Volodimir Vreshch Chemistry Ivano-Frankivsk 2013 Lections : 18h








8002-lecture_1_atom_structure.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Volodimir Vreshch Chemistry Ivano-Frankivsk 2013 Lections : 18h Seminars : 36h
Volodimir Vreshch Chemistry Ivano-Frankivsk 2013 Lections : 18h Seminars : 36h
 Plane 1
Plane 1
 Brief introduction 2 LED devices Solar cells Li+ battery Chemistry is the study of the composition, Properties and behavior of matter.
Brief introduction 2 LED devices Solar cells Li+ battery Chemistry is the study of the composition, Properties and behavior of matter.
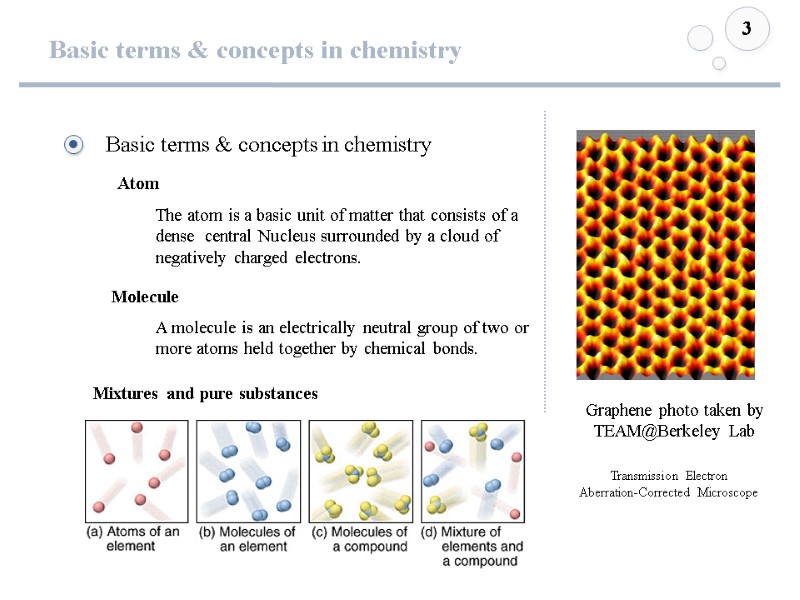
 Basic terms & concepts in chemistry 3 Atom Molecule The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central Nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. Graphene photo taken by TEAM@Berkeley Lab Mixtures and pure substances Transmission Electron Aberration-Corrected Microscope A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
Basic terms & concepts in chemistry 3 Atom Molecule The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central Nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. Graphene photo taken by TEAM@Berkeley Lab Mixtures and pure substances Transmission Electron Aberration-Corrected Microscope A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
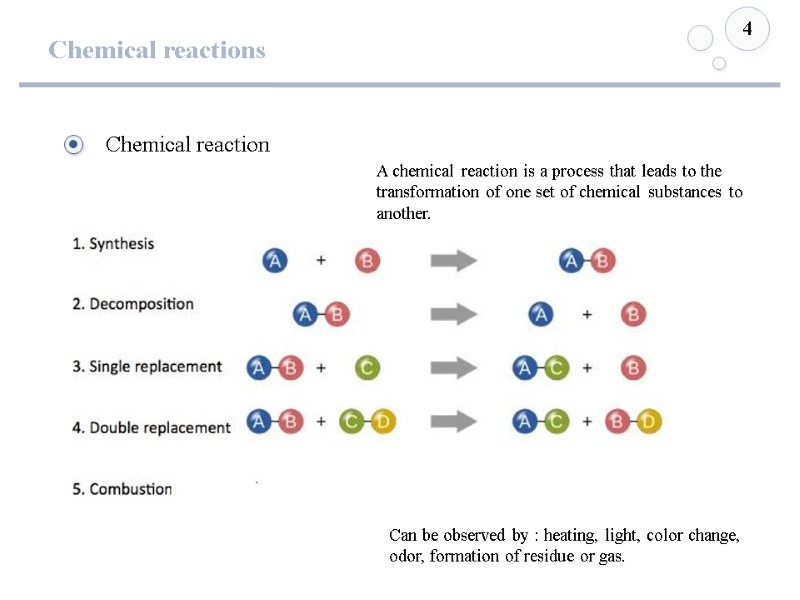
 Chemical reactions 4 A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Can be observed by : heating, light, color change, odor, formation of residue or gas.
Chemical reactions 4 A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Can be observed by : heating, light, color change, odor, formation of residue or gas.
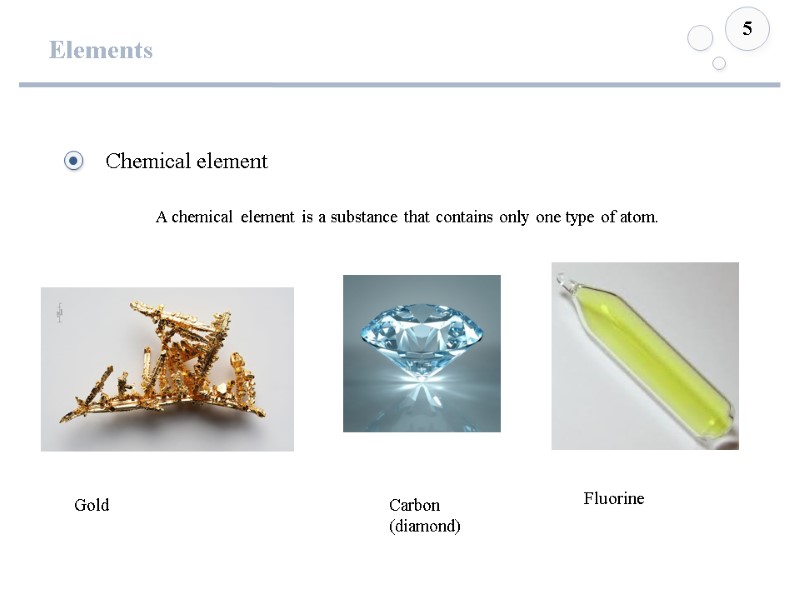
 Elements 5 Gold Carbon (diamond) Fluorine A chemical element is a substance that contains only one type of atom.
Elements 5 Gold Carbon (diamond) Fluorine A chemical element is a substance that contains only one type of atom.
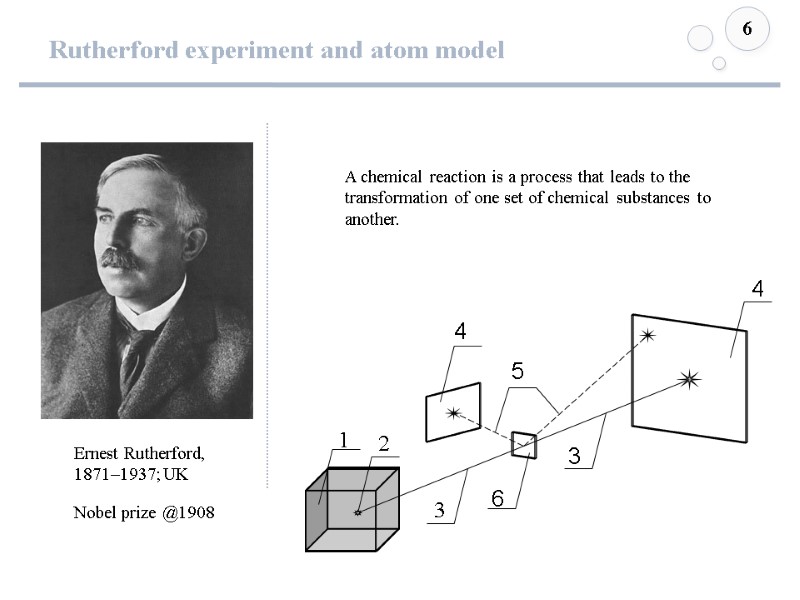
 Rutherford experiment and atom model 6 A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Ernest Rutherford, 1871–1937; UK Nobel prize @1908
Rutherford experiment and atom model 6 A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Ernest Rutherford, 1871–1937; UK Nobel prize @1908
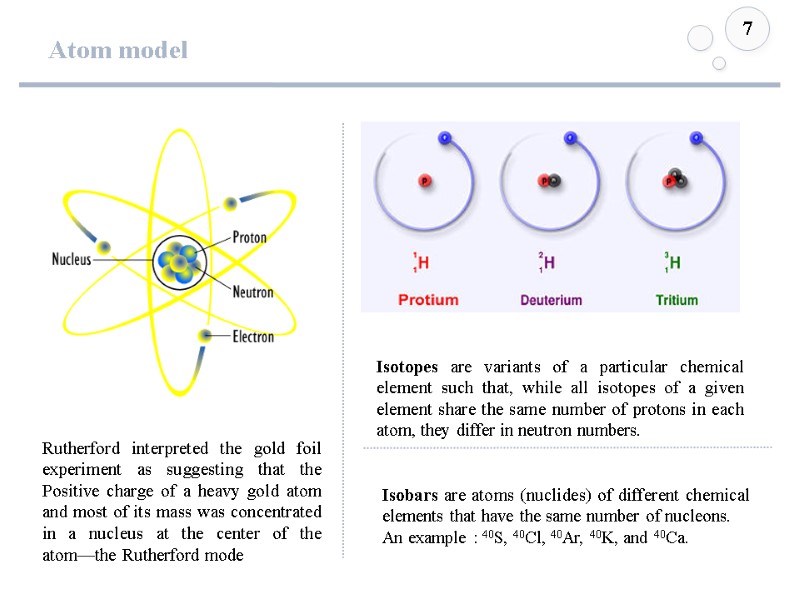
 Atom model 7 Rutherford interpreted the gold foil experiment as suggesting that the Positive charge of a heavy gold atom and most of its mass was concentrated in a nucleus at the center of the atom—the Rutherford mode Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element such that, while all isotopes of a given element share the same number of protons in each atom, they differ in neutron numbers. Isobars are atoms (nuclides) of different chemical elements that have the same number of nucleons. An example : 40S, 40Cl, 40Ar, 40K, and 40Ca.
Atom model 7 Rutherford interpreted the gold foil experiment as suggesting that the Positive charge of a heavy gold atom and most of its mass was concentrated in a nucleus at the center of the atom—the Rutherford mode Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element such that, while all isotopes of a given element share the same number of protons in each atom, they differ in neutron numbers. Isobars are atoms (nuclides) of different chemical elements that have the same number of nucleons. An example : 40S, 40Cl, 40Ar, 40K, and 40Ca.
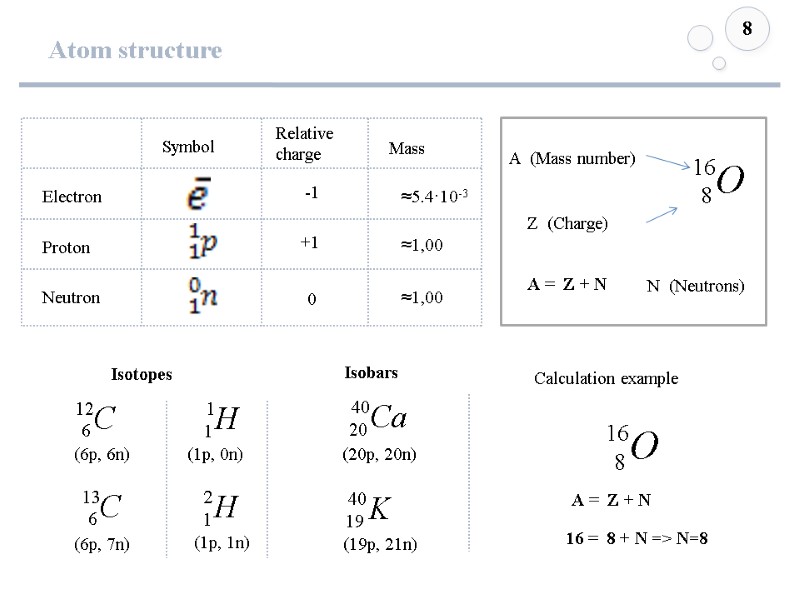
 Atom structure 8 Z (Charge) A (Mass number) A = Z + N N (Neutrons) Isotopes Isobars (6p, 6n) (6p, 7n) (1p, 0n) (1p, 1n) (20p, 20n) (19p, 21n) A = Z + N 16 = 8 + N => N=8 Calculation example
Atom structure 8 Z (Charge) A (Mass number) A = Z + N N (Neutrons) Isotopes Isobars (6p, 6n) (6p, 7n) (1p, 0n) (1p, 1n) (20p, 20n) (19p, 21n) A = Z + N 16 = 8 + N => N=8 Calculation example
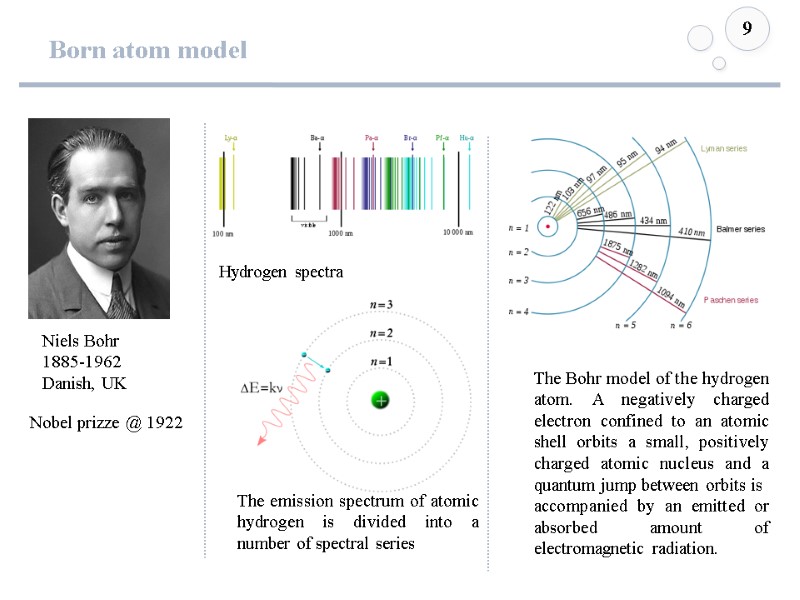
 Born atom model 9 The emission spectrum of atomic hydrogen is divided into a number of spectral series The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. A negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell orbits a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and a quantum jump between orbits is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic radiation. Niels Bohr 1885-1962 Danish, UK Nobel prizze @ 1922 Hydrogen spectra
Born atom model 9 The emission spectrum of atomic hydrogen is divided into a number of spectral series The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. A negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell orbits a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and a quantum jump between orbits is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic radiation. Niels Bohr 1885-1962 Danish, UK Nobel prizze @ 1922 Hydrogen spectra
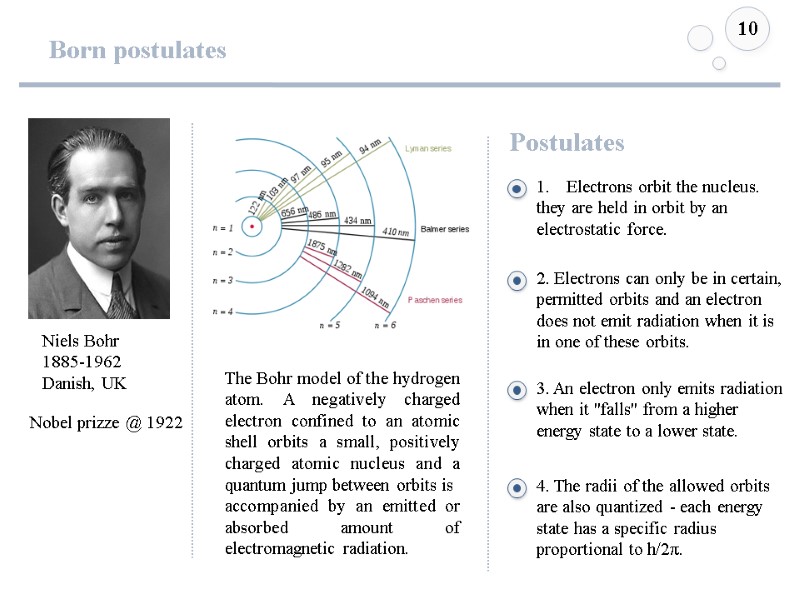
 Born postulates 10 The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. A negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell orbits a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and a quantum jump between orbits is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic radiation. Niels Bohr 1885-1962 Danish, UK Nobel prizze @ 1922 Electrons orbit the nucleus. they are held in orbit by an electrostatic force. Postulates
Born postulates 10 The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. A negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell orbits a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and a quantum jump between orbits is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic radiation. Niels Bohr 1885-1962 Danish, UK Nobel prizze @ 1922 Electrons orbit the nucleus. they are held in orbit by an electrostatic force. Postulates
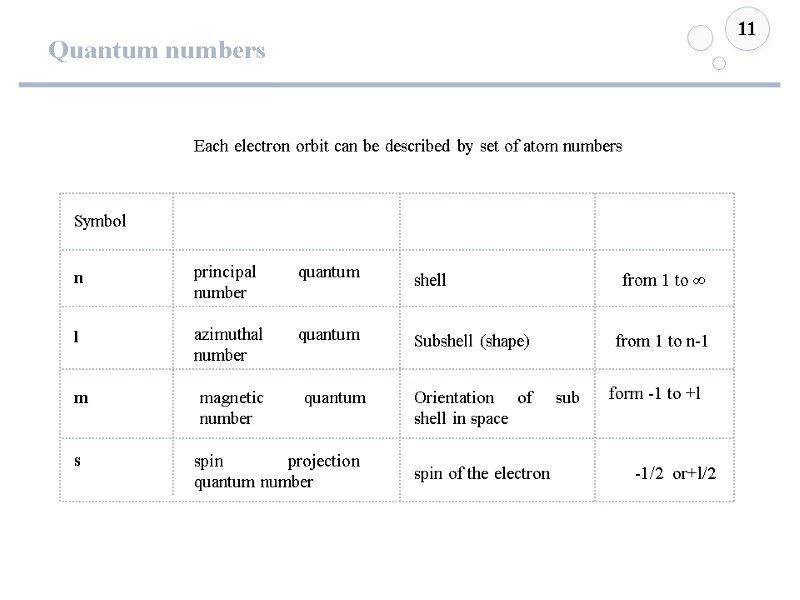
 Quantum numbers 11 Each electron orbit can be described by set of atom numbers l m n Symbol from 1 to ∞ from 1 to n-1 form -1 to +l s -1/2 or+l/2 principal quantum number azimuthal quantum number magnetic quantum number spin projection quantum number shell Subshell (shape) Orientation of sub shell in space spin of the electron
Quantum numbers 11 Each electron orbit can be described by set of atom numbers l m n Symbol from 1 to ∞ from 1 to n-1 form -1 to +l s -1/2 or+l/2 principal quantum number azimuthal quantum number magnetic quantum number spin projection quantum number shell Subshell (shape) Orientation of sub shell in space spin of the electron
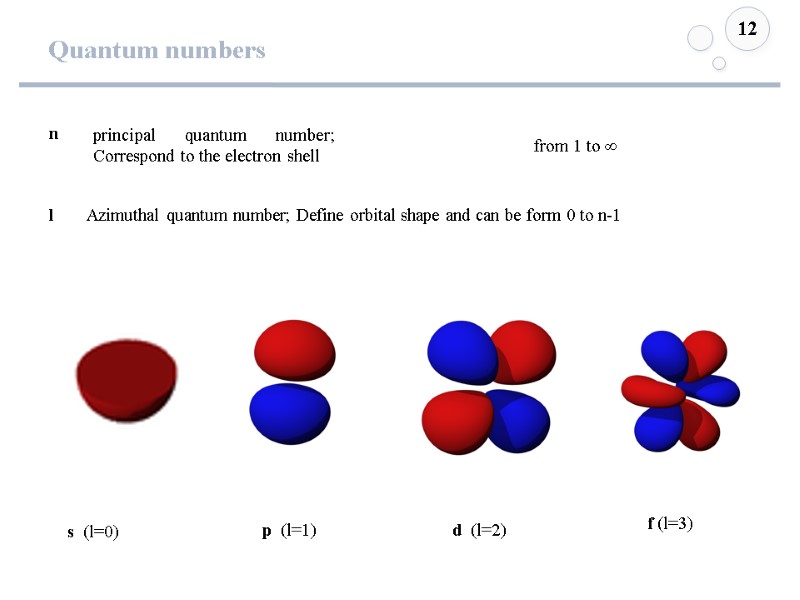
 Quantum numbers 12 n principal quantum number; Correspond to the electron shell s (l=0) Azimuthal quantum number; Define orbital shape and can be form 0 to n-1 from 1 to ∞ p (l=1) d (l=2) f (l=3) l
Quantum numbers 12 n principal quantum number; Correspond to the electron shell s (l=0) Azimuthal quantum number; Define orbital shape and can be form 0 to n-1 from 1 to ∞ p (l=1) d (l=2) f (l=3) l
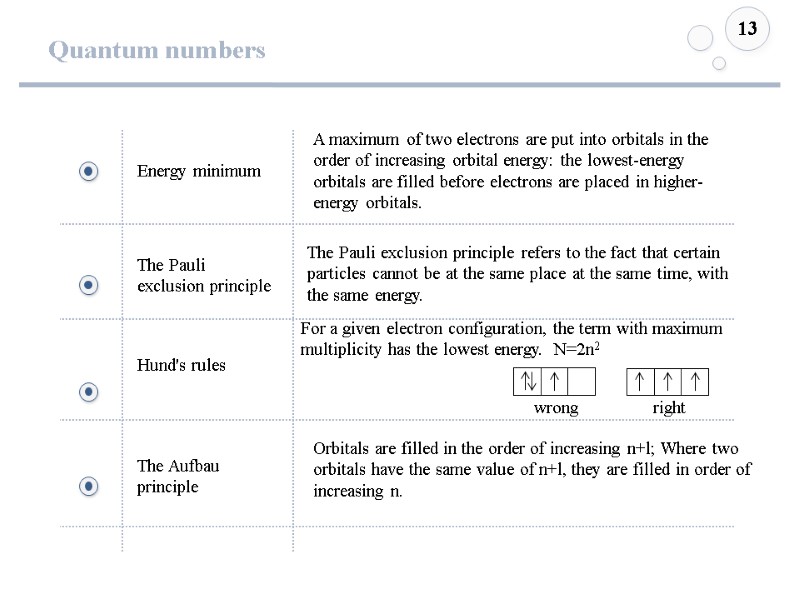
 Quantum numbers 13 Energy minimum The Pauli exclusion principle Hund's rules The Aufbau principle The Pauli exclusion principle refers to the fact that certain particles cannot be at the same place at the same time, with the same energy. For a given electron configuration, the term with maximum multiplicity has the lowest energy. N=2n2 A maximum of two electrons are put into orbitals in the order of increasing orbital energy: the lowest-energy orbitals are filled before electrons are placed in higher-energy orbitals. Orbitals are filled in the order of increasing n+l; Where two orbitals have the same value of n+l, they are filled in order of increasing n. wrong right
Quantum numbers 13 Energy minimum The Pauli exclusion principle Hund's rules The Aufbau principle The Pauli exclusion principle refers to the fact that certain particles cannot be at the same place at the same time, with the same energy. For a given electron configuration, the term with maximum multiplicity has the lowest energy. N=2n2 A maximum of two electrons are put into orbitals in the order of increasing orbital energy: the lowest-energy orbitals are filled before electrons are placed in higher-energy orbitals. Orbitals are filled in the order of increasing n+l; Where two orbitals have the same value of n+l, they are filled in order of increasing n. wrong right
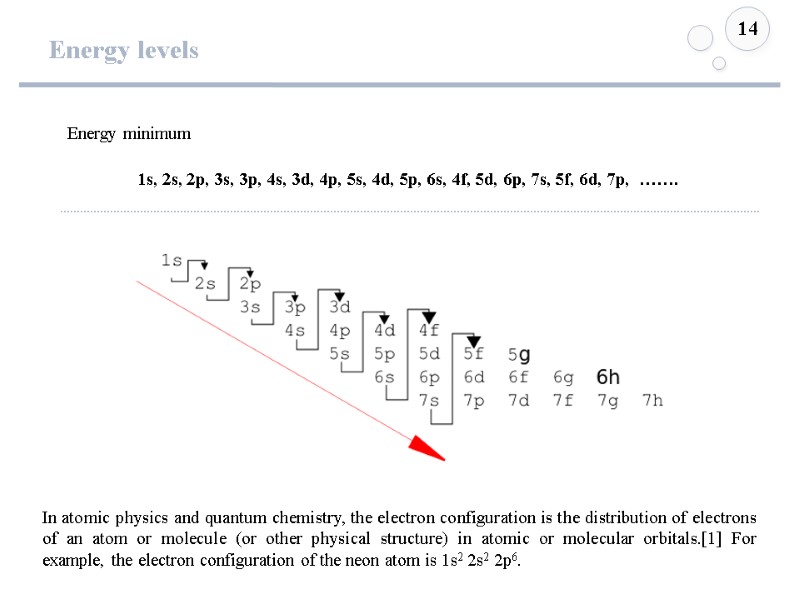
 Energy levels 14 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p, ……. Energy minimum In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals.[1] For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.
Energy levels 14 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p, ……. Energy minimum In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals.[1] For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.
 Energy levels 15 Example: 1Н І period, 1s1 3Lі ІІ period, 1s22s1 17Cl ІІІ period, VII група, 1s22s22p63s23p5 23V ІV period, 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d3 38Sr V period, 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p65s2 57Lа VІ period, 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p66s25d1 Graphical formula of the oxygen atom : 8О ІІ period, VI group, 1s22s22p4
Energy levels 15 Example: 1Н І period, 1s1 3Lі ІІ period, 1s22s1 17Cl ІІІ period, VII група, 1s22s22p63s23p5 23V ІV period, 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d3 38Sr V period, 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p65s2 57Lа VІ period, 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p66s25d1 Graphical formula of the oxygen atom : 8О ІІ period, VI group, 1s22s22p4
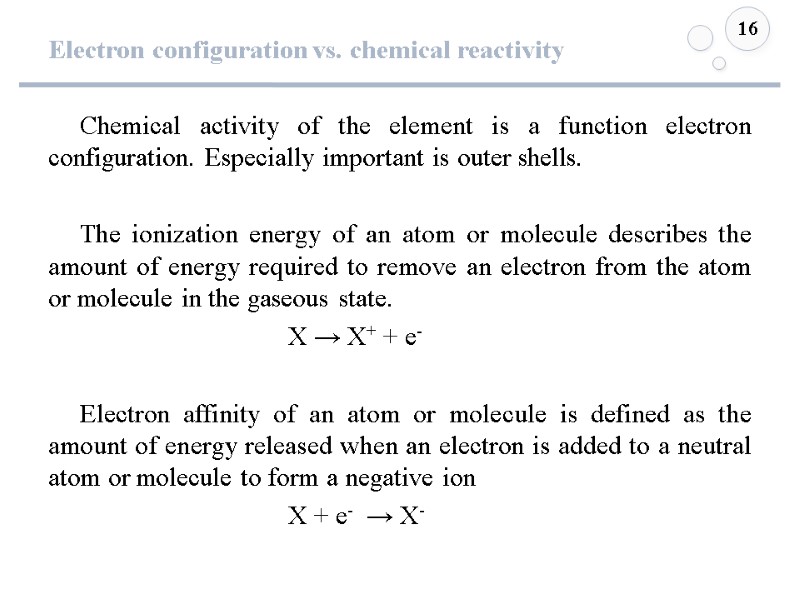
 Electron configuration vs. chemical reactivity 16 Chemical activity of the element is a function electron configuration. Especially important is outer shells. The ionization energy of an atom or molecule describes the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the atom or molecule in the gaseous state. X → X+ + e- Electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule to form a negative ion X + e- → X-
Electron configuration vs. chemical reactivity 16 Chemical activity of the element is a function electron configuration. Especially important is outer shells. The ionization energy of an atom or molecule describes the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the atom or molecule in the gaseous state. X → X+ + e- Electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule to form a negative ion X + e- → X-
 Electron configuration vs. chemical reactivity 17 Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself Sulfur : 2.58 Beryllium : 1.57 Metal Nonmetal
Electron configuration vs. chemical reactivity 17 Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself Sulfur : 2.58 Beryllium : 1.57 Metal Nonmetal
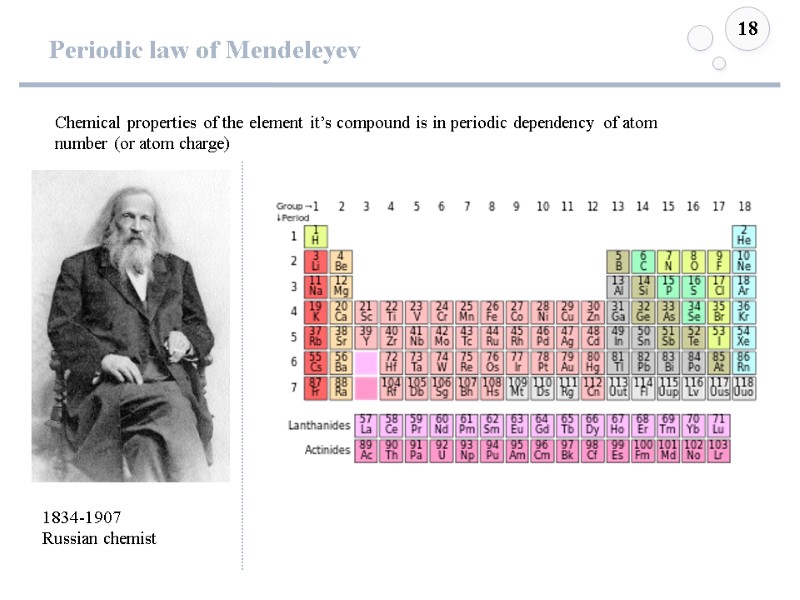
 Periodic law of Mendeleyev 18 1834-1907 Russian chemist Chemical properties of the element it’s compound is in periodic dependency of atom number (or atom charge)
Periodic law of Mendeleyev 18 1834-1907 Russian chemist Chemical properties of the element it’s compound is in periodic dependency of atom number (or atom charge)
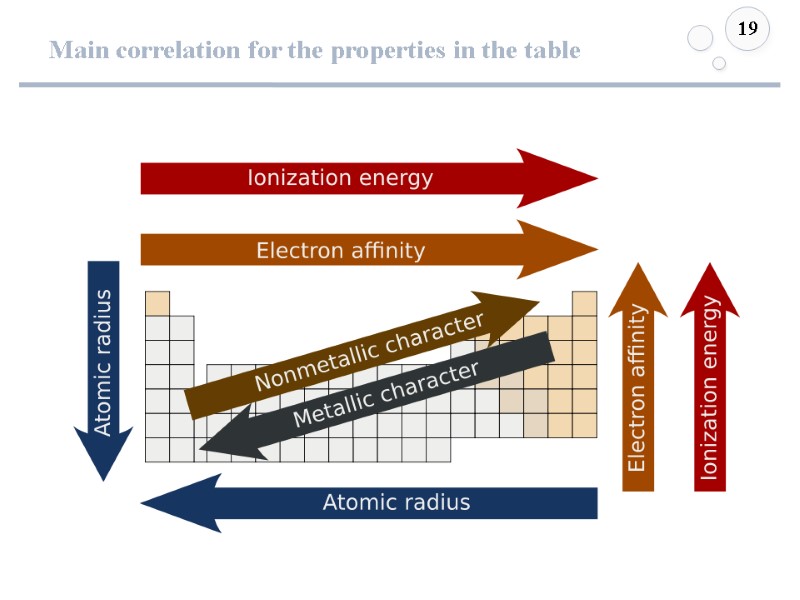
 Main correlation for the properties in the table 19
Main correlation for the properties in the table 19
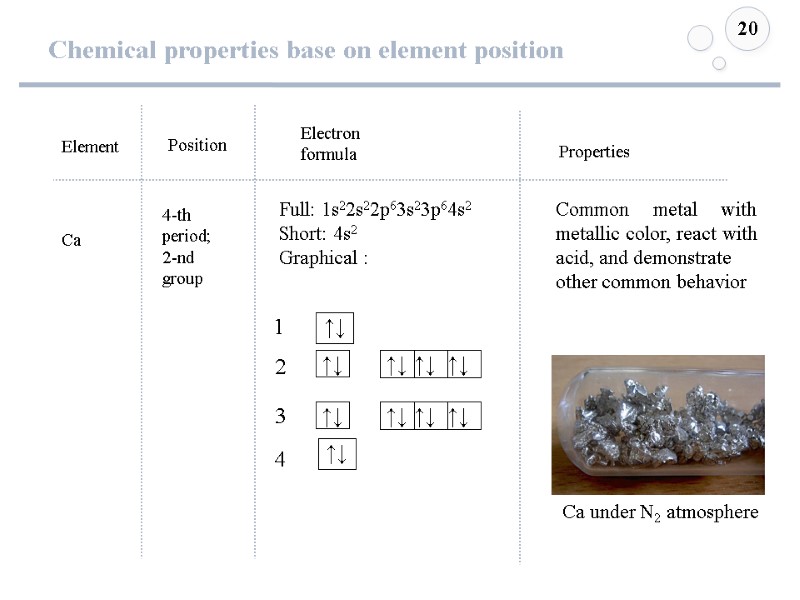
 Chemical properties base on element position 20 Element Ca Position Electron formula 4-th period; 2-nd group Full: 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 Short: 4s2 Graphical : ↑↓ ↑↓ Properties Common metal with metallic color, react with acid, and demonstrate other common behavior Ca under N2 atmosphere
Chemical properties base on element position 20 Element Ca Position Electron formula 4-th period; 2-nd group Full: 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 Short: 4s2 Graphical : ↑↓ ↑↓ Properties Common metal with metallic color, react with acid, and demonstrate other common behavior Ca under N2 atmosphere
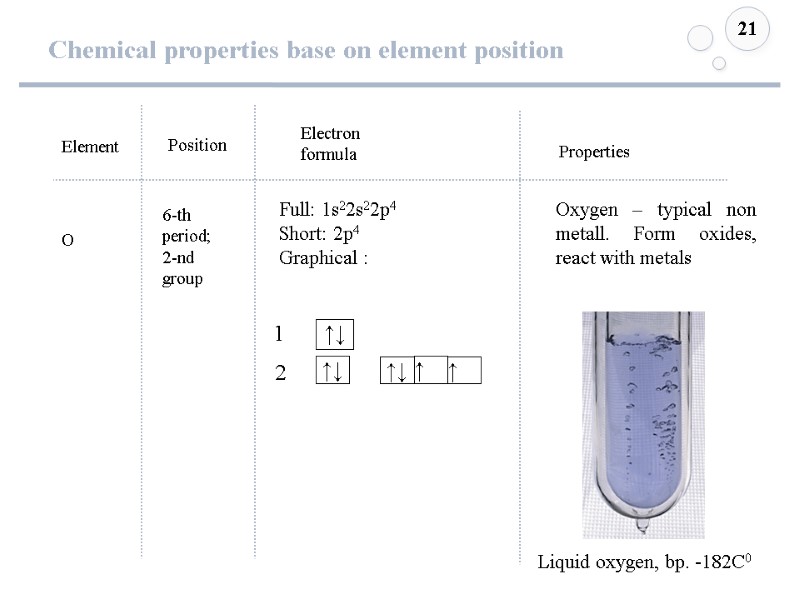
 Chemical properties base on element position 21 Element O Position Electron formula 6-th period; 2-nd group Full: 1s22s22p4 Short: 2p4 Graphical : Properties Oxygen – typical non metall. Form oxides, react with metals Liquid oxygen, bp. -182C0
Chemical properties base on element position 21 Element O Position Electron formula 6-th period; 2-nd group Full: 1s22s22p4 Short: 2p4 Graphical : Properties Oxygen – typical non metall. Form oxides, react with metals Liquid oxygen, bp. -182C0
 Must to remember:
Must to remember:
 Please, be prepared for the test Questions for the test : Calculate : protons, neutrons, and electrons for certain element Isotopes, and Isobars : be able to reveal and provide with examples Electron configuration : be able to write it down for each element Periodic law : main correlation based on the table, it’s connection with electronic configuration
Please, be prepared for the test Questions for the test : Calculate : protons, neutrons, and electrons for certain element Isotopes, and Isobars : be able to reveal and provide with examples Electron configuration : be able to write it down for each element Periodic law : main correlation based on the table, it’s connection with electronic configuration

