59f19e77af9c9305d08c8e5812a1ee7d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Warm-up: Roller Coaster 1. What is 2. the name 3. of this roller coaster? 2. What does 3. its name mean?
Warm-up: Roller Coaster 1. What is 2. the name 3. of this roller coaster? 2. What does 3. its name mean?
 1. Revolution!
1. Revolution!
 2. rev·o·lu·tion 1. the overthrow of a leader 2. a dramatic change in ideas 3. one complete circular movement made by something round (Example: Bike tires) 4. a complete circle made around something (Example: Orbit of Earth around Sun)
2. rev·o·lu·tion 1. the overthrow of a leader 2. a dramatic change in ideas 3. one complete circular movement made by something round (Example: Bike tires) 4. a complete circle made around something (Example: Orbit of Earth around Sun)
 The Colonies are headed towards a collision!!!
The Colonies are headed towards a collision!!!
 1. Navigation Acts (1651 -1733) Series of rules regulating trade in the colonies. Required that trade of tobacco and cotton must be with England ONLY.
1. Navigation Acts (1651 -1733) Series of rules regulating trade in the colonies. Required that trade of tobacco and cotton must be with England ONLY.
 2. Smuggling Resentment towards the Navigation Acts lead to smuggling. Colonists knew they could make more money by selling to other European countries like France and Spain.
2. Smuggling Resentment towards the Navigation Acts lead to smuggling. Colonists knew they could make more money by selling to other European countries like France and Spain.

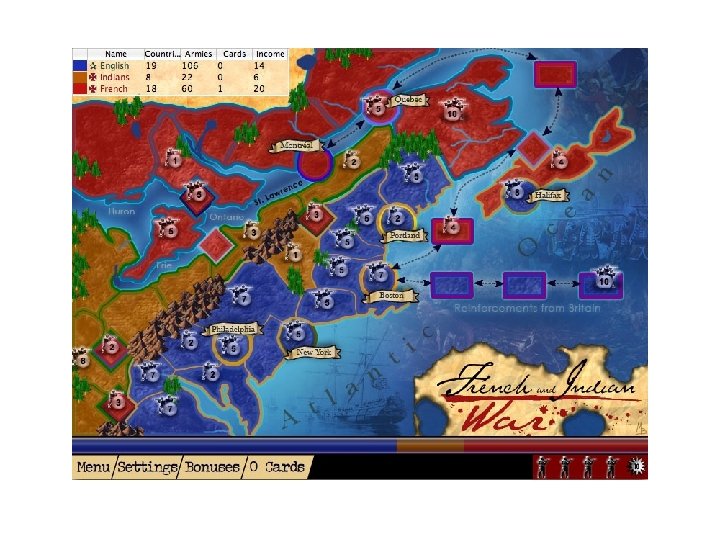
 3. French & Indian War (1754 -1763) Colonists and English fight against French and Indian allies for land. French controlled the Mississippi River and England the Ohio River Valley.
3. French & Indian War (1754 -1763) Colonists and English fight against French and Indian allies for land. French controlled the Mississippi River and England the Ohio River Valley.
 3. French & Indian War (1754 -1763) continued… Governor of Virginia sent General George Washington to tell French to leave; fighting began. This EXPENSIVE war ended with the Treaty of Paris in 1763.
3. French & Indian War (1754 -1763) continued… Governor of Virginia sent General George Washington to tell French to leave; fighting began. This EXPENSIVE war ended with the Treaty of Paris in 1763.
 4. Proclamation of 1763 Colonists could not settle lands west of the Appalachians, which had been won in the French & Indian War. Quartering Act (1764) Required colonial cities to give housing to British troops and to pay for troop supplies.
4. Proclamation of 1763 Colonists could not settle lands west of the Appalachians, which had been won in the French & Indian War. Quartering Act (1764) Required colonial cities to give housing to British troops and to pay for troop supplies.

 5. Stamp Act (1765) Tax that required colonists to buy a stamp for newspapers, legal documents, pamphlets, dice, and playing cards (all required the purchase of a stamp).
5. Stamp Act (1765) Tax that required colonists to buy a stamp for newspapers, legal documents, pamphlets, dice, and playing cards (all required the purchase of a stamp).

 6. Stamp Act Congress (1765) Lead by the House of Burgesses to protest the Stamp Act. Start the battle cry “No Taxation Without Representation!” Argued that according to the Magna Carta, the King could not tax without consent of Parliament and colonists had NO vote in Parliament so these taxes were invalid.
6. Stamp Act Congress (1765) Lead by the House of Burgesses to protest the Stamp Act. Start the battle cry “No Taxation Without Representation!” Argued that according to the Magna Carta, the King could not tax without consent of Parliament and colonists had NO vote in Parliament so these taxes were invalid.

 7. Townshend Act (1767) Taxed glass, lead, paper, paint, and tea. British officials could search ` ` for smuggled goods WITHOUT reasonable suspicion using Writs of Assistance.
7. Townshend Act (1767) Taxed glass, lead, paper, paint, and tea. British officials could search ` ` for smuggled goods WITHOUT reasonable suspicion using Writs of Assistance.
 8. Virginia Resolutions Written by Patrick Henry of Virginia. Declared only the House of Burgesses could tax the people of the colony. Sam Adams of Massachusetts creates the Sons of Liberty. Radicals or “Patriots” start to talk about Revolution.
8. Virginia Resolutions Written by Patrick Henry of Virginia. Declared only the House of Burgesses could tax the people of the colony. Sam Adams of Massachusetts creates the Sons of Liberty. Radicals or “Patriots” start to talk about Revolution.

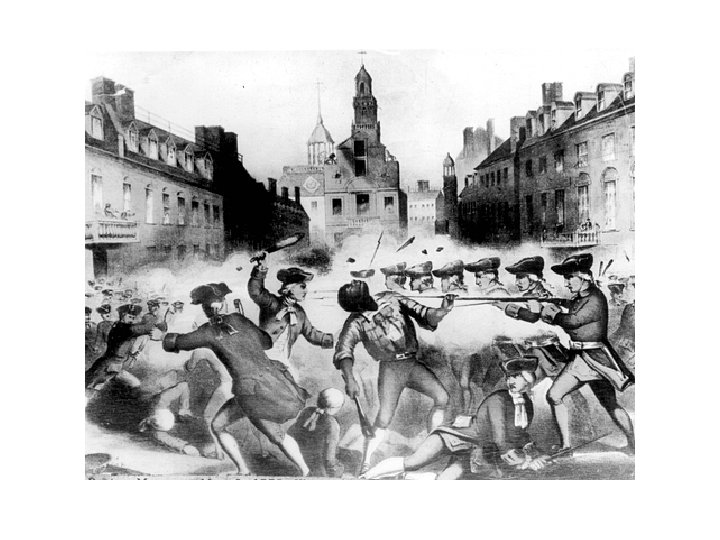
 9. Boston Massacre (March 1770) Tensions are high between British troops and colonists in Boston. Children start to throw “snowballs” at the troops. Shots ring out; a man is shot. Crispus Attucks an African American sailor is killed. 1 st blood is shed over the issue of Revolution.
9. Boston Massacre (March 1770) Tensions are high between British troops and colonists in Boston. Children start to throw “snowballs” at the troops. Shots ring out; a man is shot. Crispus Attucks an African American sailor is killed. 1 st blood is shed over the issue of Revolution.


 10. Committees of Correspondence This was the first effort made by the colonies to unite and discuss issues. These groups were formed to carry news from colony to colony by horse couriers.
10. Committees of Correspondence This was the first effort made by the colonies to unite and discuss issues. These groups were formed to carry news from colony to colony by horse couriers.

 11. Tea Act (1773) British East India Company could sell tea directly to colonists rather than use a middleman. Britain earned more money by raising tea taxes.
11. Tea Act (1773) British East India Company could sell tea directly to colonists rather than use a middleman. Britain earned more money by raising tea taxes.

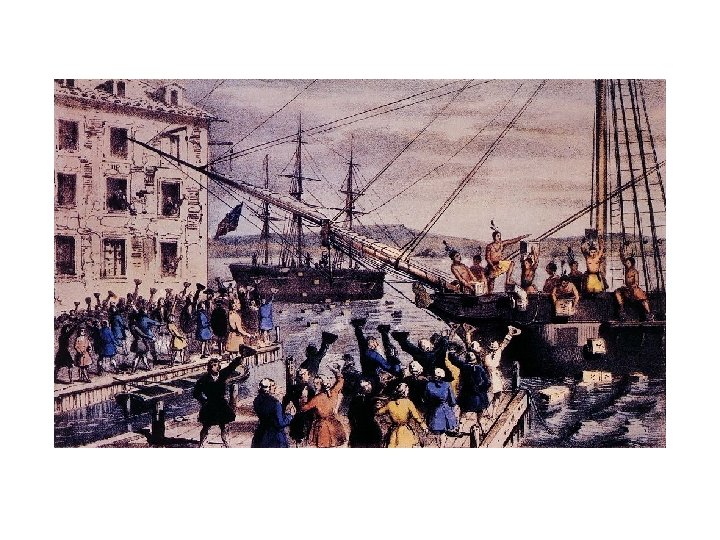
 12. Boston Tea Party (Dec. 1773) To protest the Tea Act the Sons of Liberty dressed up as Indians, snuck onto three ships, and dumped the cargo of tea into the Boston Harbor. Parliament was OUTRAGED!
12. Boston Tea Party (Dec. 1773) To protest the Tea Act the Sons of Liberty dressed up as Indians, snuck onto three ships, and dumped the cargo of tea into the Boston Harbor. Parliament was OUTRAGED!

 13. Intolerable Acts (1774) Punish Boston! Boston Port Bill -> Closed Boston Harbor to any trade. Massachusetts Government Act -> Governor could cancel Town Meetings Quartering Act strengthened. Closed Ohio River Valley to settlement.
13. Intolerable Acts (1774) Punish Boston! Boston Port Bill -> Closed Boston Harbor to any trade. Massachusetts Government Act -> Governor could cancel Town Meetings Quartering Act strengthened. Closed Ohio River Valley to settlement.

 14. 1 st Continental Congress (Sept. 1774) All colonies sent representatives to a meeting (except Georgia) in Philadelphia to discuss what was going on in Massachusetts. Decide to no longer trade with England, send a letter to the King, and set a date for another meeting.
14. 1 st Continental Congress (Sept. 1774) All colonies sent representatives to a meeting (except Georgia) in Philadelphia to discuss what was going on in Massachusetts. Decide to no longer trade with England, send a letter to the King, and set a date for another meeting.



