3f3a488a44bc873011e2352ce32fdb45.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

VXLAN Fundamentals, Architecture & Roadmap 1

Table of Contents 1. Data Center IP Fabric ‘Building a strong Foundation’ 2. What is ‘Network Virtualization’? 3. VXLAN Overview 4. VXLAN Packet details 5. VXLAN Terminology 6. VXLAN Host Discovery 7. VXLAN BUM Traffic Handling 8. VXLAN Layer 2 & Layer 3 Terminologies 9. VXLAN Arista Architecture & Vision 10. VXLAN Roadmap 11. VXLAN Visbility 2

Data Center – ‘IP Fabric’ Building A Strong Foundation 3
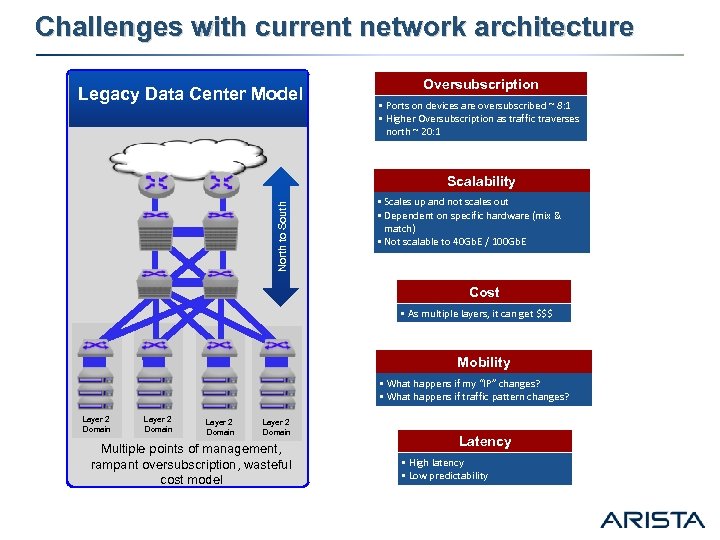
Challenges with current network architecture Legacy Data Center Model Oversubscription § Ports on devices are oversubscribed ~ 8: 1 § Higher Oversubscription as traffic traverses north ~ 20: 1 North to South Scalability § Scales up and not scales out § Dependent on specific hardware (mix & match) § Not scalable to 40 Gb. E / 100 Gb. E Cost § As multiple layers, it can get $$$ Mobility § What happens if my “IP” changes? § What happens if traffic pattern changes? Layer 2 Domain Multiple points of management, rampant oversubscription, wasteful cost model Latency § High latency § Low predictability
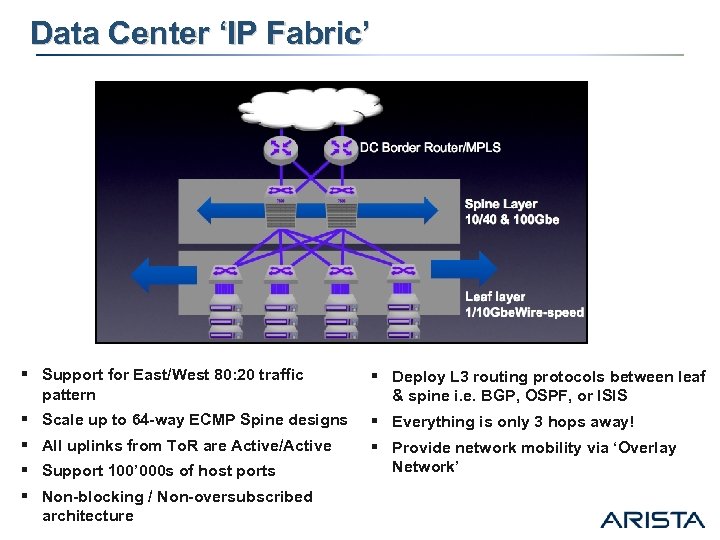
Data Center ‘IP Fabric’ § Support for East/West 80: 20 traffic pattern § § Scale up to 64 -way ECMP Spine designs All uplinks from To. R are Active/Active Support 100’ 000 s of host ports Non-blocking / Non-oversubscribed architecture § Deploy L 3 routing protocols between leaf & spine i. e. BGP, OSPF, or ISIS § Everything is only 3 hops away! § Provide network mobility via ‘Overlay Network’
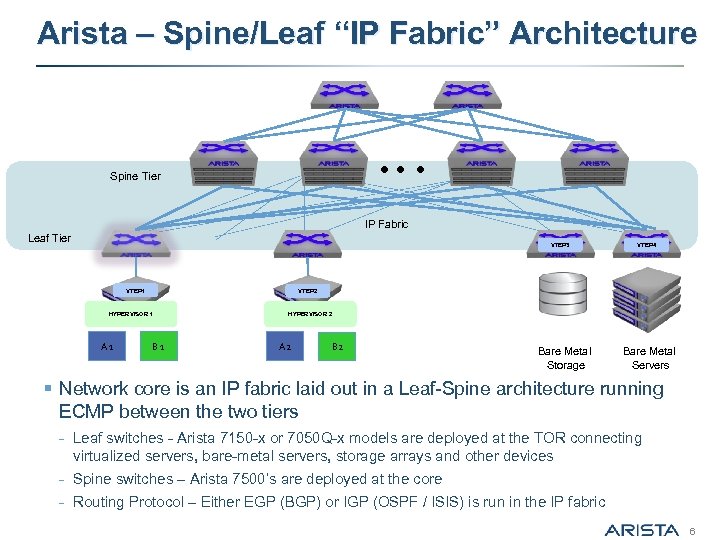
Arista – Spine/Leaf “IP Fabric” Architecture Spine Tier IP Fabric Leaf Tier VTEP 3 VTEP 1 VTEP 2 HYPERVISOR 1 A 1 VTEP 4 B 1 HYPERVISOR 2 A 2 Bare Metal Storage Bare Metal Servers § Network core is an IP fabric laid out in a Leaf-Spine architecture running ECMP between the two tiers - Leaf switches - Arista 7150 -x or 7050 Q-x models are deployed at the TOR connecting virtualized servers, bare-metal servers, storage arrays and other devices - Spine switches – Arista 7500’s are deployed at the core - Routing Protocol – Either EGP (BGP) or IGP (OSPF / ISIS) is run in the IP fabric 6

What is Network Virtualization? 7
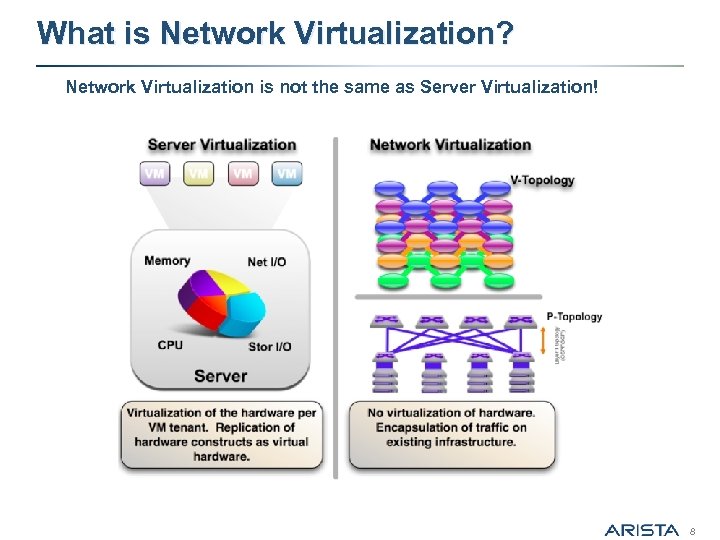
What is Network Virtualization? Network Virtualization is not the same as Server Virtualization! 8
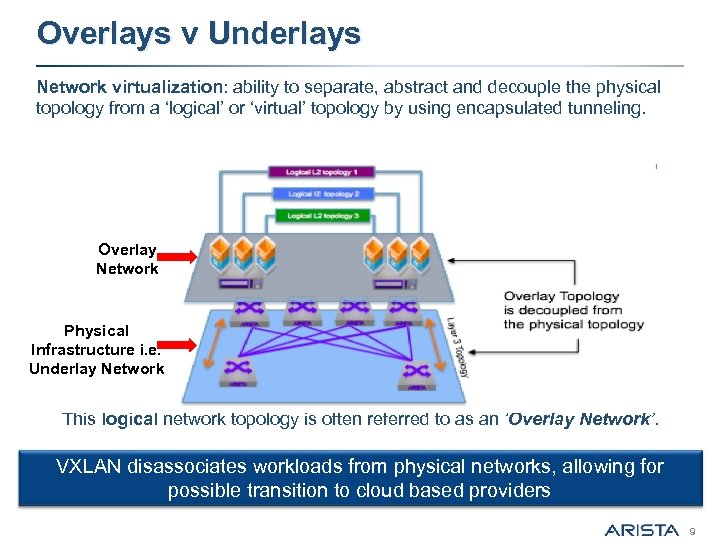
Overlays v Underlays Network virtualization: ability to separate, abstract and decouple the physical topology from a ‘logical’ or ‘virtual’ topology by using encapsulated tunneling. Overlay Network Physical Infrastructure i. e. Underlay Network This logical network topology is often referred to as an ‘Overlay Network’. VXLAN disassociates workloads from physical networks, allowing for possible transition to cloud based providers 9
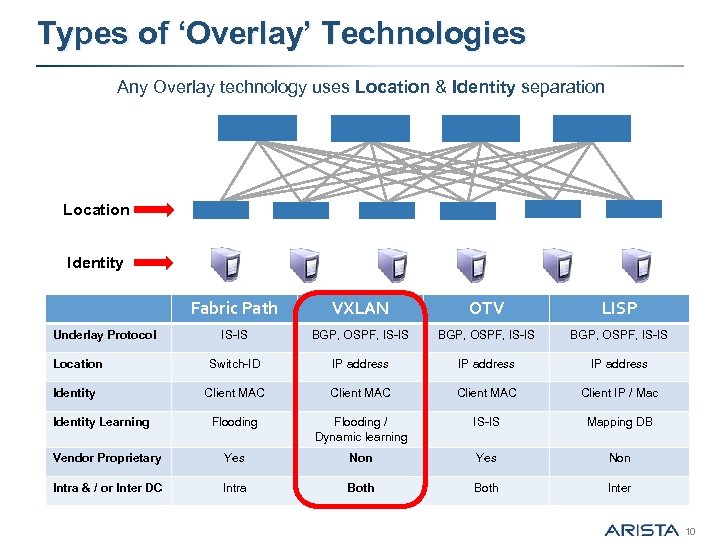
Types of ‘Overlay’ Technologies Any Overlay technology uses Location & Identity separation Location Identity Fabric Path VXLAN OTV LISP IS-IS BGP, OSPF, IS-IS Switch-ID IP address Client MAC Client IP / Mac Flooding / Dynamic learning IS-IS Mapping DB Vendor Proprietary Yes Non Intra & / or Inter DC Intra Both Inter Underlay Protocol Location Identity Learning 10

VXLAN Overview 11
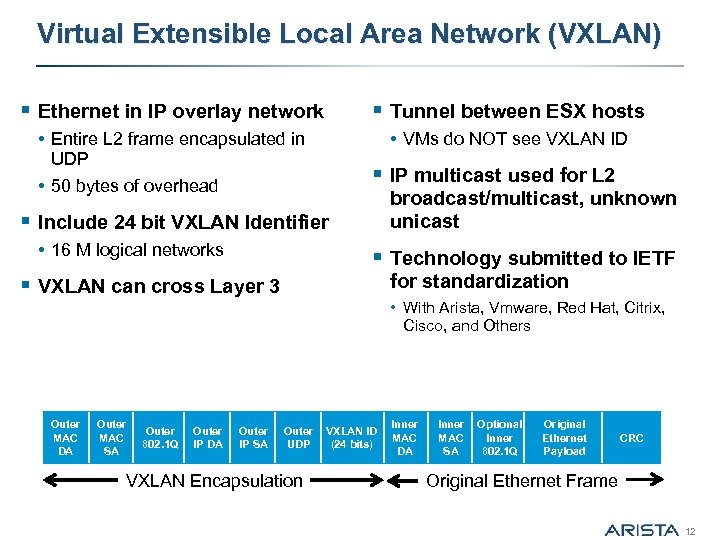
Virtual Extensible Local Area Network (VXLAN) § Ethernet in IP overlay network § Tunnel between ESX hosts • Entire L 2 frame encapsulated in • VMs do NOT see VXLAN ID UDP • 50 bytes of overhead § IP multicast used for L 2 broadcast/multicast, unknown unicast § Include 24 bit VXLAN Identifier • 16 M logical networks § Technology submitted to IETF for standardization § VXLAN can cross Layer 3 • With Arista, Vmware, Red Hat, Citrix, Cisco, and Others Outer MAC DA Outer MAC SA Outer 802. 1 Q Outer IP DA Outer IP SA Outer UDP VXLAN Encapsulation VXLAN ID (24 bits) Inner MAC DA Inner MAC SA Optional Inner 802. 1 Q Original Ethernet Payload CRC Original Ethernet Frame 12
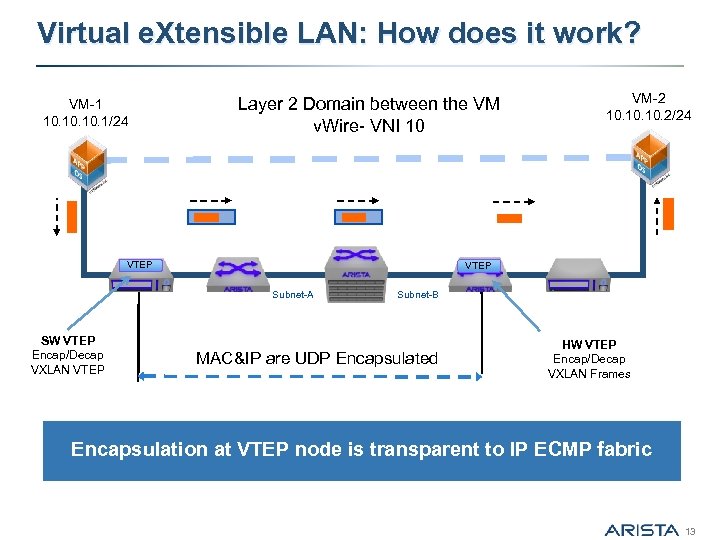
Virtual e. Xtensible LAN: How does it work? VM-1 10. 10. 1/24 Layer 2 Domain between the VM v. Wire- VNI 10 VTEP Subnet-A SW VTEP Encap/Decap VXLAN VTEP VM-2 10. 10. 2/24 Subnet-B MAC&IP are UDP Encapsulated HW VTEP Encap/Decap VXLAN Frames Encapsulation at VTEP node is transparent to IP ECMP fabric 13
VXLAN Benefits § Feature Benefits - Eliminates current networking challenges in the way of on-demand, virtual environment: - VLAN Sprawl - Single fault domains - Scalability beyond 4096 segments - Proprietary fabric solutions - IP mobility - Physical cluster size and locality - Enables multi-tenancy at scale - Decouples logical networks from physical infrastructure so that applications can be deployed without worrying about physical rack location, IP address or VLAN - Based on open and well known standards 14
VXLAN Use Cases § Physical to Virtual internetworking § Multi-hypervisor connectivity and integration § Multi-tenant Cloud environments § HA clusters across failure domains § Dynamic growth § Dynamic resource management 15

VXLAN Packet Details 16
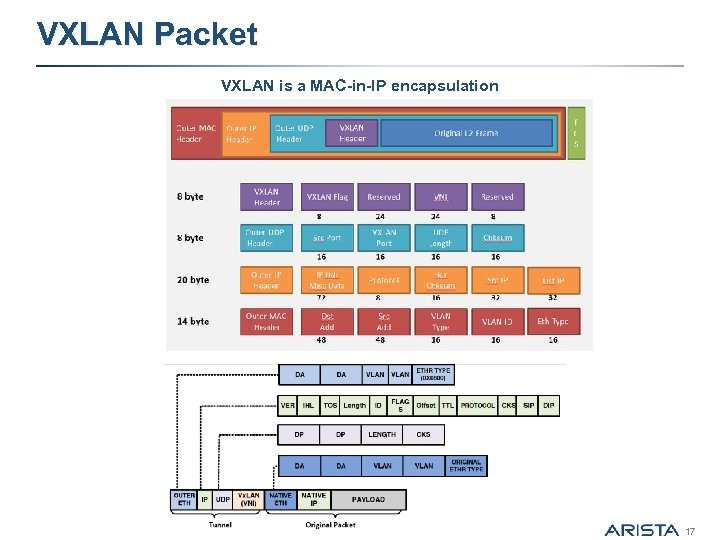
VXLAN Packet VXLAN is a MAC-in-IP encapsulation 17
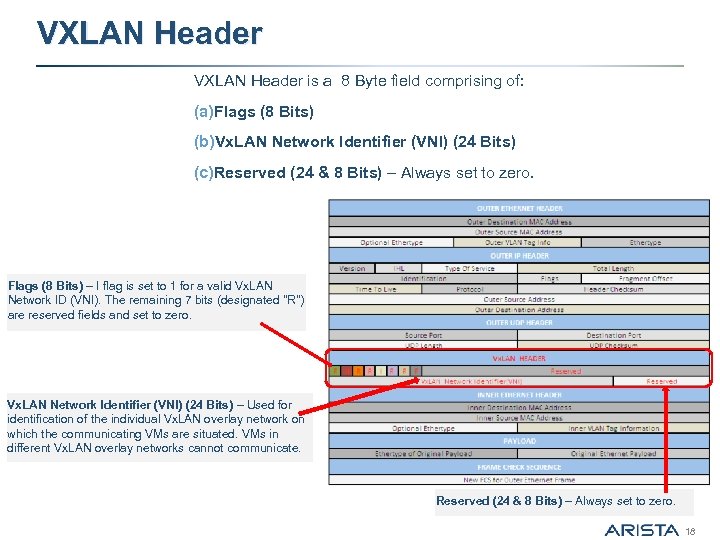
VXLAN Header is a 8 Byte field comprising of: (a)Flags (8 Bits) (b)Vx. LAN Network Identifier (VNI) (24 Bits) (c)Reserved (24 & 8 Bits) – Always set to zero. Flags (8 Bits) – I flag is set to 1 for a valid Vx. LAN Network ID (VNI). The remaining 7 bits (designated "R") are reserved fields and set to zero. Vx. LAN Network Identifier (VNI) (24 Bits) – Used for identification of the individual Vx. LAN overlay network on which the communicating VMs are situated. VMs in different Vx. LAN overlay networks cannot communicate. Reserved (24 & 8 Bits) – Always set to zero. 18

VXLAN Terminology 19
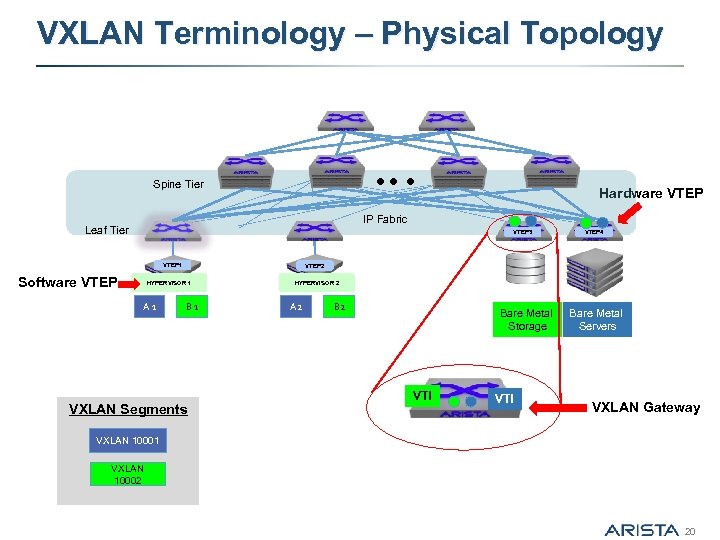
VXLAN Terminology – Physical Topology Spine Tier Hardware VTEP IP Fabric Leaf Tier VTEP 3 VTEP 1 Software VTEP 2 HYPERVISOR 1 A 1 VTEP 4 B 1 VXLAN Segments HYPERVISOR 2 A 2 Bare Metal Storage VTI Bare Metal Servers VXLAN Gateway VXLAN 10001 VXLAN 10002 20
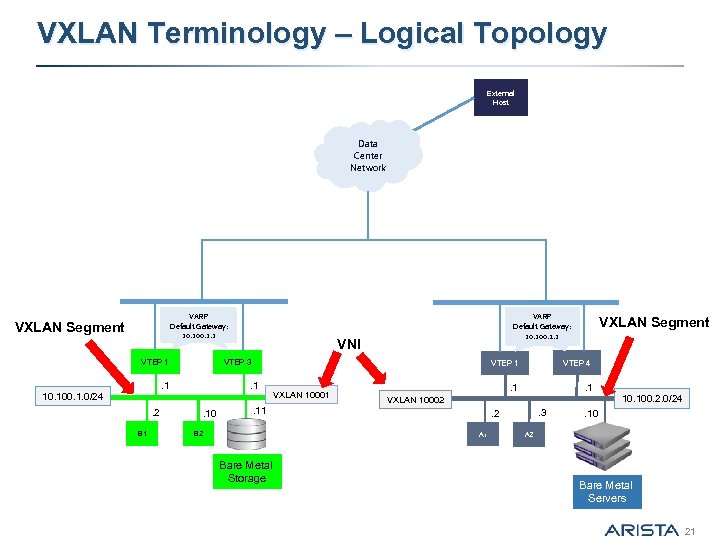
VXLAN Terminology – Logical Topology External Host Data Center Network VARP Default Gateway: 10. 100. 1. 1 VXLAN Segment VTEP 1 . 2 B 1 VNI VTEP 3 . 1 10. 100. 1. 0/24 VARP Default Gateway: 10. 100. 2. 1 VTEP 1 . 1. 10 VXLAN Segment VXLAN 10001 . 1. 3 . 2 A 1 Bare Metal Storage . 1 VXLAN 10002 . 11 B 2 VTEP 4 10. 100. 2. 0/24 . 10 A 2 Bare Metal Servers 21
VXLAN Terminology Explained § VTEP: VXLAN Tunnel End Point - VXLAN encapsulation and decapsulation happens at the VTEP § VXLAN Gateway - A device which bridges traffic from VXLAN and non-VXLAN environments. - VXLAN gateways allow for physical and non virtualized devices to communicate with VXLAN networks - A VXLAN gateway can be either a hardware or software device § VNI: Virtual Network Identifier - a 24 -bit number is also called the VXLAN segment ID. The system uses the VNI, along with the VLAN ID, to identify the appropriate tunnel. § VXLAN Header – is an 8 -byte header that contains the 24 -bit VNI value. It lives in between the UDP header and the inner MAC frame being carried over the VTI. § VTI: VTEP Tunnel Interface - a switchport linked to a UDP socket that can be shared between many VLANs. Packets bridged through a vlan into the VTI are sent out the UDP socket with a VXLAN header including a VNI. The socket is bound to a fixed local port, but is not connected to any particular destination port or IP address; logically, we use sendto() (not send()) to transmit VXLAN-encapsulated frames on the socket. Packets arriving on the VTI (via the UDP socket, based on their UDP destination port) are demultiplexed into a VLAN for bridging. A 24 -bit VNI within the packet determines which VLAN the packet is mapped to for bridging. § VXLAN Segment - is a Layer 2 overlay network over which VMs communicate. Only VMs within the same VXLAN segment can communicate with each other. 22

VXLAN Visibility 23

VXLAN Visibility - Arista’s vm. Tracer § Full physical to virtual visibility § Network audit to ensure reachability § Automated provisioning § Workflow without finger pointing § Other awesome capabilities 24
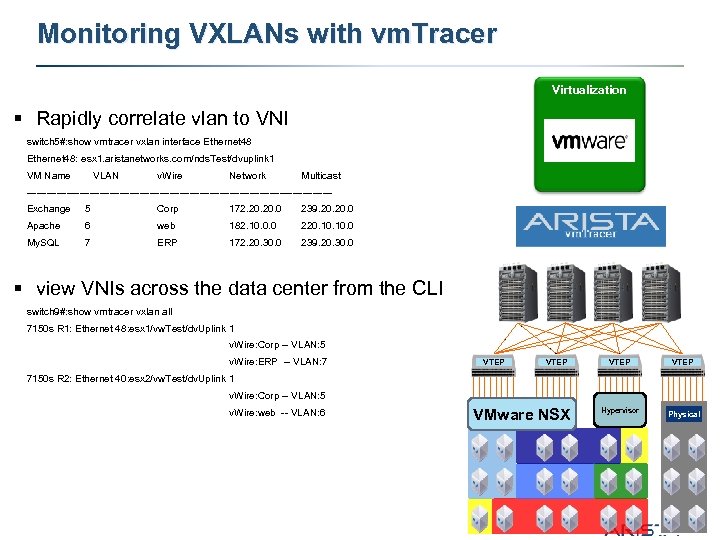
Monitoring VXLANs with vm. Tracer Virtualization § Rapidly correlate vlan to VNI switch 5#: show vmtracer vxlan interface Ethernet 48: esx 1. aristanetworks. com/nds. Test/dvuplink 1 VM Name VLAN v. Wire Network Multicast ----------------------------------------------Exchange 5 Corp 172. 20. 0 239. 20. 0 Apache 6 web 182. 10. 0. 0 220. 10. 0 My. SQL 7 ERP 172. 20. 30. 0 239. 20. 30. 0 § view VNIs across the data center from the CLI switch 9#: show vmtracer vxlan all 7150 s R 1: Ethernet 48: esx 1/vw. Test/dv. Uplink 1 v. Wire: Corp -- VLAN: 5 v. Wire: ERP -- VLAN: 7 VTEP 7150 s R 2: Ethernet 40: esx 2/vw. Test/dv. Uplink 1 v. Wire: Corp -- VLAN: 5 v. Wire: web -- VLAN: 6 VMware NSX Hypervisor Physical 25
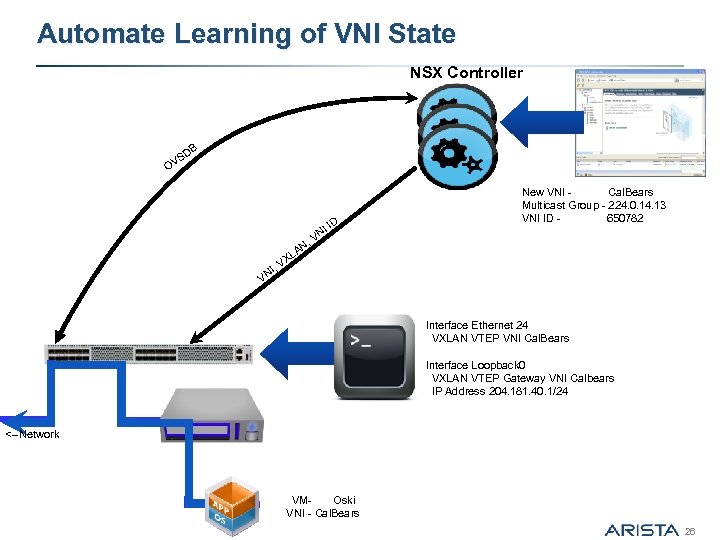
Automate Learning of VNI State NSX Controller DB S OV D I I VN New VNI - Cal. Bears Multicast Group - 224. 0. 14. 13 VNI ID - 650782 , AN L VX , NI V Interface Ethernet 24 VXLAN VTEP VNI Cal. Bears Interface Loopback 0 VXLAN VTEP Gateway VNI Calbears IP Address 204. 181. 40. 1/24 <--Network VM- Oski VNI - Cal. Bears 26
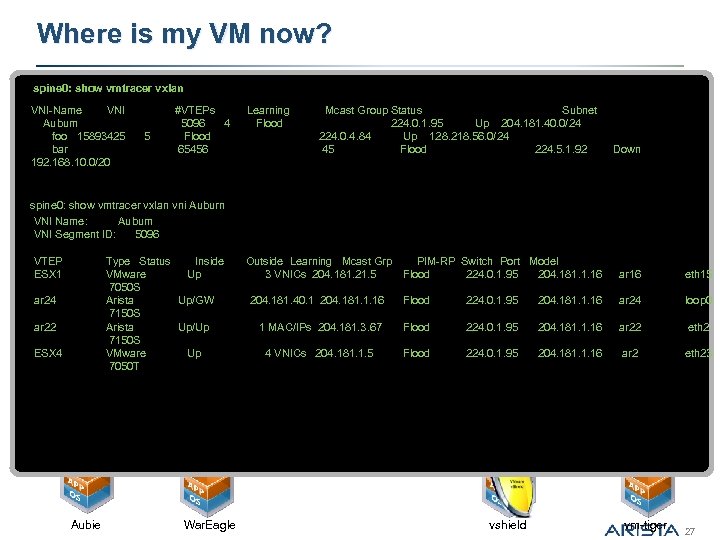
Where is my VM now? spine 0: show vmtracer vxlan VNI-Name VNI Auburn foo 15893425 5 bar 192. 168. 10. 0/20 #VTEPs 5096 4 Flood 65456 Learning Flood Mcast Group Status Subnet 224. 0. 1. 95 Up 204. 181. 40. 0/24 224. 0. 4. 84 Up 128. 218. 56. 0/24 45 Flood 224. 5. 1. 92 Down spine 0: show vmtracer vxlan vni Auburn spine 0 VNI Name: Auburn VNI Segment ID: 5096 leaf 1 leaf 2 VTEP Type Status Inside Outside Learning Mcast Grp PIM-RP Switch Port Model ESX 1 VMware Up 3 VNICs 204. 181. 21. 5 Flood 224. 0. 1. 95 204. 181. 1. 16 7050 S ar 24 Arista Up/GW 204. 181. 40. 1 204. 181. 1. 16 Flood 224. 0. 1. 95 204. 181. 1. 16 7150 S ar 22 Arista Up/Up 1 MAC/IPs 204. 181. 3. 67 Flood 224. 0. 1. 95 204. 181. 1. 16 7150 S ESX 4 VMware Up 4 VNICs 204. 181. 1. 5 Flood 224. 0. 1. 95 204. 181. 1. 16 7050 T esx 10 ar 16 eth 15 ar 24 loop 0 ar 22 eth 2 ar 2 eth 23 esx 11 VNI ‘Test’: 224. 0. 0. 12 Aubie War. Eagle vshield vm-tiger 27
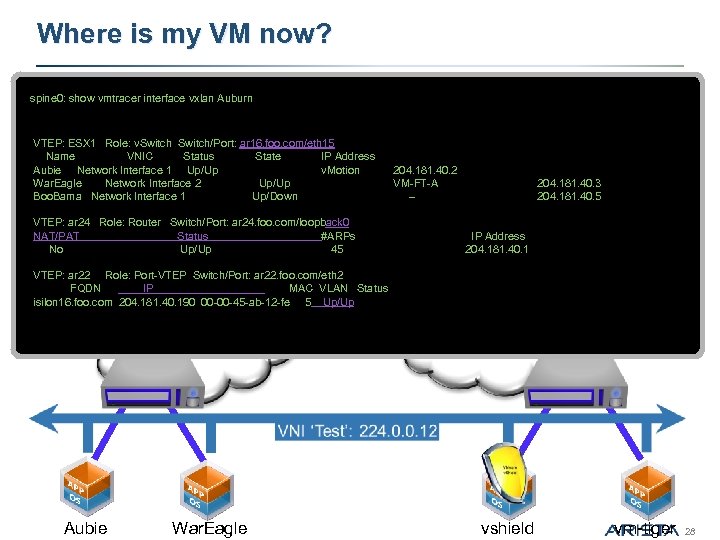
Where is my VM now? spine 0: show vmtracer interface vxlan Auburn VTEP: ESX 1 Role: v. Switch/Port: ar 16. foo. com/eth 15 Name VNIC Status State IP Address Aubie Network Interface 1 Up/Up v. Motion 204. 181. 40. 2 War. Eagle Network Interface 2 Up/Up VM-FT-A Boo. Bama Network Interface 1 Up/Down -- 204. 181. 40. 3 204. 181. 40. 5 spine 0 VTEP: ar 24 Role: Router Switch/Port: ar 24. foo. com/loopback 0 NAT/PAT #ARPs leaf 1 Status No Up/Up 45 IP Address 204. 181. 40. 1 leaf 2 VTEP: ar 22 Role: Port-VTEP Switch/Port: ar 22. foo. com/eth 2 FQDN IP MAC VLAN Status isilon 16. foo. com 204. 181. 40. 190 00 -00 -45 -ab-12 -fe 5 Up/Up 128. 218. 10. x 128. 218. 11. x esx 1 Aubie esx 11 War. Eagle vshield vm-tiger 28

THANK YOU 29
3f3a488a44bc873011e2352ce32fdb45.ppt