W10.1-2+Chapter+10+Understanding+Work+Teams.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 W 10. 1 -2 Chapter 10 Understanding Work Teams
W 10. 1 -2 Chapter 10 Understanding Work Teams
 • Work group – A group that interacts primarily to share information and to make decisions to help each group member perform within his or her area of responsibility • Work team – A group whose individual efforts result in a performance that is greater than the sum of the individual inputs
• Work group – A group that interacts primarily to share information and to make decisions to help each group member perform within his or her area of responsibility • Work team – A group whose individual efforts result in a performance that is greater than the sum of the individual inputs
 • Why teamwork?
• Why teamwork?
 Comparing work groups and work teams • • Goal Collective work / collective performance Synergy Neutral / positive Accountability Individual / individual and mutual Skills Random and Varied / Complementary
Comparing work groups and work teams • • Goal Collective work / collective performance Synergy Neutral / positive Accountability Individual / individual and mutual Skills Random and Varied / Complementary
 Types of teams • Problem-solving • Cross-Functional • Virtual
Types of teams • Problem-solving • Cross-Functional • Virtual
 Learning Teams (self-managed teams) • A learning team a team that facilitates the learning of its members and continuously transforms itself
Learning Teams (self-managed teams) • A learning team a team that facilitates the learning of its members and continuously transforms itself
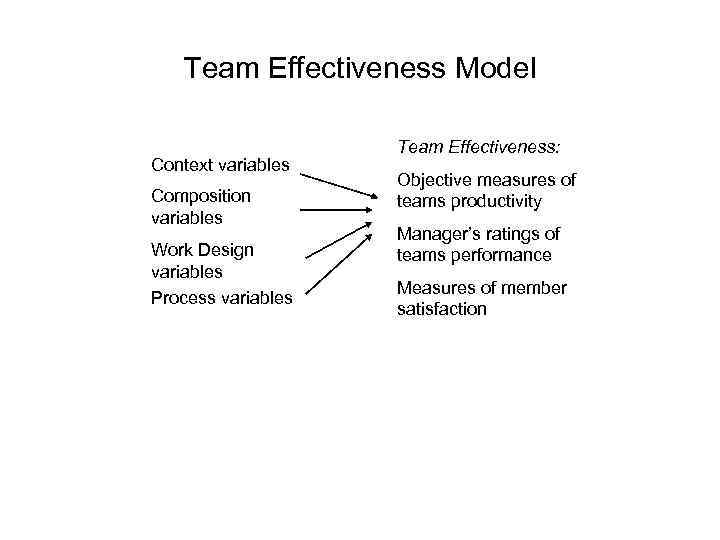 Team Effectiveness Model Context variables Composition variables Work Design variables Process variables Team Effectiveness: Objective measures of teams productivity Manager’s ratings of teams performance Measures of member satisfaction
Team Effectiveness Model Context variables Composition variables Work Design variables Process variables Team Effectiveness: Objective measures of teams productivity Manager’s ratings of teams performance Measures of member satisfaction
 Team Effectiveness Model • Context • Adequate resources • Leadership and Structure • Positive Team Climate • Performance Evaluation and Reward System
Team Effectiveness Model • Context • Adequate resources • Leadership and Structure • Positive Team Climate • Performance Evaluation and Reward System
 Team Effectiveness Model • Team Composition • Abilities of Members • Personality of Members • Allocation of Roles • Diversity of Members • Size of Teams • Member Preferences
Team Effectiveness Model • Team Composition • Abilities of Members • Personality of Members • Allocation of Roles • Diversity of Members • Size of Teams • Member Preferences
 Team Effectiveness Model • Work Design • Skill Variety • Task Significance • Task Identity
Team Effectiveness Model • Work Design • Skill Variety • Task Significance • Task Identity
 Team Effectiveness Model • Team Processes • Common plan and purpose • Specific Goals • Team Efficacy • Mental Models (decision-making) • Member exchange (communication)
Team Effectiveness Model • Team Processes • Common plan and purpose • Specific Goals • Team Efficacy • Mental Models (decision-making) • Member exchange (communication)
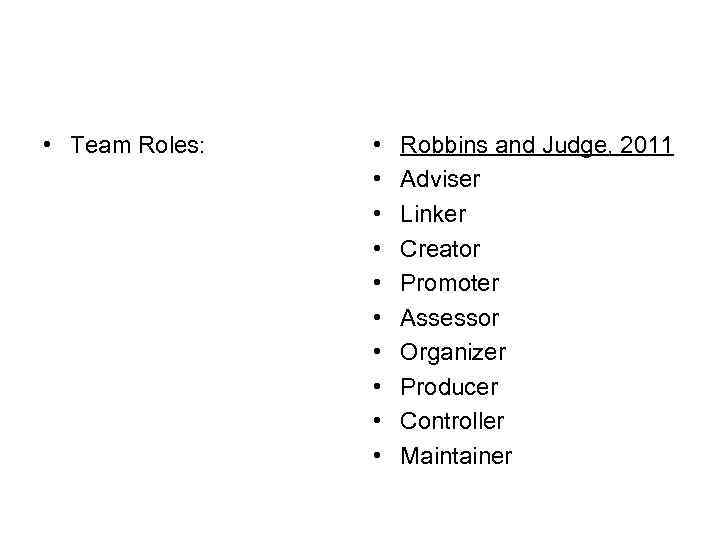 • Team Roles: • • • Robbins and Judge, 2011 Adviser Linker Creator Promoter Assessor Organizer Producer Controller Maintainer
• Team Roles: • • • Robbins and Judge, 2011 Adviser Linker Creator Promoter Assessor Organizer Producer Controller Maintainer
 Team Players • Selecting • Training • Rewarding
Team Players • Selecting • Training • Rewarding
 Why teams can be ineffective? • Three tests to see if a team fits the situation: 1. Is the work complex and is there a need for different perspectives – will it be better with the insights of more than one person? 2. Does the work create a common purpose or set of goals for the group that is larger than the aggregate of the goals for individuals? 3. Are members of the group involved in interdependent tasks?
Why teams can be ineffective? • Three tests to see if a team fits the situation: 1. Is the work complex and is there a need for different perspectives – will it be better with the insights of more than one person? 2. Does the work create a common purpose or set of goals for the group that is larger than the aggregate of the goals for individuals? 3. Are members of the group involved in interdependent tasks?
 Why teams can be ineffective? • • The theory of constraints (TOC) is a management paradigm that views any manageable system as being limited in achieving more of its goals by a very small number of constraints. • • The evolution theory ‘Evolution’ may, in this context, relates to how team’s characteristics evolve and • transform Levels of Stress and individual responses to stress: alarm – fightor-flight (resistance) – exhaustion – return to normal Holding responsible (not blaming) Social Learning, Self-Reference and Critical points An example put forth by Rogers in Diffusion of Innovations was that of the fax machine, which had been around for almost 150 years before it became popular and widely used. Conte et al (2001) two temporal individual difference variables time urgency and time perspective which they suggested have direct and important influences on perceptions of deadlines and subsequent deadline-oriented behaviors in teams.
Why teams can be ineffective? • • The theory of constraints (TOC) is a management paradigm that views any manageable system as being limited in achieving more of its goals by a very small number of constraints. • • The evolution theory ‘Evolution’ may, in this context, relates to how team’s characteristics evolve and • transform Levels of Stress and individual responses to stress: alarm – fightor-flight (resistance) – exhaustion – return to normal Holding responsible (not blaming) Social Learning, Self-Reference and Critical points An example put forth by Rogers in Diffusion of Innovations was that of the fax machine, which had been around for almost 150 years before it became popular and widely used. Conte et al (2001) two temporal individual difference variables time urgency and time perspective which they suggested have direct and important influences on perceptions of deadlines and subsequent deadline-oriented behaviors in teams.
 Summary and implications for managers: • Effective teams have common characteristics: – – – – Adequate resources Effective leadership A climate of trust Appropriate reward and evaluation systems Composed of members with correct skills and roles The tasks are whole and significant and Has members who believe in the team’s capabilities
Summary and implications for managers: • Effective teams have common characteristics: – – – – Adequate resources Effective leadership A climate of trust Appropriate reward and evaluation systems Composed of members with correct skills and roles The tasks are whole and significant and Has members who believe in the team’s capabilities


