ac28b81ec49ca77506e1660a621b21a3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Warm up – August 29, 2016 For each item, think about how many of each you would buy at the specific prices. Write this in your notebook. 1. Song downloads: $2, $1. 00, . 50, . 25, . 10 2. Candy bars: $2, $1. 50, $1, . 50, . 20 3. Jeans: $100, $50, $30, $20, $10
Warm up – August 29, 2016 For each item, think about how many of each you would buy at the specific prices. Write this in your notebook. 1. Song downloads: $2, $1. 00, . 50, . 25, . 10 2. Candy bars: $2, $1. 50, $1, . 50, . 20 3. Jeans: $100, $50, $30, $20, $10
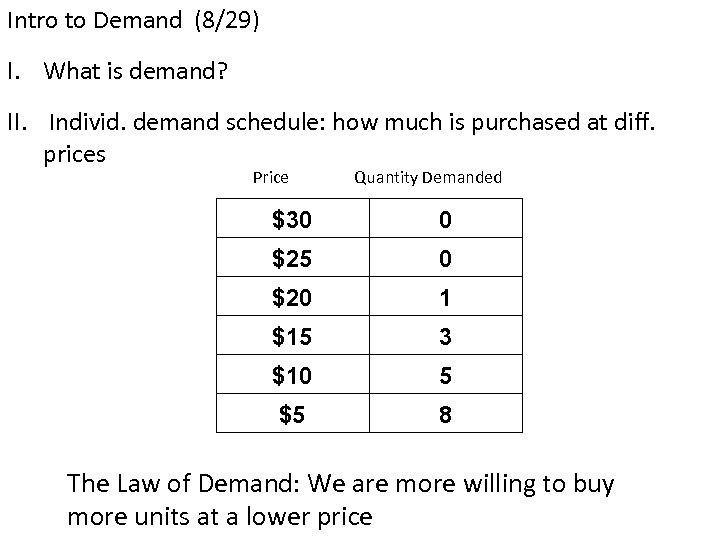 Intro to Demand (8/29) I. What is demand? II. Individ. demand schedule: how much is purchased at diff. prices Price Quantity Demanded $30 0 $25 0 $20 1 $15 3 $10 5 $5 8 The Law of Demand: We are more willing to buy more units at a lower price
Intro to Demand (8/29) I. What is demand? II. Individ. demand schedule: how much is purchased at diff. prices Price Quantity Demanded $30 0 $25 0 $20 1 $15 3 $10 5 $5 8 The Law of Demand: We are more willing to buy more units at a lower price
 III. Individ. demand curve: plot demand schedule onto graph A. X-axis is ALWAYS quantity B. Y-axis is ALWAYS price C. Demand curve practice: plot one demand schedule from your warm-up onto a set of axes.
III. Individ. demand curve: plot demand schedule onto graph A. X-axis is ALWAYS quantity B. Y-axis is ALWAYS price C. Demand curve practice: plot one demand schedule from your warm-up onto a set of axes.
 IV. The market demand curve A. Definition: shows quantities demanded by EVERYONE B. Find 2 or 3 partners in your area and choose one warm up example to form a market demand schedule. Each partner must write in their Quantity Demanded notebook. Example: Price (Market) $30 $25 $20 0+0+0 = 0 0+1+0 = 1 1+2+2 = 5 $15 3+4+3 = 10
IV. The market demand curve A. Definition: shows quantities demanded by EVERYONE B. Find 2 or 3 partners in your area and choose one warm up example to form a market demand schedule. Each partner must write in their Quantity Demanded notebook. Example: Price (Market) $30 $25 $20 0+0+0 = 0 0+1+0 = 1 1+2+2 = 5 $15 3+4+3 = 10
 C. Market demand curve: Plot your group’s market demand schedule.
C. Market demand curve: Plot your group’s market demand schedule.
 VI. Demand marginal utility A. Marginal utility: the extra satisfaction we get from using one more unit of a product B. Diminishing marginal utility: that extra satisfaction diminishes as we use more units 1. Example: candy bars a. Aren’t willing to pay as much for the 2 nd, 3 rd, 4 th one b. Explains why demand curve is downward sloping
VI. Demand marginal utility A. Marginal utility: the extra satisfaction we get from using one more unit of a product B. Diminishing marginal utility: that extra satisfaction diminishes as we use more units 1. Example: candy bars a. Aren’t willing to pay as much for the 2 nd, 3 rd, 4 th one b. Explains why demand curve is downward sloping
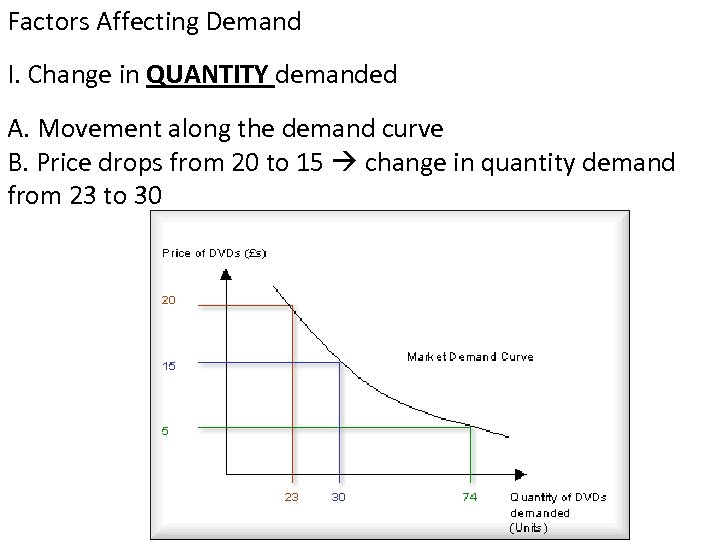 Factors Affecting Demand I. Change in QUANTITY demanded A. Movement along the demand curve B. Price drops from 20 to 15 change in quantity demand from 23 to 30
Factors Affecting Demand I. Change in QUANTITY demanded A. Movement along the demand curve B. Price drops from 20 to 15 change in quantity demand from 23 to 30
 C. The Income Effect 1. If prices drop, consumers have more real income to spend 2. Ex: CDs are $15 each, buy 6 CDs ($90 spent) If price falls to $10, you only spend $60. You may buy even MORE CDs with your “extra” $30 Quantity demanded: increases from 6 to 9 units
C. The Income Effect 1. If prices drop, consumers have more real income to spend 2. Ex: CDs are $15 each, buy 6 CDs ($90 spent) If price falls to $10, you only spend $60. You may buy even MORE CDs with your “extra” $30 Quantity demanded: increases from 6 to 9 units
 D. The Substitution Effect 1. Price of CDs falls from $15 to $10 – CDs are relatively cheaper now than alternatives 2. Therefore, you are more likely to replace a high cost item with a lower cost item (ex: buy more CDs instead of DVDs)
D. The Substitution Effect 1. Price of CDs falls from $15 to $10 – CDs are relatively cheaper now than alternatives 2. Therefore, you are more likely to replace a high cost item with a lower cost item (ex: buy more CDs instead of DVDs)
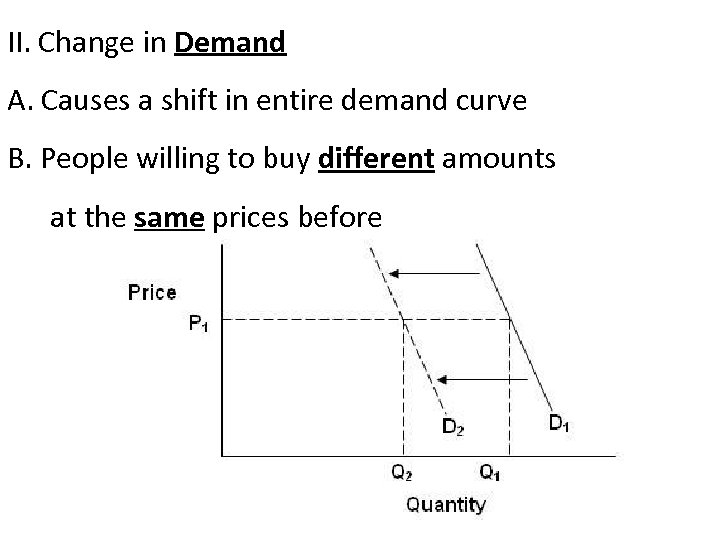 II. Change in Demand A. Causes a shift in entire demand curve B. People willing to buy different amounts at the same prices before
II. Change in Demand A. Causes a shift in entire demand curve B. People willing to buy different amounts at the same prices before
 III. Factors affecting demand A. Consumer income 1. What happens to demand when increased? B. Consumer tastes/tech 1. Example 1: trends 2. Example 2: VCRs income is
III. Factors affecting demand A. Consumer income 1. What happens to demand when increased? B. Consumer tastes/tech 1. Example 1: trends 2. Example 2: VCRs income is
 C. Substitutes 1. Example: butter vs. margarine D. Complements 1. Example: computers and software E. Change in expectation 1. Example: future shortages/sales F. Number of consumers 1. Increase in # of consumers shift in market demand curve
C. Substitutes 1. Example: butter vs. margarine D. Complements 1. Example: computers and software E. Change in expectation 1. Example: future shortages/sales F. Number of consumers 1. Increase in # of consumers shift in market demand curve
 Demand Shift Practice (8/30) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Product: SUVs. Scenario: Because of world shortages, the price of oil has sharply increased. Product: TVs (considered a normal good). Scenario: People are earning more money this year than last. Product: Coffee in the US. Scenario: Immigration into the US continues to increase. Product: LA Lakers season tickets. Scenario: The LA Clippers (the other basketball team in LA) have raised the price of their season tickets. Product: pinto beans (time of year is Spring). Scenario: Many more farmers planted beans this year, and a huge supply of beans has been forecasted for harvest (which takes place in the fall). Product: hockey apparel in Las Vegas. Scenario: A new NHL team is created for Las Vegas. Product: chicken. Scenario: There is a huge surplus of beef on the market. Product: tickets to Disneyland. Scenario: Major airlines are promoting cheaper fares throughout the US.
Demand Shift Practice (8/30) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Product: SUVs. Scenario: Because of world shortages, the price of oil has sharply increased. Product: TVs (considered a normal good). Scenario: People are earning more money this year than last. Product: Coffee in the US. Scenario: Immigration into the US continues to increase. Product: LA Lakers season tickets. Scenario: The LA Clippers (the other basketball team in LA) have raised the price of their season tickets. Product: pinto beans (time of year is Spring). Scenario: Many more farmers planted beans this year, and a huge supply of beans has been forecasted for harvest (which takes place in the fall). Product: hockey apparel in Las Vegas. Scenario: A new NHL team is created for Las Vegas. Product: chicken. Scenario: There is a huge surplus of beef on the market. Product: tickets to Disneyland. Scenario: Major airlines are promoting cheaper fares throughout the US.
 Let’s say you were making cookies to sell to people at school. How many would you be willing to sell at each price below? $. 10, $. 25, $. 50, $1. 00, $2. 00, $5. 00, $10. 00
Let’s say you were making cookies to sell to people at school. How many would you be willing to sell at each price below? $. 10, $. 25, $. 50, $1. 00, $2. 00, $5. 00, $10. 00
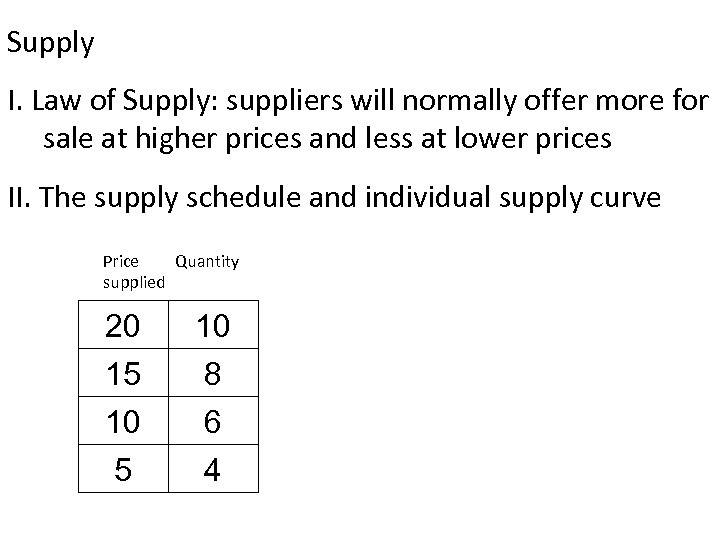 Supply I. Law of Supply: suppliers will normally offer more for sale at higher prices and less at lower prices II. The supply schedule and individual supply curve Price Quantity supplied 20 15 10 8 6 4
Supply I. Law of Supply: suppliers will normally offer more for sale at higher prices and less at lower prices II. The supply schedule and individual supply curve Price Quantity supplied 20 15 10 8 6 4
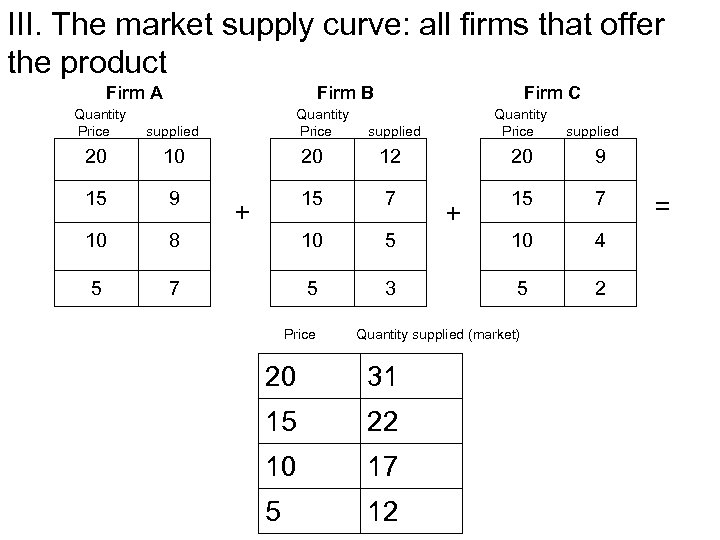 III. The market supply curve: all firms that offer the product Firm A Quantity Price Firm B Quantity Price supplied Firm C Quantity Price supplied 20 10 20 12 20 9 15 7 10 8 10 5 10 4 5 7 5 3 5 2 + Price + Quantity supplied (market) 20 31 15 22 10 17 5 12 =
III. The market supply curve: all firms that offer the product Firm A Quantity Price Firm B Quantity Price supplied Firm C Quantity Price supplied 20 10 20 12 20 9 15 7 10 8 10 5 10 4 5 7 5 3 5 2 + Price + Quantity supplied (market) 20 31 15 22 10 17 5 12 =
 IV. Change in QUANTITY supplied: movement along the supply curve V. Change in supply: shift in the supply curve (increase or decrease)
IV. Change in QUANTITY supplied: movement along the supply curve V. Change in supply: shift in the supply curve (increase or decrease)
 V. Factors affecting supply 1. Cost of inputs: if costs are high, supply decreases 2. Changes in prices of related goods/services Ex: Bakeries that sell cookies and pies. Price of pies increases supply of cookies falls Ex: Wheat and straw. Increase in price of wheat inc in quantity supplied of wheat inc in supply of straw (complement in production)
V. Factors affecting supply 1. Cost of inputs: if costs are high, supply decreases 2. Changes in prices of related goods/services Ex: Bakeries that sell cookies and pies. Price of pies increases supply of cookies falls Ex: Wheat and straw. Increase in price of wheat inc in quantity supplied of wheat inc in supply of straw (complement in production)
 3. Technology/motivation: a. Better technology = more efficient production = increase supply 4. Taxes and subsidies: a. Increase in taxes = increase in costs lower supply b. Subsidies: govt payment to encourage a specific economic activity Example: farmers
3. Technology/motivation: a. Better technology = more efficient production = increase supply 4. Taxes and subsidies: a. Increase in taxes = increase in costs lower supply b. Subsidies: govt payment to encourage a specific economic activity Example: farmers
 5. Expectations: 6. Government regulations a. Scenario: the govt forces car manufacturers to update safety features decrease supply 7. Number of sellers: as more firms enter the industry, the market supply will increase
5. Expectations: 6. Government regulations a. Scenario: the govt forces car manufacturers to update safety features decrease supply 7. Number of sellers: as more firms enter the industry, the market supply will increase
 Partner activity: 1. With your partner, come up with a product that your business produces. 2. Using six factors that affect supply (every one except for # of sellers), come up with scenarios that would shift your supply curves in whatever direction you choose. Write out the scenario and graph the shift in supply for each
Partner activity: 1. With your partner, come up with a product that your business produces. 2. Using six factors that affect supply (every one except for # of sellers), come up with scenarios that would shift your supply curves in whatever direction you choose. Write out the scenario and graph the shift in supply for each
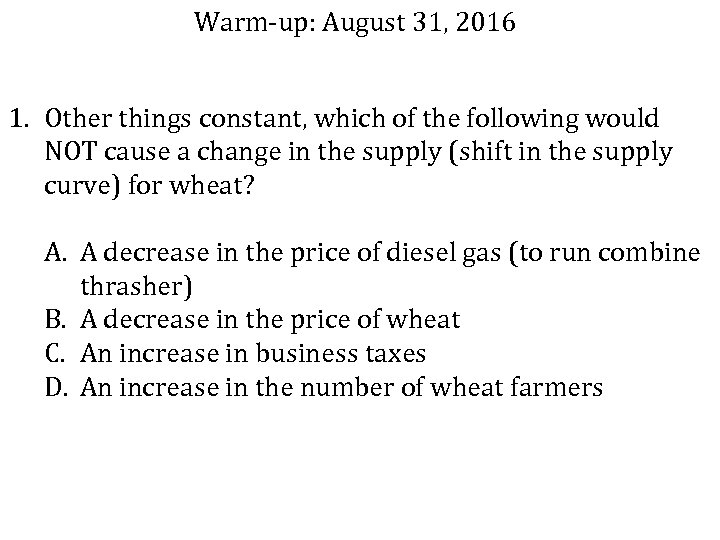 Warm-up: August 31, 2016 1. Other things constant, which of the following would NOT cause a change in the supply (shift in the supply curve) for wheat? A. A decrease in the price of diesel gas (to run combine thrasher) B. A decrease in the price of wheat C. An increase in business taxes D. An increase in the number of wheat farmers
Warm-up: August 31, 2016 1. Other things constant, which of the following would NOT cause a change in the supply (shift in the supply curve) for wheat? A. A decrease in the price of diesel gas (to run combine thrasher) B. A decrease in the price of wheat C. An increase in business taxes D. An increase in the number of wheat farmers
 2. “Rising oil prices have caused a sharp increase in the supply for oil. ” Speaking precisely, and using terms as they are defined by economists, choose the statement that best describes this quotation. A. The quotation is correct: An increase in price always causes an increase in supply. B. The quotation is incorrect: An increase in price always causes a decrease in supply, not a increase in supply. C. The quotation is incorrect: An increase in price causes an increase in the quantity supplied, not an increase in supply. D. The quotation is incorrect: An increase in price causes a decrease in the quantity supplied, not a increase in supply.
2. “Rising oil prices have caused a sharp increase in the supply for oil. ” Speaking precisely, and using terms as they are defined by economists, choose the statement that best describes this quotation. A. The quotation is correct: An increase in price always causes an increase in supply. B. The quotation is incorrect: An increase in price always causes a decrease in supply, not a increase in supply. C. The quotation is incorrect: An increase in price causes an increase in the quantity supplied, not an increase in supply. D. The quotation is incorrect: An increase in price causes a decrease in the quantity supplied, not a increase in supply.
 3. “As the price of domestic automobiles has inched upwards, customers have found foreign autos to be a better bargain. Consequently, domestic auto sales have been decreasing, and foreign auto sales have been increasing. ” Using only the info in the quotation and assuming everything else constant, which of the following best describes this statement? A. A shift in the demand curves of both domestic and foreign autos. B. A movement along the demand curves for both domestic and foreign autos. C. A movement along the demand curve for domestic autos, and a shift in the demand curve foreign autos. D. A shift in the demand curve for domestic autos, and a movement along the demand curve foreign autos.
3. “As the price of domestic automobiles has inched upwards, customers have found foreign autos to be a better bargain. Consequently, domestic auto sales have been decreasing, and foreign auto sales have been increasing. ” Using only the info in the quotation and assuming everything else constant, which of the following best describes this statement? A. A shift in the demand curves of both domestic and foreign autos. B. A movement along the demand curves for both domestic and foreign autos. C. A movement along the demand curve for domestic autos, and a shift in the demand curve foreign autos. D. A shift in the demand curve for domestic autos, and a movement along the demand curve foreign autos.
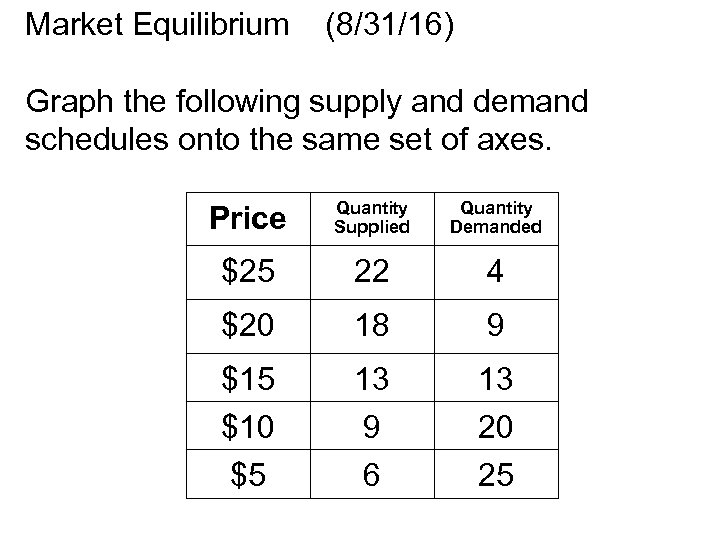 Market Equilibrium (8/31/16) Graph the following supply and demand schedules onto the same set of axes. Price Quantity Supplied Quantity Demanded $25 22 4 $20 18 9 $15 13 13 $10 9 20 $5 6 25
Market Equilibrium (8/31/16) Graph the following supply and demand schedules onto the same set of axes. Price Quantity Supplied Quantity Demanded $25 22 4 $20 18 9 $15 13 13 $10 9 20 $5 6 25
 Surplus: Quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded Example 1: $25 Example 2: $20 Real-life example: Shortage: Quantity supplied is less than quantity demanded Example 1: $5 Example 2: $10 Real-life example:
Surplus: Quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded Example 1: $25 Example 2: $20 Real-life example: Shortage: Quantity supplied is less than quantity demanded Example 1: $5 Example 2: $10 Real-life example:
 Changes in Supply and Demand Draw a generic supply and demand graph for coffee. Don’t forget labels! Scenario: The price of tea has increased. 1. Effect on demand/why? : 2. Effect on equilibrium price: 3. Effect on equilibrium quantity:
Changes in Supply and Demand Draw a generic supply and demand graph for coffee. Don’t forget labels! Scenario: The price of tea has increased. 1. Effect on demand/why? : 2. Effect on equilibrium price: 3. Effect on equilibrium quantity:
 Draw a generic supply and demand graph for cakes. Scenario: The price of flour has increased. 1. Effect on supply/why? : 2. Effect on equilibrium price: 3. Effect on equilibrium quantity:
Draw a generic supply and demand graph for cakes. Scenario: The price of flour has increased. 1. Effect on supply/why? : 2. Effect on equilibrium price: 3. Effect on equilibrium quantity:
 Draw a generic supply and demand graph for pants Scenario: Because of a decrease in the price of cotton, pants are now cheaper, despite the repeal of school rules that force all girls to wear skirts.
Draw a generic supply and demand graph for pants Scenario: Because of a decrease in the price of cotton, pants are now cheaper, despite the repeal of school rules that force all girls to wear skirts.
 Warm-up: September 1, 2016 1. If the demand for baseball cards rises and the supply curve does not shift, then the price a. will rise and quantity will fall b. and quantity will rise c. will fall and quantity will rise d. and quantity will fall e. will rise, but quantity may rise or fall 2. Which of the following would increase the amount of an inferior good that buyers would like to purchase? a. an increase in buyers' incomes b. an increase in the price of a complement c. a decrease in the price of a substitute d. a decrease in buyers' incomes e. a decrease in its expected future price
Warm-up: September 1, 2016 1. If the demand for baseball cards rises and the supply curve does not shift, then the price a. will rise and quantity will fall b. and quantity will rise c. will fall and quantity will rise d. and quantity will fall e. will rise, but quantity may rise or fall 2. Which of the following would increase the amount of an inferior good that buyers would like to purchase? a. an increase in buyers' incomes b. an increase in the price of a complement c. a decrease in the price of a substitute d. a decrease in buyers' incomes e. a decrease in its expected future price
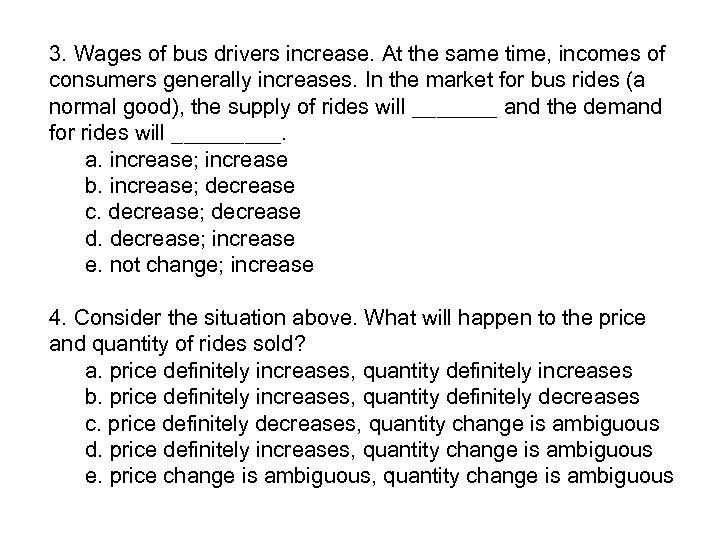 3. Wages of bus drivers increase. At the same time, incomes of consumers generally increases. In the market for bus rides (a normal good), the supply of rides will _______ and the demand for rides will _____. a. increase; increase b. increase; decrease c. decrease; decrease d. decrease; increase e. not change; increase 4. Consider the situation above. What will happen to the price and quantity of rides sold? a. price definitely increases, quantity definitely increases b. price definitely increases, quantity definitely decreases c. price definitely decreases, quantity change is ambiguous d. price definitely increases, quantity change is ambiguous e. price change is ambiguous, quantity change is ambiguous
3. Wages of bus drivers increase. At the same time, incomes of consumers generally increases. In the market for bus rides (a normal good), the supply of rides will _______ and the demand for rides will _____. a. increase; increase b. increase; decrease c. decrease; decrease d. decrease; increase e. not change; increase 4. Consider the situation above. What will happen to the price and quantity of rides sold? a. price definitely increases, quantity definitely increases b. price definitely increases, quantity definitely decreases c. price definitely decreases, quantity change is ambiguous d. price definitely increases, quantity change is ambiguous e. price change is ambiguous, quantity change is ambiguous


