8aa86b6e022f5fc9e2450508ab5ae721.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

WAFC CAT verification Objective verification of GRIB CAT forecasts Dr Philip G Gill, WAFC Science Meeting, Washington, 20 April 2009 © Crown copyright Met Office

Contents This presentation covers the following areas • Introduction • SIGWX forecast comparison • Aircraft data • Verification methodology • Verification results • Summary • Further improvements © Crown copyright Met Office

Introduction • What – Objective verification of gridded binary (GRIB) and significant weather (SIGWX) Clear Air Turbulence (CAT) forecasts • Where – Global verification • When – November 2008 to January 2009 • Why – To demonstrate the quality of the new GRIB forecasts using objective verification. • How – Verification against aircraft observations from the Global Aircraft Data Set (GADS) © Crown copyright Met Office
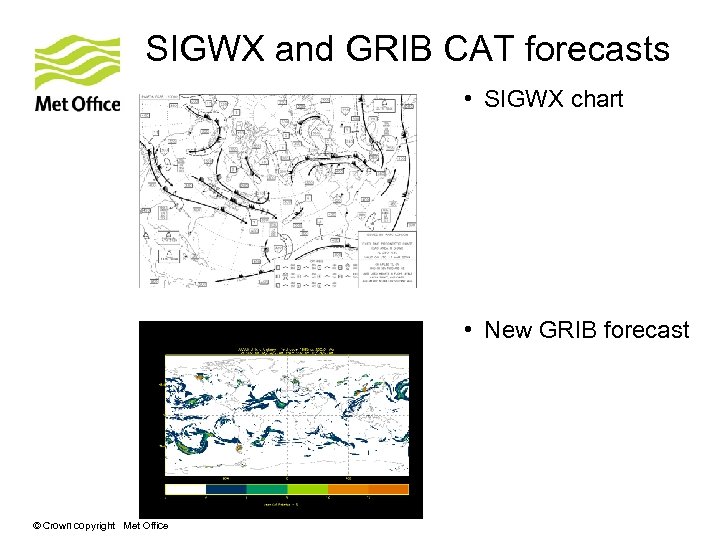
SIGWX and GRIB CAT forecasts • SIGWX chart • New GRIB forecast © Crown copyright Met Office
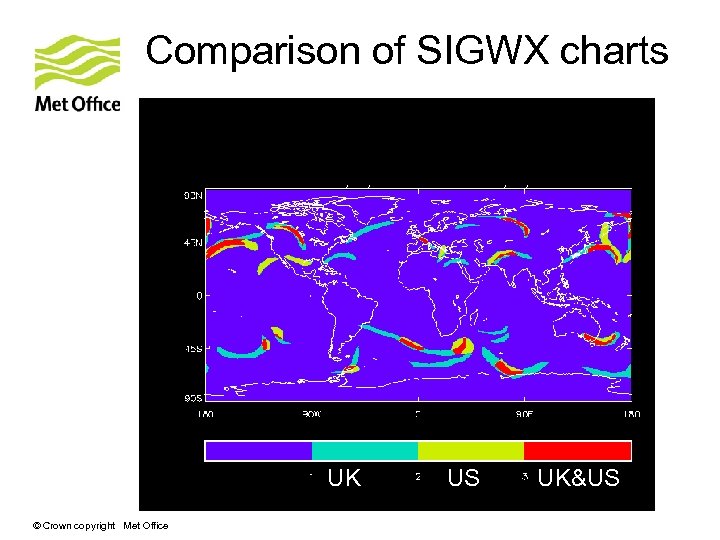
Comparison of SIGWX charts UK © Crown copyright Met Office US UK&US
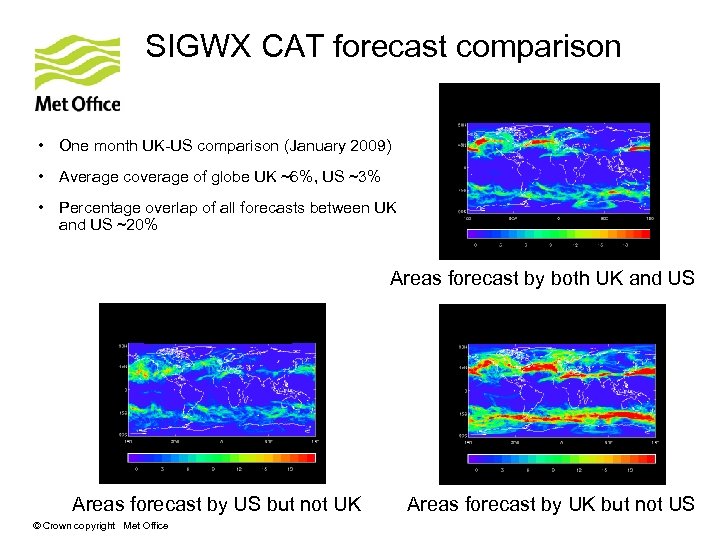
SIGWX CAT forecast comparison • One month UK-US comparison (January 2009) • Average coverage of globe UK ~6%, US ~3% • Percentage overlap of all forecasts between UK and US ~20% Areas forecast by both UK and US Areas forecast by US but not UK © Crown copyright Met Office Areas forecast by UK but not US
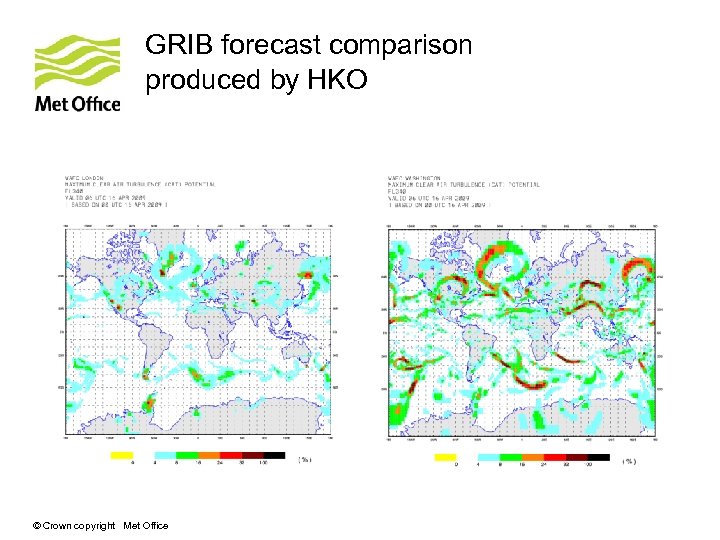
GRIB forecast comparison produced by HKO © Crown copyright Met Office

Global Aircraft Data Set • Archive of aircraft data set up by Joel Tenenbaum (State University of New York) • British Airways fleet of Boeing 747 -400 aircraft • Global coverage, but flights mainly over northern hemisphere • Automated aircraft observations every 4 seconds • Indicator of turbulence derived from vertical acceleration, aircraft mass, altitude and airspeed called the derived equivalent vertical gust (DEVG). © Crown copyright Met Office
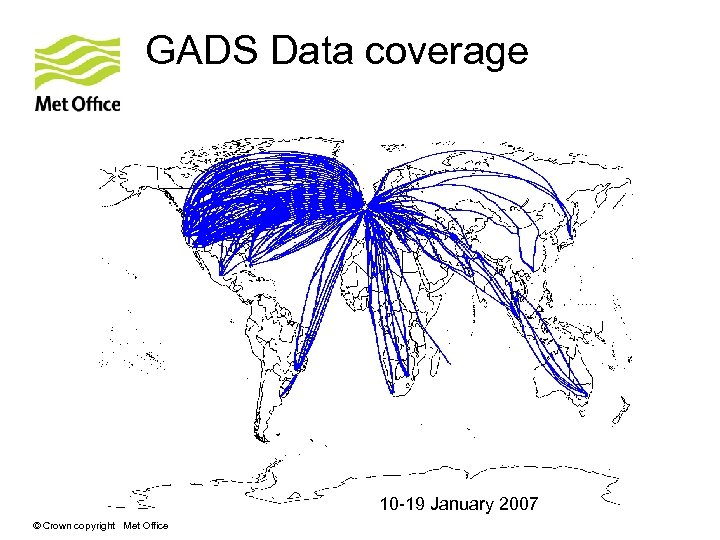
GADS Data coverage 10 -19 January 2007 © Crown copyright Met Office
Verification methodology © Crown copyright Met Office
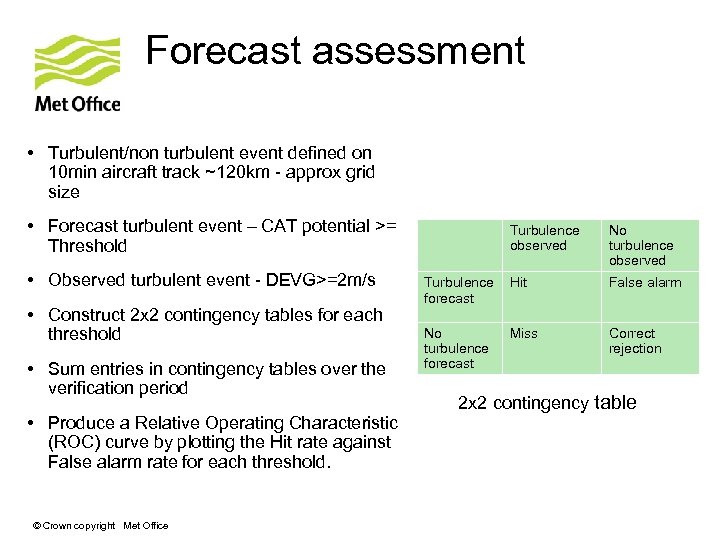
Forecast assessment • Turbulent/non turbulent event defined on 10 min aircraft track ~120 km - approx grid size • Forecast turbulent event – CAT potential >= Threshold • Observed turbulent event - DEVG>=2 m/s • Construct 2 x 2 contingency tables for each threshold • Sum entries in contingency tables over the verification period • Produce a Relative Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve by plotting the Hit rate against False alarm rate for each threshold. © Crown copyright Met Office Turbulence observed No turbulence observed Turbulence forecast Hit False alarm No turbulence forecast Miss Correct rejection 2 x 2 contingency table
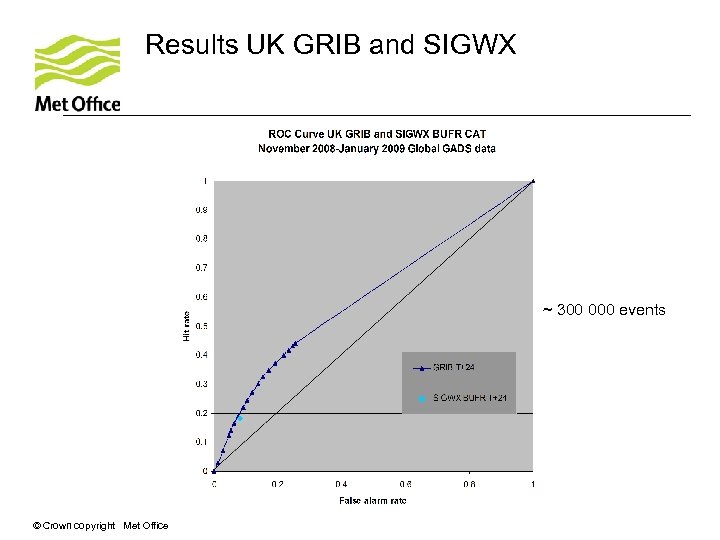
Results UK GRIB and SIGWX ~ 300 000 events © Crown copyright Met Office
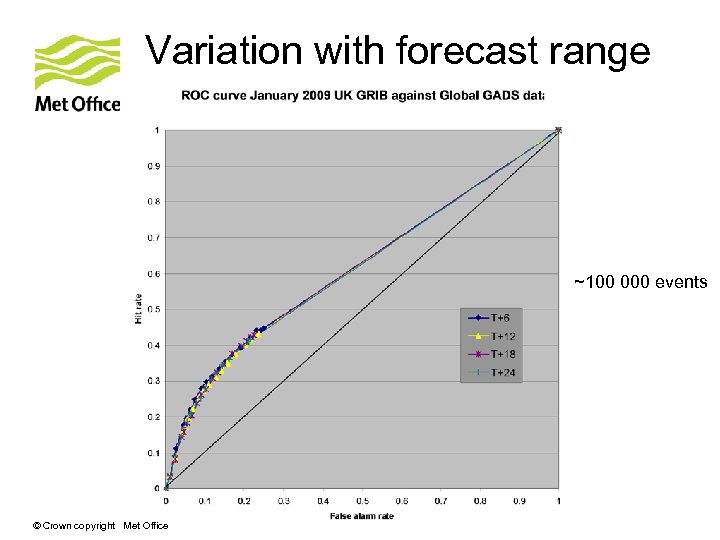
Variation with forecast range ~100 000 events © Crown copyright Met Office
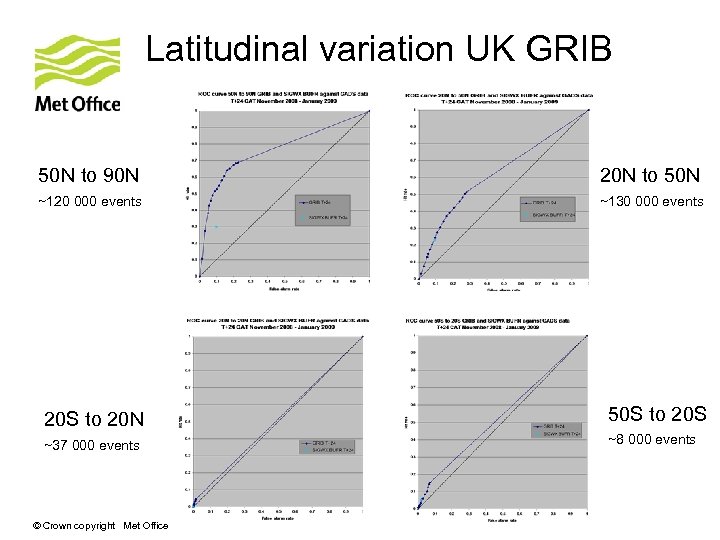
Latitudinal variation UK GRIB 50 N to 90 N 20 N to 50 N ~120 000 events ~130 000 events 20 S to 20 N 50 S to 20 S ~37 000 events ~8 000 events © Crown copyright Met Office
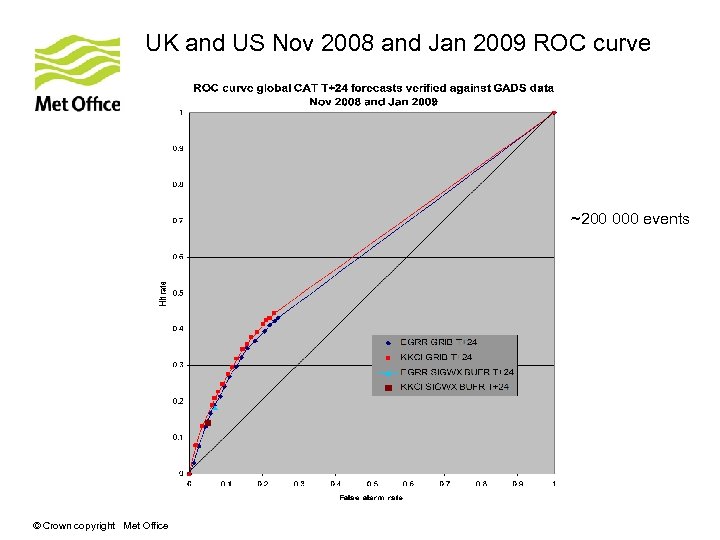
UK and US Nov 2008 and Jan 2009 ROC curve ~200 000 events © Crown copyright Met Office
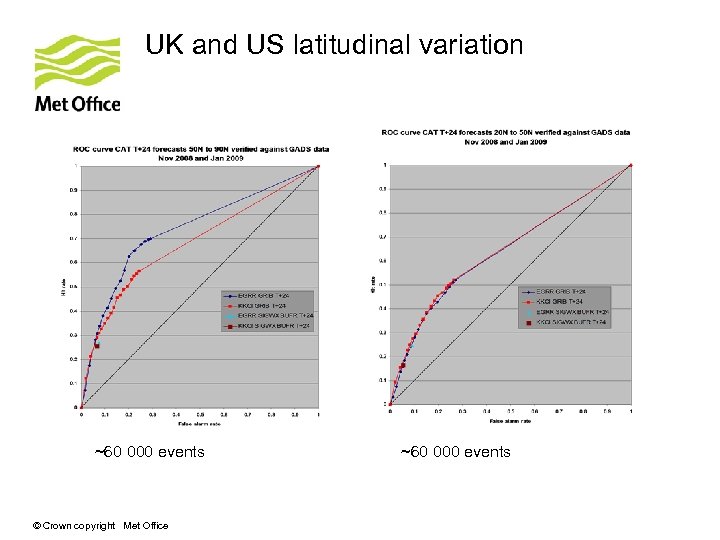
UK and US latitudinal variation ~60 000 events © Crown copyright Met Office ~60 000 events
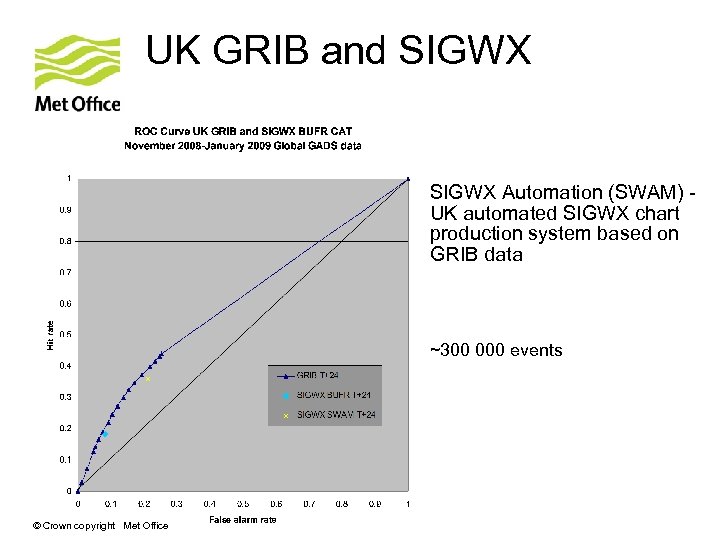
UK GRIB and SIGWX Automation (SWAM) UK automated SIGWX chart production system based on GRIB data ~300 000 events © Crown copyright Met Office
Summary of results • Both UK and US GRIB products show more skill than the manual SIGWX products. • Global UK and US GRIB CAT forecasts score similarly • Slight difference in scores as forecast range increases • Some differences in scores at individual latitude bands – best performance between 20 N and 90 N. • UK CAT coverage on SIGWX charts greater than the US © Crown copyright Met Office

Further improvements • Automate verification process • Produce statistics by ICAO and WMO regions • Improve consistency of forecasts by analysing verification data and altering production systems. • Use verification to test future model upgrades and retune algorithms © Crown copyright Met Office

Questions and answers © Crown copyright Met Office
8aa86b6e022f5fc9e2450508ab5ae721.ppt