Wage Determination Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by


Wage Determination McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.

Labor, Wages, and Earnings Wages Price paid for labor Direct pay plus fringe benefits Wage rate Nominal wage Real wage General level of wages LO1 13-2

Role of Productivity Labor demand depends on productivity U.S. labor is highly productive Plentiful capital Access to abundant natural resources Advanced technology Labor quality Other factors LO1 13-3
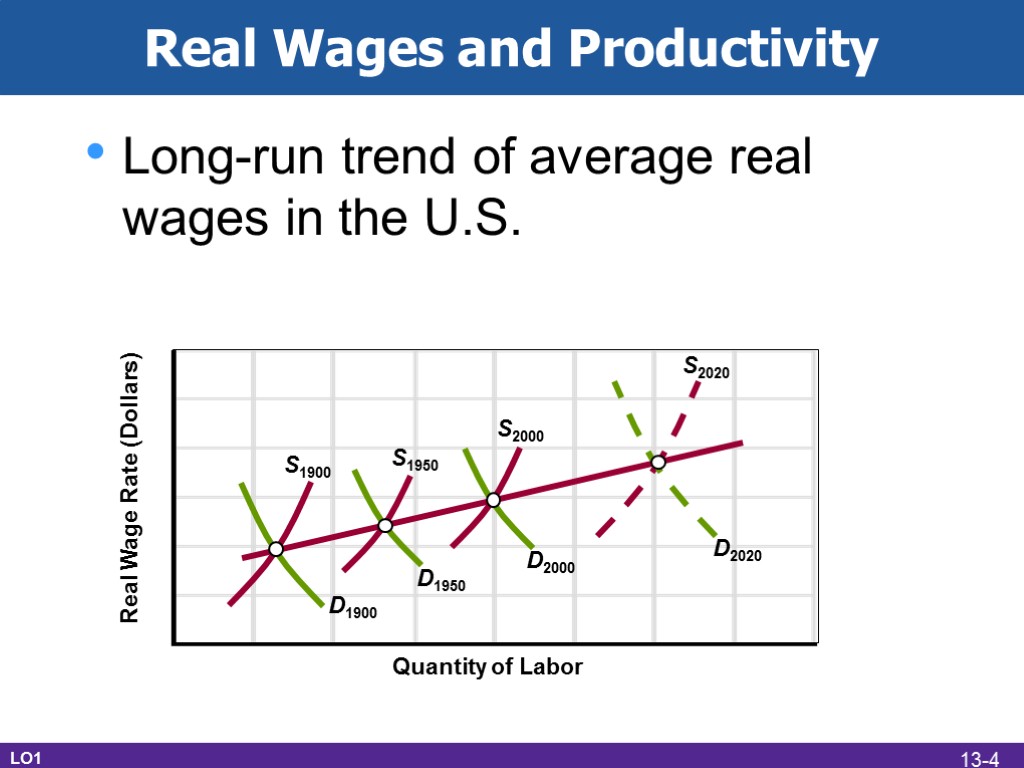
Real Wages and Productivity Long-run trend of average real wages in the U.S. Real Wage Rate (Dollars) Quantity of Labor D1900 S1900 D1950 D2000 D2020 S1950 S2000 S2020 LO1 13-4
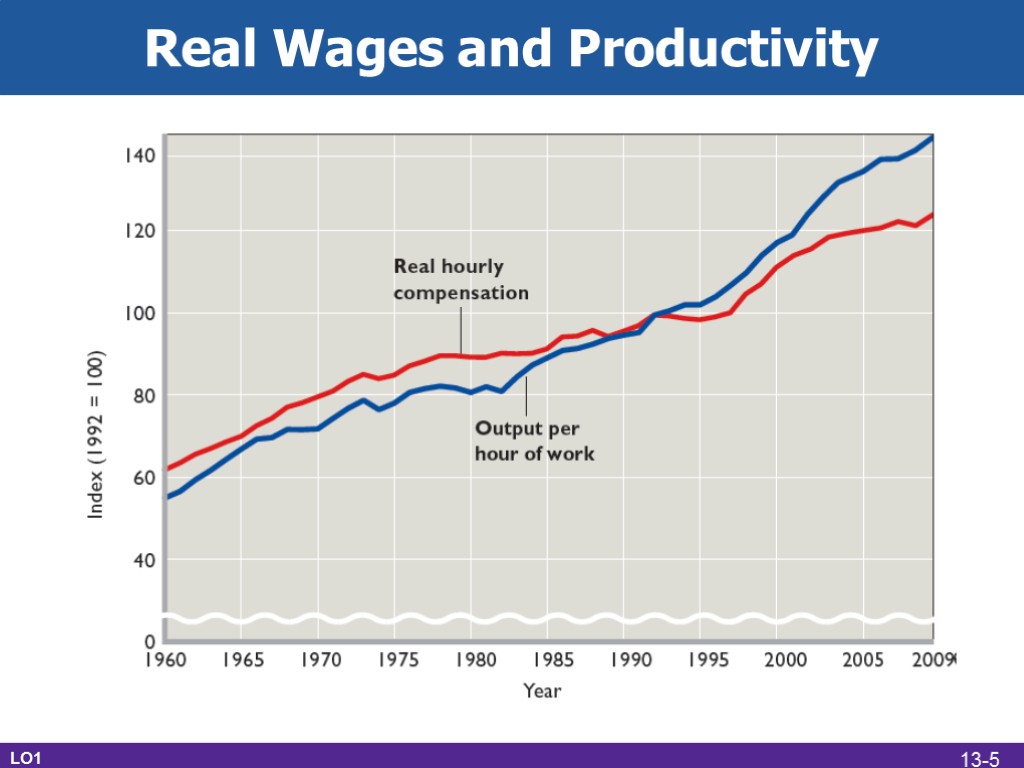
Real Wages and Productivity LO1 13-5
Competitive Labor Market Market demand for labor Sum of firm demand Example: carpenters Market supply for labor Upward sloping Competition among industries Labor market equilibrium MRP = MRC rule LO2 13-6
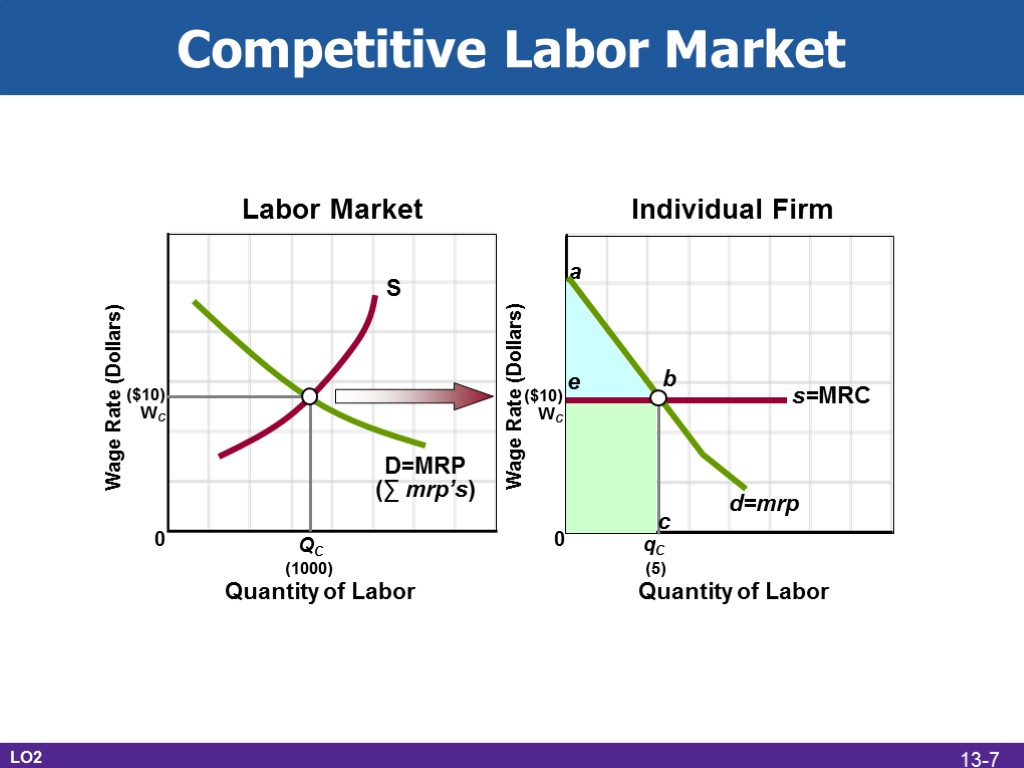
($10) WC ($10) WC QC (1000) 0 0 d=mrp qC (5) s=MRC Competitive Labor Market LO2 D=MRP (∑ mrp’s) S e b a c 13-7
Monopsony Model Employer has buying power Characteristics Single buyer Labor immobile Firm “wage maker” Firm labor supply is upward sloping MRC higher than wage rate Equilibrium LO3 13-8
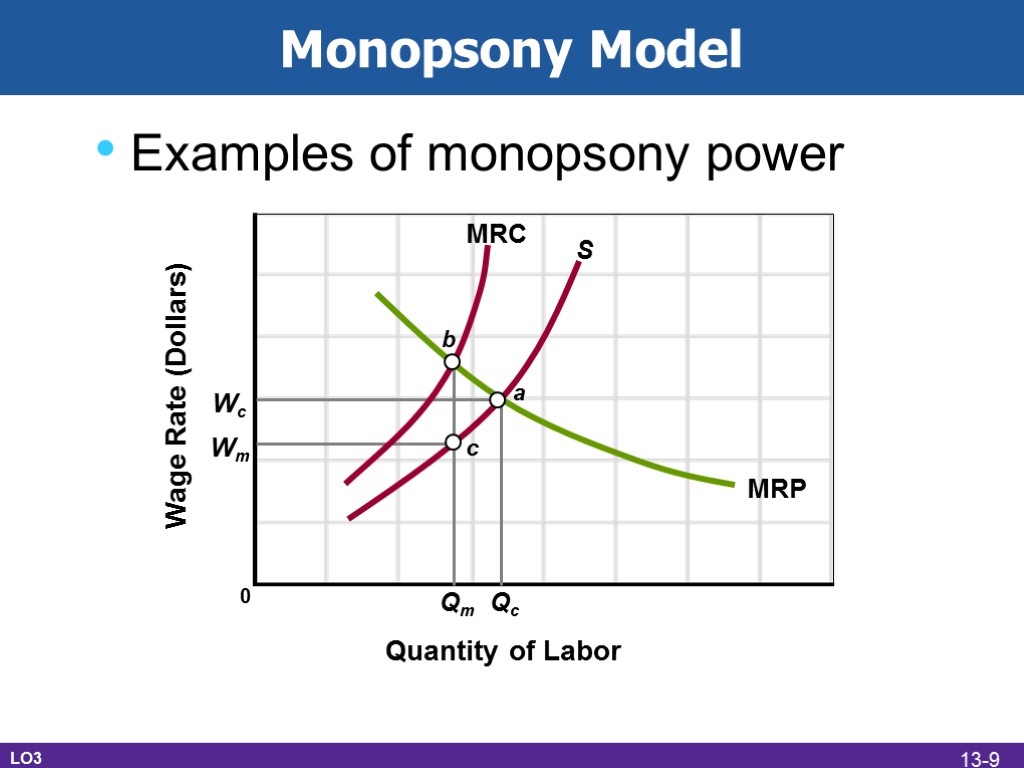
Examples of monopsony power Monopsony Model Wage Rate (Dollars) Quantity of Labor 0 S MRP MRC c b a Wc Wm Qm Qc LO3 13-9

Monopsony Power Maximize profit by hiring smaller number of workers Examples of monopsony power Nurses Professional Athletes Teachers Three union models LO3 13-10
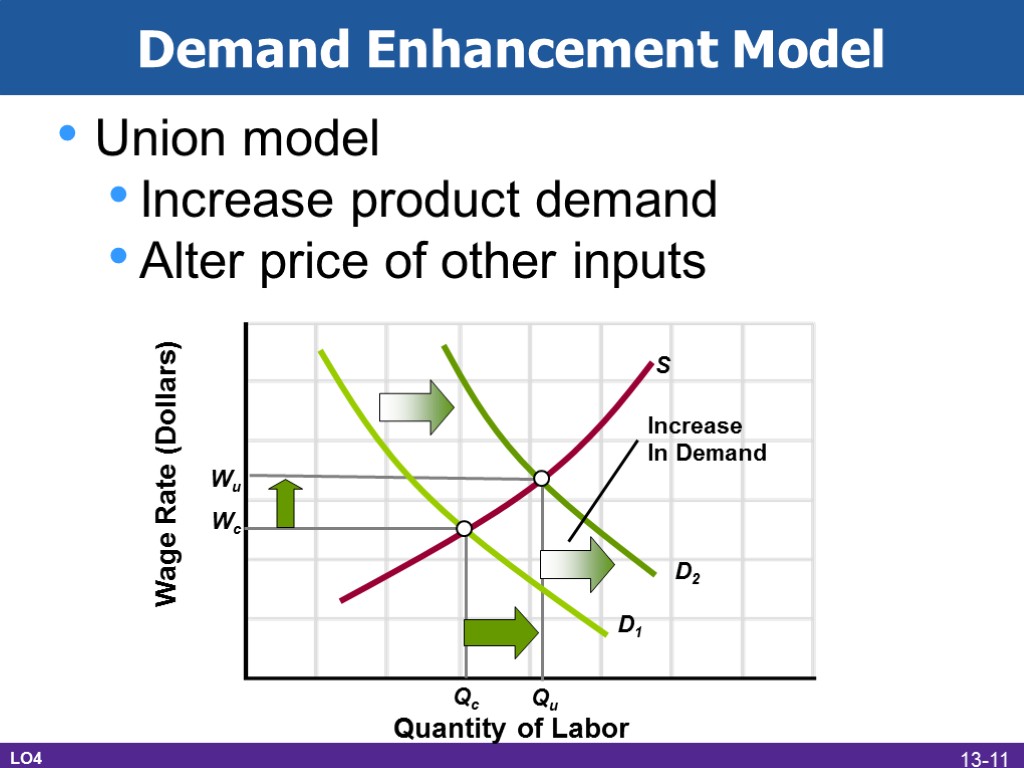
Demand Enhancement Model Union model Increase product demand Alter price of other inputs Wage Rate (Dollars) Quantity of Labor Wu Qc Qu Wc D1 D2 S Increase In Demand LO4 13-11
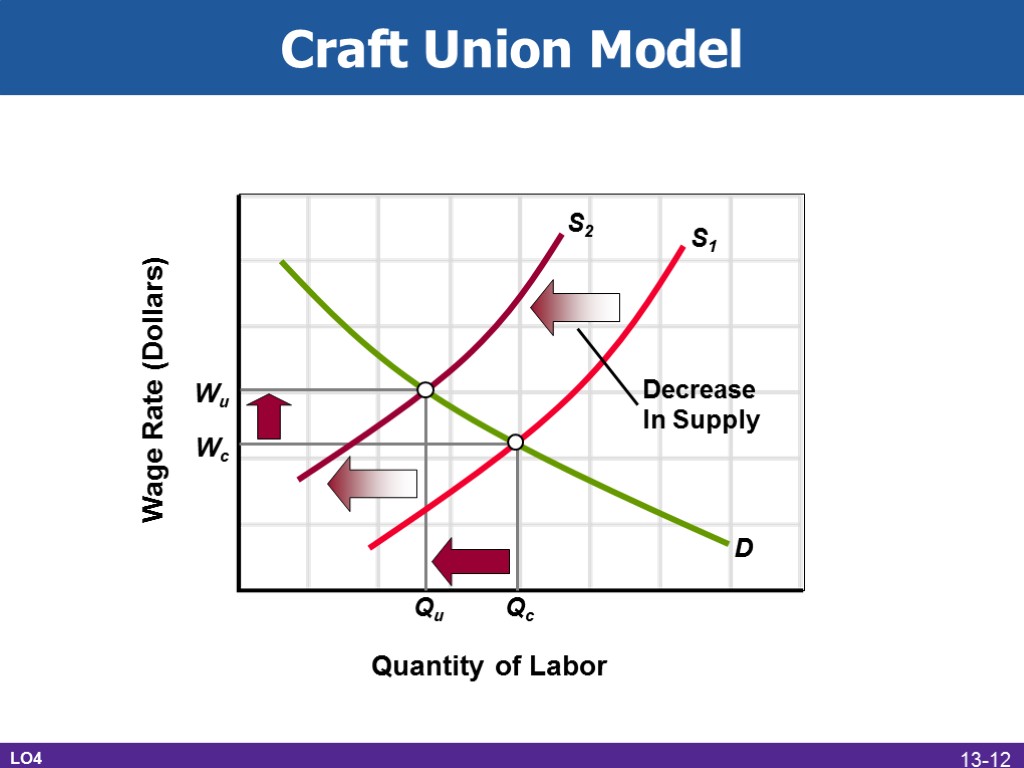
Wage Rate (Dollars) Quantity of Labor D S1 Qc Wc S2 Wu Qu Decrease In Supply Craft Union Model LO4 13-12
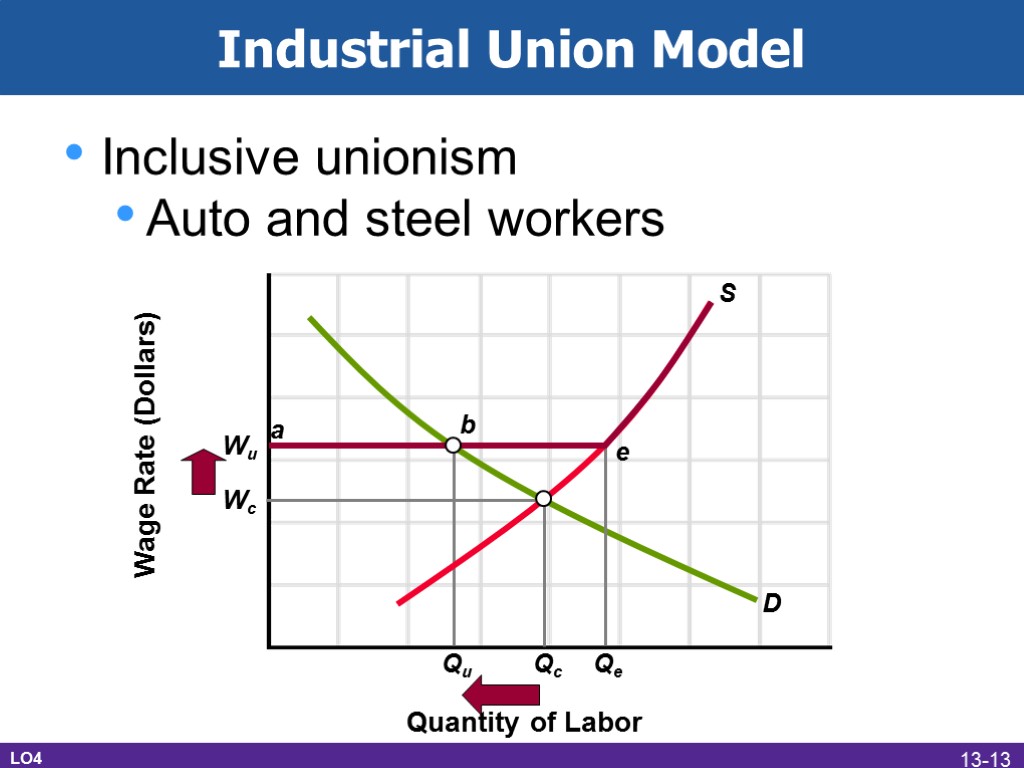
Industrial Union Model Inclusive unionism Auto and steel workers Wage Rate (Dollars) Quantity of Labor D S Qc Wc Wu Qu Qe a b e LO4 13-13

Bilateral Monopoly Model Monopsony and inclusive unionism Single buyer and seller Not uncommon Indeterminate outcome Desirability LO4 13-14
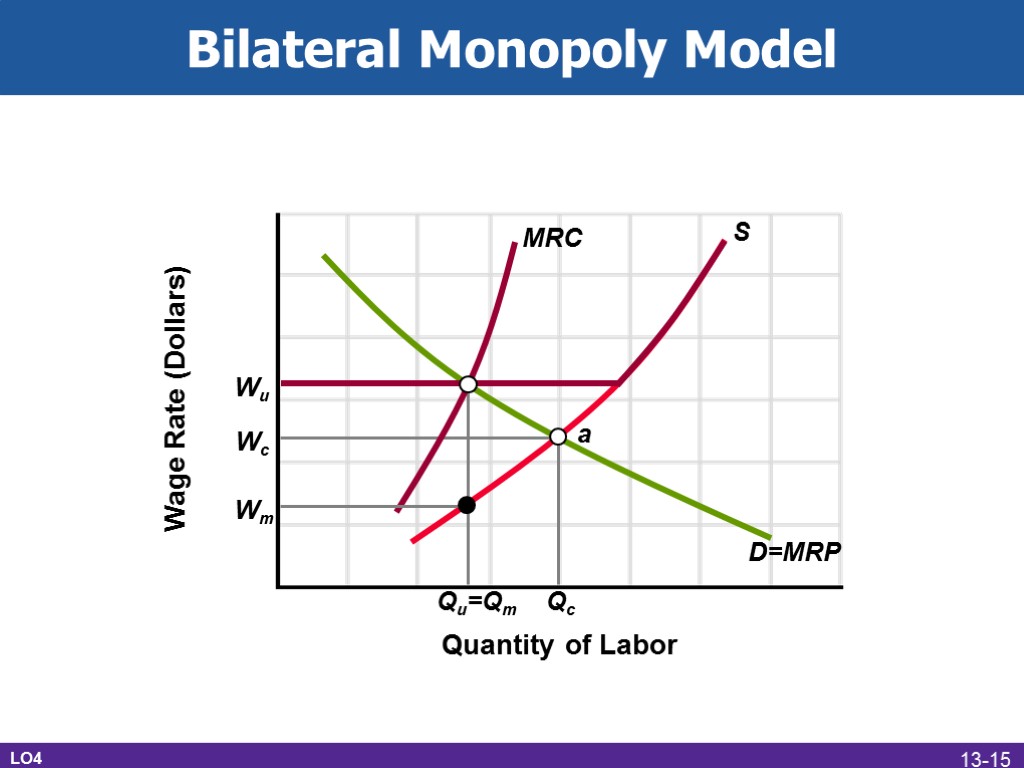
Bilateral Monopoly Model LO4 Wage Rate (Dollars) Quantity of Labor D=MRP S Qc Wc Wu Qu=Qm MRC Wm a 13-15

The Minimum Wage Controversy Case against minimum wage Case for minimum wage State and locally set rates Evidence and conclusions LO5 13-16

Differences across occupations What explains wage differentials? Marginal revenue productivity Noncompeting groups Ability Education and training Compensating differences LO5 Wage Differentials 13-17
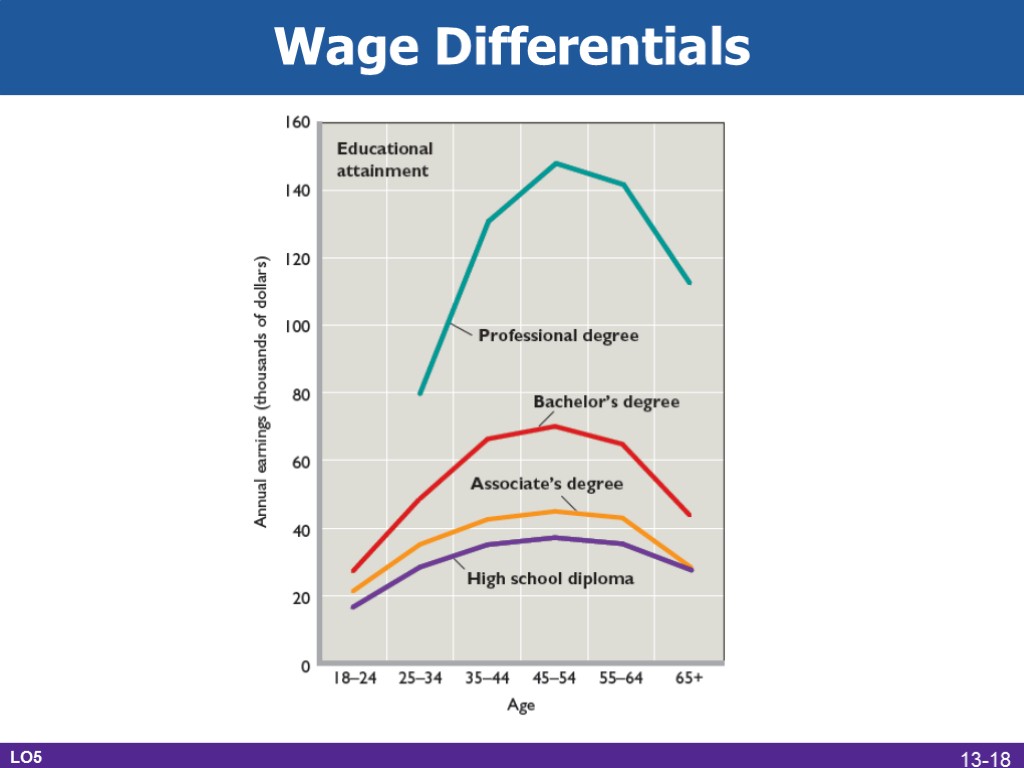
Wage Differentials LO5 13-18

Wage Differentials Workers prevented from moving to higher paying jobs Market imperfections Lack of job information Geographic immobility Unions and government restraints Discrimination LO5 13-19

Pay for Performance The principal-agent problem Incentive pay plan Piece rates Commissions or royalties Bonuses, stock options, and profit sharing Efficiency wages Negative side-effects LO6 13-20
wage_determination.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

