| NNN Intera ctive< /TITLE > <META HTTPEQUIV= "Refre sh" CONTEN T="180 0, URL=/i ndex. h tml"> Wireless network WAP <WML> <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT"> <GO URL="/submit? Name=$N"/> </DO> Enter name: <INPUT TYPE="TEXT" KEY="N"/> </CARD> </WML> Content encoding 010011 110110 010011 011101 010010 011010 © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WHY WAP ? z Good relationships with standards l Several Liaisons with ETSI l" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-9.jpg" alt="WHY WAP ? z Good relationships with standards l Several Liaisons with ETSI l" />
WHY WAP ? z Good relationships with standards l Several Liaisons with ETSI l ETSI / WAP compliance profile for GSM and UMTS. l CTIA official Liaison Officer to the WAP Forum l WAP is actively working with the W 3 C and IETF l HTML-NG (HTML Next Generation) l HTTP-NG (HTML Next Generation) © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
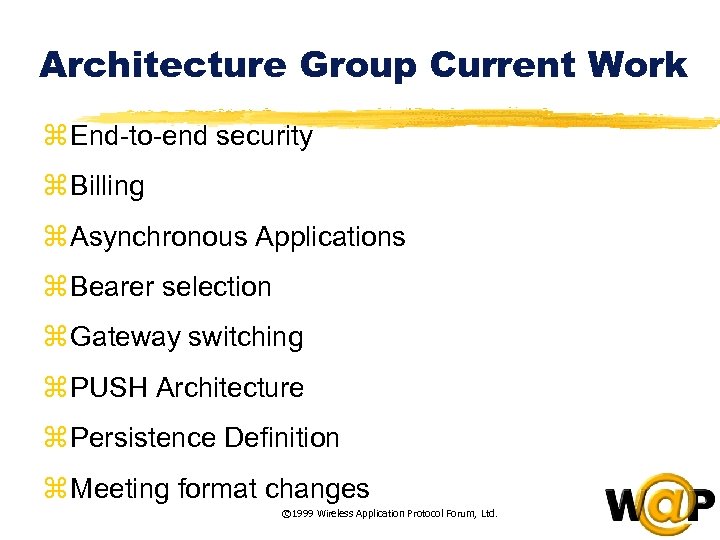
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Architecture Group Current Work z End-to-end security z Billing z Asynchronous Applications z Bearer" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-10.jpg" alt="Architecture Group Current Work z End-to-end security z Billing z Asynchronous Applications z Bearer" />
Architecture Group Current Work z End-to-end security z Billing z Asynchronous Applications z Bearer selection z Gateway switching z PUSH Architecture z Persistence Definition z Meeting format changes © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WAP Application Environment WML and WMLScript Wireless Telephony Architecture Content Formats Push User Agent" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-11.jpg" alt="WAP Application Environment WML and WMLScript Wireless Telephony Architecture Content Formats Push User Agent" />
WAP Application Environment WML and WMLScript Wireless Telephony Architecture Content Formats Push User Agent Profile </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WAE Goals z Network-neutral application environment; z For narrowband wireless devices; z With an" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-12.jpg" alt="WAE Goals z Network-neutral application environment; z For narrowband wireless devices; z With an" />
WAE Goals z Network-neutral application environment; z For narrowband wireless devices; z With an Internet/WWW programming model; z And a high degree of interoperability. © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WAE Requirements z Leverage WSP and WTP z Leverage Internet standard technology z Device" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-13.jpg" alt="WAE Requirements z Leverage WSP and WTP z Leverage Internet standard technology z Device" />
WAE Requirements z Leverage WSP and WTP z Leverage Internet standard technology z Device Independent z Network Independent z International Support © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
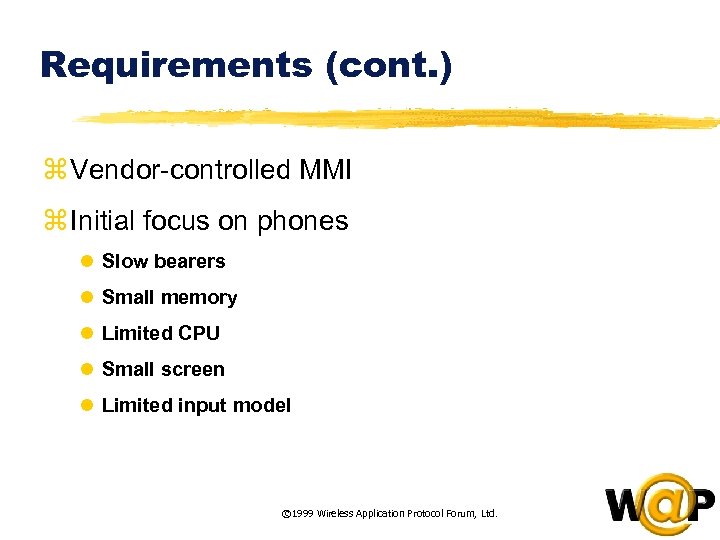
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Requirements (cont. ) z Vendor-controlled MMI z Initial focus on phones l Slow bearers" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-14.jpg" alt="Requirements (cont. ) z Vendor-controlled MMI z Initial focus on phones l Slow bearers" />
Requirements (cont. ) z Vendor-controlled MMI z Initial focus on phones l Slow bearers l Small memory l Limited CPU l Small screen l Limited input model © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
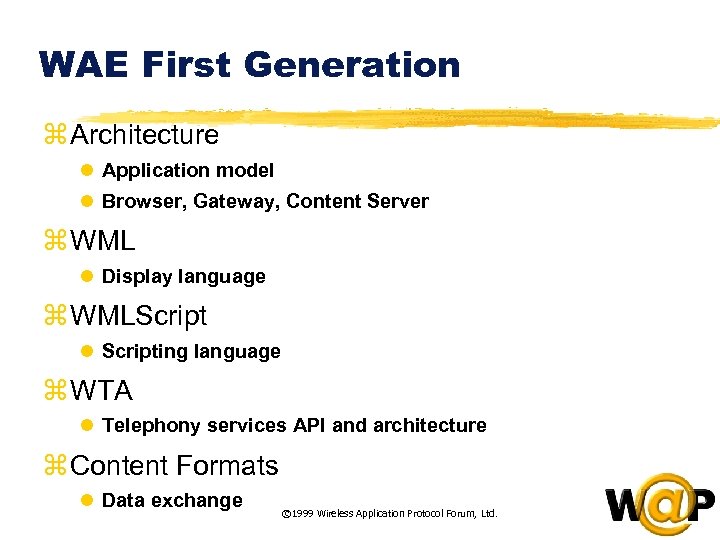
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WAE First Generation z Architecture l Application model l Browser, Gateway, Content Server z" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-15.jpg" alt="WAE First Generation z Architecture l Application model l Browser, Gateway, Content Server z" />
WAE First Generation z Architecture l Application model l Browser, Gateway, Content Server z WML l Display language z WMLScript l Scripting language z WTA l Telephony services API and architecture z Content Formats l Data exchange © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
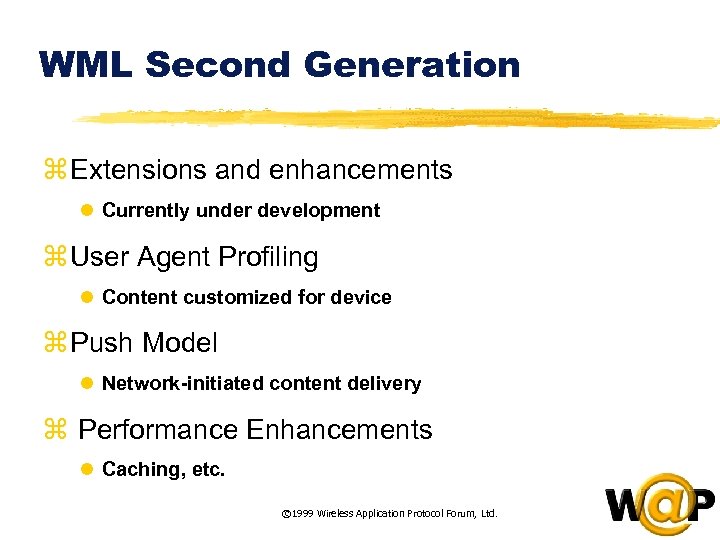
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WML Second Generation z Extensions and enhancements l Currently under development z User Agent" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-16.jpg" alt="WML Second Generation z Extensions and enhancements l Currently under development z User Agent" />
WML Second Generation z Extensions and enhancements l Currently under development z User Agent Profiling l Content customized for device z Push Model l Network-initiated content delivery z Performance Enhancements l Caching, etc. © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
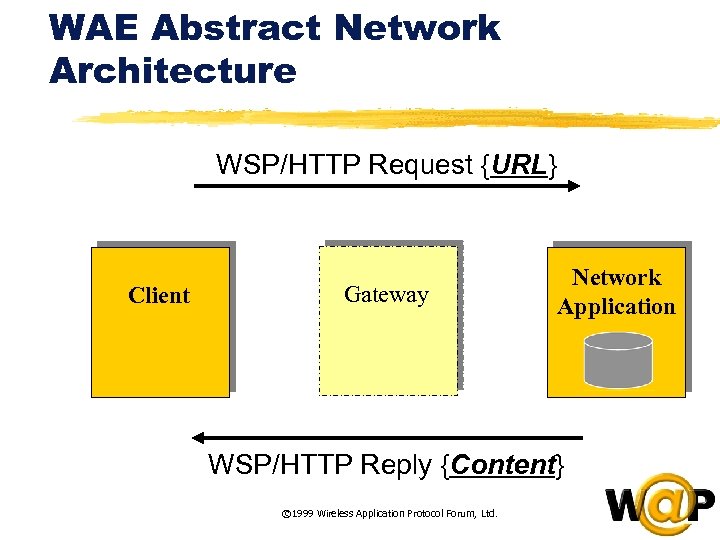
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WAE Abstract Network Architecture WSP/HTTP Request {URL} Client Gateway Network Application WSP/HTTP Reply {Content}" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-17.jpg" alt="WAE Abstract Network Architecture WSP/HTTP Request {URL} Client Gateway Network Application WSP/HTTP Reply {Content}" />
WAE Abstract Network Architecture WSP/HTTP Request {URL} Client Gateway Network Application WSP/HTTP Reply {Content} © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
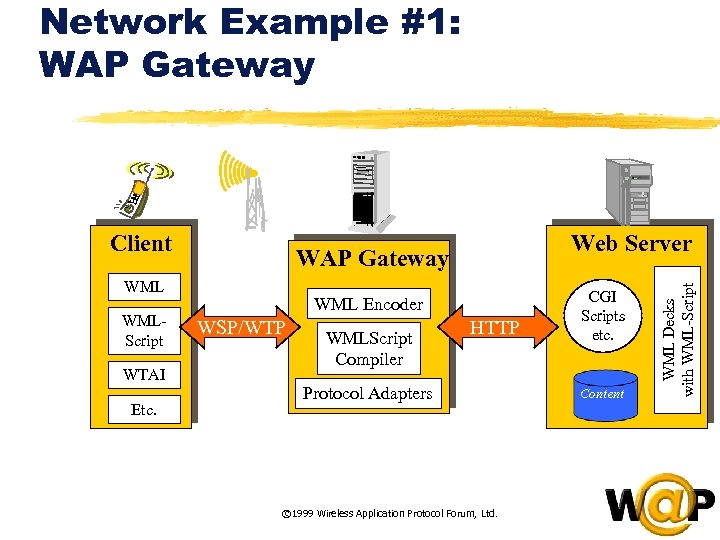
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Network Example #1: WAP Gateway WMLScript WTAI Etc. Web Server WML Encoder WSP/WTP WMLScript" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-18.jpg" alt="Network Example #1: WAP Gateway WMLScript WTAI Etc. Web Server WML Encoder WSP/WTP WMLScript" />
Network Example #1: WAP Gateway WMLScript WTAI Etc. Web Server WML Encoder WSP/WTP WMLScript Compiler HTTP Protocol Adapters © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. CGI Scripts etc. Content WML Decks with WML-Script Client </p>
</div>
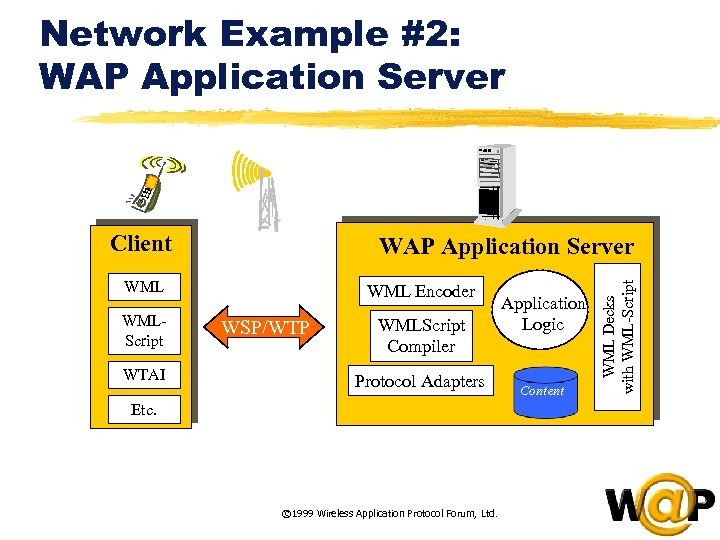
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Network Example #2: WAP Application Server Client WMLScript WTAI WML Encoder WSP/WTP WMLScript Compiler" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-19.jpg" alt="Network Example #2: WAP Application Server Client WMLScript WTAI WML Encoder WSP/WTP WMLScript Compiler" />
Network Example #2: WAP Application Server Client WMLScript WTAI WML Encoder WSP/WTP WMLScript Compiler Protocol Adapters Etc. © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. Application Logic Content WML Decks with WML-Script WAP Application Server </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WML z Tag-based browsing language: l Screen management (text, images) l Data input (text," src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-20.jpg" alt="WML z Tag-based browsing language: l Screen management (text, images) l Data input (text," />
WML z Tag-based browsing language: l Screen management (text, images) l Data input (text, selection lists, etc. ) l Hyperlinks & navigation support z W 3 C XML-based language z Inherits technology from HDML and HTML © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
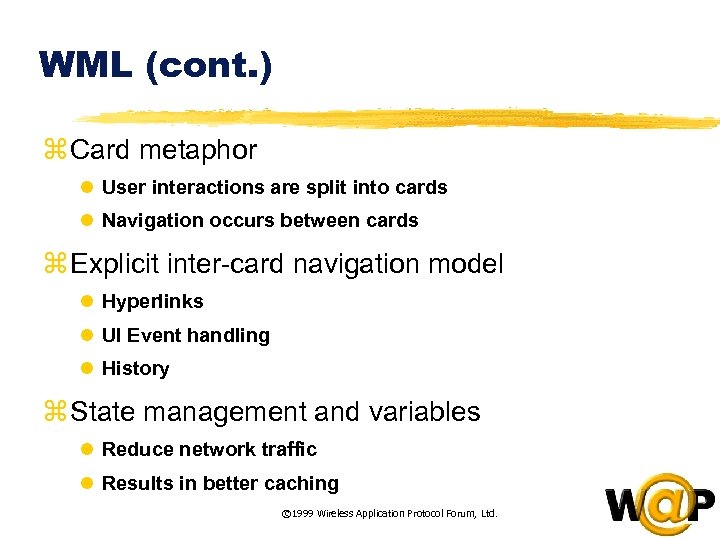
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WML (cont. ) z Card metaphor l User interactions are split into cards l" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-21.jpg" alt="WML (cont. ) z Card metaphor l User interactions are split into cards l" />
WML (cont. ) z Card metaphor l User interactions are split into cards l Navigation occurs between cards z Explicit inter-card navigation model l Hyperlinks l UI Event handling l History z State management and variables l Reduce network traffic l Results in better caching © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="All decks must contain. . . z Document prologue l XML & document type" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-22.jpg" alt="All decks must contain. . . z Document prologue l XML & document type" />
All decks must contain. . . z Document prologue l XML & document type declaration z <WML> element l Must contain one or more cards <? xml version="1. 0"? > <!DOCTYPE WML PUBLIC "-//WAPFORUM//DTD WML 1. 0//EN" "http: //www. wapforum. org/DTD/wml. xml"> <WML>. . . </WML> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
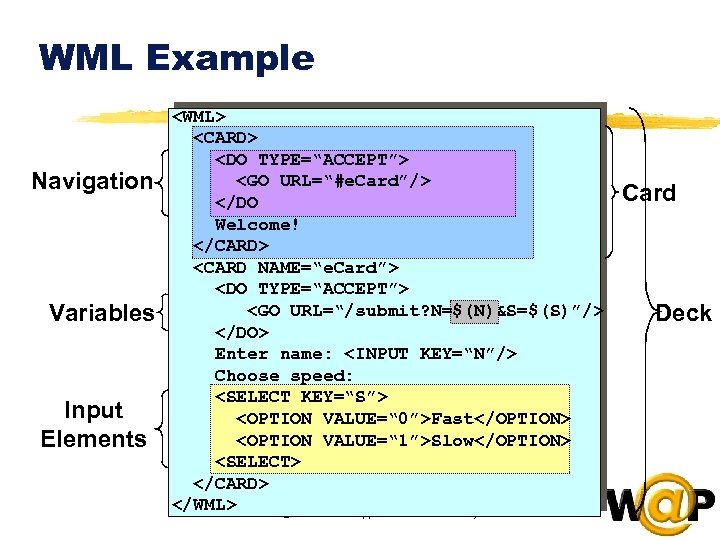
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WML Example Navigation Variables Input Elements <WML> <CARD> <DO TYPE=“ACCEPT”> <GO URL=“#e. Card”/> </DO" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-23.jpg" alt="WML Example Navigation Variables Input Elements <WML> <CARD> <DO TYPE=“ACCEPT”> <GO URL=“#e. Card”/> </DO" />
WML Example Navigation Variables Input Elements <WML> <CARD> <DO TYPE=“ACCEPT”> <GO URL=“#e. Card”/> </DO Welcome! </CARD> <CARD NAME=“e. Card”> <DO TYPE=“ACCEPT”> <GO URL=“/submit? N=$(N)&S=$(S)”/> </DO> Enter name: <INPUT KEY=“N”/> Choose speed: <SELECT KEY=“S”> <OPTION VALUE=“ 0”>Fast</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE=“ 1”>Slow</OPTION> <SELECT> </CARD> </WML> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. Card Deck </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="A Deck of Cards <WML> <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT" LABEL="Next"> <GO URL="#card 2"/> </DO> Acme" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-24.jpg" alt="A Deck of Cards <WML> <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT" LABEL="Next"> <GO URL="#card 2"/> </DO> Acme" />
A Deck of Cards <WML> <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT" LABEL="Next"> <GO URL="#card 2"/> </DO> Acme Inc. <BR/>Directory </CARD> <CARD NAME="card 2"> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT"> <GO URL="? send=$type"/> </DO> Services <SELECT KEY="type"> <OPTION VALUE="em">Email</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="ph">Phone</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="fx">Fax</OPTION> </SELECT> </CARD> </WML> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. Acme Inc. Directory _______ Next Services 1>Email 2 Phone ______ OK </p>
</div>
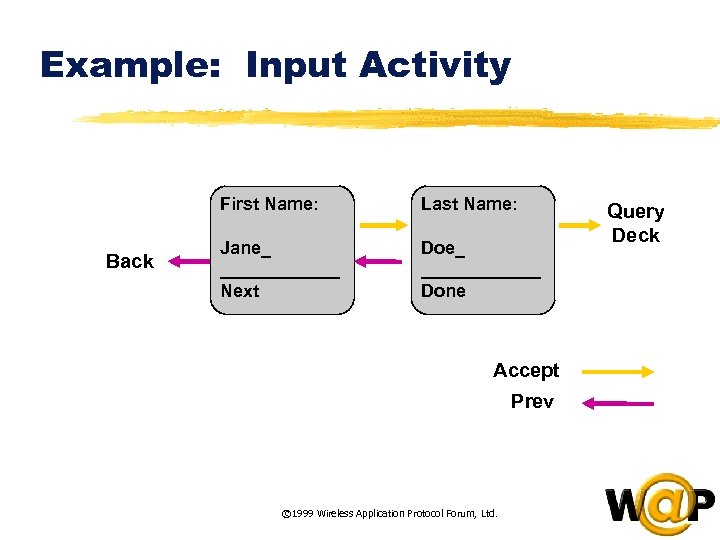
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Example: Input Activity First Name: Back Last Name: Jane_ ______ Next Doe_ ______ Done" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-25.jpg" alt="Example: Input Activity First Name: Back Last Name: Jane_ ______ Next Doe_ ______ Done" />
Example: Input Activity First Name: Back Last Name: Jane_ ______ Next Doe_ ______ Done Accept Prev © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. Query Deck </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Defining the Navigation Path <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT" LABEL="Next"> <GO URL="#card 2"/> </DO> First name:" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-26.jpg" alt="Defining the Navigation Path <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT" LABEL="Next"> <GO URL="#card 2"/> </DO> First name:" />
Defining the Navigation Path <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT" LABEL="Next"> <GO URL="#card 2"/> </DO> First name: <INPUT KEY="fname"/> </CARD> <CARD NAME="card 2"> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT" LABEL="Done"> <GO URL="? get=person" METHOD="POST" POSTDATA="first=$fname& last=$lname"/> </DO> Last name: <INPUT KEY="lname"/> </CARD> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
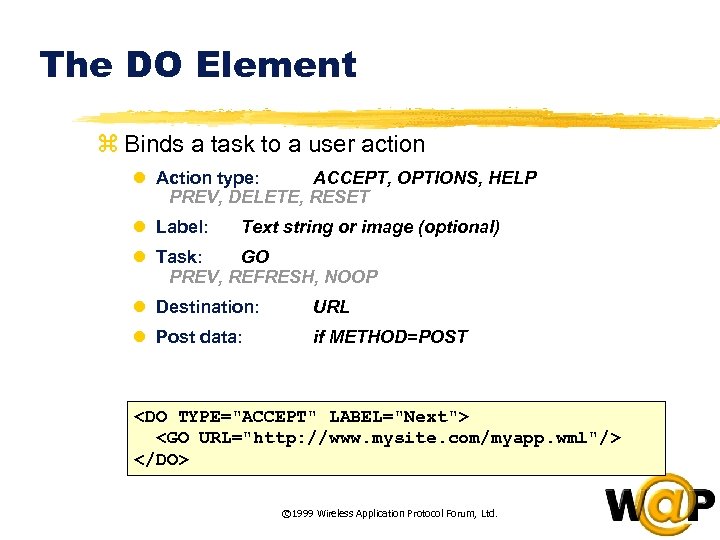
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="The DO Element z Binds a task to a user action l Action type:" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-27.jpg" alt="The DO Element z Binds a task to a user action l Action type:" />
The DO Element z Binds a task to a user action l Action type: ACCEPT, OPTIONS, HELP PREV, DELETE, RESET l Label: Text string or image (optional) l Task: GO PREV, REFRESH, NOOP l Destination: URL l Post data: if METHOD=POST <DO TYPE="ACCEPT" LABEL="Next"> <GO URL="http: //www. mysite. com/myapp. wml"/> </DO> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
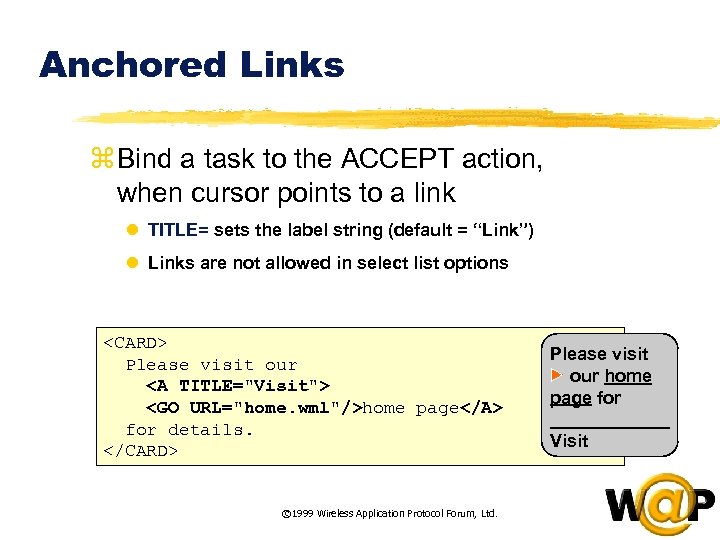
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Anchored Links z Bind a task to the ACCEPT action, when cursor points to" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-28.jpg" alt="Anchored Links z Bind a task to the ACCEPT action, when cursor points to" />
Anchored Links z Bind a task to the ACCEPT action, when cursor points to a link l TITLE= sets the label string (default = “Link”) l Links are not allowed in select list options <CARD> Please visit our <A TITLE="Visit"> <GO URL="home. wml"/>home page</A> for details. </CARD> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. Please visit our home page for ______ Visit </p>
</div>
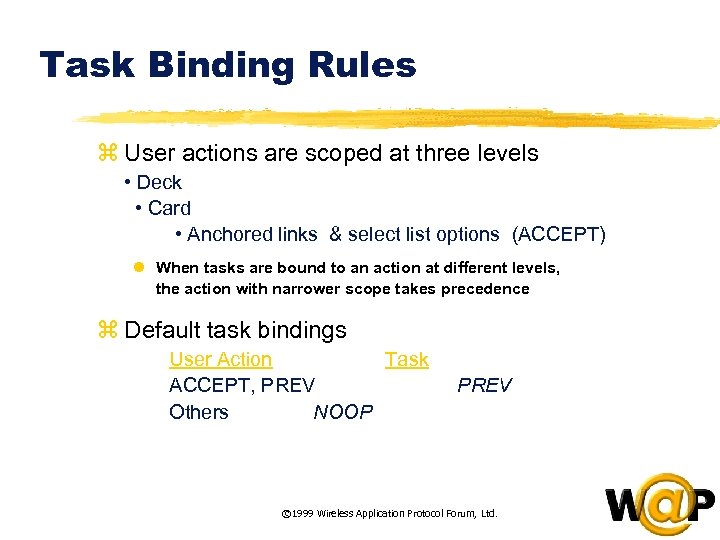
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Task Binding Rules z User actions are scoped at three levels • Deck •" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-29.jpg" alt="Task Binding Rules z User actions are scoped at three levels • Deck •" />
Task Binding Rules z User actions are scoped at three levels • Deck • Card • Anchored links & select list options (ACCEPT) l When tasks are bound to an action at different levels, the action with narrower scope takes precedence z Default task bindings User Action Task ACCEPT, PREV Others NOOP PREV © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
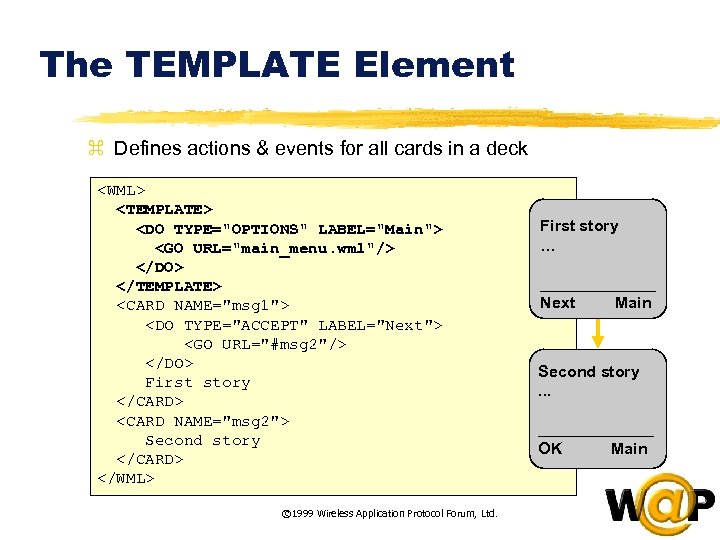
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="The TEMPLATE Element z Defines actions & events for all cards in a deck" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-30.jpg" alt="The TEMPLATE Element z Defines actions & events for all cards in a deck" />
The TEMPLATE Element z Defines actions & events for all cards in a deck <WML> <TEMPLATE> <DO TYPE="OPTIONS" LABEL="Main"> <GO URL="main_menu. wml"/> </DO> </TEMPLATE> <CARD NAME="msg 1"> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT" LABEL="Next"> <GO URL="#msg 2"/> </DO> First story </CARD> <CARD NAME="msg 2"> Second story </CARD> </WML> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. First story … _______ Next Main Second story. . . _______ OK Main </p>
</div>
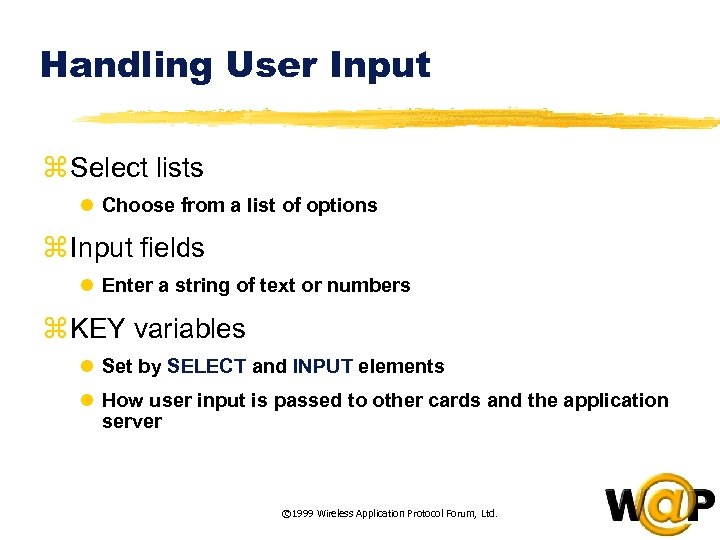
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Handling User Input z Select lists l Choose from a list of options z" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-31.jpg" alt="Handling User Input z Select lists l Choose from a list of options z" />
Handling User Input z Select lists l Choose from a list of options z Input fields l Enter a string of text or numbers z KEY variables l Set by SELECT and INPUT elements l How user input is passed to other cards and the application server © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
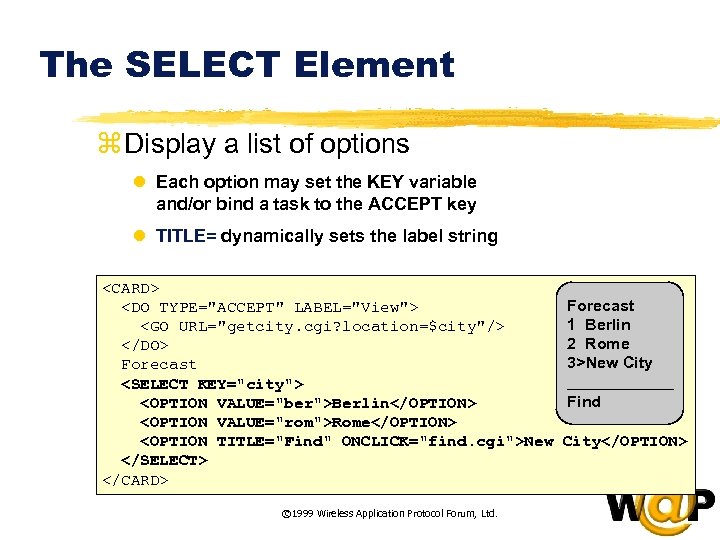
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="The SELECT Element z Display a list of options l Each option may set" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-32.jpg" alt="The SELECT Element z Display a list of options l Each option may set" />
The SELECT Element z Display a list of options l Each option may set the KEY variable and/or bind a task to the ACCEPT key l TITLE= dynamically sets the label string <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT" LABEL="View"> <GO URL="getcity. cgi? location=$city"/> </DO> Forecast <SELECT KEY="city"> <OPTION VALUE="ber">Berlin</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="rom">Rome</OPTION> <OPTION TITLE="Find" ONCLICK="find. cgi">New </SELECT> </CARD> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. Forecast 1 Berlin 2 Rome 3>New City ______ Find City</OPTION> </p>
</div>
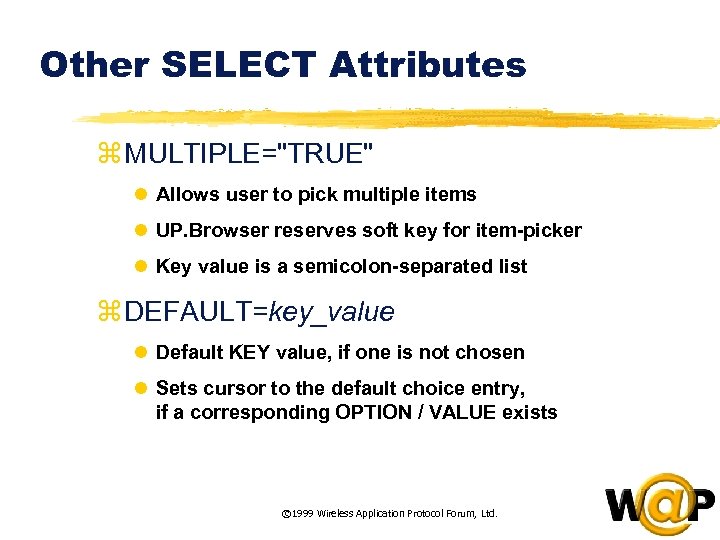
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Other SELECT Attributes z MULTIPLE="TRUE" l Allows user to pick multiple items l UP." src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-33.jpg" alt="Other SELECT Attributes z MULTIPLE="TRUE" l Allows user to pick multiple items l UP." />
Other SELECT Attributes z MULTIPLE="TRUE" l Allows user to pick multiple items l UP. Browser reserves soft key for item-picker l Key value is a semicolon-separated list z DEFAULT=key_value l Default KEY value, if one is not chosen l Sets cursor to the default choice entry, if a corresponding OPTION / VALUE exists © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="A Long Select List <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT"> <GO URL="get_addr. cgi? id=$recid"/> </DO> Addr [1." src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-34.jpg" alt="A Long Select List <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT"> <GO URL="get_addr. cgi? id=$recid"/> </DO> Addr [1." />
A Long Select List <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT"> <GO URL="get_addr. cgi? id=$recid"/> </DO> Addr [1. . 9] <SELECT KEY="recid" MULTIPLE="TRUE" DEFAULT="1; 3; 5"> <OPTION VALUE="1">Neil</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="2">Kurt</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="3">Jim</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="4">Natasha</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="5">Liz</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="6">Aneesh</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="7">Jennifer</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="8">Jesse</OPTION> <OPTION VALUE="9">Dawnell</OPTION> <OPTION ONCLICK="#card 2">More. . . </OPTION> </SELECT> </CARD> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
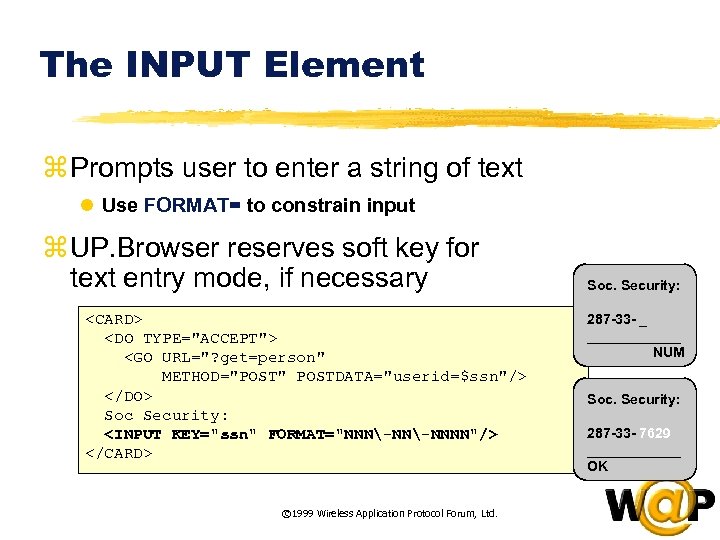
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="The INPUT Element z Prompts user to enter a string of text l Use" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-35.jpg" alt="The INPUT Element z Prompts user to enter a string of text l Use" />
The INPUT Element z Prompts user to enter a string of text l Use FORMAT= to constrain input z UP. Browser reserves soft key for text entry mode, if necessary <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT"> <GO URL="? get=person" METHOD="POST" POSTDATA="userid=$ssn"/> </DO> Soc Security: <INPUT KEY="ssn" FORMAT="NNN-NNNN"/> </CARD> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. Soc. Security: 287 -33 - _ ______ NUM Soc. Security: 287 -33 - 7629 ______ OK </p>
</div>
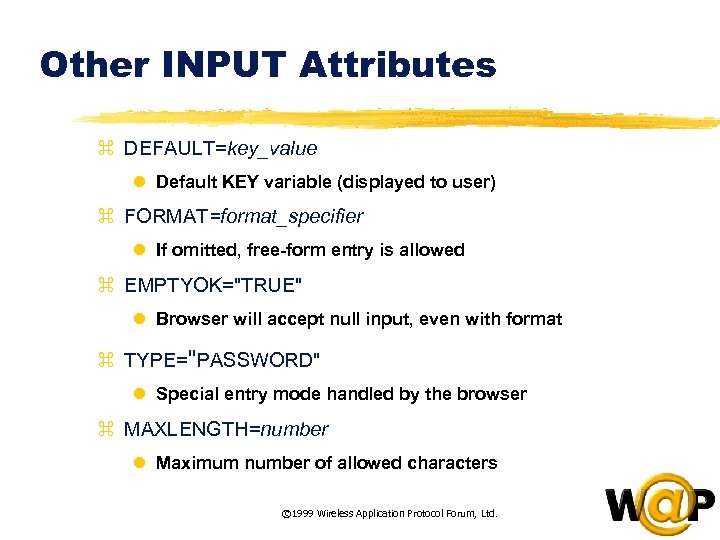
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Other INPUT Attributes z DEFAULT=key_value l Default KEY variable (displayed to user) z FORMAT=format_specifier" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-36.jpg" alt="Other INPUT Attributes z DEFAULT=key_value l Default KEY variable (displayed to user) z FORMAT=format_specifier" />
Other INPUT Attributes z DEFAULT=key_value l Default KEY variable (displayed to user) z FORMAT=format_specifier l If omitted, free-form entry is allowed z EMPTYOK="TRUE" l Browser will accept null input, even with format z TYPE="PASSWORD" l Special entry mode handled by the browser z MAXLENGTH=number l Maximum number of allowed characters © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
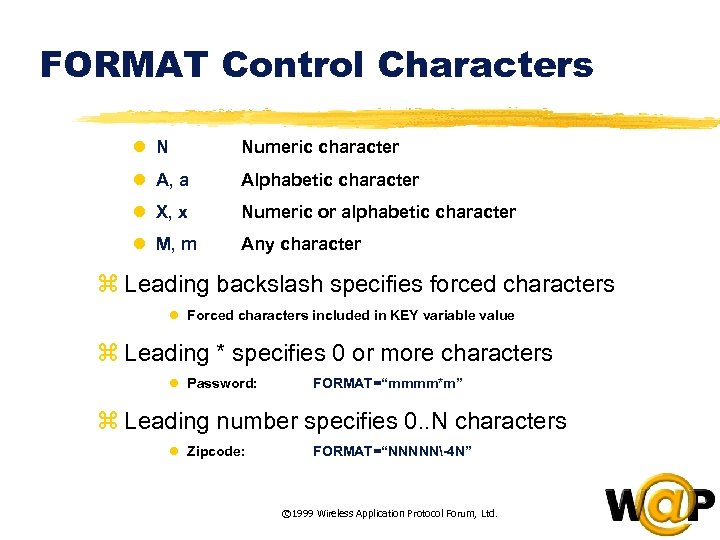
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="FORMAT Control Characters l N Numeric character l A, a Alphabetic character l X," src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-37.jpg" alt="FORMAT Control Characters l N Numeric character l A, a Alphabetic character l X," />
FORMAT Control Characters l N Numeric character l A, a Alphabetic character l X, x Numeric or alphabetic character l M, m Any character z Leading backslash specifies forced characters l Forced characters included in KEY variable value z Leading * specifies 0 or more characters l Password: FORMAT=“mmmm*m” z Leading number specifies 0. . N characters l Zipcode: FORMAT=“NNNNN-4 N” © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
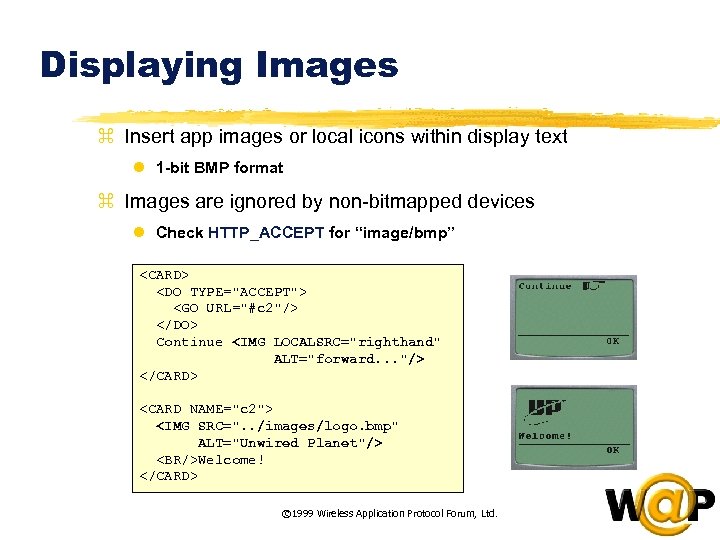
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Displaying Images z Insert app images or local icons within display text l 1" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-38.jpg" alt="Displaying Images z Insert app images or local icons within display text l 1" />
Displaying Images z Insert app images or local icons within display text l 1 -bit BMP format z Images are ignored by non-bitmapped devices l Check HTTP_ACCEPT for “image/bmp” <CARD> <DO TYPE="ACCEPT"> <GO URL="#c 2"/> </DO> Continue <IMG LOCALSRC="righthand" ALT="forward. . . "/> </CARD> <CARD NAME="c 2"> <IMG SRC=". . /images/logo. bmp" ALT="Unwired Planet"/> <BR/>Welcome! </CARD> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
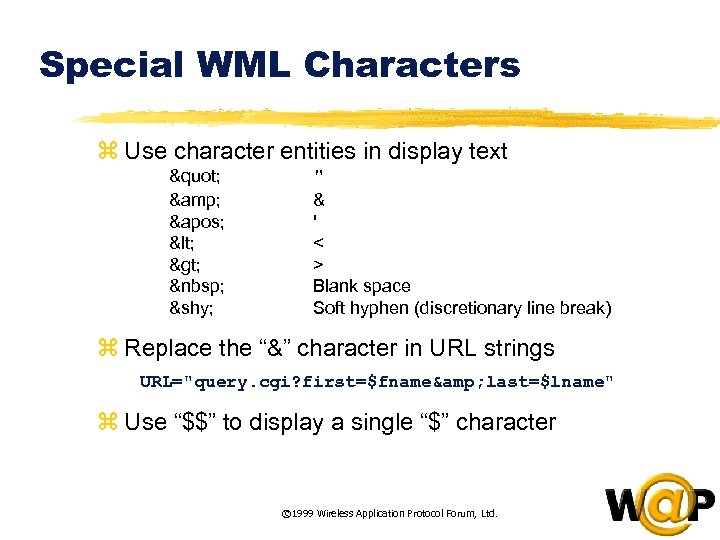
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Special WML Characters z Use character entities in display text " & ' <" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-39.jpg" alt="Special WML Characters z Use character entities in display text " & ' <" />
Special WML Characters z Use character entities in display text " & ' < > " & ' < > Blank space Soft hyphen (discretionary line break) z Replace the “&” character in URL strings URL="query. cgi? first=$fname& last=$lname" z Use “$$” to display a single “$” character © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Doing more with WML z Setting card styles to create forms z Using variables" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-40.jpg" alt="Doing more with WML z Setting card styles to create forms z Using variables" />
Doing more with WML z Setting card styles to create forms z Using variables to cache user data z Using card intrinsic events to trigger transparent tasks z Using timers z Securing WML decks z Bookmarking decks © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
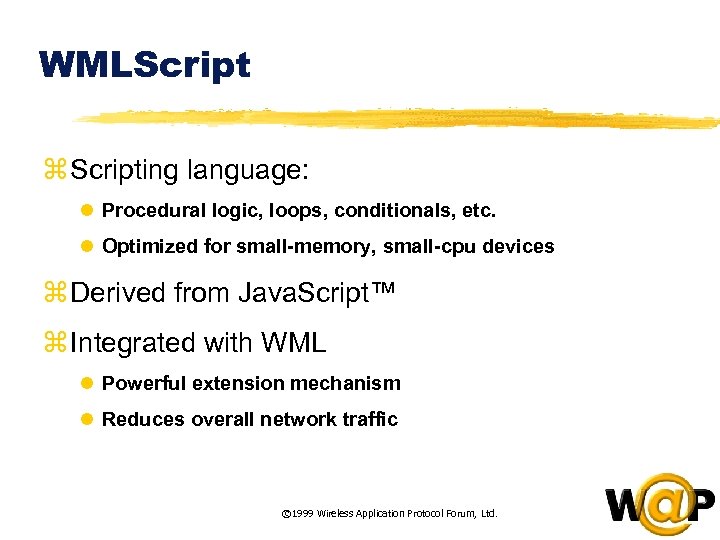
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WMLScript z Scripting language: l Procedural logic, loops, conditionals, etc. l Optimized for small-memory," src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-41.jpg" alt="WMLScript z Scripting language: l Procedural logic, loops, conditionals, etc. l Optimized for small-memory," />
WMLScript z Scripting language: l Procedural logic, loops, conditionals, etc. l Optimized for small-memory, small-cpu devices z Derived from Java. Script™ z Integrated with WML l Powerful extension mechanism l Reduces overall network traffic © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
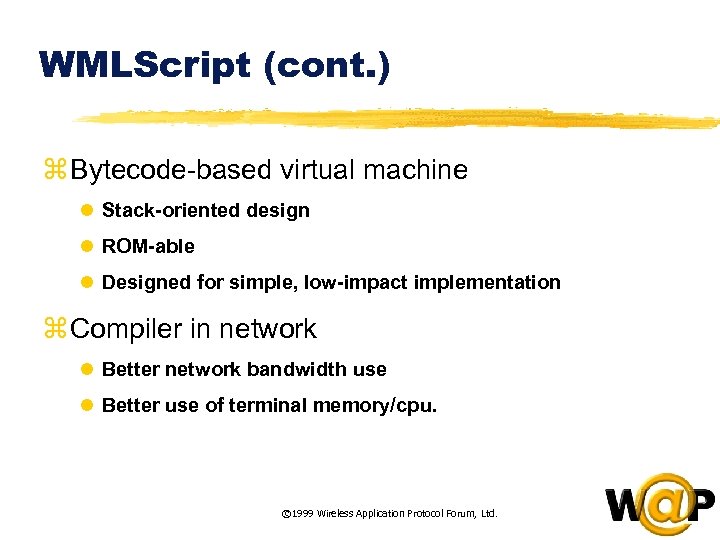
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WMLScript (cont. ) z Bytecode-based virtual machine l Stack-oriented design l ROM-able l Designed" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-42.jpg" alt="WMLScript (cont. ) z Bytecode-based virtual machine l Stack-oriented design l ROM-able l Designed" />
WMLScript (cont. ) z Bytecode-based virtual machine l Stack-oriented design l ROM-able l Designed for simple, low-impact implementation z Compiler in network l Better network bandwidth use l Better use of terminal memory/cpu. © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
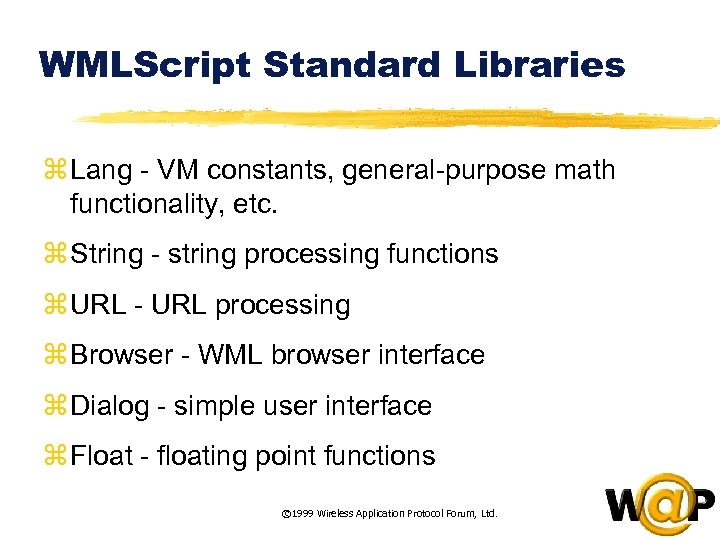
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WMLScript Standard Libraries z Lang - VM constants, general-purpose math functionality, etc. z String" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-43.jpg" alt="WMLScript Standard Libraries z Lang - VM constants, general-purpose math functionality, etc. z String" />
WMLScript Standard Libraries z Lang - VM constants, general-purpose math functionality, etc. z String - string processing functions z URL - URL processing z Browser - WML browser interface z Dialog - simple user interface z Float - floating point functions © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
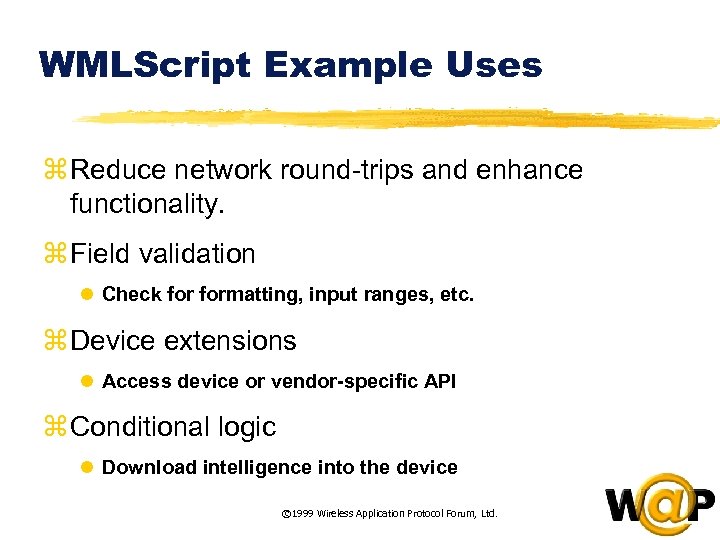
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WMLScript Example Uses z Reduce network round-trips and enhance functionality. z Field validation l" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-44.jpg" alt="WMLScript Example Uses z Reduce network round-trips and enhance functionality. z Field validation l" />
WMLScript Example Uses z Reduce network round-trips and enhance functionality. z Field validation l Check formatting, input ranges, etc. z Device extensions l Access device or vendor-specific API z Conditional logic l Download intelligence into the device © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
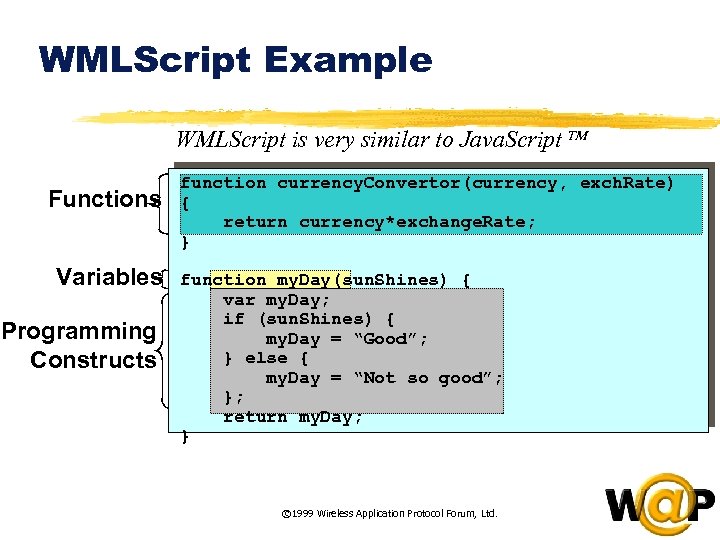
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WMLScript Example WMLScript is very similar to Java. Script Functions Variables Programming Constructs function" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-45.jpg" alt="WMLScript Example WMLScript is very similar to Java. Script Functions Variables Programming Constructs function" />
WMLScript Example WMLScript is very similar to Java. Script Functions Variables Programming Constructs function currency. Convertor(currency, exch. Rate) { return currency*exchange. Rate; } function my. Day(sun. Shines) { var my. Day; if (sun. Shines) { my. Day = “Good”; } else { my. Day = “Not so good”; }; return my. Day; } © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WTA z Tools for building telephony applications z Designed primarily for: l Network Operators" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-46.jpg" alt="WTA z Tools for building telephony applications z Designed primarily for: l Network Operators" />
WTA z Tools for building telephony applications z Designed primarily for: l Network Operators / Carriers l Equipment Vendors z Network security and reliability a major consideration © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
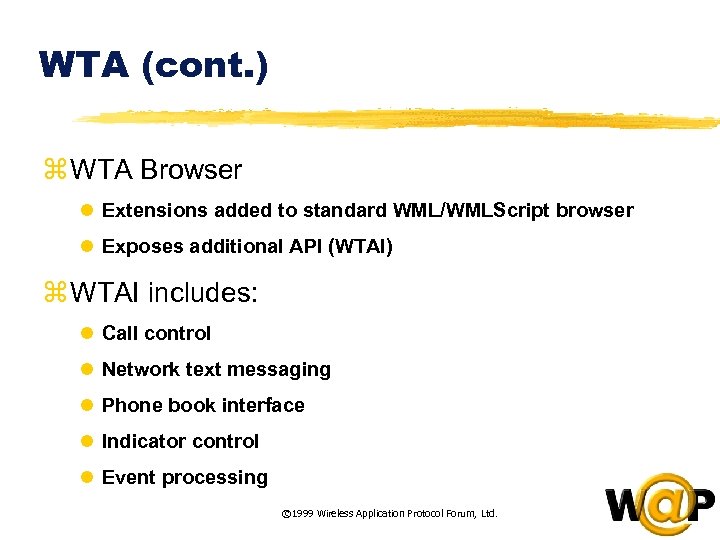
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WTA (cont. ) z WTA Browser l Extensions added to standard WML/WMLScript browser l" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-47.jpg" alt="WTA (cont. ) z WTA Browser l Extensions added to standard WML/WMLScript browser l" />
WTA (cont. ) z WTA Browser l Extensions added to standard WML/WMLScript browser l Exposes additional API (WTAI) z WTAI includes: l Call control l Network text messaging l Phone book interface l Indicator control l Event processing © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
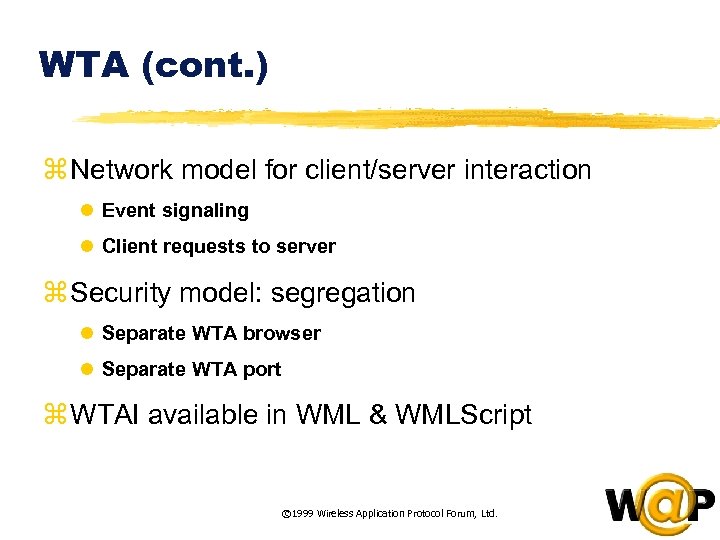
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WTA (cont. ) z Network model for client/server interaction l Event signaling l Client" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-48.jpg" alt="WTA (cont. ) z Network model for client/server interaction l Event signaling l Client" />
WTA (cont. ) z Network model for client/server interaction l Event signaling l Client requests to server z Security model: segregation l Separate WTA browser l Separate WTA port z WTAI available in WML & WMLScript © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
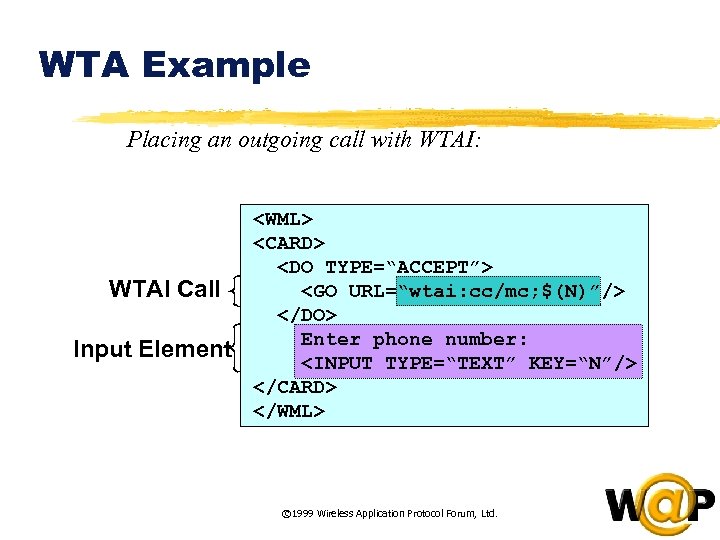
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WTA Example Placing an outgoing call with WTAI: WTAI Call Input Element <WML> <CARD>" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-49.jpg" alt="WTA Example Placing an outgoing call with WTAI: WTAI Call Input Element <WML> <CARD>" />
WTA Example Placing an outgoing call with WTAI: WTAI Call Input Element <WML> <CARD> <DO TYPE=“ACCEPT”> <GO URL=“wtai: cc/mc; $(N)”/> </DO> Enter phone number: <INPUT TYPE=“TEXT” KEY=“N”/> </CARD> </WML> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
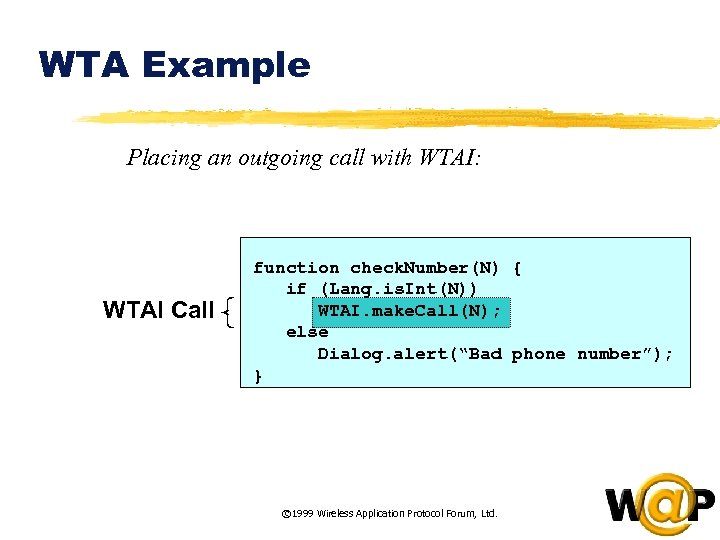
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WTA Example Placing an outgoing call with WTAI: WTAI Call function check. Number(N) {" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-50.jpg" alt="WTA Example Placing an outgoing call with WTAI: WTAI Call function check. Number(N) {" />
WTA Example Placing an outgoing call with WTAI: WTAI Call function check. Number(N) { if (Lang. is. Int(N)) WTAI. make. Call(N); else Dialog. alert(“Bad phone number”); } © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Content Formats z Common interchange formats z Promoting interoperability z Formats: l Business cards:" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-51.jpg" alt="Content Formats z Common interchange formats z Promoting interoperability z Formats: l Business cards:" />
Content Formats z Common interchange formats z Promoting interoperability z Formats: l Business cards: IMC v. Card standard l Calendar: IMC v. Calendar standard l Images: WBMP (Wireless Bit. Ma. P) l Compiled WML, WMLScript © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
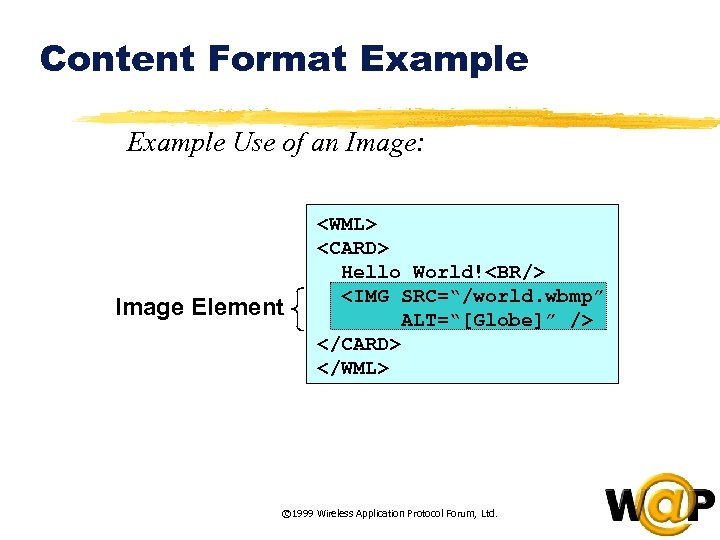
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Content Format Example Use of an Image: Image Element <WML> <CARD> Hello World!<BR/> <IMG" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-52.jpg" alt="Content Format Example Use of an Image: Image Element <WML> <CARD> Hello World!<BR/> <IMG" />
Content Format Example Use of an Image: Image Element <WML> <CARD> Hello World!<BR/> <IMG SRC=“/world. wbmp” ALT=“[Globe]” /> </CARD> </WML> © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Push z Push is under development z Network-push of content l Alerts or service" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-53.jpg" alt="Push z Push is under development z Network-push of content l Alerts or service" />
Push z Push is under development z Network-push of content l Alerts or service indications l Pre-caching of data z Goals: l Extensibility and simplicity l Build upon WAP 1. 0 l End-to-end solution l Security l User friendly © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="User Agent Profiles (UAProf) z UAProf is under development z Goal: content personalization, based" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-54.jpg" alt="User Agent Profiles (UAProf) z UAProf is under development z Goal: content personalization, based" />
User Agent Profiles (UAProf) z UAProf is under development z Goal: content personalization, based upon: l Device characteristics, user preferences l Other profile information z Working with W 3 C on CC/PP l RDF-based content format l Describes “capability and profile” info z Efficient transport over wireless links, caching, etc. © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WAE Technical Collaboration z W 3 C l White paper published l Technical collaboration" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-55.jpg" alt="WAE Technical Collaboration z W 3 C l White paper published l Technical collaboration" />
WAE Technical Collaboration z W 3 C l White paper published l Technical collaboration l CC/PP l HTML-NG l HTTP-NG l Etc. z ETSI/MEx. E z Others coming soon © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Summary: WAE Status z First generation released l Implementations are in progress l Specifications" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-56.jpg" alt="Summary: WAE Status z First generation released l Implementations are in progress l Specifications" />
Summary: WAE Status z First generation released l Implementations are in progress l Specifications include: l WAE, WMLScript l WBMP, WTAI, etc. z Second generation in development l Focusing on: l Push, Interoperability, UAProf l Telephony, Internationalization, etc. © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Wireless Transport Protocols Wireless Session Protocol Wireless Transaction Protocol Wireless Datagram Protocol " src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-57.jpg" alt="Wireless Transport Protocols Wireless Session Protocol Wireless Transaction Protocol Wireless Datagram Protocol " />
Wireless Transport Protocols Wireless Session Protocol Wireless Transaction Protocol Wireless Datagram Protocol </p>
</div>
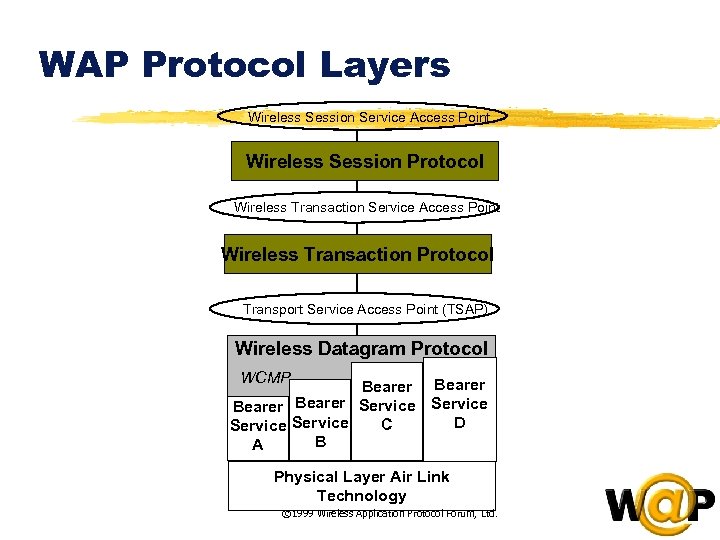
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WAP Protocol Layers Wireless Session Service Access Point Wireless Session Protocol Wireless Transaction Service" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-58.jpg" alt="WAP Protocol Layers Wireless Session Service Access Point Wireless Session Protocol Wireless Transaction Service" />
WAP Protocol Layers Wireless Session Service Access Point Wireless Session Protocol Wireless Transaction Service Access Point Wireless Transaction Protocol Transport Service Access Point (TSAP) Wireless Datagram Protocol WCMP Bearer Service D C Service B A Physical Layer Air Link Technology © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WAP Transport Services z WSP is the Session Layer Protocol z WTP is the" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-59.jpg" alt="WAP Transport Services z WSP is the Session Layer Protocol z WTP is the" />
WAP Transport Services z WSP is the Session Layer Protocol z WTP is the Transaction-Oriented protocol z WDP is the Datagram protocol © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
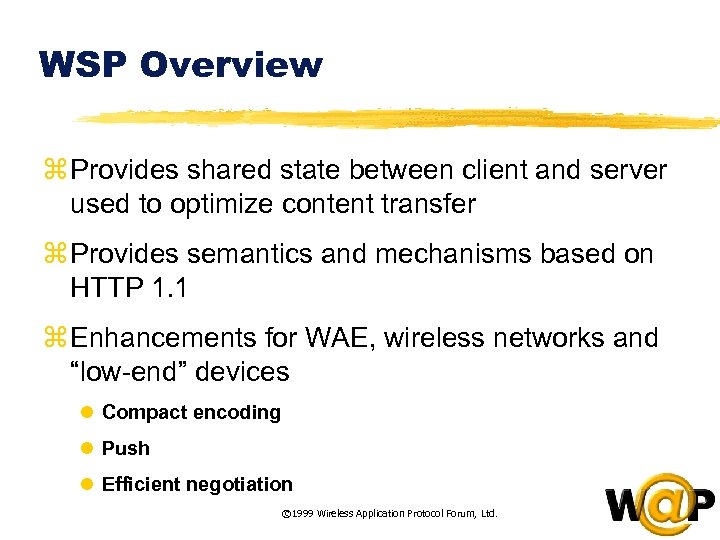
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WSP Overview z Provides shared state between client and server used to optimize content" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-60.jpg" alt="WSP Overview z Provides shared state between client and server used to optimize content" />
WSP Overview z Provides shared state between client and server used to optimize content transfer z Provides semantics and mechanisms based on HTTP 1. 1 z Enhancements for WAE, wireless networks and “low-end” devices l Compact encoding l Push l Efficient negotiation © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Capabilities z Capabilities are defined for: l Message Size, client and server l Protocol" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-61.jpg" alt="Capabilities z Capabilities are defined for: l Message Size, client and server l Protocol" />
Capabilities z Capabilities are defined for: l Message Size, client and server l Protocol Options: Confirmed Push Facility, Session Suspend Facility, Acknowledgement headers l Maximum Outstanding Requests l Extended Methods l Header Code Pages © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Suspend and Resume z Server knows when client can accept a push z Multi-bearer" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-62.jpg" alt="Suspend and Resume z Server knows when client can accept a push z Multi-bearer" />
Suspend and Resume z Server knows when client can accept a push z Multi-bearer devices z Dynamic addressing z Allows the release of underlying bearer resources © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
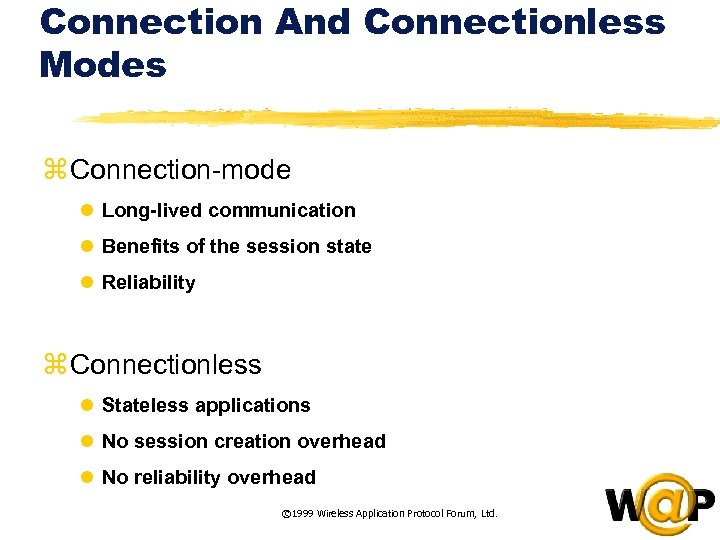
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Connection And Connectionless Modes z Connection-mode l Long-lived communication l Benefits of the session" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-63.jpg" alt="Connection And Connectionless Modes z Connection-mode l Long-lived communication l Benefits of the session" />
Connection And Connectionless Modes z Connection-mode l Long-lived communication l Benefits of the session state l Reliability z Connectionless l Stateless applications l No session creation overhead l No reliability overhead © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
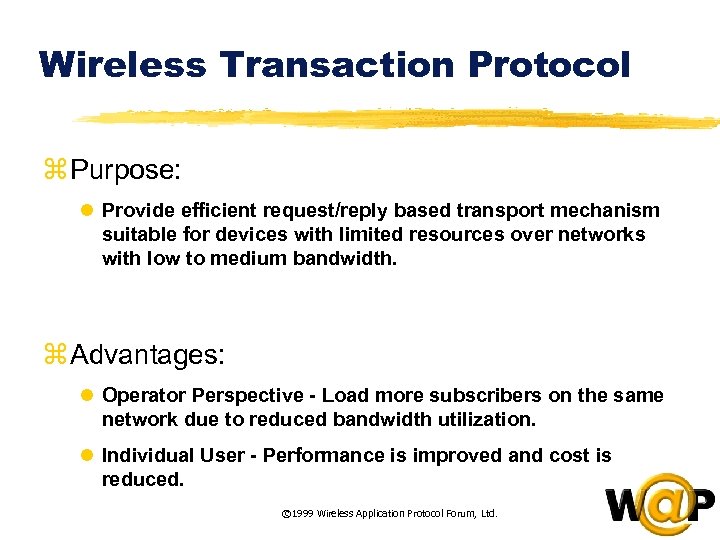
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Wireless Transaction Protocol z Purpose: l Provide efficient request/reply based transport mechanism suitable for" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-64.jpg" alt="Wireless Transaction Protocol z Purpose: l Provide efficient request/reply based transport mechanism suitable for" />
Wireless Transaction Protocol z Purpose: l Provide efficient request/reply based transport mechanism suitable for devices with limited resources over networks with low to medium bandwidth. z Advantages: l Operator Perspective - Load more subscribers on the same network due to reduced bandwidth utilization. l Individual User - Performance is improved and cost is reduced. © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
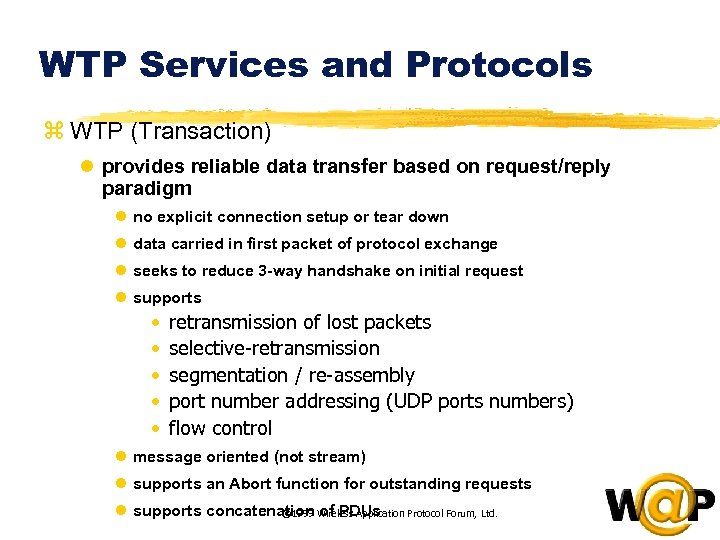
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WTP Services and Protocols z WTP (Transaction) l provides reliable data transfer based on" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-65.jpg" alt="WTP Services and Protocols z WTP (Transaction) l provides reliable data transfer based on" />
WTP Services and Protocols z WTP (Transaction) l provides reliable data transfer based on request/reply paradigm l no explicit connection setup or tear down l data carried in first packet of protocol exchange l seeks to reduce 3 -way handshake on initial request l supports • • • retransmission of lost packets selective-retransmission segmentation / re-assembly port number addressing (UDP ports numbers) flow control l message oriented (not stream) l supports an Abort function for outstanding requests l supports concatenation Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. © 1999 of PDUs </p>
</div>
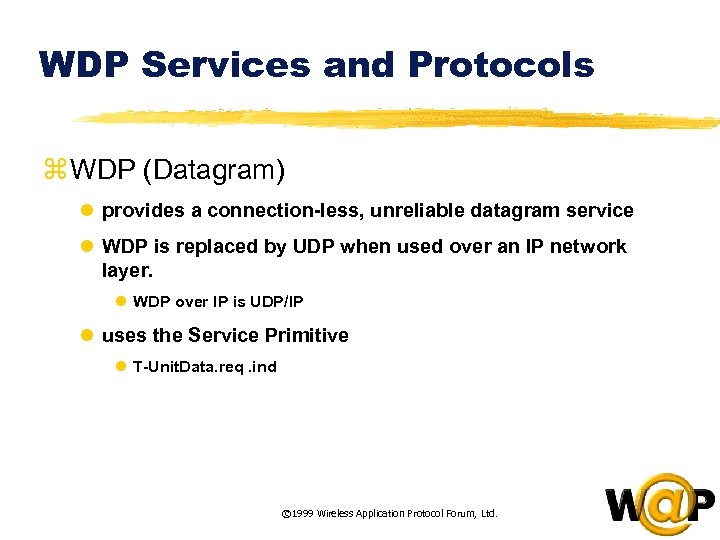
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WDP Services and Protocols z WDP (Datagram) l provides a connection-less, unreliable datagram service" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-66.jpg" alt="WDP Services and Protocols z WDP (Datagram) l provides a connection-less, unreliable datagram service" />
WDP Services and Protocols z WDP (Datagram) l provides a connection-less, unreliable datagram service l WDP is replaced by UDP when used over an IP network layer. l WDP over IP is UDP/IP l uses the Service Primitive l T-Unit. Data. req. ind © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
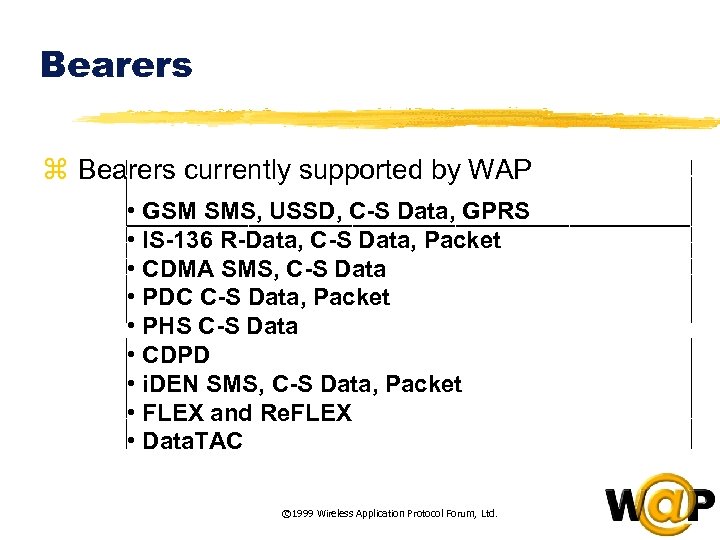
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Bearers z Bearers currently supported by WAP • GSM SMS, USSD, C-S Data, GPRS" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-67.jpg" alt="Bearers z Bearers currently supported by WAP • GSM SMS, USSD, C-S Data, GPRS" />
Bearers z Bearers currently supported by WAP • GSM SMS, USSD, C-S Data, GPRS • IS-136 R-Data, C-S Data, Packet • CDMA SMS, C-S Data • PDC C-S Data, Packet • PHS C-S Data • CDPD • i. DEN SMS, C-S Data, Packet • FLEX and Re. FLEX • Data. TAC © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
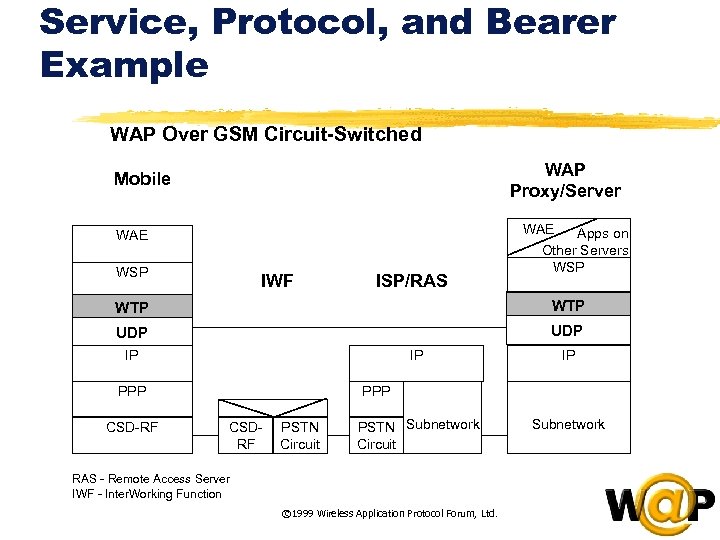
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Service, Protocol, and Bearer Example WAP Over GSM Circuit-Switched WAP Proxy/Server Mobile WAE WSP" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-68.jpg" alt="Service, Protocol, and Bearer Example WAP Over GSM Circuit-Switched WAP Proxy/Server Mobile WAE WSP" />
Service, Protocol, and Bearer Example WAP Over GSM Circuit-Switched WAP Proxy/Server Mobile WAE WSP IWF ISP/RAS WAE Apps on Other Servers WSP WTP UDP IP IP PPP CSD-RF IP PSTN Subnetwork Circuit Subnetwork PPP CSDRF PSTN Circuit RAS - Remote Access Server IWF - Inter. Working Function © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
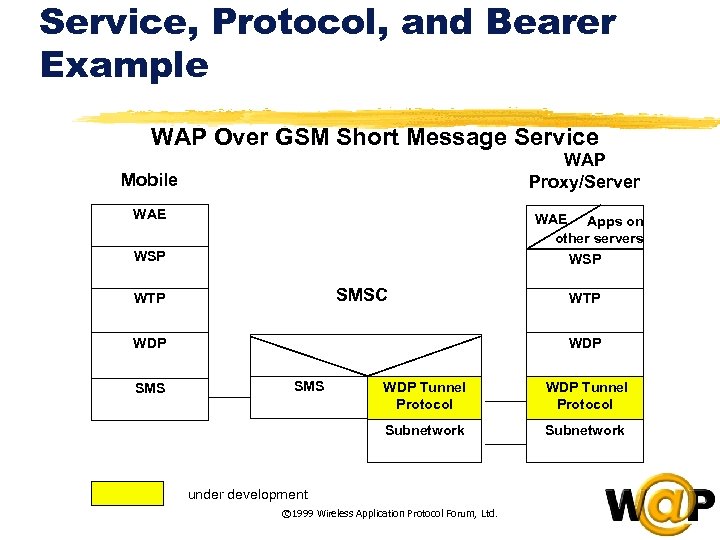
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Service, Protocol, and Bearer Example WAP Over GSM Short Message Service WAP Proxy/Server Mobile" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-69.jpg" alt="Service, Protocol, and Bearer Example WAP Over GSM Short Message Service WAP Proxy/Server Mobile" />
Service, Protocol, and Bearer Example WAP Over GSM Short Message Service WAP Proxy/Server Mobile WAE Apps on other servers WSP SMSC WTP WDP SMS WDP Tunnel Protocol Subnetwork under development © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WAP Security WTLS Services & Characteristics " src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-70.jpg" alt="WAP Security WTLS Services & Characteristics " />
WAP Security WTLS Services & Characteristics </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WSG Work Area z Provide mechanisms for secure transfer of content, to allow for" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-71.jpg" alt="WSG Work Area z Provide mechanisms for secure transfer of content, to allow for" />
WSG Work Area z Provide mechanisms for secure transfer of content, to allow for applications needing privacy, identification, verified message integrity and non-repudiation z Transport level security is WTLS, based on SSL and TLS from the Internet community z Working on various mechanisms for improved end-to-end security and application-level security © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WTLS Services and Characteristics z Specifies a framework for secure connections, using protocol elements" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-72.jpg" alt="WTLS Services and Characteristics z Specifies a framework for secure connections, using protocol elements" />
WTLS Services and Characteristics z Specifies a framework for secure connections, using protocol elements from common Internet security protocols like SSL and TLS. z Provides security facilities for encryption, strong authentication, integrity, and key management z Compliance with regulations on the use of cryptographic algorithms and key lengths in different countries z Provides end-to-end security between protocol end points © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
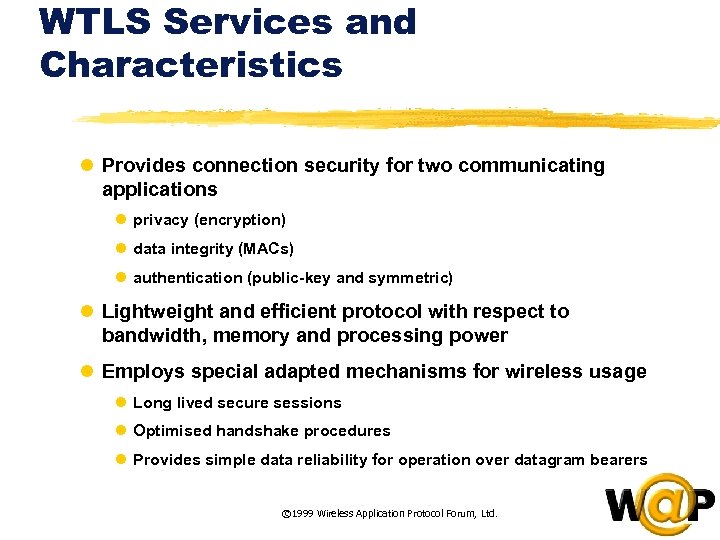
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WTLS Services and Characteristics l Provides connection security for two communicating applications l privacy" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-73.jpg" alt="WTLS Services and Characteristics l Provides connection security for two communicating applications l privacy" />
WTLS Services and Characteristics l Provides connection security for two communicating applications l privacy (encryption) l data integrity (MACs) l authentication (public-key and symmetric) l Lightweight and efficient protocol with respect to bandwidth, memory and processing power l Employs special adapted mechanisms for wireless usage l Long lived secure sessions l Optimised handshake procedures l Provides simple data reliability for operation over datagram bearers © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Goals and Requirements for WTLS z Interoperable protocols z Scalability to allow large scale" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-74.jpg" alt="Goals and Requirements for WTLS z Interoperable protocols z Scalability to allow large scale" />
Goals and Requirements for WTLS z Interoperable protocols z Scalability to allow large scale application deployment z First class security level z Support for public-key certificates z Support for WAP transport protocols © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
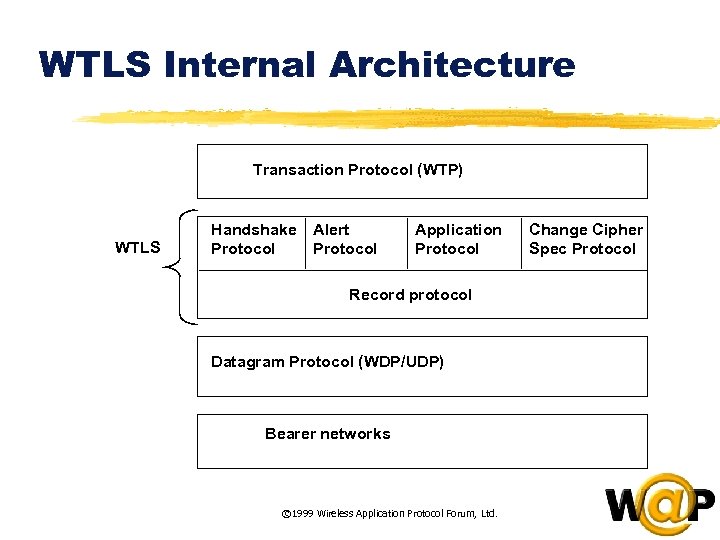
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WTLS Internal Architecture Transaction Protocol (WTP) WTLS Handshake Protocol Alert Protocol Application Protocol Record" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-75.jpg" alt="WTLS Internal Architecture Transaction Protocol (WTP) WTLS Handshake Protocol Alert Protocol Application Protocol Record" />
WTLS Internal Architecture Transaction Protocol (WTP) WTLS Handshake Protocol Alert Protocol Application Protocol Record Protocol protocol Record Datagram Protocol (WDP/UDP) Bearer networks © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. Change Cipher Spec Protocol </p>
</div>
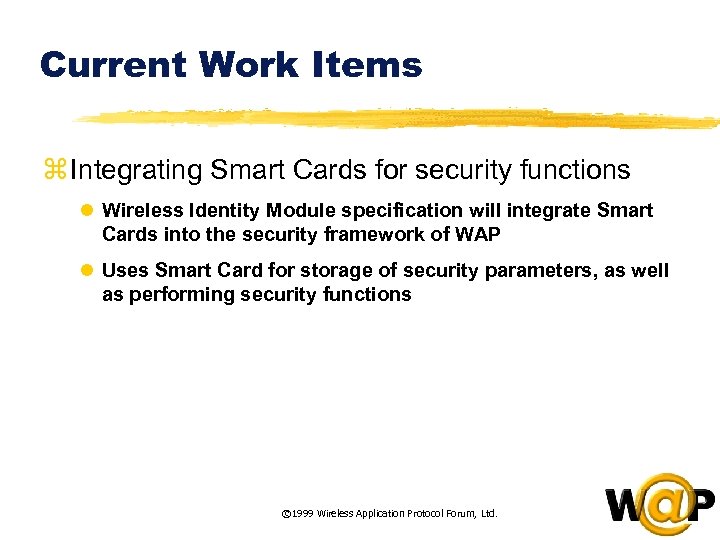
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Current Work Items z Integrating Smart Cards for security functions l Wireless Identity Module" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-76.jpg" alt="Current Work Items z Integrating Smart Cards for security functions l Wireless Identity Module" />
Current Work Items z Integrating Smart Cards for security functions l Wireless Identity Module specification will integrate Smart Cards into the security framework of WAP l Uses Smart Card for storage of security parameters, as well as performing security functions © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
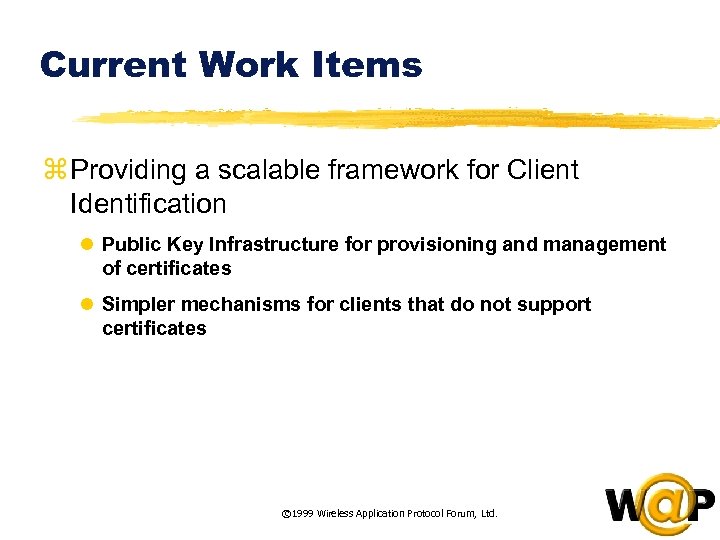
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Current Work Items z Providing a scalable framework for Client Identification l Public Key" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-77.jpg" alt="Current Work Items z Providing a scalable framework for Client Identification l Public Key" />
Current Work Items z Providing a scalable framework for Client Identification l Public Key Infrastructure for provisioning and management of certificates l Simpler mechanisms for clients that do not support certificates © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Wireless Interoperability Group " src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-78.jpg" alt="Wireless Interoperability Group " />
Wireless Interoperability Group </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WIG Mission statement “To ensure that WAP products are conformant to WAP specs and" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-79.jpg" alt="WIG Mission statement “To ensure that WAP products are conformant to WAP specs and" />
WIG Mission statement “To ensure that WAP products are conformant to WAP specs and interwork with each other. ” © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
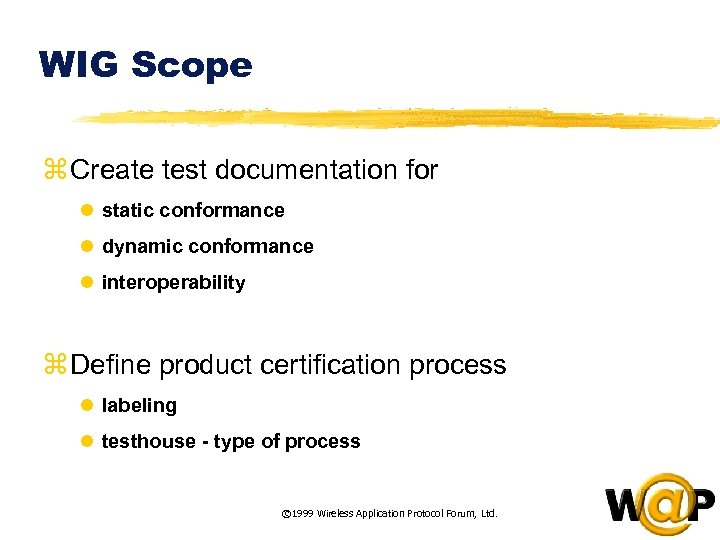
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WIG Scope z Create test documentation for l static conformance l dynamic conformance l" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-80.jpg" alt="WIG Scope z Create test documentation for l static conformance l dynamic conformance l" />
WIG Scope z Create test documentation for l static conformance l dynamic conformance l interoperability z Define product certification process l labeling l testhouse - type of process © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
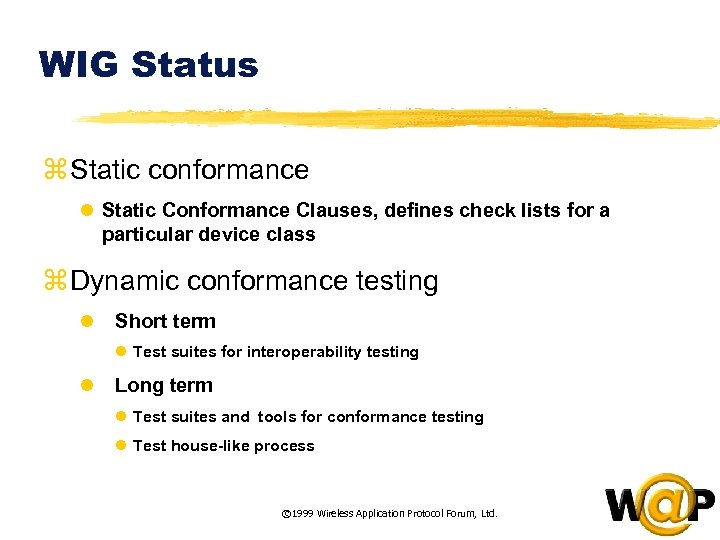
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WIG Status z Static conformance l Static Conformance Clauses, defines check lists for a" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-81.jpg" alt="WIG Status z Static conformance l Static Conformance Clauses, defines check lists for a" />
WIG Status z Static conformance l Static Conformance Clauses, defines check lists for a particular device class z Dynamic conformance testing l Short term l Test suites for interoperability testing l Long term l Test suites and tools for conformance testing l Test house-like process © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="SMS Expert Group WDP Tunnel Specification " src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-82.jpg" alt="SMS Expert Group WDP Tunnel Specification " />
SMS Expert Group WDP Tunnel Specification </p>
</div>
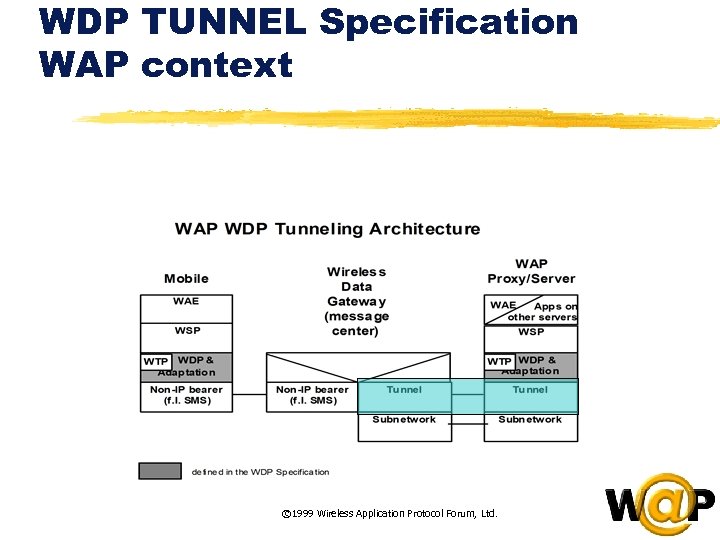
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WDP TUNNEL Specification WAP context © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. " src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-83.jpg" alt="WDP TUNNEL Specification WAP context © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. " />
WDP TUNNEL Specification WAP context © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
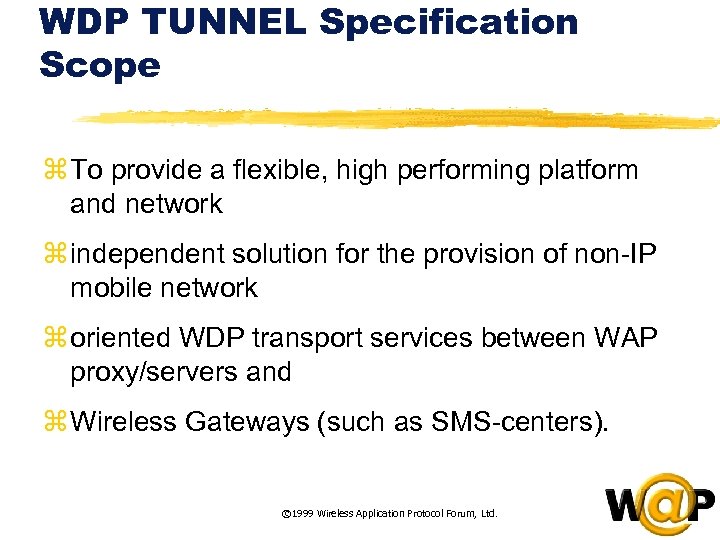
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WDP TUNNEL Specification Scope z To provide a flexible, high performing platform and network" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-84.jpg" alt="WDP TUNNEL Specification Scope z To provide a flexible, high performing platform and network" />
WDP TUNNEL Specification Scope z To provide a flexible, high performing platform and network z independent solution for the provision of non-IP mobile network z oriented WDP transport services between WAP proxy/servers and z Wireless Gateways (such as SMS-centers). © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. </p>
</div>
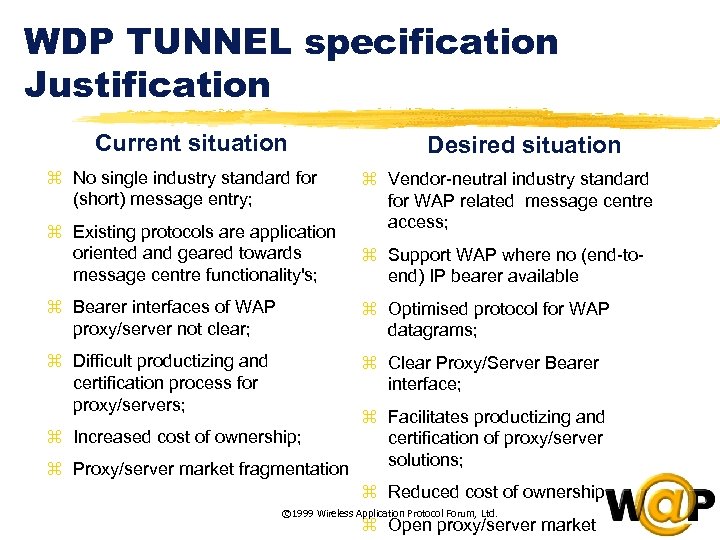
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="WDP TUNNEL specification Justification Current situation z No single industry standard for (short) message" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-85.jpg" alt="WDP TUNNEL specification Justification Current situation z No single industry standard for (short) message" />
WDP TUNNEL specification Justification Current situation z No single industry standard for (short) message entry; z Existing protocols are application oriented and geared towards message centre functionality's; Desired situation z Vendor-neutral industry standard for WAP related message centre access; z Support WAP where no (end-toend) IP bearer available z Bearer interfaces of WAP proxy/server not clear; z Optimised protocol for WAP datagrams; z Difficult productizing and certification process for proxy/servers; z Clear Proxy/Server Bearer interface; z Increased cost of ownership; z Proxy/server market fragmentation z Facilitates productizing and certification of proxy/server solutions; z Reduced cost of ownership © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. z Open proxy/server market </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Thank You ! " src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-86.jpg" alt="Thank You ! " />
Thank You ! </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="Discussion and Q&A Cindy Dahm cindy@corp. phone. com Natasha Flaherty natasha@corp. phone. com " src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-87.jpg" alt="Discussion and Q&A Cindy Dahm cindy@corp. phone. com Natasha Flaherty natasha@corp. phone. com " />
Discussion and Q&A Cindy Dahm cindy@corp. phone. com Natasha Flaherty natasha@corp. phone. com </p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="" src="https://present5.com/presentation/ac353db174736646d3bb8608d0dd3cb9/image-88.jpg" alt="" />
</p>
</div>
<div style="width: auto;" class="description columns twelve"><p><img class="imgdescription" title="" src="" alt="" />
</p>
</div>
</div>
<div id="inputform">
<script>$("#inputform").load("https://present5.com/wp-content/plugins/report-content/inc/report-form-aj.php");
</script>
</div>
</p>
<!--end entry-content-->
</div>
</article><!-- .post -->
</section><!-- #content -->
<div class="three columns">
<div class="widget-entry">
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- #content-wrapper -->
<footer id="footer" style="padding: 5px 0 5px;">
<div class="container">
<div class="columns twelve">
<!--noindex-->
<!--LiveInternet counter--><script type="text/javascript"><!--
document.write("<img src='//counter.yadro.ru/hit?t26.10;r"+
escape(document.referrer)+((typeof(screen)=="undefined")?"":
";s"+screen.width+"*"+screen.height+"*"+(screen.colorDepth?
screen.colorDepth:screen.pixelDepth))+";u"+escape(document.URL)+
";"+Math.random()+
"' alt='' title='"+" ' "+
"border='0' width='1' height='1'><\/a>")
//--></script><!--/LiveInternet-->
<a href="https://slidetodoc.com/" alt="Наш международный проект SlideToDoc.com!" target="_blank"><img src="https://present5.com/SlideToDoc.png"></a> <script>
$(window).load(function() {
var owl = document.getElementsByClassName('owl-carousel owl-theme owl-loaded owl-drag')[0];
document.getElementById("owlheader").insertBefore(owl, null);
$('#owlheader').css('display', 'inline-block');
});
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var yaParams = {'typepage': '1000_top_300k',
'author': '1000_top_300k'
};
</script>
<!-- Yandex.Metrika counter --> <script type="text/javascript" > (function(m,e,t,r,i,k,a){m[i]=m[i]||function(){(m[i].a=m[i].a||[]).push(arguments)}; m[i].l=1*new Date(); for (var j = 0; j < document.scripts.length; j++) {if (document.scripts[j].src === r) { return; }} k=e.createElement(t),a=e.getElementsByTagName(t)[0],k.async=1,k.src=r,a.parentNode.insertBefore(k,a)}) (window, document, "script", "https://mc.yandex.ru/metrika/tag.js", "ym"); ym(32395810, "init", { clickmap:true, trackLinks:true, accurateTrackBounce:true, webvisor:true }); </script> <noscript><div><img src="https://mc.yandex.ru/watch/32395810" style="position:absolute; left:-9999px;" alt="" /></div></noscript> <!-- /Yandex.Metrika counter -->
<!--/noindex-->
<nav id="top-nav">
<ul id="menu-top" class="top-menu clearfix">
</ul> </nav>
</div>
</div><!--.container-->
</footer>
<script type='text/javascript'>
/* <![CDATA[ */
var wpcf7 = {"apiSettings":{"root":"https:\/\/present5.com\/wp-json\/contact-form-7\/v1","namespace":"contact-form-7\/v1"}};
/* ]]> */
</script>
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://present5.com/wp-content/plugins/contact-form-7/includes/js/scripts.js?ver=5.1.4'></script>
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://present5.com/wp-content/themes/sampression-lite/lib/js/jquery.shuffle.js?ver=4.9.26'></script>
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://present5.com/wp-content/themes/sampression-lite/lib/js/scripts.js?ver=1.13'></script>
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://present5.com/wp-content/themes/sampression-lite/lib/js/shuffle.js?ver=4.9.26'></script>
<!--[if lt IE 9]>
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://present5.com/wp-content/themes/sampression-lite/lib/js/selectivizr.js?ver=1.0.2'></script>
<![endif]-->
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://present5.com/wp-content/themes/sampression-lite/lib/js/notify.js?ver=1770497866'></script>
<script type='text/javascript'>
/* <![CDATA[ */
var my_ajax_object = {"ajax_url":"https:\/\/present5.com\/wp-admin\/admin-ajax.php","nonce":"33a1179831"};
/* ]]> */
</script>
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://present5.com/wp-content/themes/sampression-lite/lib/js/filer.js?ver=1770497866'></script>
</body>
</html> |
 WAP Forum Wireless Application Protocol Technical Overview Natasha Flaherty Senior Marketing Manager Phone. com
WAP Forum Wireless Application Protocol Technical Overview Natasha Flaherty Senior Marketing Manager Phone. com  Agenda z WAP Architecture z Wireless Application Environment z Protocol Layers z Interoperability z Security © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd.
Agenda z WAP Architecture z Wireless Application Environment z Protocol Layers z Interoperability z Security © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd.  WAP Architecture Introduction and Overview
WAP Architecture Introduction and Overview 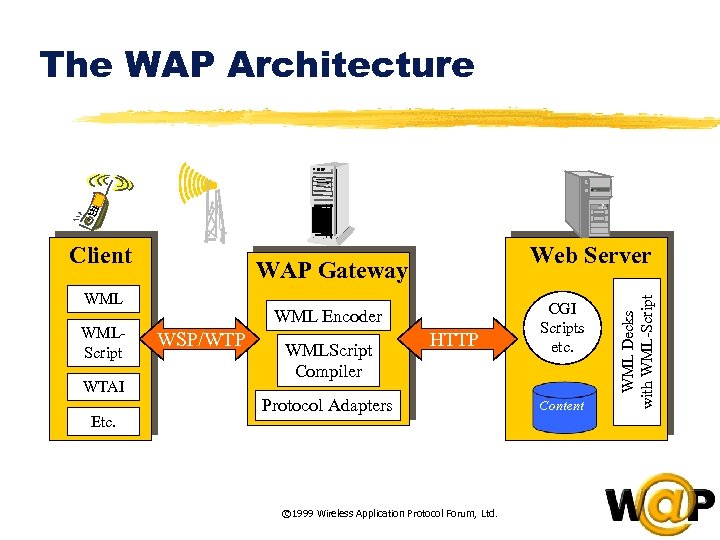 The WAP Architecture WAP Gateway WMLScript WTAI Etc. Web Server WML Encoder WSP/WTP WMLScript Compiler HTTP Protocol Adapters © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. CGI Scripts etc. Content WML Decks with WML-Script Client
The WAP Architecture WAP Gateway WMLScript WTAI Etc. Web Server WML Encoder WSP/WTP WMLScript Compiler HTTP Protocol Adapters © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. CGI Scripts etc. Content WML Decks with WML-Script Client 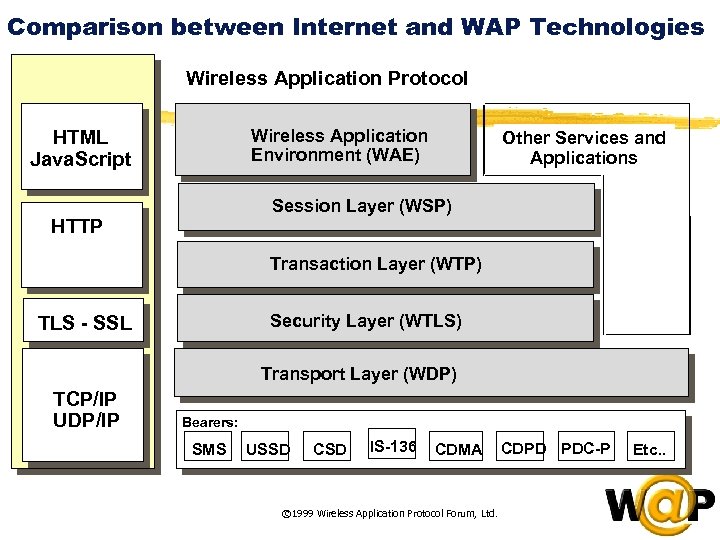 Comparison between Internet and WAP Technologies Wireless Application Protocol Internet HTML Java. Script Wireless Application Environment (WAE) Other Services and Applications Session Layer (WSP) HTTP Transaction Layer (WTP) Security Layer (WTLS) TLS - SSL Transport Layer (WDP) TCP/IP UDP/IP Bearers: SMS USSD CSD IS-136 CDMA © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. CDPD PDC-P Etc. .
Comparison between Internet and WAP Technologies Wireless Application Protocol Internet HTML Java. Script Wireless Application Environment (WAE) Other Services and Applications Session Layer (WSP) HTTP Transaction Layer (WTP) Security Layer (WTLS) TLS - SSL Transport Layer (WDP) TCP/IP UDP/IP Bearers: SMS USSD CSD IS-136 CDMA © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. CDPD PDC-P Etc. . 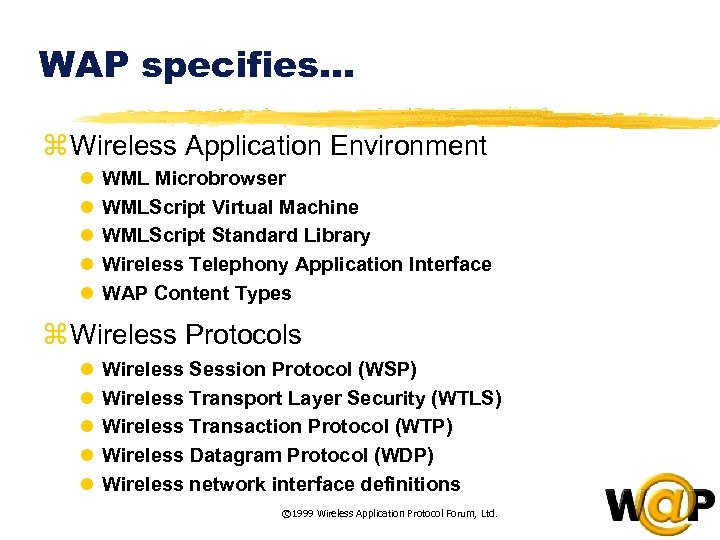 WAP specifies… z Wireless Application Environment l l l WML Microbrowser WMLScript Virtual Machine WMLScript Standard Library Wireless Telephony Application Interface WAP Content Types z Wireless Protocols l l l Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS) Wireless Transaction Protocol (WTP) Wireless Datagram Protocol (WDP) Wireless network interface definitions © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd.
WAP specifies… z Wireless Application Environment l l l WML Microbrowser WMLScript Virtual Machine WMLScript Standard Library Wireless Telephony Application Interface WAP Content Types z Wireless Protocols l l l Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS) Wireless Transaction Protocol (WTP) Wireless Datagram Protocol (WDP) Wireless network interface definitions © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd.  WHY WAP ? z WAP utilizes standard Internet markup language technology (XML) z Optimizing the content and airlink protocols z The WML UI components map well onto existing mobile phone user interfaces l no re-education of the end-users l leveraging market penetration of mobile devices z WAP utilizes plain Web HTTP 1. 1 servers l leveraging existing development methodologies l CGI, ASP, NSAPI, JAVA, Servlets, etc. © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd.
WHY WAP ? z WAP utilizes standard Internet markup language technology (XML) z Optimizing the content and airlink protocols z The WML UI components map well onto existing mobile phone user interfaces l no re-education of the end-users l leveraging market penetration of mobile devices z WAP utilizes plain Web HTTP 1. 1 servers l leveraging existing development methodologies l CGI, ASP, NSAPI, JAVA, Servlets, etc. © 1999 Wireless Application Protocol Forum, Ltd. 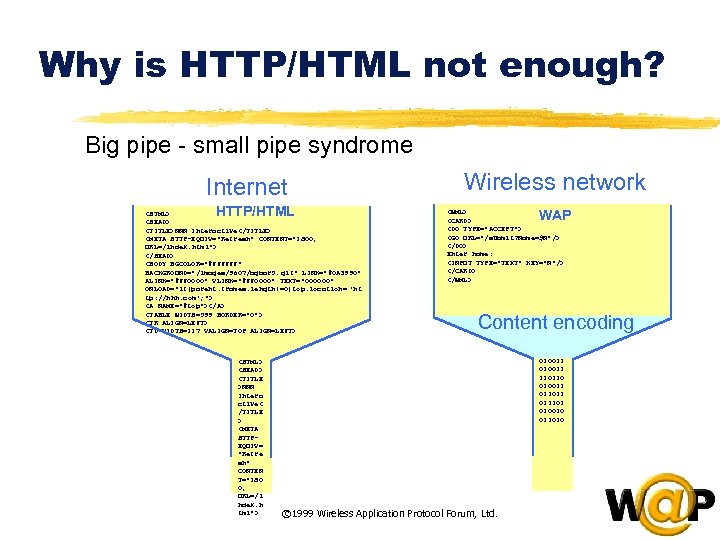 Why is HTTP/HTML not enough? Big pipe - small pipe syndrome Internet HTTP/HTML
Why is HTTP/HTML not enough? Big pipe - small pipe syndrome Internet HTTP/HTML