3bd4d100df75f2771adcc9aff7dc75ae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9

Warm-up: • What is the idea/concept behind this cartoon?

Freedom at last?

Freedom…Changes Many freedmen left the South ◦ Had no money or property ◦ Many migrated North or West (Exodusters) Most visible “new” black organizations in South were churches For the first time, African American marriages were legalized Southern agriculture depended on cash crops---crops grown to make money.

Freedmen’s Bureau ◦ Established by Congressional Reconstruction plan to help newly freed slaves ◦ Negotiated labor contracts ◦ Provided medical care, clothing, food ◦ Set up schools for education ◦ Helped reunite families separated by slavery


Sharecropping vs. Tenant Farming Sharecropping: • Had no ownership of land, house or equipment • Farmer had no control of what they planted or how crops were sold • Landowner would hold all profits and after paying any outstanding debts the farmer had, would give the farmer their share (often nothing or Tenant farming: • Farmer would rent land house from landowner • Farmer had control over crops that were grown and could sell them at will and keep the profits • Farmer’s responsibility to pay their rent to the landowner farmer still owed him) Kept the farmer in a cycle of debt & poverty
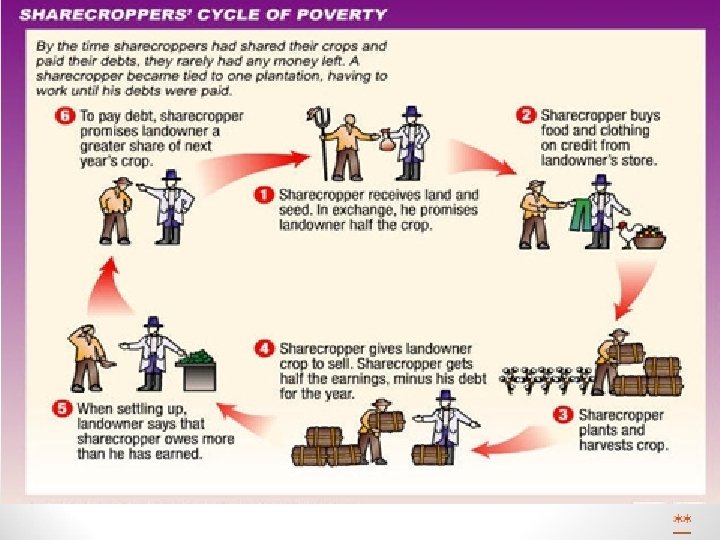
Job Availability • Freedmen remained dependent on white “masters” • Sharecropping & tenant farming • A different type of slavery • Many poor white Southerners now had to compete for jobs with freedmen • Tenant farming caused the rise of a new class of wealthy merchants

Opposition • Southern state governments restricted the rights of the newly freed African Americans by passing “black codes” • Later called Jim Crow laws • Also main goal of Ku Klux Klan • Keep African Americans submissive to white superiority using terror and violence to keep them from voting • Congress passed the Enforcement Act 1870 in reaction to Klan terror

Activity: Google Classroom 3 reading activities
3bd4d100df75f2771adcc9aff7dc75ae.ppt