880fa7671c4c3b8cc9f0a086c8509269.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Warm-Up 12/9/2015 1. Germany was divided into 4 parts after WWII. Why do you think this happened? (Answer this question on your Warm-Up sheet for this week) 2. Create pages in your vocabulary journals for the following words and write what you think they mean: 4. Berlin Wall (page 113) 1. Cold War (page 110) 5. Eastern Bloc (page 114) 2. Superpowers (page 111) 6. Western Bloc (page 115) 3. Iron Curtain (page 112)
Warm-Up 12/9/2015 1. Germany was divided into 4 parts after WWII. Why do you think this happened? (Answer this question on your Warm-Up sheet for this week) 2. Create pages in your vocabulary journals for the following words and write what you think they mean: 4. Berlin Wall (page 113) 1. Cold War (page 110) 5. Eastern Bloc (page 114) 2. Superpowers (page 111) 6. Western Bloc (page 115) 3. Iron Curtain (page 112)
 Impact of WWII SS 6 H 7 b. Explain the impact of WWII in terms of the Holocaust, the origins of the Cold War, and the rise of Superpowers.
Impact of WWII SS 6 H 7 b. Explain the impact of WWII in terms of the Holocaust, the origins of the Cold War, and the rise of Superpowers.
 E. Q. • How did WWII impact the world in terms of the Holocaust, the origins of the Cold War, and the rise of Superpowers?
E. Q. • How did WWII impact the world in terms of the Holocaust, the origins of the Cold War, and the rise of Superpowers?
 Holocaust Review of Key Facts • Holocaust: systematic killing of 6 million Jews • Key person: Adolph Hitler • Location: Germany (which later spread to parts all over central Europe) • Time period: WWII • Genocide: planned killing of a race of people • How: – – 1. identified Jews with yellow star 2. took away rights/freedoms 3. gathered/imprisoned Jews in ghettos 4. shipped Jews to concentration camps http: //www. ushmm. org/wlc/en/media_fi. php? Module. Id=10005143&Media. Id=183
Holocaust Review of Key Facts • Holocaust: systematic killing of 6 million Jews • Key person: Adolph Hitler • Location: Germany (which later spread to parts all over central Europe) • Time period: WWII • Genocide: planned killing of a race of people • How: – – 1. identified Jews with yellow star 2. took away rights/freedoms 3. gathered/imprisoned Jews in ghettos 4. shipped Jews to concentration camps http: //www. ushmm. org/wlc/en/media_fi. php? Module. Id=10005143&Media. Id=183
 Review! Concentration Camps Left • • Old, weak, young Sent to “showers” Gassed to death cremated • • • Right Workers Sent to showers Heads shaved Given prison clothes Tattooed with number Worked to death
Review! Concentration Camps Left • • Old, weak, young Sent to “showers” Gassed to death cremated • • • Right Workers Sent to showers Heads shaved Given prison clothes Tattooed with number Worked to death
 Review! • • Not Just Jews Killed Political prisoners Mentally ill Disabled Gypsies, Poles, and others Helene Gotthold, a Jehovah's Witness, was beheaded for her religious beliefs on December 8, 1944, in Berlin. She is pictured with her children. Germany, June 25, 1936.
Review! • • Not Just Jews Killed Political prisoners Mentally ill Disabled Gypsies, Poles, and others Helene Gotthold, a Jehovah's Witness, was beheaded for her religious beliefs on December 8, 1944, in Berlin. She is pictured with her children. Germany, June 25, 1936.
 After • Survivors – no homes left • United Nations divided Palestine into Arab and Jewish “states” (countries) • Israel became a Jewish nation – 1948 http: //www. unog. ch/80256 EDD 006 AC 19 C/( http. Pages)/242056 AEA 671 DEF 780256 EF 30037 A 2 A 8? Open. Document http: //www. ushmm. org/wlc/en/media_fi. php? Module. Id=10005129&M edia. Id=177
After • Survivors – no homes left • United Nations divided Palestine into Arab and Jewish “states” (countries) • Israel became a Jewish nation – 1948 http: //www. unog. ch/80256 EDD 006 AC 19 C/( http. Pages)/242056 AEA 671 DEF 780256 EF 30037 A 2 A 8? Open. Document http: //www. ushmm. org/wlc/en/media_fi. php? Module. Id=10005129&M edia. Id=177
 Liberation (freedom) & The End of WWII… • Soviet (USSR) & allied forces of WWII were surrounding Germany, Austria- Hungry, and Poland (Central Powers) and were closing in. As they came through, the Nazis had to destroy the evidence of the concentration camps to try to keep the evil secret. Several camps were found destroyed in 1944 and info 1945, but when Auschwitz was discovered with some living poisoners able to tell their stories, the secret was out! Hitler, knowing his regime was over and he’d have to pay the consequences, committed suicide on April 30, 1945. Only eight days later, Germany & the Nazi regime surrendered on May 7, 1945 officially ending WWII in Europe. [***The Pacific (Asian) side of WWII, did not end until August 1945 with the USA dropping atomic bombs on the Japanese (Nagasaki & Hiroshima). ] • http: //www. ushmm. org/wlc/en/article. php? Module. Id=10005131 • http: //www. eyewitnesstohistory. com/vosurrender. htm
Liberation (freedom) & The End of WWII… • Soviet (USSR) & allied forces of WWII were surrounding Germany, Austria- Hungry, and Poland (Central Powers) and were closing in. As they came through, the Nazis had to destroy the evidence of the concentration camps to try to keep the evil secret. Several camps were found destroyed in 1944 and info 1945, but when Auschwitz was discovered with some living poisoners able to tell their stories, the secret was out! Hitler, knowing his regime was over and he’d have to pay the consequences, committed suicide on April 30, 1945. Only eight days later, Germany & the Nazi regime surrendered on May 7, 1945 officially ending WWII in Europe. [***The Pacific (Asian) side of WWII, did not end until August 1945 with the USA dropping atomic bombs on the Japanese (Nagasaki & Hiroshima). ] • http: //www. ushmm. org/wlc/en/article. php? Module. Id=10005131 • http: //www. eyewitnesstohistory. com/vosurrender. htm
 Review Questions 1. What is genocide? The planned killing of a race of people 2. Who created the country of Israel? United Nations 3. Who was spared in the Holocaust? None of the above 4. What actions did the United Nations take as a result of the Holocaust? Created a Jewish state and made genocide a crime
Review Questions 1. What is genocide? The planned killing of a race of people 2. Who created the country of Israel? United Nations 3. Who was spared in the Holocaust? None of the above 4. What actions did the United Nations take as a result of the Holocaust? Created a Jewish state and made genocide a crime
 Cold War Key Facts • When: end of WWII – 1945 • What: period of distrust and misunderstanding • Who: between Soviet Union (U. S. S. R. ) & U. S. A. (and former allies) • Why: Soviet Union was communist/command (strong central government controls businesses). U. S. A. believed businesses should be privately owned.
Cold War Key Facts • When: end of WWII – 1945 • What: period of distrust and misunderstanding • Who: between Soviet Union (U. S. S. R. ) & U. S. A. (and former allies) • Why: Soviet Union was communist/command (strong central government controls businesses). U. S. A. believed businesses should be privately owned.
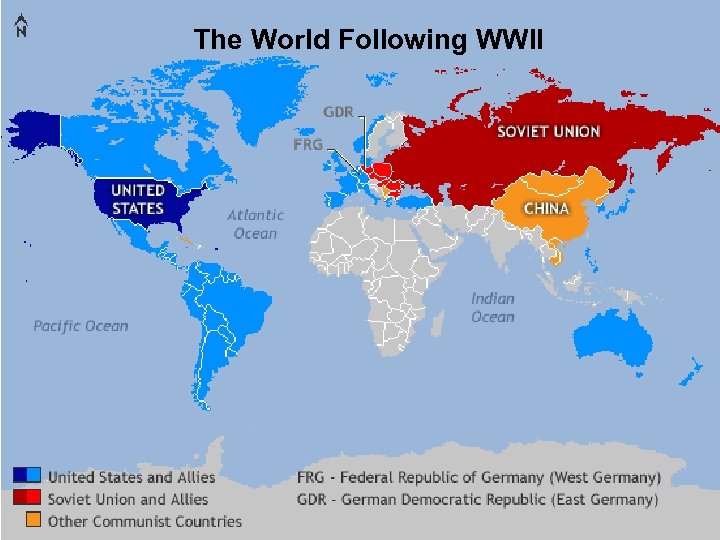 The World Following WWII
The World Following WWII
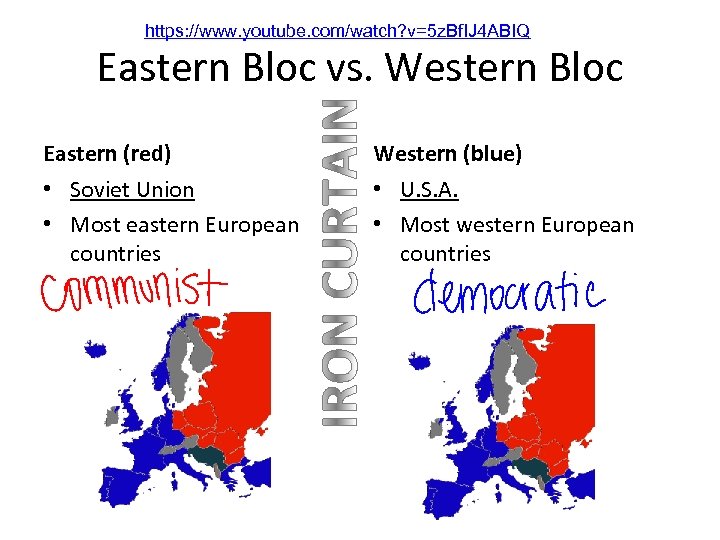 https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=5 z. Bf. IJ 4 ABIQ Eastern Bloc vs. Western Bloc Eastern (red) Western (blue) • Soviet Union • Most eastern European countries • U. S. A. • Most western European countries
https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=5 z. Bf. IJ 4 ABIQ Eastern Bloc vs. Western Bloc Eastern (red) Western (blue) • Soviet Union • Most eastern European countries • U. S. A. • Most western European countries
 Germany • Divided after WWII into 4 parts • 1948: divided into West Germany (free) and East Germany (Soviet controlled) • Capital – Berlin – divided into East Berlin and West Berlin • 1961: Berlin Wall built to separate city
Germany • Divided after WWII into 4 parts • 1948: divided into West Germany (free) and East Germany (Soviet controlled) • Capital – Berlin – divided into East Berlin and West Berlin • 1961: Berlin Wall built to separate city
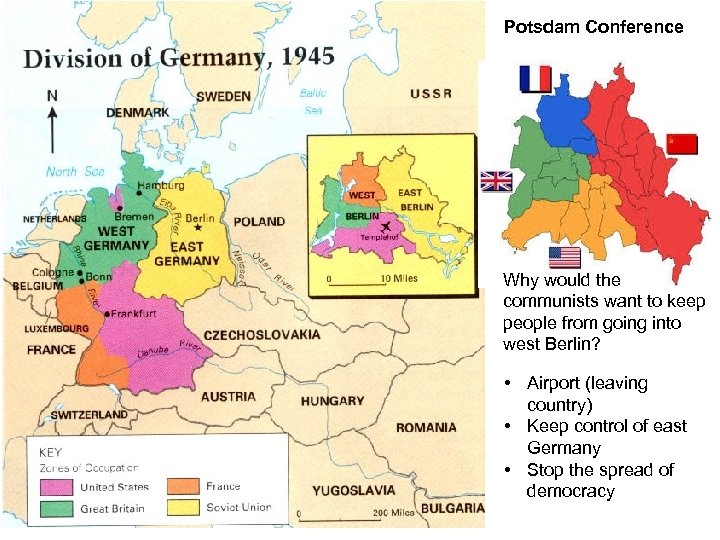 Potsdam Conference Why would the communists want to keep people from going into west Berlin? • Airport (leaving country) • Keep control of east Germany • Stop the spread of democracy
Potsdam Conference Why would the communists want to keep people from going into west Berlin? • Airport (leaving country) • Keep control of east Germany • Stop the spread of democracy
 Fears “red scare” • Each side believed the other wanted to rule the world. • People feared a nuclear would happen. • Countries formed alliances for protection. • 1949 – Western Bloc plus Canada formed North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – Eastern Bloc formed Warsaw Pact
Fears “red scare” • Each side believed the other wanted to rule the world. • People feared a nuclear would happen. • Countries formed alliances for protection. • 1949 – Western Bloc plus Canada formed North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – Eastern Bloc formed Warsaw Pact
 Review Questions 5. Which country was the leader of the Eastern Bloc? Soviet Union 6. What 2 terms describe the dividing line between eastern & western, communist & noncommunist areas? Berlin Wall & Iron Curtain 7. Which was 1 of the areas of disagreement between the U. S. S. R. & the U. S. during the Cold War? Best type of economic system 8. When was the Cold War? After WWII 9. The Warsaw Pact was to the U. S. S. R. as NATO was to the U. S.
Review Questions 5. Which country was the leader of the Eastern Bloc? Soviet Union 6. What 2 terms describe the dividing line between eastern & western, communist & noncommunist areas? Berlin Wall & Iron Curtain 7. Which was 1 of the areas of disagreement between the U. S. S. R. & the U. S. during the Cold War? Best type of economic system 8. When was the Cold War? After WWII 9. The Warsaw Pact was to the U. S. S. R. as NATO was to the U. S.
 . . D A M. World Superpowers
. . D A M. World Superpowers
 Rise of the Superpowers • • • U. S. A. Constitutional Republic, Free market Permanent seat on U. N. Security Council 4 th most populated country in world Powerful military support from NATO Largest navy in world Military bases all over world CIA (spies) Large reserve of nukes Influenced world events Soviet Union • Communist, Command • Permanent seat on U. N. Security Council • Largest country in the world • Military and space technology • World-wide spy network (KGB) • One of largest stockpiles of nukes in world • Influenced world events
Rise of the Superpowers • • • U. S. A. Constitutional Republic, Free market Permanent seat on U. N. Security Council 4 th most populated country in world Powerful military support from NATO Largest navy in world Military bases all over world CIA (spies) Large reserve of nukes Influenced world events Soviet Union • Communist, Command • Permanent seat on U. N. Security Council • Largest country in the world • Military and space technology • World-wide spy network (KGB) • One of largest stockpiles of nukes in world • Influenced world events
 Review Questions 10. As a world superpower, the U. S. S. R. had A seat on the UN Security Council 11. As a world superpower, the U. S. had Military bases all over the world 12. Which condition is required to be a world superpower? Influence over world events
Review Questions 10. As a world superpower, the U. S. S. R. had A seat on the UN Security Council 11. As a world superpower, the U. S. had Military bases all over the world 12. Which condition is required to be a world superpower? Influence over world events
 http: //www. history. com/topics/cold-war/fall-of-soviet-union Collapse of the Soviet Union • Problem: Soviet Union spent $$$$$$$ – Putting down revolts in its countries – protecting its borders – keeping up with the arms race against the U. S. A
http: //www. history. com/topics/cold-war/fall-of-soviet-union Collapse of the Soviet Union • Problem: Soviet Union spent $$$$$$$ – Putting down revolts in its countries – protecting its borders – keeping up with the arms race against the U. S. A
 http: //www. wikiwand. com/en/Post-Soviet_states#/States_and_geographical_groupings Collapse of the Soviet Union 1985 • leader Mikhail Gorbachev – reduced government control of business – increased freedom for citizens Result – improved relations with U. S. A. – inspired other Eastern Bloc countries to demand freedom
http: //www. wikiwand. com/en/Post-Soviet_states#/States_and_geographical_groupings Collapse of the Soviet Union 1985 • leader Mikhail Gorbachev – reduced government control of business – increased freedom for citizens Result – improved relations with U. S. A. – inspired other Eastern Bloc countries to demand freedom

 German Reunification • Nov 1989: Berlin Wall torn down • Germany began to reunify • Germany was 1 country again in 1990 • Cold War was over • Soviet republics gained freedom from Soviet Union. • Many new countries were made. Russia is the largest.
German Reunification • Nov 1989: Berlin Wall torn down • Germany began to reunify • Germany was 1 country again in 1990 • Cold War was over • Soviet republics gained freedom from Soviet Union. • Many new countries were made. Russia is the largest.
 Review Questions 13. Why did Gorbachev reduce government control of the economy? An unstable economy due to increased military spending 14. What marked the end of the Cold War? Destruction of the Berlin Wall 15. What was the largest country created from the former Soviet Union? Russia
Review Questions 13. Why did Gorbachev reduce government control of the economy? An unstable economy due to increased military spending 14. What marked the end of the Cold War? Destruction of the Berlin Wall 15. What was the largest country created from the former Soviet Union? Russia


