f1416f23679d0ca7c35dd399003b0d00.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Voter turnout and civic participation in the EU FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Voter turnout and civic participation in the EU FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Overview 1. Relevance of participation 2. Turnout in EP elections - Development since 1979 Comparison with NP elections Types of voters Multivariate analysis 3. Non-electoral participation in Europe - Frequencies Dimensions of non-electoral participation Multivariate analysis FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Overview 1. Relevance of participation 2. Turnout in EP elections - Development since 1979 Comparison with NP elections Types of voters Multivariate analysis 3. Non-electoral participation in Europe - Frequencies Dimensions of non-electoral participation Multivariate analysis FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Relevance of participation • Two important approaches in theories of democracy: – Input-oriented approaches: aim: maximum of turnout/participation low turnout/participation: declining support, symptom for a crisis – Output-oriented approaches: elections as an instrument for the allocation of power and legitimation of the political system low turnout/participation: satisfaction and consent with the political system General evaluation of turnout/participation level is quite difficult. FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Relevance of participation • Two important approaches in theories of democracy: – Input-oriented approaches: aim: maximum of turnout/participation low turnout/participation: declining support, symptom for a crisis – Output-oriented approaches: elections as an instrument for the allocation of power and legitimation of the political system low turnout/participation: satisfaction and consent with the political system General evaluation of turnout/participation level is quite difficult. FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
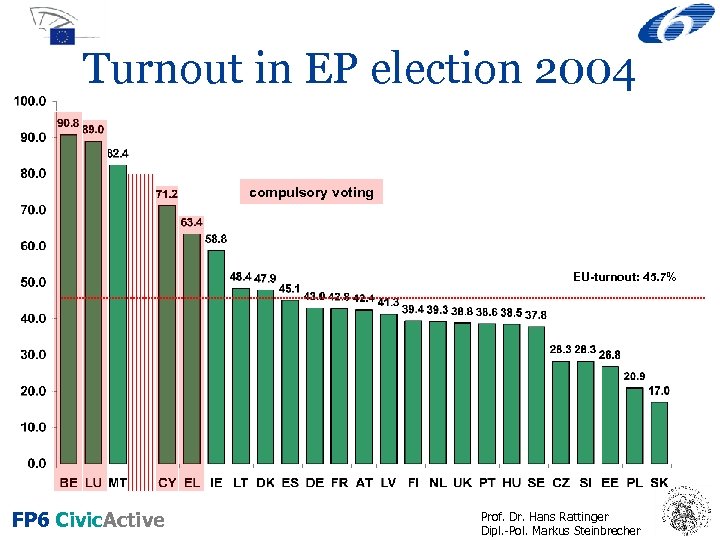 Turnout in EP election 2004 compulsory voting EU-turnout: 45. 7% FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Turnout in EP election 2004 compulsory voting EU-turnout: 45. 7% FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
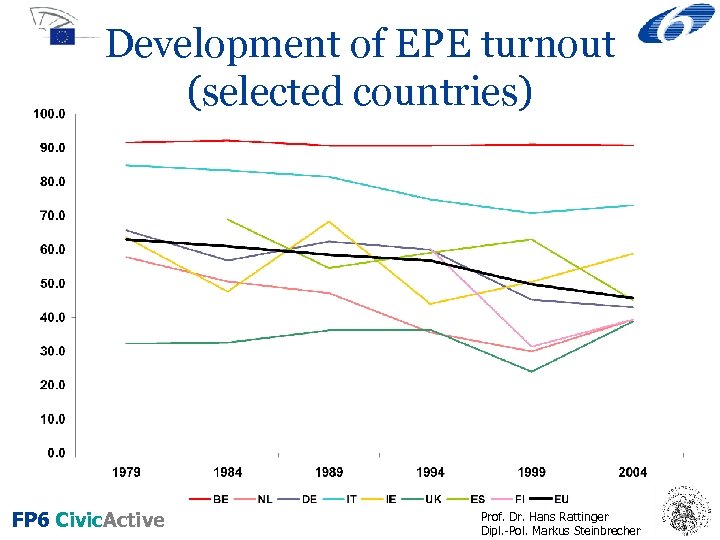 Development of EPE turnout (selected countries) FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Development of EPE turnout (selected countries) FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
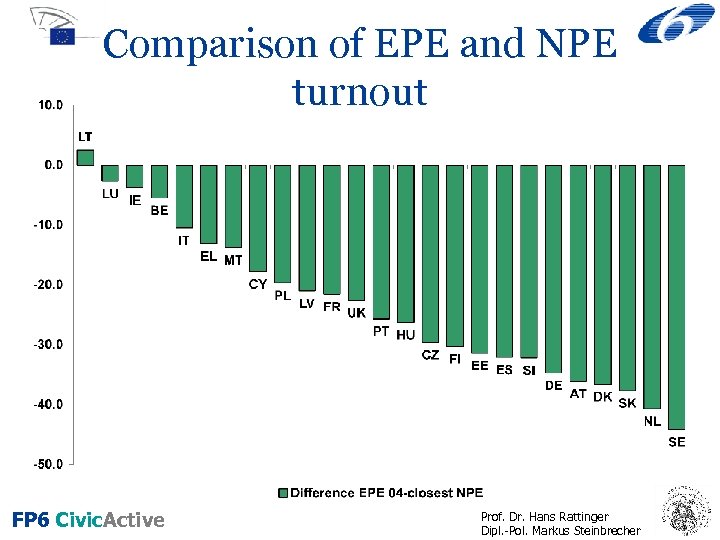 Comparison of EPE and NPE turnout FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Comparison of EPE and NPE turnout FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Database for analysis of turnout • Mass survey from Intune-project http: //www. intune. it/ • Timing: March-April 2007 • 17 European countries: AT, BE, BG, DE, DK, EE, EL, ES, FR, HU, IT, PL, PT, SI, SK, SR, UK • Turnout: last EPE, last NPE FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Database for analysis of turnout • Mass survey from Intune-project http: //www. intune. it/ • Timing: March-April 2007 • 17 European countries: AT, BE, BG, DE, DK, EE, EL, ES, FR, HU, IT, PL, PT, SI, SK, SR, UK • Turnout: last EPE, last NPE FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Logistic regression: Turnout EPE • Nagelkerke‘s R 2= 0. 252 • Most important predictors: – Perceived duty to vote (EU/Nat. ) – Strength of party identification – Media consumption – EU support – Internal efficacy – EU identity – Trust in EU institutions FP 6 Civic. Active + + + - Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Logistic regression: Turnout EPE • Nagelkerke‘s R 2= 0. 252 • Most important predictors: – Perceived duty to vote (EU/Nat. ) – Strength of party identification – Media consumption – EU support – Internal efficacy – EU identity – Trust in EU institutions FP 6 Civic. Active + + + - Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
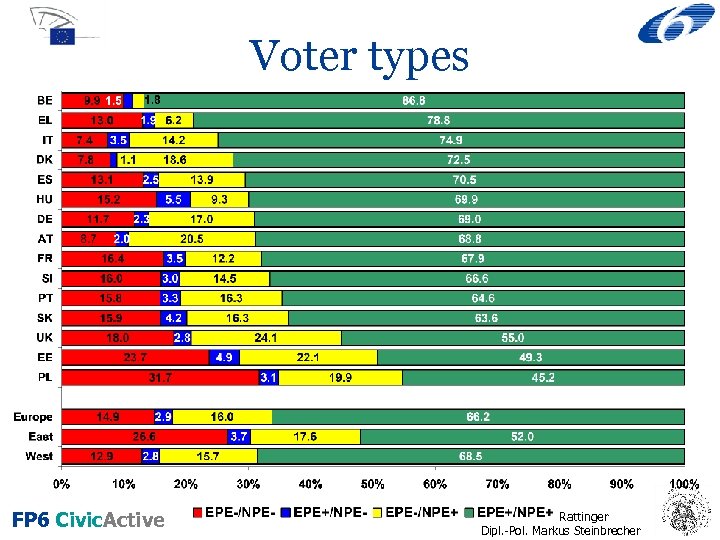 Voter types FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Voter types FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Logistic regression: EPE-only (1) versus NPE-only (0) voters • Nagelkerke‘s R 2= 0. 103 • Most important predictors: – Strength of party identification – EU Identity – Satisfaction with democracy EU – EU Benefit – Class – Perceived economic situation – Urbanisation FP 6 Civic. Active + + + - Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Logistic regression: EPE-only (1) versus NPE-only (0) voters • Nagelkerke‘s R 2= 0. 103 • Most important predictors: – Strength of party identification – EU Identity – Satisfaction with democracy EU – EU Benefit – Class – Perceived economic situation – Urbanisation FP 6 Civic. Active + + + - Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Logistic regression: EPE- and NPE-voters (1) vs. NPE-only (0) voters • Nagelkerke‘s R 2= 0. 134 • Most important predictors: – Perceived duty to vote (EU/nat. ) – Media consumption – Strength of party identification – EU Identity – EU Support – Perceived economic situation – Internal efficacy FP 6 Civic. Active + + + Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Logistic regression: EPE- and NPE-voters (1) vs. NPE-only (0) voters • Nagelkerke‘s R 2= 0. 134 • Most important predictors: – Perceived duty to vote (EU/nat. ) – Media consumption – Strength of party identification – EU Identity – EU Support – Perceived economic situation – Internal efficacy FP 6 Civic. Active + + + Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Conclusions turnout EPE • Important variables for turnout in EPE: – Perceived duty to vote – Strength of party identification – EU Identity/Support/Trust • Possibilities to boost turnout in EPE: – Raise perceived importance of European level – Emphasise duty to vote FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Conclusions turnout EPE • Important variables for turnout in EPE: – Perceived duty to vote – Strength of party identification – EU Identity/Support/Trust • Possibilities to boost turnout in EPE: – Raise perceived importance of European level – Emphasise duty to vote FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Database for analysis of civic participation • ESS, Round 1, 2002/03 • 17 EU member states: AT, BE, CZ, DE, DK, ES, FI, FR, GB, GR, HU, IE, IT, LU, NL, PT, SE, SI • 11 forms of non-electoral participation: contact politician, work in party, work in organisation, display badge, sign petition, public demonstration, boycott product, buy product, donate money, illegal protest, party member FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Database for analysis of civic participation • ESS, Round 1, 2002/03 • 17 EU member states: AT, BE, CZ, DE, DK, ES, FI, FR, GB, GR, HU, IE, IT, LU, NL, PT, SE, SI • 11 forms of non-electoral participation: contact politician, work in party, work in organisation, display badge, sign petition, public demonstration, boycott product, buy product, donate money, illegal protest, party member FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
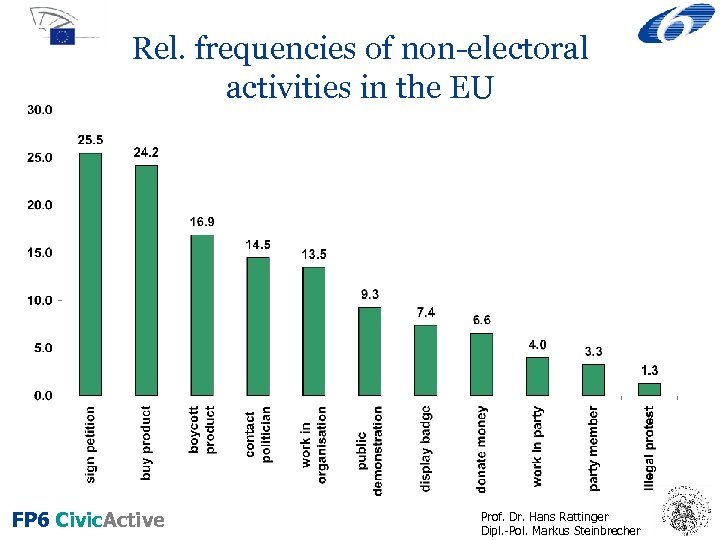 Rel. frequencies of non-electoral activities in the EU FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Rel. frequencies of non-electoral activities in the EU FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
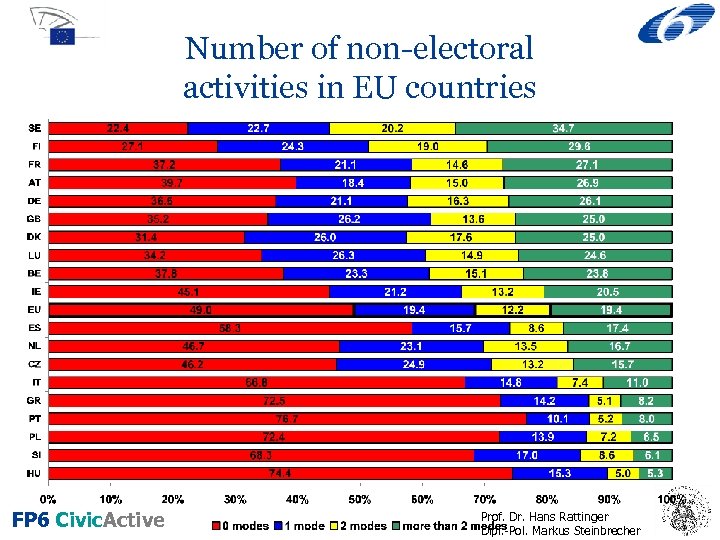 Number of non-electoral activities in EU countries FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Number of non-electoral activities in EU countries FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
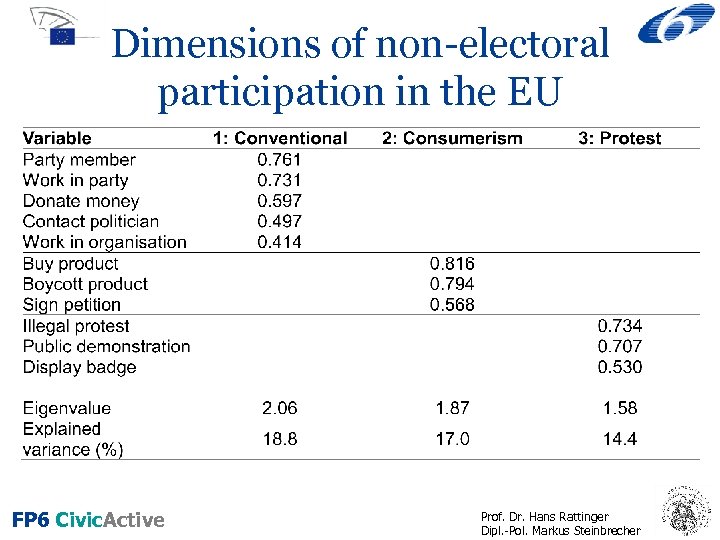 Dimensions of non-electoral participation in the EU FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Dimensions of non-electoral participation in the EU FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Multivariate regression: conventional participation • R 2= 0. 143 • Most important predictors: – Strength of party identification – Internal efficacy – Social participation – Perceived duty to participate – Interest in politics – Woman – Age FP 6 Civic. Active + + + Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Multivariate regression: conventional participation • R 2= 0. 143 • Most important predictors: – Strength of party identification – Internal efficacy – Social participation – Perceived duty to participate – Interest in politics – Woman – Age FP 6 Civic. Active + + + Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Multivariate regression: consumerism • R 2= 0. 199 • Most important predictors: – Social participation – Woman – Interest in politics – Education – Income – Internal efficacy – Left-right-scale FP 6 Civic. Active + + + Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Multivariate regression: consumerism • R 2= 0. 199 • Most important predictors: – Social participation – Woman – Interest in politics – Education – Income – Internal efficacy – Left-right-scale FP 6 Civic. Active + + + Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Multivariate regression: protest activities • R 2= 0. 034 • Most important predictors: – – – – Social participation Left-right-scale Age Strength of party identification Income Internal efficacy Religious attendance Perceived duty to participate FP 6 Civic. Active + + Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Multivariate regression: protest activities • R 2= 0. 034 • Most important predictors: – – – – Social participation Left-right-scale Age Strength of party identification Income Internal efficacy Religious attendance Perceived duty to participate FP 6 Civic. Active + + Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Multivariate regression: participation index • R 2= 0. 289 • Most important predictors: – Social participation – Internal efficacy – Strength of party identification – Interest in politics – Left-right-scale – Education – Income FP 6 Civic. Active + + + Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Multivariate regression: participation index • R 2= 0. 289 • Most important predictors: – Social participation – Internal efficacy – Strength of party identification – Interest in politics – Left-right-scale – Education – Income FP 6 Civic. Active + + + Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
 Conclusions non-electoral participation • Only minorities participate in non-electoral participation • Social participation as important predictor for all non-electoral forms of participation • Besides social participation: very heterogeneous explanations FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher
Conclusions non-electoral participation • Only minorities participate in non-electoral participation • Social participation as important predictor for all non-electoral forms of participation • Besides social participation: very heterogeneous explanations FP 6 Civic. Active Prof. Dr. Hans Rattinger Dipl. -Pol. Markus Steinbrecher


