e3e3b4910d13bf3b94fdc3fd2ffe4c3a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65
 Warm Up #13 Sometimes the stores are all out of ____. Explain how that makes you feel and why does this happen that the store would be out of _____. NEXT
Warm Up #13 Sometimes the stores are all out of ____. Explain how that makes you feel and why does this happen that the store would be out of _____. NEXT
 Class Focus We the Senior Class of 2016 will complete ALL of our assignments to best of our abilities and behave appropriately in class. We will respect all faculty, staff, substitutes, classmates, especially Mr. Wilcox. We will graduate on time May 20, 2016 and become productive citizens in society. NEXT
Class Focus We the Senior Class of 2016 will complete ALL of our assignments to best of our abilities and behave appropriately in class. We will respect all faculty, staff, substitutes, classmates, especially Mr. Wilcox. We will graduate on time May 20, 2016 and become productive citizens in society. NEXT
 SSEMI 2 You will be able to explain how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. B. Define the Law of Supply. Determine and define vocabulary. Identify key terms within the standard. Define each term. ________________________________________ ________________________________________ NEXT
SSEMI 2 You will be able to explain how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. B. Define the Law of Supply. Determine and define vocabulary. Identify key terms within the standard. Define each term. ________________________________________ ________________________________________ NEXT
 Scaffold understanding of the standard(s) and/or element(s). Paraphrase the standard(s) and/or element(s). Rewrite the standard including synonyms or brief definitions in parentheses and in a different color following the key terms found in step 1. You will be able to explain (clarify) how the Law of Demand (want), the Law of Supply (amount), prices, and profits (income) work to determine production and distribution (delivery) in a market (shop) economy. NEXT
Scaffold understanding of the standard(s) and/or element(s). Paraphrase the standard(s) and/or element(s). Rewrite the standard including synonyms or brief definitions in parentheses and in a different color following the key terms found in step 1. You will be able to explain (clarify) how the Law of Demand (want), the Law of Supply (amount), prices, and profits (income) work to determine production and distribution (delivery) in a market (shop) economy. NEXT
 The Law of Supply Nature of Supply SSEMI 2 NEXT
The Law of Supply Nature of Supply SSEMI 2 NEXT
 Nature of Supply KEY CONCEPT • Supply is the willingness and ability of producers to offer goods and services for sale. WHY THE CONCEPT MATTERS • Most people are producers. Doing household chores, working at a job, providing rides to others are ways of producing goods and services. Participating on a team is a way of supplying skills, knowledge, and support to one’s school. Producers incur (earn) costs and receive rewards for the work they do. NEXT
Nature of Supply KEY CONCEPT • Supply is the willingness and ability of producers to offer goods and services for sale. WHY THE CONCEPT MATTERS • Most people are producers. Doing household chores, working at a job, providing rides to others are ways of producing goods and services. Participating on a team is a way of supplying skills, knowledge, and support to one’s school. Producers incur (earn) costs and receive rewards for the work they do. NEXT
 The Law of Supply KEY CONCEPTS • Supply—willingness and ability of producers to offer goods, services • Anyone who provides goods or services is a producer • Law of supply: – producers willing to sell more of producer at higher than at lower price $ ↑, QS ↑ $ ↓, QS ↓ Direct Relationship NEXT
The Law of Supply KEY CONCEPTS • Supply—willingness and ability of producers to offer goods, services • Anyone who provides goods or services is a producer • Law of supply: – producers willing to sell more of producer at higher than at lower price $ ↑, QS ↑ $ ↓, QS ↓ Direct Relationship NEXT
 What is the difference between Supply and Quantity Supplied: 1. Supply—quantity of goods and services that producers are willing and able to offer at various prices during a given time period 2. Quantity Supplied—the amount of a good or service that producers are willing to supply at each particular price NEXT
What is the difference between Supply and Quantity Supplied: 1. Supply—quantity of goods and services that producers are willing and able to offer at various prices during a given time period 2. Quantity Supplied—the amount of a good or service that producers are willing to supply at each particular price NEXT
 Ralph Lauren’s Polo Shirts What is Supply? NEXT
Ralph Lauren’s Polo Shirts What is Supply? NEXT
 Nature of Supply Law of supply: More goods and services are supplied when they can be sold at higher prices, and fewer goods and services are supplied when they must be sold at lower prices. $ ↑, QS ↑ $ ↓, QS ↓ NEXT
Nature of Supply Law of supply: More goods and services are supplied when they can be sold at higher prices, and fewer goods and services are supplied when they must be sold at lower prices. $ ↑, QS ↑ $ ↓, QS ↓ NEXT
 What causes producers to vary their supply of goods and services? Profit Motive • The desire to make money NEXT
What causes producers to vary their supply of goods and services? Profit Motive • The desire to make money NEXT
 Profit The amount of money remaining after producers have paid all of their costs NEXT
Profit The amount of money remaining after producers have paid all of their costs NEXT
 Costs of Production A business makes a profit when revenues are greater than costs of production. • Wages, salaries, rent, loans, etc. NEXT
Costs of Production A business makes a profit when revenues are greater than costs of production. • Wages, salaries, rent, loans, etc. NEXT
 What do supply schedules and supply curves illustrate: Supply schedule • The quantity of a product that a producer is willing to supply at various prices Supply curve • graphs the data shown in supply schedules • indicates a product’s market over a specific period of time NEXT
What do supply schedules and supply curves illustrate: Supply schedule • The quantity of a product that a producer is willing to supply at various prices Supply curve • graphs the data shown in supply schedules • indicates a product’s market over a specific period of time NEXT
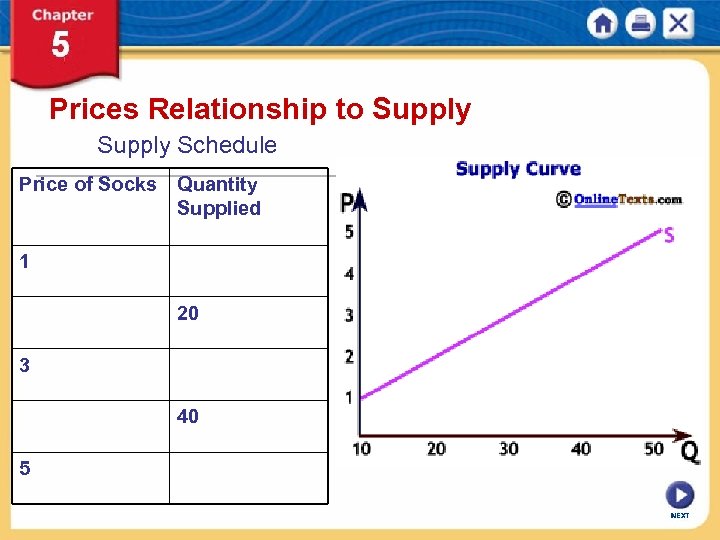 Prices Relationship to Supply Schedule Price of Socks Quantity Supplied 1 20 3 40 5 NEXT
Prices Relationship to Supply Schedule Price of Socks Quantity Supplied 1 20 3 40 5 NEXT
 Nature of Supply Elasticity Indicates the extent to which price changes affect the quantity supplied. NEXT
Nature of Supply Elasticity Indicates the extent to which price changes affect the quantity supplied. NEXT
 Elastic Supply *Small change in price causes a major change in the quantity supplied: – i. e. Sports teams T-shirts, posters, and hats • Products can be made: – Quickly – Inexpensively, and – Using a few, readily available resources NEXT
Elastic Supply *Small change in price causes a major change in the quantity supplied: – i. e. Sports teams T-shirts, posters, and hats • Products can be made: – Quickly – Inexpensively, and – Using a few, readily available resources NEXT
 Inelastic Supply Exists when a change in a good’s price has little impact on the quantity supplied. – If a producer cannot increase supply regardless of price. i. e. Gold, Land, Space Shuttles • Products require a great deal of: – Time – Money – Resources that are not readily available NEXT
Inelastic Supply Exists when a change in a good’s price has little impact on the quantity supplied. – If a producer cannot increase supply regardless of price. i. e. Gold, Land, Space Shuttles • Products require a great deal of: – Time – Money – Resources that are not readily available NEXT
 Closure Activity #11 Explain the differences between the terms in each of these pairs: • supply and law of supply • supply schedule and supply curve • market supply schedule and market supply curve NEXT
Closure Activity #11 Explain the differences between the terms in each of these pairs: • supply and law of supply • supply schedule and supply curve • market supply schedule and market supply curve NEXT
 Show What You Know! Georgia Milestone Practice Question The amount of a good or service that a producer is willing to sell at various prices Supply schedule Law of supply Supply Profit NEXT
Show What You Know! Georgia Milestone Practice Question The amount of a good or service that a producer is willing to sell at various prices Supply schedule Law of supply Supply Profit NEXT
 Show What You Know! Georgia Milestone Practice Question The relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied Inverse Direct Profit All of the above NEXT
Show What You Know! Georgia Milestone Practice Question The relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied Inverse Direct Profit All of the above NEXT
 Show What You Know! Georgia Milestone Practice Question If a producer of a good cannot produce it fast enough for consumers to purchase regardless of the price than that product is said to have Demand elasticity Demand inelasticity Supply inelasticity NEXT
Show What You Know! Georgia Milestone Practice Question If a producer of a good cannot produce it fast enough for consumers to purchase regardless of the price than that product is said to have Demand elasticity Demand inelasticity Supply inelasticity NEXT
 The End Any questions? Any Questions? NEXT
The End Any questions? Any Questions? NEXT
 Warm Up #14 What happens to the supply curve during the Labor Day holiday for sodas? Explain what happens. NEXT
Warm Up #14 What happens to the supply curve during the Labor Day holiday for sodas? Explain what happens. NEXT
 Do the following assignment in your textbook. Chapter 5 Section 1 Do Application Analyzing Effects pgs. 131, 133 & 136. Analyze Graphs pgs. , 134 & 135 The NBA Goes International- Connecting Across the Globe p. 136 Section 1 Assessment p. 137 2 -5 Chapter 5 Section 2 Analyze Tables p. 139 Application Drawing Conclusions p. 139, 141, & 143 Section 2 Assessment 2 -5 NEXT
Do the following assignment in your textbook. Chapter 5 Section 1 Do Application Analyzing Effects pgs. 131, 133 & 136. Analyze Graphs pgs. , 134 & 135 The NBA Goes International- Connecting Across the Globe p. 136 Section 1 Assessment p. 137 2 -5 Chapter 5 Section 2 Analyze Tables p. 139 Application Drawing Conclusions p. 139, 141, & 143 Section 2 Assessment 2 -5 NEXT
 Class Focus We the Senior Class of 2016 will complete ALL of our assignments to best of our abilities and behave appropriately in class. We will respect all faculty, staff, substitutes, classmates, and especially Mr. Wilcox. We will graduate on time May 20, 2016 and become productive citizens in society. NEXT
Class Focus We the Senior Class of 2016 will complete ALL of our assignments to best of our abilities and behave appropriately in class. We will respect all faculty, staff, substitutes, classmates, and especially Mr. Wilcox. We will graduate on time May 20, 2016 and become productive citizens in society. NEXT
 SSEMI 3 c You will be able to explain how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. c. Define price elasticity of demand supply. Determine and define vocabulary. Identify key terms within the standard. Define each term. ________________________________________ ________________________________________ NEXT
SSEMI 3 c You will be able to explain how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. c. Define price elasticity of demand supply. Determine and define vocabulary. Identify key terms within the standard. Define each term. ________________________________________ ________________________________________ NEXT
 Scaffold understanding of the standard(s) and/or element(s). Paraphrase the standard(s) and/or element(s). Rewrite the standard including synonyms or brief definitions in parentheses and in a different color following the key terms found in step 1. You will be able to explain (clarify) how the Law of Demand (want), the Law of Supply (amount), prices, and profits (income) work to determine production and distribution (delivery) in a market (shop) economy. NEXT
Scaffold understanding of the standard(s) and/or element(s). Paraphrase the standard(s) and/or element(s). Rewrite the standard including synonyms or brief definitions in parentheses and in a different color following the key terms found in step 1. You will be able to explain (clarify) how the Law of Demand (want), the Law of Supply (amount), prices, and profits (income) work to determine production and distribution (delivery) in a market (shop) economy. NEXT
 Supply Changes in Supply SSEM 13 NEXT
Supply Changes in Supply SSEM 13 NEXT
 Changes in Supply KEY CONCEPT When a product’s supply shifts, different quantities of products are supplied at every possible price. NEXT
Changes in Supply KEY CONCEPT When a product’s supply shifts, different quantities of products are supplied at every possible price. NEXT
 Acronym for Non- Price Determinants of Supply Come Go To Papa John’s Pizza Right Now. NEXT
Acronym for Non- Price Determinants of Supply Come Go To Papa John’s Pizza Right Now. NEXT
 Non-Price Determinants supply shifts: Competition Government tools Technology Prices of related goods Producer expectations Resource prices NEXT
Non-Price Determinants supply shifts: Competition Government tools Technology Prices of related goods Producer expectations Resource prices NEXT
 Competition A larger number of suppliers in a market tends to increase the supply. • A lack of competition tends to decrease supply. NEXT
Competition A larger number of suppliers in a market tends to increase the supply. • A lack of competition tends to decrease supply. NEXT
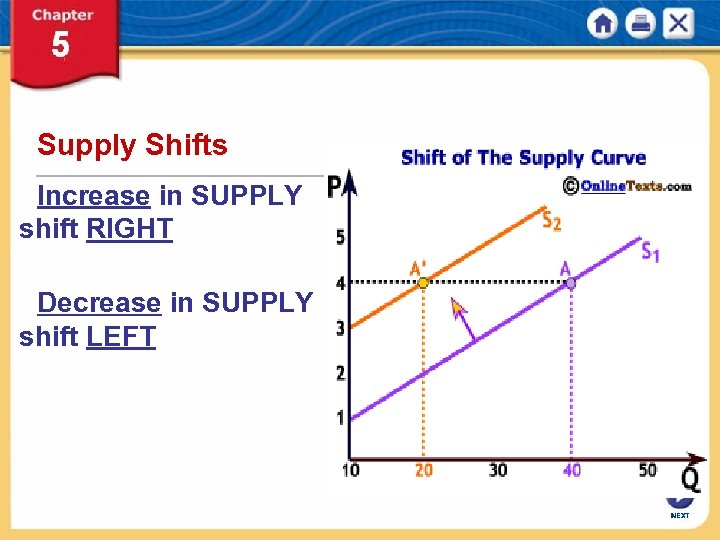 Supply Shifts Increase in SUPPLY shift RIGHT Decrease in SUPPLY shift LEFT NEXT
Supply Shifts Increase in SUPPLY shift RIGHT Decrease in SUPPLY shift LEFT NEXT
 Government Tools Tax—Required payment to the government Subsidy— Payment to private businesses by the government Regulation- Rules about how companies conduct business. NEXT
Government Tools Tax—Required payment to the government Subsidy— Payment to private businesses by the government Regulation- Rules about how companies conduct business. NEXT
 Technology New technology makes production more efficient and less expensive. NEXT
Technology New technology makes production more efficient and less expensive. NEXT
 Prices of Related Goods Means that the changes in a product’s price can affect the supply for the product’s related goods. • SUV/Gas • Cereal/ Milk NEXT
Prices of Related Goods Means that the changes in a product’s price can affect the supply for the product’s related goods. • SUV/Gas • Cereal/ Milk NEXT
 Producer Expectations The expectations producers have of the future of the price of their products can affect how much of their products they supply to the market now. NEXT
Producer Expectations The expectations producers have of the future of the price of their products can affect how much of their products they supply to the market now. NEXT
 Resources (prices) The most common determinant • Includes raw materials • Electricity • Wages NEXT
Resources (prices) The most common determinant • Includes raw materials • Electricity • Wages NEXT
 What Is Elasticity of Supply? KEY CONCEPTS • Elasticity of supply—measures producer response to price changes –Elastic—price change leads to larger change in quantity supplied • Inelastic—price change leads to smaller change in quantity supplied –Unit elastic—price and quantity supplied change by same percentage NEXT
What Is Elasticity of Supply? KEY CONCEPTS • Elasticity of supply—measures producer response to price changes –Elastic—price change leads to larger change in quantity supplied • Inelastic—price change leads to smaller change in quantity supplied –Unit elastic—price and quantity supplied change by same percentage NEXT
 Elasticity of Supply EXAMPLE: Elastic Supply • As product gains popularity, shortage develops, price increase • Producers can increase supply if: –resources are easy to come by, inexpensive –production uncomplicated, easy to increase NEXT
Elasticity of Supply EXAMPLE: Elastic Supply • As product gains popularity, shortage develops, price increase • Producers can increase supply if: –resources are easy to come by, inexpensive –production uncomplicated, easy to increase NEXT
 Elasticity of Supply EXAMPLE: Inelastic Supply • Producers may not increase supply if: –availability of resources limited –production capacity cannot be increased –shipping too costly, unavailable or difficult to get NEXT
Elasticity of Supply EXAMPLE: Inelastic Supply • Producers may not increase supply if: –availability of resources limited –production capacity cannot be increased –shipping too costly, unavailable or difficult to get NEXT
 Conclusion: What Affects Elasticity of Supply? KEY CONCEPTS • Main factor determining elasticity is ease of changing production – Given enough time, elasticity rises for most goods and services • Industries that respond quickly to rising or falling prices: – Do not need much capital, skilled labor, hard-toobtain resources • Other industries need a lot of time to shift resources NEXT
Conclusion: What Affects Elasticity of Supply? KEY CONCEPTS • Main factor determining elasticity is ease of changing production – Given enough time, elasticity rises for most goods and services • Industries that respond quickly to rising or falling prices: – Do not need much capital, skilled labor, hard-toobtain resources • Other industries need a lot of time to shift resources NEXT
 Show What You Know! EOCT Question If an item is difficult to get, this market situation is an example of Demand elasticity Demand inelasticity Supply inelasticity NEXT
Show What You Know! EOCT Question If an item is difficult to get, this market situation is an example of Demand elasticity Demand inelasticity Supply inelasticity NEXT
 The End Any questions? Any Questions? NEXT
The End Any questions? Any Questions? NEXT
 Warm Up #15 Do Application Analyzing Effects pgs. 131, 133 & 136. Analyze Graphs pgs. , 134 & 135 NEXT
Warm Up #15 Do Application Analyzing Effects pgs. 131, 133 & 136. Analyze Graphs pgs. , 134 & 135 NEXT
 Class Focus We the Senior Class of 2016 will complete ALL of our assignments to best of our abilities and behave appropriately in class. We will respect all faculty, staff, substitutes, classmates, and especially Mr. Wilcox. We will graduate on time May 20, 2016 and become productive citizens in society. NEXT
Class Focus We the Senior Class of 2016 will complete ALL of our assignments to best of our abilities and behave appropriately in class. We will respect all faculty, staff, substitutes, classmates, and especially Mr. Wilcox. We will graduate on time May 20, 2016 and become productive citizens in society. NEXT
 SSEF 6 You will be able to explain how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. c. Define price elasticity of demand supply. Determine and define vocabulary. Identify key terms within the standard. Define each term. ________________________________________ ________________________________________ NEXT
SSEF 6 You will be able to explain how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. c. Define price elasticity of demand supply. Determine and define vocabulary. Identify key terms within the standard. Define each term. ________________________________________ ________________________________________ NEXT
 Scaffold understanding of the standard(s) and/or element(s). Paraphrase the standard(s) and/or element(s). Rewrite the standard including synonyms or brief definitions in parentheses and in a different color following the key terms found in step 1. You will be able to explain (clarify) how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits (proceeds) work to determine production (manufacture) and distribution (spreading) in a market economy. c. Define price elasticity (springiness) of demand supply. NEXT
Scaffold understanding of the standard(s) and/or element(s). Paraphrase the standard(s) and/or element(s). Rewrite the standard including synonyms or brief definitions in parentheses and in a different color following the key terms found in step 1. You will be able to explain (clarify) how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits (proceeds) work to determine production (manufacture) and distribution (spreading) in a market economy. c. Define price elasticity (springiness) of demand supply. NEXT
 Supply Making Production Decisions SSEM 12 NEXT
Supply Making Production Decisions SSEM 12 NEXT
 Why do producers look at Productivity when making supply decisions: A. to determine how efficiently their resources are being used in production B. to maximize efficiency C. Increase profits NEXT
Why do producers look at Productivity when making supply decisions: A. to determine how efficiently their resources are being used in production B. to maximize efficiency C. Increase profits NEXT
 Varying levels of input affects the levels of output: Adding levels of input increases productivity up to a point and then eventually results in decreased productivity and in negative marginal product. NEXT
Varying levels of input affects the levels of output: Adding levels of input increases productivity up to a point and then eventually results in decreased productivity and in negative marginal product. NEXT
 Total Product All of the product a company makes in a given period of time- with a given amount of input. NEXT
Total Product All of the product a company makes in a given period of time- with a given amount of input. NEXT
 Three Stages of Production (Marginal Return): A. Increasing Marginal Returns • Each additional person increases production usually with specialization. B. Diminishing Marginal Returns • Each additional person added increases production but at a slower rate C. Negative Marginal Returns • Each additional person lowers total production NEXT
Three Stages of Production (Marginal Return): A. Increasing Marginal Returns • Each additional person increases production usually with specialization. B. Diminishing Marginal Returns • Each additional person added increases production but at a slower rate C. Negative Marginal Returns • Each additional person lowers total production NEXT
 Costs of Production: Fixed Costs • Rent, interest on loans, insurance, taxes, and salaries • Overhead – Costs except wages • Depreciation – Decreasing value NEXT
Costs of Production: Fixed Costs • Rent, interest on loans, insurance, taxes, and salaries • Overhead – Costs except wages • Depreciation – Decreasing value NEXT
 Costs of Production Variable Costs • Raw materials and wages NEXT
Costs of Production Variable Costs • Raw materials and wages NEXT
 Costs of Production Total Costs • The sum of the fixed and variable production costs NEXT
Costs of Production Total Costs • The sum of the fixed and variable production costs NEXT
 GM Assembly Line workers NEXT
GM Assembly Line workers NEXT
 Marginal Costs It is the additional costs The additional costs of producing one more divided by the additional product produced. unit of output NEXT
Marginal Costs It is the additional costs The additional costs of producing one more divided by the additional product produced. unit of output NEXT
 Earning the Highest Profit KEY CONCEPTS • Marginal revenue—money made from sale of each additional unit sold – same as price • Total revenue—income from selling a product – Total revenue = P (price) x Q (quantity purchased at that price) NEXT
Earning the Highest Profit KEY CONCEPTS • Marginal revenue—money made from sale of each additional unit sold – same as price • Total revenue—income from selling a product – Total revenue = P (price) x Q (quantity purchased at that price) NEXT
 Earning the Highest Profit EXAMPLE: Production Costs and Revenues Schedule 1. To make most profit, owner decides number workers hired, units made 2. To decide, owner performs marginal analysis – comparison of costs, benefits of adding a worker, making another unit 3. Profit-maximizing output—level of production yielding highest profit – marginal cost and marginal revenue are equal NEXT
Earning the Highest Profit EXAMPLE: Production Costs and Revenues Schedule 1. To make most profit, owner decides number workers hired, units made 2. To decide, owner performs marginal analysis – comparison of costs, benefits of adding a worker, making another unit 3. Profit-maximizing output—level of production yielding highest profit – marginal cost and marginal revenue are equal NEXT
 How does changes in production costs affect producers’ supply decisions: 1. By determining the prices at which producers supply quantities of goods or services 2. By determining production goals NEXT
How does changes in production costs affect producers’ supply decisions: 1. By determining the prices at which producers supply quantities of goods or services 2. By determining production goals NEXT
 Closure Activity #13: Robert Johnson: Supplying African-American Entertainment EXAMPLE: Expanding the Number of Producers • Johnson recognized cable TV industry ignored African-American market • 1980, launched Black Entertainment Television: music, public affairs • Cable operators in U. S. , Canada, Caribbean began to buy BET’s shows • Started BET. com—number one Internet portal for African Americans • In 2001, Johnson sold BET, became first black billionaire NEXT
Closure Activity #13: Robert Johnson: Supplying African-American Entertainment EXAMPLE: Expanding the Number of Producers • Johnson recognized cable TV industry ignored African-American market • 1980, launched Black Entertainment Television: music, public affairs • Cable operators in U. S. , Canada, Caribbean began to buy BET’s shows • Started BET. com—number one Internet portal for African Americans • In 2001, Johnson sold BET, became first black billionaire NEXT
 The End Any questions? Any Questions? NEXT
The End Any questions? Any Questions? NEXT
 TEST Tomorrow!! Productivity Supply Quantity supplied Profit Motive Profit Costs of production Supply schedule Supply curve Supply elasticity Elastic supply Inelastic supply Tax Subsidy Regulation Total product Increasing marginal returns Diminishing marginal returns Negative marginal returns Fixed costs Overhead Depreciation Marginal costs Total costs Marginal revenue Total revenue **Be able to shift the supply curve left or right. NEXT 65
TEST Tomorrow!! Productivity Supply Quantity supplied Profit Motive Profit Costs of production Supply schedule Supply curve Supply elasticity Elastic supply Inelastic supply Tax Subsidy Regulation Total product Increasing marginal returns Diminishing marginal returns Negative marginal returns Fixed costs Overhead Depreciation Marginal costs Total costs Marginal revenue Total revenue **Be able to shift the supply curve left or right. NEXT 65


