / L
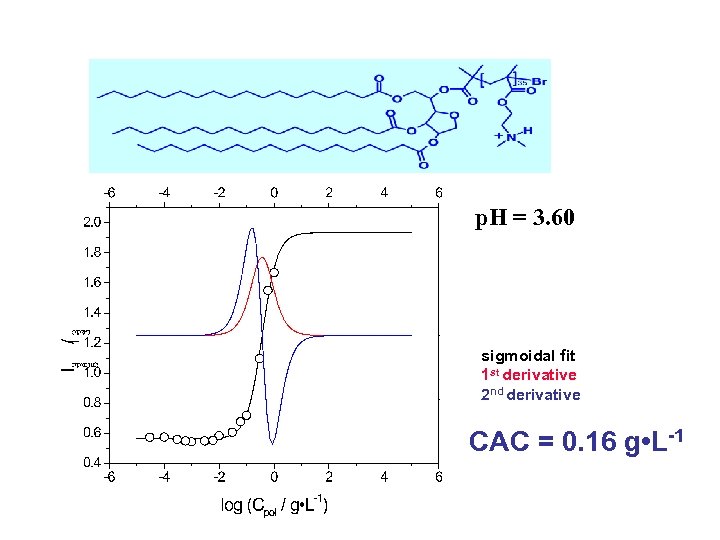 p. H = 3. 60 sigmoidal fit 1 st derivative 2 nd derivative CAC = 0. 16 g • L-1
p. H = 3. 60 sigmoidal fit 1 st derivative 2 nd derivative CAC = 0. 16 g • L-1
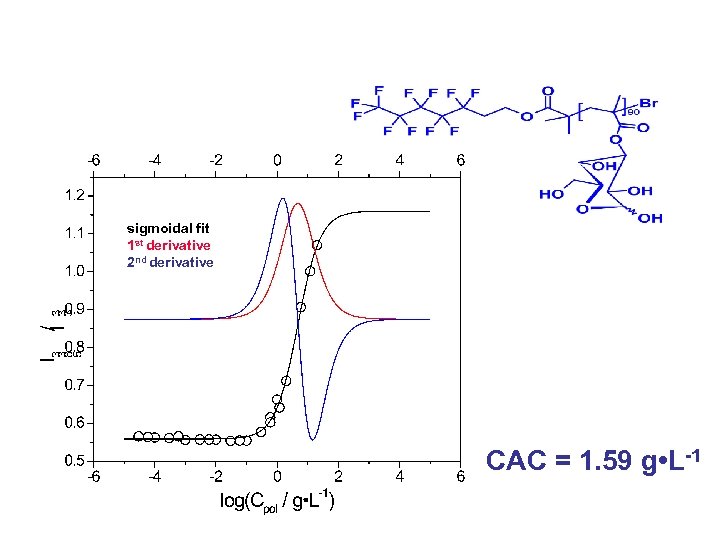 sigmoidal fit 1 st derivative 2 nd derivative CAC = 1. 59 g • L-1
sigmoidal fit 1 st derivative 2 nd derivative CAC = 1. 59 g • L-1
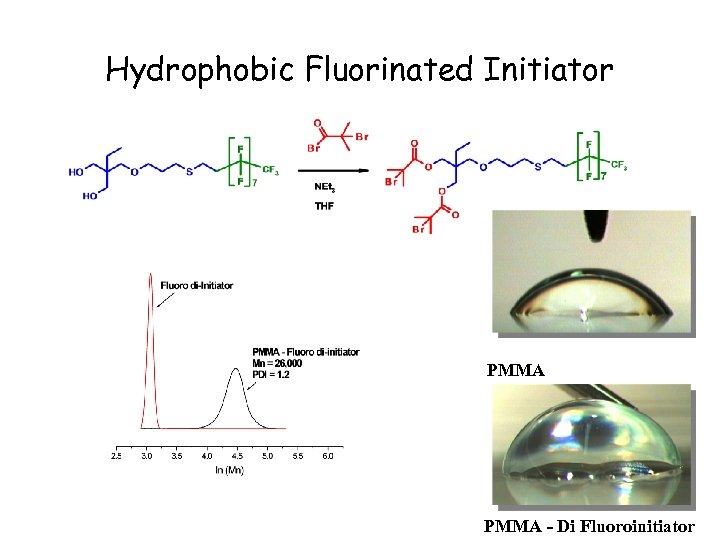 Hydrophobic Fluorinated Initiator PMMA - Di Fluoroinitiator
Hydrophobic Fluorinated Initiator PMMA - Di Fluoroinitiator

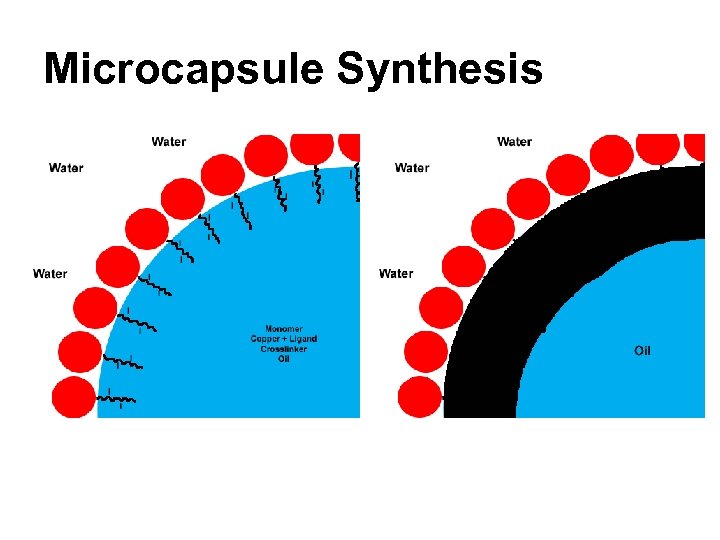 Microcapsule Synthesis
Microcapsule Synthesis
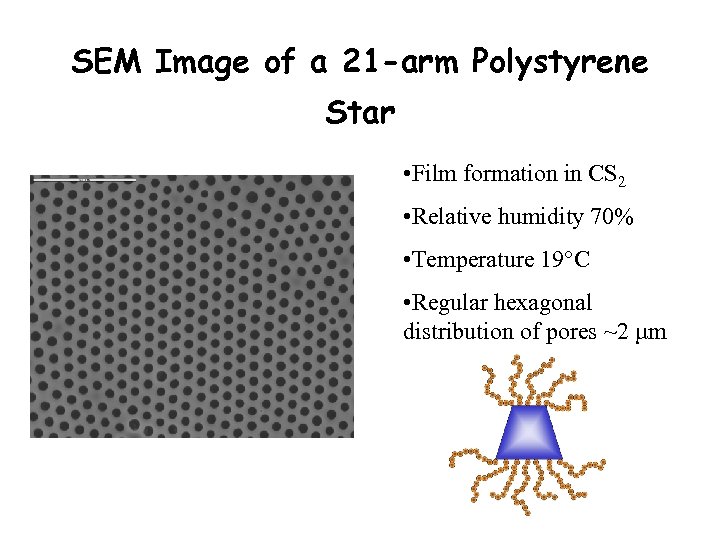 SEM Image of a 21 -arm Polystyrene Star • Film formation in CS 2 • Relative humidity 70% • Temperature 19°C • Regular hexagonal distribution of pores ~2 µm
SEM Image of a 21 -arm Polystyrene Star • Film formation in CS 2 • Relative humidity 70% • Temperature 19°C • Regular hexagonal distribution of pores ~2 µm
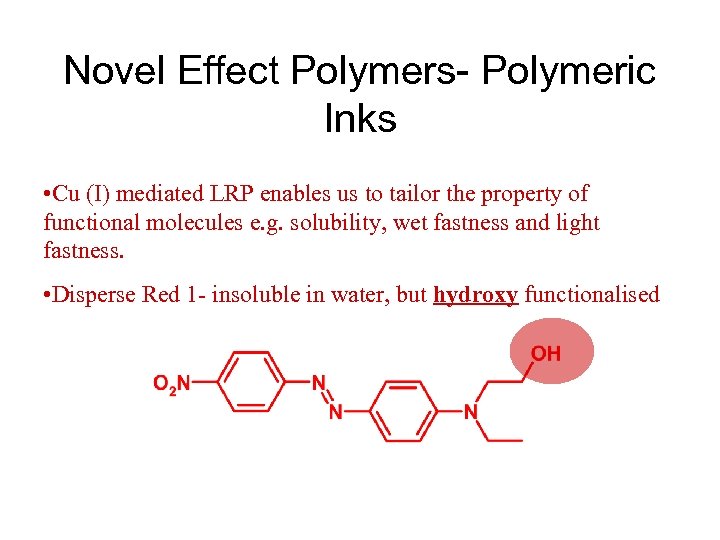 Novel Effect Polymers- Polymeric Inks • Cu (I) mediated LRP enables us to tailor the property of functional molecules e. g. solubility, wet fastness and light fastness. • Disperse Red 1 - insoluble in water, but hydroxy functionalised
Novel Effect Polymers- Polymeric Inks • Cu (I) mediated LRP enables us to tailor the property of functional molecules e. g. solubility, wet fastness and light fastness. • Disperse Red 1 - insoluble in water, but hydroxy functionalised
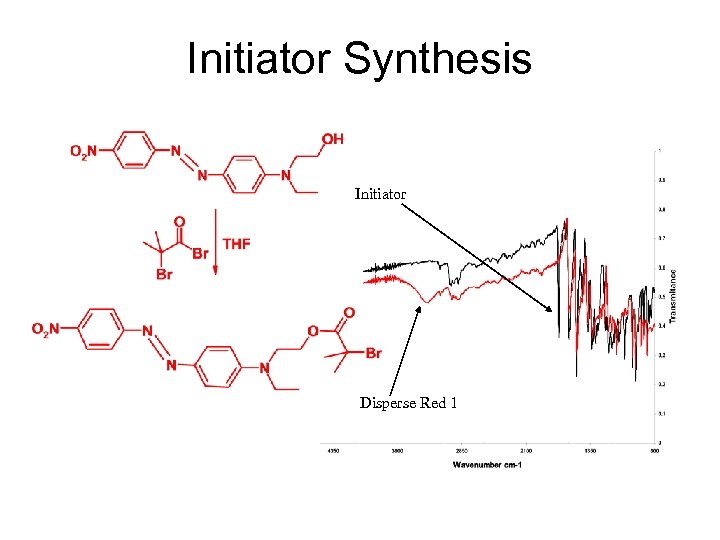 Initiator Synthesis Initiator Disperse Red 1
Initiator Synthesis Initiator Disperse Red 1
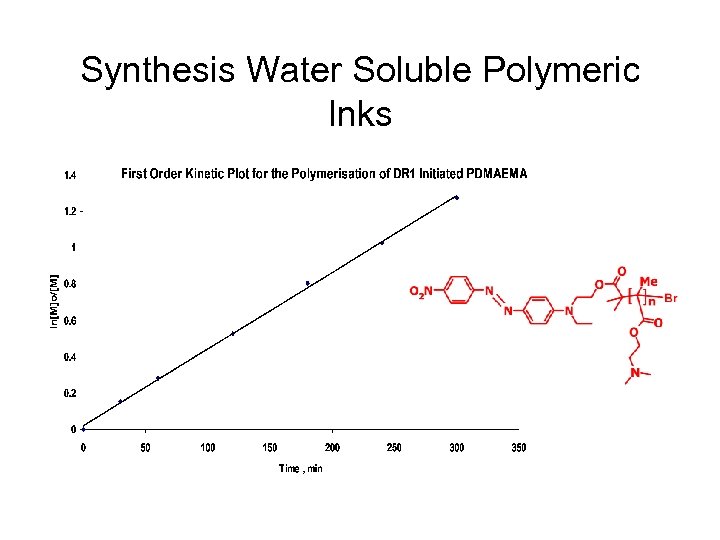 Synthesis Water Soluble Polymeric Inks
Synthesis Water Soluble Polymeric Inks
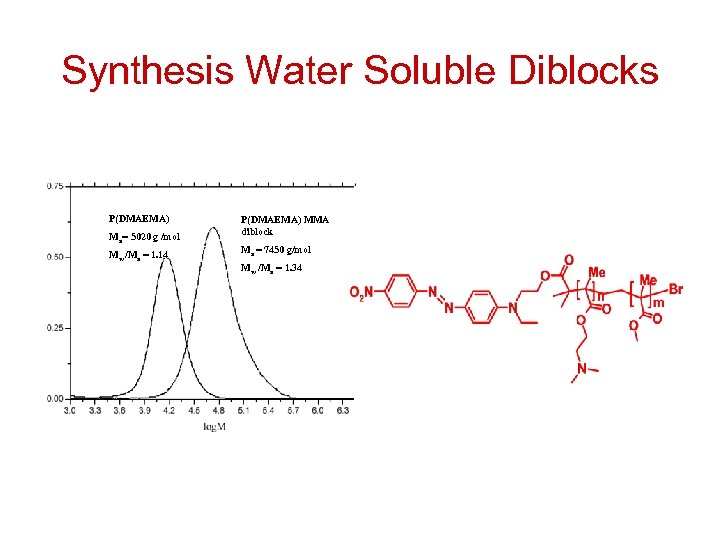 Synthesis Water Soluble Diblocks P(DMAEMA) Mn= 5020 g /mol Mw /Mn = 1. 14 P(DMAEMA) MMA diblock Mn = 7450 g/mol Mw /Mn = 1. 34
Synthesis Water Soluble Diblocks P(DMAEMA) Mn= 5020 g /mol Mw /Mn = 1. 14 P(DMAEMA) MMA diblock Mn = 7450 g/mol Mw /Mn = 1. 34
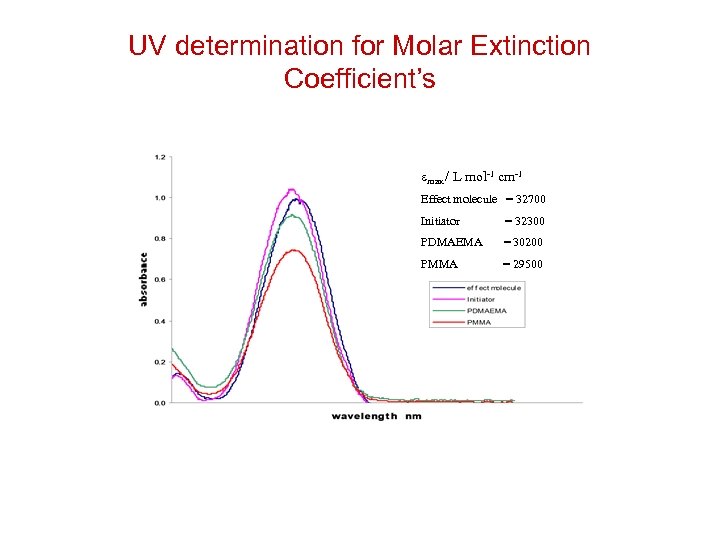 UV determination for Molar Extinction Coefficient’s emax / L mol-1 cm-1 Effect molecule = 32700 Initiator = 32300 PDMAEMA = 30200 PMMA = 29500
UV determination for Molar Extinction Coefficient’s emax / L mol-1 cm-1 Effect molecule = 32700 Initiator = 32300 PDMAEMA = 30200 PMMA = 29500
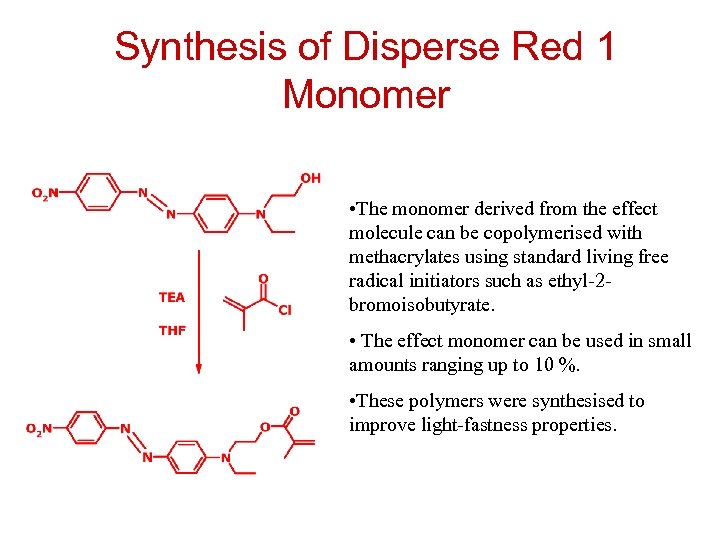 Synthesis of Disperse Red 1 Monomer • The monomer derived from the effect molecule can be copolymerised with methacrylates using standard living free radical initiators such as ethyl-2 bromoisobutyrate. • The effect monomer can be used in small amounts ranging up to 10 %. • These polymers were synthesised to improve light-fastness properties.
Synthesis of Disperse Red 1 Monomer • The monomer derived from the effect molecule can be copolymerised with methacrylates using standard living free radical initiators such as ethyl-2 bromoisobutyrate. • The effect monomer can be used in small amounts ranging up to 10 %. • These polymers were synthesised to improve light-fastness properties.
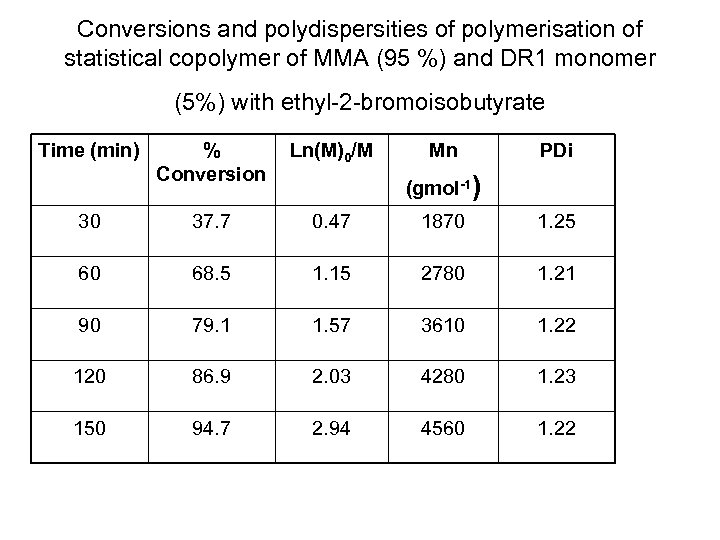 Conversions and polydispersities of polymerisation of statistical copolymer of MMA (95 %) and DR 1 monomer (5%) with ethyl-2 -bromoisobutyrate Time (min) % Conversion Ln(M)0/M Mn PDi 30 37. 7 0. 47 1870 1. 25 60 68. 5 1. 15 2780 1. 21 90 79. 1 1. 57 3610 1. 22 120 86. 9 2. 03 4280 1. 23 150 94. 7 2. 94 4560 1. 22 (gmol-1)
Conversions and polydispersities of polymerisation of statistical copolymer of MMA (95 %) and DR 1 monomer (5%) with ethyl-2 -bromoisobutyrate Time (min) % Conversion Ln(M)0/M Mn PDi 30 37. 7 0. 47 1870 1. 25 60 68. 5 1. 15 2780 1. 21 90 79. 1 1. 57 3610 1. 22 120 86. 9 2. 03 4280 1. 23 150 94. 7 2. 94 4560 1. 22 (gmol-1)
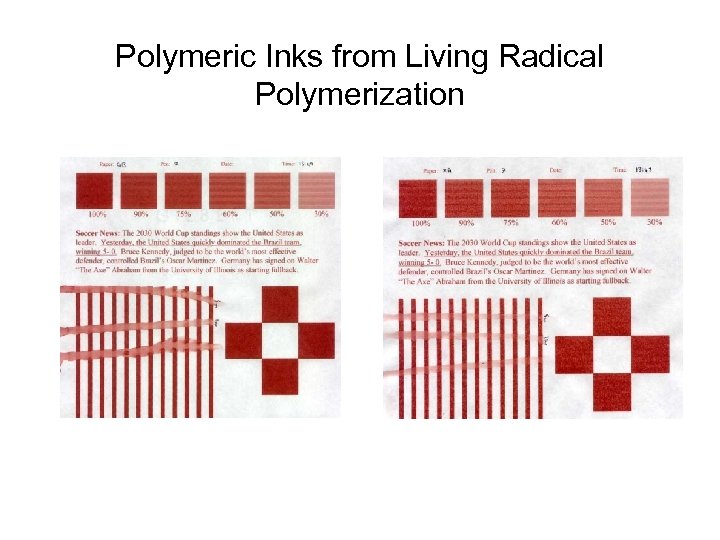 Polymeric Inks from Living Radical Polymerization Gibbet Bond Paper Xerox Acid Paper
Polymeric Inks from Living Radical Polymerization Gibbet Bond Paper Xerox Acid Paper
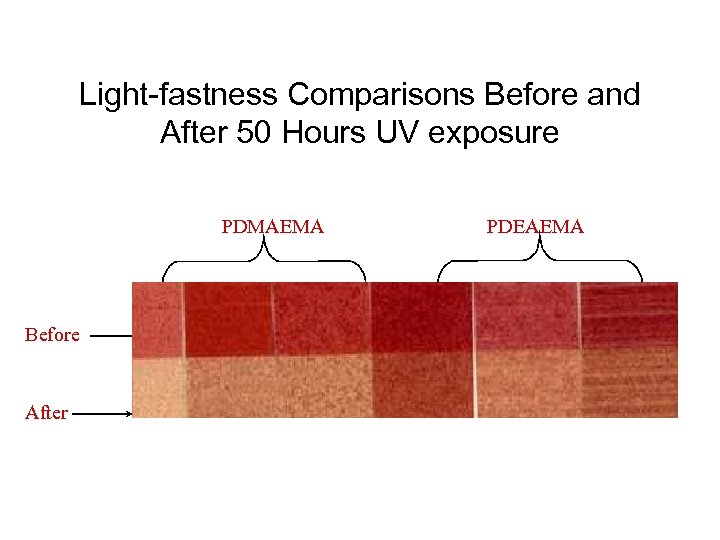 Light-fastness Comparisons Before and After 50 Hours UV exposure PDMAEMA Before After PDEAEMA
Light-fastness Comparisons Before and After 50 Hours UV exposure PDMAEMA Before After PDEAEMA
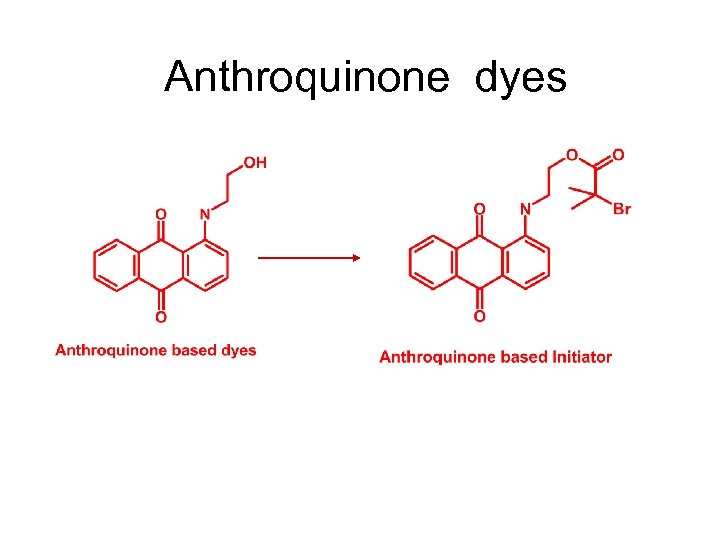 Anthroquinone dyes
Anthroquinone dyes
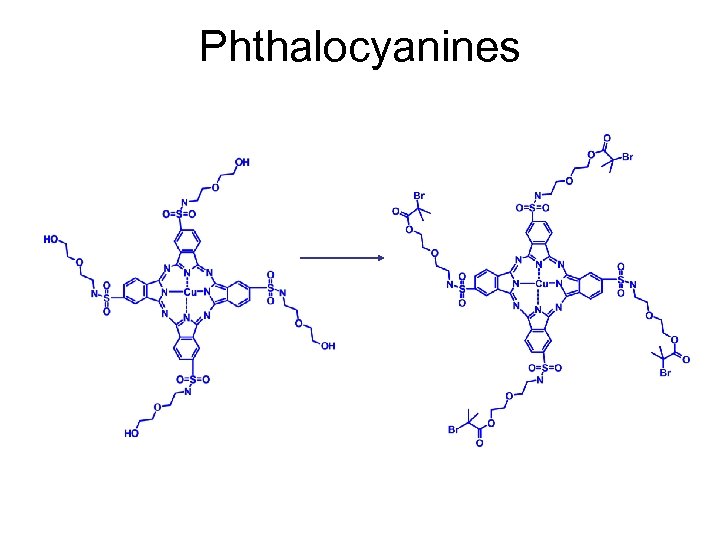 Phthalocyanines
Phthalocyanines
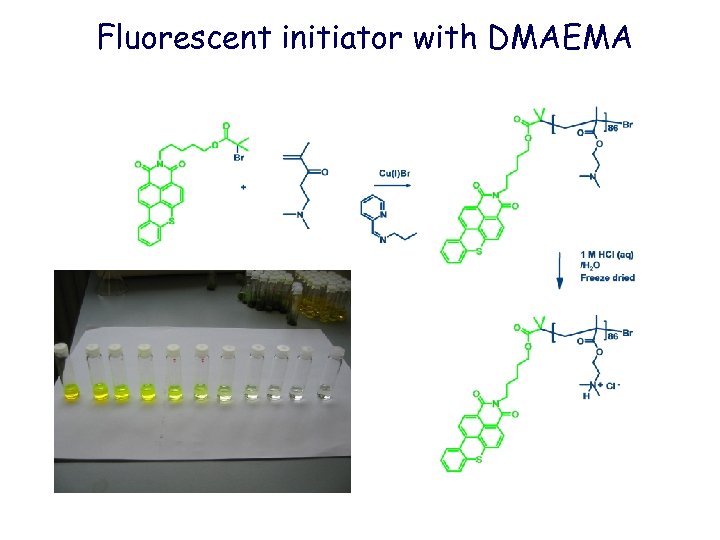 Fluorescent initiator with DMAEMA
Fluorescent initiator with DMAEMA
 Protein Based Drugs • Insulin, Interferon – Diabetes, Osteoporosis, Inflam. Bowel disease • A need for Oral delivery – Longer stability to enzyme degradation – Enhanced absorption across the GI tract – Optimised hydrophilic/hydrophobic balance
Protein Based Drugs • Insulin, Interferon – Diabetes, Osteoporosis, Inflam. Bowel disease • A need for Oral delivery – Longer stability to enzyme degradation – Enhanced absorption across the GI tract – Optimised hydrophilic/hydrophobic balance
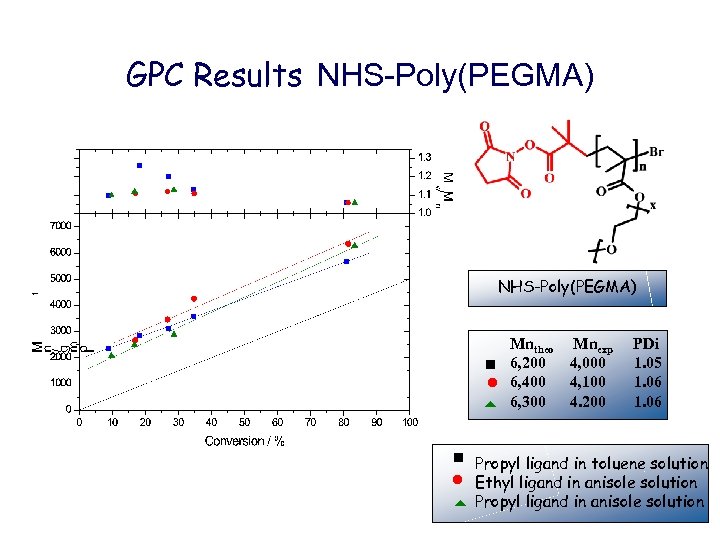 GPC Results NHS-Poly(PEGMA) Mntheo 6, 200 ● 6, 400 6, 300 t Mnexp 4, 000 4, 100 4. 200 PDi 1. 05 1. 06 Propyl ligand in toluene solution ● Ethyl ligand in anisole solution t Propyl ligand in anisole solution
GPC Results NHS-Poly(PEGMA) Mntheo 6, 200 ● 6, 400 6, 300 t Mnexp 4, 000 4, 100 4. 200 PDi 1. 05 1. 06 Propyl ligand in toluene solution ● Ethyl ligand in anisole solution t Propyl ligand in anisole solution
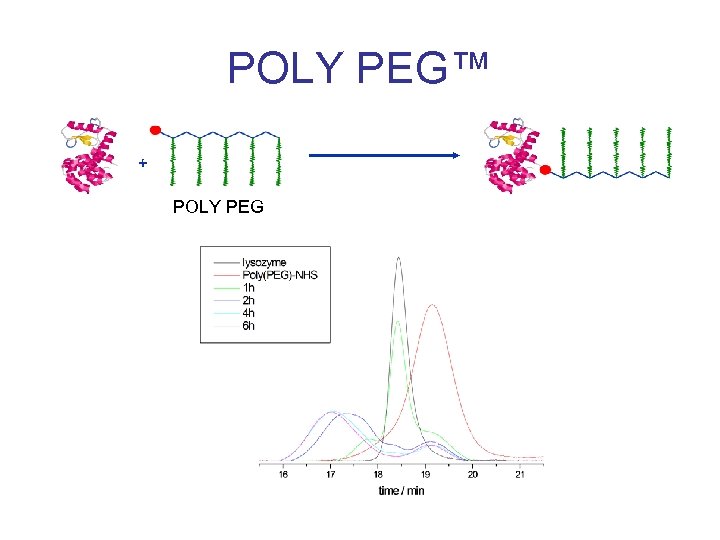 POLY PEG™ + POLY PEG
POLY PEG™ + POLY PEG
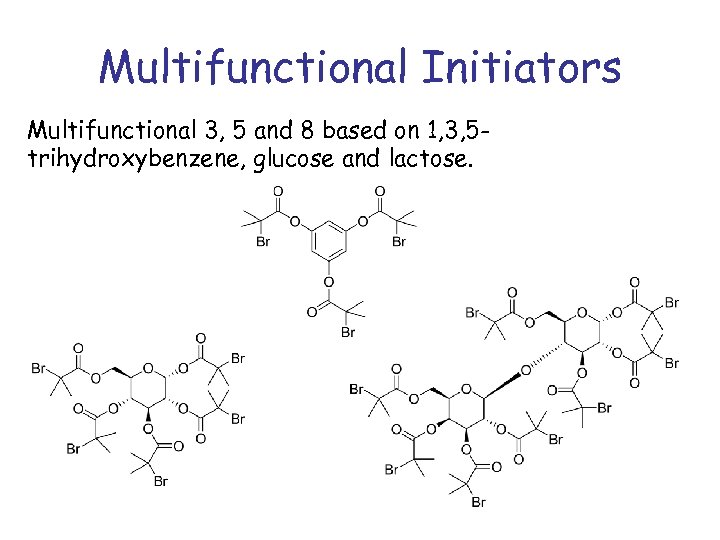 Multifunctional Initiators Multifunctional 3, 5 and 8 based on 1, 3, 5 trihydroxybenzene, glucose and lactose.
Multifunctional Initiators Multifunctional 3, 5 and 8 based on 1, 3, 5 trihydroxybenzene, glucose and lactose.
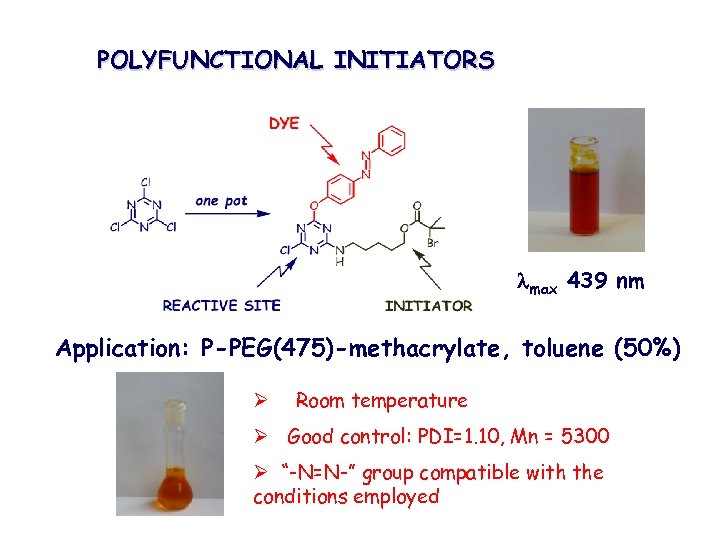 POLYFUNCTIONAL INITIATORS lmax 439 nm Application: P-PEG(475)-methacrylate, toluene (50%) Ø Room temperature Ø Good control: PDI=1. 10, Mn = 5300 Ø “-N=N-” group compatible with the conditions employed
POLYFUNCTIONAL INITIATORS lmax 439 nm Application: P-PEG(475)-methacrylate, toluene (50%) Ø Room temperature Ø Good control: PDI=1. 10, Mn = 5300 Ø “-N=N-” group compatible with the conditions employed
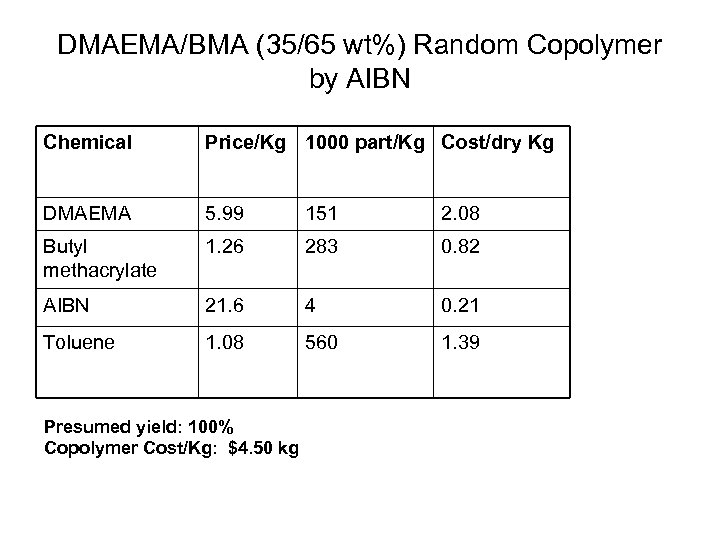 DMAEMA/BMA (35/65 wt%) Random Copolymer by AIBN Chemical Price/Kg 1000 part/Kg Cost/dry Kg DMAEMA 5. 99 151 2. 08 Butyl methacrylate 1. 26 283 0. 82 AIBN 21. 6 4 0. 21 Toluene 1. 08 560 1. 39 Presumed yield: 100% Copolymer Cost/Kg: $4. 50 kg
DMAEMA/BMA (35/65 wt%) Random Copolymer by AIBN Chemical Price/Kg 1000 part/Kg Cost/dry Kg DMAEMA 5. 99 151 2. 08 Butyl methacrylate 1. 26 283 0. 82 AIBN 21. 6 4 0. 21 Toluene 1. 08 560 1. 39 Presumed yield: 100% Copolymer Cost/Kg: $4. 50 kg
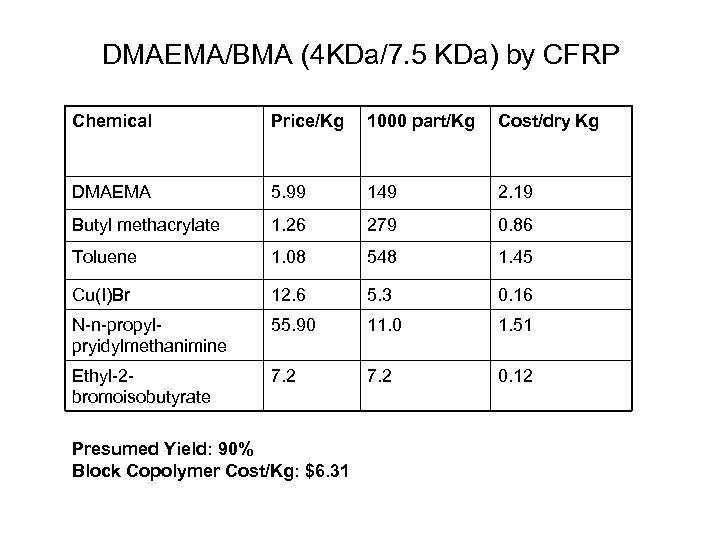 DMAEMA/BMA (4 KDa/7. 5 KDa) by CFRP Chemical Price/Kg 1000 part/Kg Cost/dry Kg DMAEMA 5. 99 149 2. 19 Butyl methacrylate 1. 26 279 0. 86 Toluene 1. 08 548 1. 45 Cu(I)Br 12. 6 5. 3 0. 16 N-n-propylpryidylmethanimine 55. 90 11. 0 1. 51 Ethyl-2 bromoisobutyrate 7. 2 0. 12 Presumed Yield: 90% Block Copolymer Cost/Kg: $6. 31
DMAEMA/BMA (4 KDa/7. 5 KDa) by CFRP Chemical Price/Kg 1000 part/Kg Cost/dry Kg DMAEMA 5. 99 149 2. 19 Butyl methacrylate 1. 26 279 0. 86 Toluene 1. 08 548 1. 45 Cu(I)Br 12. 6 5. 3 0. 16 N-n-propylpryidylmethanimine 55. 90 11. 0 1. 51 Ethyl-2 bromoisobutyrate 7. 2 0. 12 Presumed Yield: 90% Block Copolymer Cost/Kg: $6. 31
 Conclusion/Discussion • CFRP offers some unique advantages with respect to control of structure • WEP has scaled technology to >100 kg; 1000 kg by Q 1 ‘ 05 • Cost of technology versus performance • WEP is open to a partnership in various technology areas; wide variety of deal structures/interactions possible
Conclusion/Discussion • CFRP offers some unique advantages with respect to control of structure • WEP has scaled technology to >100 kg; 1000 kg by Q 1 ‘ 05 • Cost of technology versus performance • WEP is open to a partnership in various technology areas; wide variety of deal structures/interactions possible


