338caa8d23b924dd9e4d5a6a3f998419.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Warehousing Equipment – – Tompkins et al. , “Facilities Planning”, John Wiley & Sons, 1996: Chapters 6, 9 College-Industry Council on Material Handling Education: Material Handling Equipment Taxonomy: http: //www. mhia. org/et/mhe_tax. htm
Warehousing Equipment – – Tompkins et al. , “Facilities Planning”, John Wiley & Sons, 1996: Chapters 6, 9 College-Industry Council on Material Handling Education: Material Handling Equipment Taxonomy: http: //www. mhia. org/et/mhe_tax. htm
 The role of equipment in warehouse operations • Reduce cost (labor + space) – enhance space utilization by, e. g. , • enabling the exploitation of the vertical dimension of the facility • allowing for denser packing – allow for more efficient order-picking by, e. g. , • increasing the sku density • supporting the automated transfer of material from storage to sorting and consolidation area • Enhance responsiveness – increase throughput of the facility, e. g. , • increasing the sku density • establishing a more ergonomic environment/arrangement for the warehouse operators • facilitating the parallelization of order picking • by parallelizing the tasks of order-picking and replensihment
The role of equipment in warehouse operations • Reduce cost (labor + space) – enhance space utilization by, e. g. , • enabling the exploitation of the vertical dimension of the facility • allowing for denser packing – allow for more efficient order-picking by, e. g. , • increasing the sku density • supporting the automated transfer of material from storage to sorting and consolidation area • Enhance responsiveness – increase throughput of the facility, e. g. , • increasing the sku density • establishing a more ergonomic environment/arrangement for the warehouse operators • facilitating the parallelization of order picking • by parallelizing the tasks of order-picking and replensihment
 The role of equipment in warehouse operations (cont. ) • Maintain Quality of Product and Operations – – – provide an orderly storage environment provide efficient ways for product tracing and identification provide safe and secure material handling facilitate order sortation and consolidation establish and maintain a controlled environment e. g. , • temperature control • access control
The role of equipment in warehouse operations (cont. ) • Maintain Quality of Product and Operations – – – provide an orderly storage environment provide efficient ways for product tracing and identification provide safe and secure material handling facilitate order sortation and consolidation establish and maintain a controlled environment e. g. , • temperature control • access control
 Equipment Classification (Tompkins et. al. , pgs 170 -173) • Containers & Unitizing Equipment • Storage and Retrieval Equipment – Unit Load – Small Load • Conveyors • Warehouse docks and dock-related equipment • Automatic Identification and Communication Equipment
Equipment Classification (Tompkins et. al. , pgs 170 -173) • Containers & Unitizing Equipment • Storage and Retrieval Equipment – Unit Load – Small Load • Conveyors • Warehouse docks and dock-related equipment • Automatic Identification and Communication Equipment
 For detailed functional descriptions, discussion on supported efficiencies, and pictures – College-Industry Council on Material Handling Education: Material Handling Equipment Taxonomy: http: //www. mhia. org/et/mhe_tax. htm – Tompkins et al. , “Facilities Planning”, John Wiley & Sons, 1996: Chapters 6, 9
For detailed functional descriptions, discussion on supported efficiencies, and pictures – College-Industry Council on Material Handling Education: Material Handling Equipment Taxonomy: http: //www. mhia. org/et/mhe_tax. htm – Tompkins et al. , “Facilities Planning”, John Wiley & Sons, 1996: Chapters 6, 9
 Pallet Storage Modes • Block Stacking • Rack Storage – – – Single-Deep Double-Deep Drive-In/Through Pallet Flow Unit Load AS/RS etc.
Pallet Storage Modes • Block Stacking • Rack Storage – – – Single-Deep Double-Deep Drive-In/Through Pallet Flow Unit Load AS/RS etc.
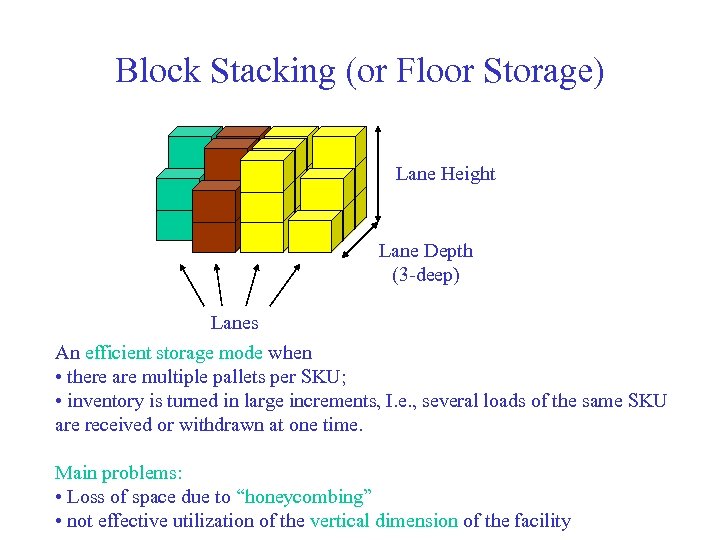 Block Stacking (or Floor Storage) Lane Height Lane Depth (3 -deep) Lanes An efficient storage mode when • there are multiple pallets per SKU; • inventory is turned in large increments, I. e. , several loads of the same SKU are received or withdrawn at one time. Main problems: • Loss of space due to “honeycombing” • not effective utilization of the vertical dimension of the facility
Block Stacking (or Floor Storage) Lane Height Lane Depth (3 -deep) Lanes An efficient storage mode when • there are multiple pallets per SKU; • inventory is turned in large increments, I. e. , several loads of the same SKU are received or withdrawn at one time. Main problems: • Loss of space due to “honeycombing” • not effective utilization of the vertical dimension of the facility
 Selective or Single-Deep or Simple Pallet Rack • The “benchmark” storage mode • Due to rack supports, each pallet is independently accessible (i. e. it supports totally random access) • Trade-off: too many aisles => inefficient space utilization
Selective or Single-Deep or Simple Pallet Rack • The “benchmark” storage mode • Due to rack supports, each pallet is independently accessible (i. e. it supports totally random access) • Trade-off: too many aisles => inefficient space utilization
 Double-deep rack • Two selective racks placed back-to-back => 2 -deep lanes • Each lane dedicated to one SKU => space loss in case of SKU’s with odd number of pallets • Less aisle space required (upto 50% savings in aisle space) • Trade-off: More work and/or specialized equipment for retrieving
Double-deep rack • Two selective racks placed back-to-back => 2 -deep lanes • Each lane dedicated to one SKU => space loss in case of SKU’s with odd number of pallets • Less aisle space required (upto 50% savings in aisle space) • Trade-off: More work and/or specialized equipment for retrieving
 Other pallet rack types • Drive-In/Through rack: 5 -10 loads deep – Better space utilization – More difficult, even dangerous retrieval • Pallet flow rack: up to 8 pallets deep – The rack shelves are slanted and have rollers, and therefore, every time a pallet is retrieved from a lane, the pallet behind it takes its position. – Allows for simultaneous picking and restocking – Supports FIFO operation – Typically used in high-throughput facilities • Cantilever rack: – Supports long items like timber and pipes
Other pallet rack types • Drive-In/Through rack: 5 -10 loads deep – Better space utilization – More difficult, even dangerous retrieval • Pallet flow rack: up to 8 pallets deep – The rack shelves are slanted and have rollers, and therefore, every time a pallet is retrieved from a lane, the pallet behind it takes its position. – Allows for simultaneous picking and restocking – Supports FIFO operation – Typically used in high-throughput facilities • Cantilever rack: – Supports long items like timber and pipes
 Unit-Load Retrieval Equipment • Key Differentiation factors: – – – aisle width requirements lift height/weight capacity Lane depth they can reach degree of automation capital expense • Major types – – Walkie Stacker Counterbalance Lift Truck Narrow Aisle Vehicles Automated Storage/Retrieval Machines
Unit-Load Retrieval Equipment • Key Differentiation factors: – – – aisle width requirements lift height/weight capacity Lane depth they can reach degree of automation capital expense • Major types – – Walkie Stacker Counterbalance Lift Truck Narrow Aisle Vehicles Automated Storage/Retrieval Machines
 Small Load Storage and Retrieval Equipment • Operator-to-Stock (or Man-to-Part or in-the-aisle) system: the operator travels to the storage location to retrieve material • Stock-to-Operator (or Part-to-Man or end-of-aisle) system: the material is mechanically transported to the operator for retrieval • Advantages of STO: – higher productivity – easier supervision – better item security and protection • Disadvantages of STO: – more expensive – more maintenance – more difficult to reconfigure
Small Load Storage and Retrieval Equipment • Operator-to-Stock (or Man-to-Part or in-the-aisle) system: the operator travels to the storage location to retrieve material • Stock-to-Operator (or Part-to-Man or end-of-aisle) system: the material is mechanically transported to the operator for retrieval • Advantages of STO: – higher productivity – easier supervision – better item security and protection • Disadvantages of STO: – more expensive – more maintenance – more difficult to reconfigure
 Operator-to-Stock Storage Equipment • • • Bin Shelving Modular Storage Drawers in Cabinets Carton Flow Racks Mobile Storage All the above equipment can also be arranged in mezzanines to get a better exploitation of the building cube.
Operator-to-Stock Storage Equipment • • • Bin Shelving Modular Storage Drawers in Cabinets Carton Flow Racks Mobile Storage All the above equipment can also be arranged in mezzanines to get a better exploitation of the building cube.
 Operator-to-Stock Retrieval Equipment • Picking Cart • Order Picker Truck (for higher placed loads) • Person-aboard Automated Storage/Retrieval Machine – captive aisle – free roaming • (Robotic Retrieval)
Operator-to-Stock Retrieval Equipment • Picking Cart • Order Picker Truck (for higher placed loads) • Person-aboard Automated Storage/Retrieval Machine – captive aisle – free roaming • (Robotic Retrieval)
 Stock-to-Operator Equipment • Carousels – Horizontal – Vertical – Independently Rotating Racks • Miniload Automated Storage and Retrieval Machine • Automatic Dispenser • Productivity gains – Allow for extensive parallelization of order retrievals – Focus on extracting rather than traveling and searching
Stock-to-Operator Equipment • Carousels – Horizontal – Vertical – Independently Rotating Racks • Miniload Automated Storage and Retrieval Machine • Automatic Dispenser • Productivity gains – Allow for extensive parallelization of order retrievals – Focus on extracting rather than traveling and searching
 Conveyors • • • (Flat) Belt Roller Telescoping Belt Chute Sorting – – – Deflector Push Diverter Pop-up Skewed Wheels Pop-up Roller Tilt tray • Remarks: – Conveyors change the economics of travel. – They can partition physically the warehouse into zones
Conveyors • • • (Flat) Belt Roller Telescoping Belt Chute Sorting – – – Deflector Push Diverter Pop-up Skewed Wheels Pop-up Roller Tilt tray • Remarks: – Conveyors change the economics of travel. – They can partition physically the warehouse into zones
 Warehouse docks and dock-related equipment • Warehouse docks: The facility interface with the shipping carriers • Dock configurations and dimensioning
Warehouse docks and dock-related equipment • Warehouse docks: The facility interface with the shipping carriers • Dock configurations and dimensioning
 Equipment facilitating the interfacing between docks and shipping carriers • Dock levelers: compensate the height difference between the carrier platform and the dock door – – mobile yard ramps permanent adjustable dock boards truck levelers scissors-type lifting docks • Bumper pads: absorb the shock from the impact of the shipping trailer with the dock walls (laminated rubber cushions) • 40, 000 lb load traveling 4 mph => 150, 000 lb force • Dock shelter: a flexible shield that when engaged to the carrier provides a closed-environment interface between it and the inner area of the warehouse – energy savings, increased safety, product protection, etc.
Equipment facilitating the interfacing between docks and shipping carriers • Dock levelers: compensate the height difference between the carrier platform and the dock door – – mobile yard ramps permanent adjustable dock boards truck levelers scissors-type lifting docks • Bumper pads: absorb the shock from the impact of the shipping trailer with the dock walls (laminated rubber cushions) • 40, 000 lb load traveling 4 mph => 150, 000 lb force • Dock shelter: a flexible shield that when engaged to the carrier provides a closed-environment interface between it and the inner area of the warehouse – energy savings, increased safety, product protection, etc.
 Automatic Identification and Communication Equipment • Permits real-time, nearly flawless data collection and communication, and therefore, it facilitates and increases the real-time awareness of the location, amount, origin, destination and schedule of the material.
Automatic Identification and Communication Equipment • Permits real-time, nearly flawless data collection and communication, and therefore, it facilitates and increases the real-time awareness of the location, amount, origin, destination and schedule of the material.
 Automatic Identification and Recognition • Bar coding technology: – bar codes – bar code readers – bar code printers • Optical character recognition • Radio Frequency (RF) and Surface Accoustical Wave (SAW) tags • Magnetic Stripes • Machine Vision
Automatic Identification and Recognition • Bar coding technology: – bar codes – bar code readers – bar code printers • Optical character recognition • Radio Frequency (RF) and Surface Accoustical Wave (SAW) tags • Magnetic Stripes • Machine Vision
 Automatic Paperless Communication • • RF data terminal Voice headset Light and Computer Aids Smart card
Automatic Paperless Communication • • RF data terminal Voice headset Light and Computer Aids Smart card


