Bioelectricity_12.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 109

ВЛИЯНИЕ ЭЛЕКТРОМАГНИТН ЫХ ПОЛЕЙ НА ОРГАНИЗМ Лечебное воздействие

Magnet Therapy Although they may seem magical in their capacity to heal, magnets are not magic. Magnet Therapy assists the body to regain its self healing balance. “Lack of magnetism may cause stress, mental disorders, headaches, arthritis, muscle pain, chronic fatigue, allergies, insomnia, inflammation, bowel disorders and many other degenerative diseases afflicting people today. Ken Wianco, MD, FRCS(C) FACS “In man’s search for a universal cure-all, none fits the description nearly as well as magnetic energy fields. ” Medical Magnets by Barbara Gordon, Magnetic Therapist

Serenity 2000 Magnetic Bracelets Jupiter Serenity 2000 carries a large variety of magnetic bracelets to suit every taste and budget. Some Important Benefits Relieves any type of pain in Improves energy & stamina. the hand, wrist, elbow, arm Accelerates recovery from and shoulder. stroke related paralysis. Helps lower/stabilize blood Helps relieve motion pressure. Relieves stress & sickness & jetlag. anxiety.

Serenity 2000 Magnetic Necklaces Many attractive styles to choose from – effective magnetic therapy. Some Important Benefits Relieves any type of pain in the neck, shoulder, upper back. E. g. whiplash, fibromyalgia, arthritis. Helps improve circulation in the head and upper body. Improves energy & stamina. Chronic Fatigue. Helps relieve sinus congestion. Prevents headaches, reduces the frequency and/or severity of migraines.

Serenity 2000 Magnetic Supports & Insoles Some Important Benefits Helps relieve pain and swelling. Accelerates healing & recovery from injury. Provides good, adjustable support. Easy & Comfortable to wear. Washable

Serenity 2000 Magnetic Hairbrush All the bristles are magnetized! Some Important Benefits Thicker, more luxurious hair. Improves circulation in the head and scalp. Magnetic Earrings Held on by magnetic attraction. No need for pierced ears! Some Important Benefits Helps control appetite and cravings. Slows and reverses graying. Stimulates important acupuncture points on the ear. Accelerates hair growth and helps reduce hair loss. May help ringing in the ears, dizziness, nausea.

Serenity 2000 Magnetic Mask Some Important Benefits 12 powerful sewn in magnets. Helps relieve most eye conditions. Promotes deep, restorative sleep. Promotes relaxation. Helps relieve/prevent headaches/migraines Soothing, luxurious inner lining Adjustable satin strap One size fits all Use on any area of the face or under chin for better complexion, younger looking skin Helps relieve sinus congestion.

Serenity 2000 Multi Purpose Magnets Deep Therapy Kit Super Bio-Mags Bar Magnet Some Important Benefits Powerful magnets to be used on any area of the body. Depending on desired penetration, choose any or all three of the above. Relieves chronic or occasional pain. Improved circulation. Accelerated healing.

Serenity 2000 Magnetic Pads & Cushions Availabl e in: Twin, Full, Queen, King Sleep Systems Magnet Therapy Pad Twin Full Queen King Foam Seat Cushion Some Important Benefits Each of these products provides a uniform North Pole magnetic field with over 20” penetration. Relax & fall asleep faster. Deep, rejuvenating sleep – wake up re-energized, re-balanced. Pain relief from most chronic conditions including arthritis, fibromyalgia etc. Improves circulation throughout the body. Accelerates recovery from illness and injury.

Serenity 2000 Magnetic Water Treatment Magnetic Mug Single Line Some Important Benefits Whole House Better digestion. Improved elimination of toxins. Helps prevents kidney stones, gallbladder stones, arterial sclerosis. More efficient absorption of nutrients from food and supplements. Improves the taste of water. Saves on laundry & cleaning products. Helps prevent scale buildup in pipes and appliances, cuts down energy costs.

Serenity 2000 Magnetic Pet Collars Magnetic Pet Pads Small 18” Round Large 24”X 36” High grade ceramic magnets sewn into durable nylon collar. Available in 4 adjustable sizes Premium strength magnets cushioned in high grade foam with luxurious faux fur cover Some Important Benefits Helps relieve any type of muscle or joint pain. Accelerates recovery from illness or injury. Ensures good health, vitality and balance for your pet.

Первичное действие постоянного тока связано с движением ионов, их пространственным разделением и изменением концентраций в тканях. Поэтому прохождение электрического тока через биоткани как проводник второго рода (электролит) сопровождается явлением электролиза. Масса вещества, которая выделяется на электродах при прохождении тока через электролит, пропорциональна величине перенесенного заряда и может быть описана первым законом электролиза Фарадея M = K·q = K·I· t K = A/(F·Z), где q – заряд, t – время протекания тока, К – коэффициент пропорциональности, F – число Фарадея, А – атомный вес, Z – валентность вещества ионов. Для живых тканей закон электролиза выполняется условно, поэтому более справедливо выражение M ~ K·I·t. Рассмотрим некоторые примеры использования постоянных токов в медицине для диагностических и терапевтических целей.
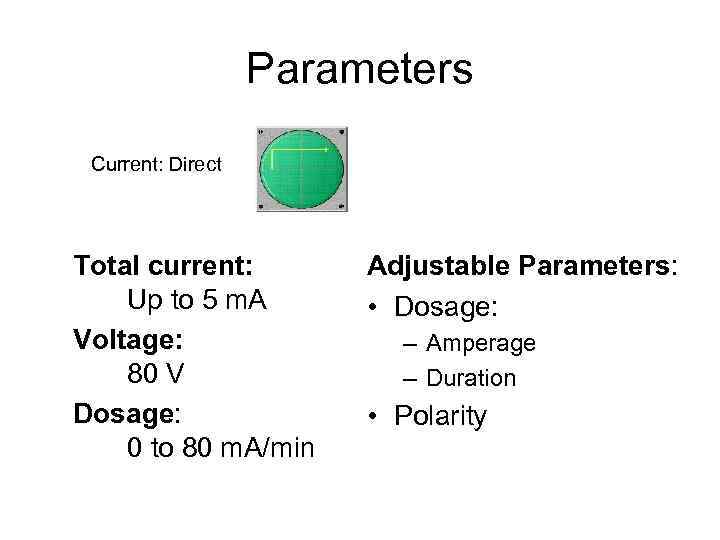
Parameters Current: Direct Total current: Up to 5 m. A Voltage: 80 V Dosage: 0 to 80 m. A/min Adjustable Parameters: • Dosage: – Amperage – Duration • Polarity
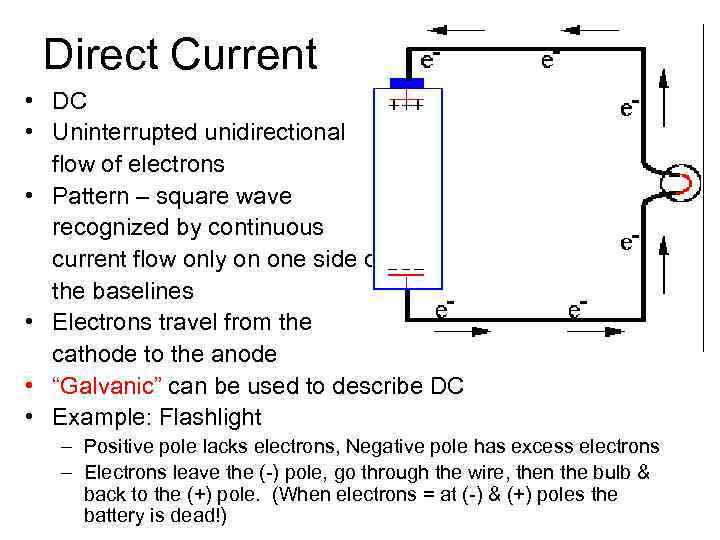
Direct Current • DC • Uninterrupted unidirectional flow of electrons • Pattern – square wave recognized by continuous current flow only on one side of the baselines • Electrons travel from the cathode to the anode • “Galvanic” can be used to describe DC • Example: Flashlight – Positive pole lacks electrons, Negative pole has excess electrons – Electrons leave the (-) pole, go through the wire, then the bulb & back to the (+) pole. (When electrons = at (-) & (+) poles the battery is dead!)
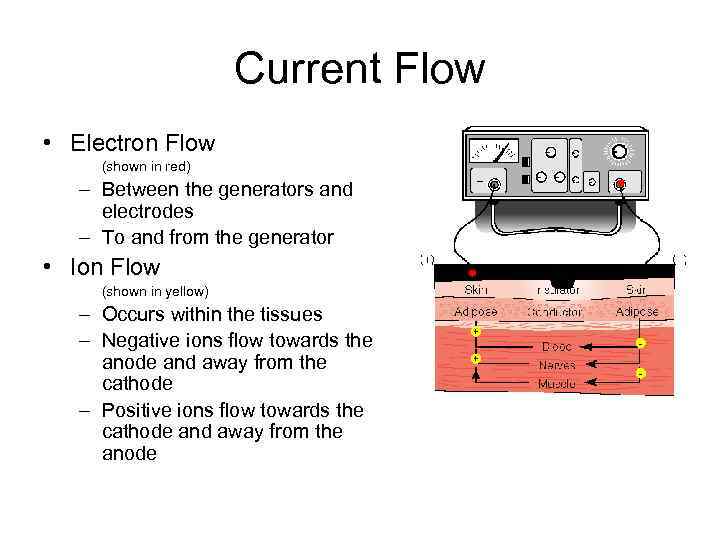
Current Flow • Electron Flow (shown in red) – Between the generators and electrodes – To and from the generator • Ion Flow (shown in yellow) – Occurs within the tissues – Negative ions flow towards the anode and away from the cathode – Positive ions flow towards the cathode and away from the anode + + -

Polarity • Anode – Positive Electrode With Lowest Concentration of Electrons • Cathode – Negative Electrode With Greatest Concentration of Electrons • Polarity Switch Designates One Electrode As Positive and One As Negative

What happens in the Body? • Cathode – p. H becomes basic (greater than 7) • Anode – p. H becomes acidic (less than 7) • Na+ move towards cathode, picks up an electron, & through reaction with H 2 O, liquefies proteins, causing a general softening of the tissues in the area & a decrease in nerve irritability • Tissues under anode harden because chemical mediators for a coagulation of protein • Effects not as pronounced when monophasic, biphasic or AC are used • Na+ moves from inside the cell to the outside the cell allowing K+ to move into the cell (Sodiumpotassium pump)
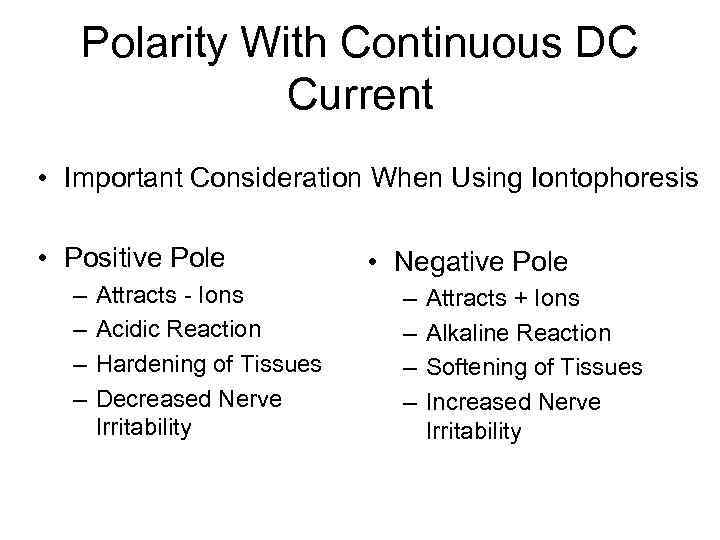
Polarity With Continuous DC Current • Important Consideration When Using Iontophoresis • Positive Pole – – Attracts - Ions Acidic Reaction Hardening of Tissues Decreased Nerve Irritability • Negative Pole – – Attracts + Ions Alkaline Reaction Softening of Tissues Increased Nerve Irritability
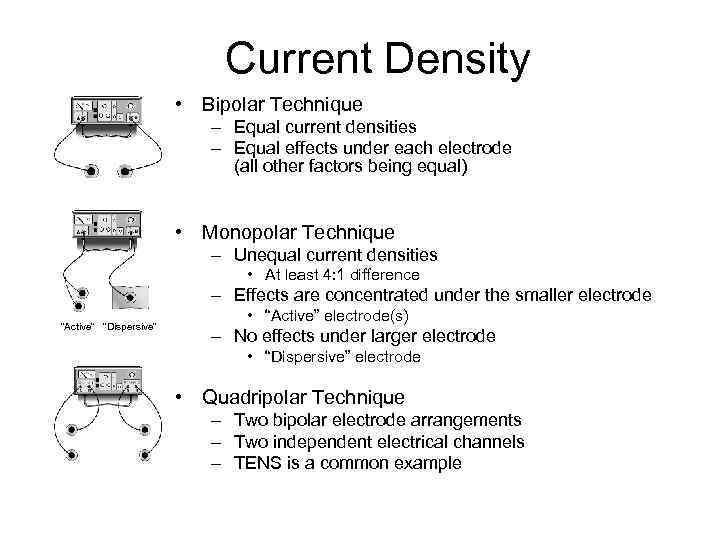
Current Density • Bipolar Technique – Equal current densities – Equal effects under each electrode (all other factors being equal) • Monopolar Technique – Unequal current densities • At least 4: 1 difference – Effects are concentrated under the smaller electrode “Active” “Dispersive” • “Active” electrode(s) – No effects under larger electrode • “Dispersive” electrode • Quadripolar Technique – Two bipolar electrode arrangements – Two independent electrical channels – TENS is a common example
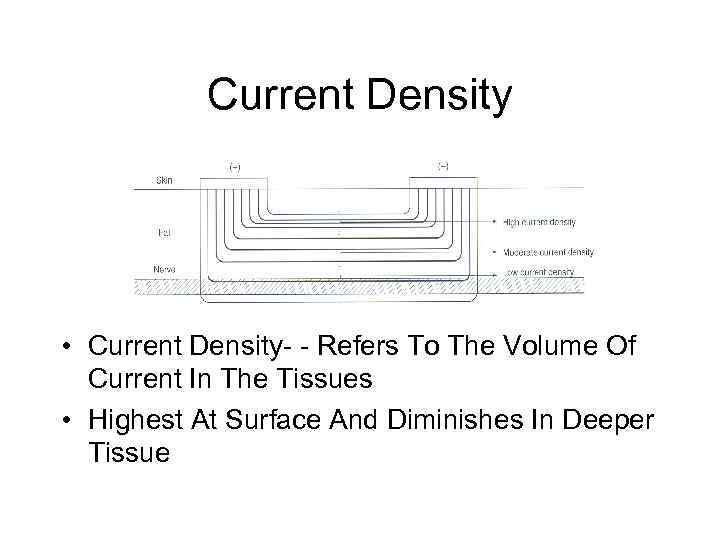
Current Density • Current Density- - Refers To The Volume Of Current In The Tissues • Highest At Surface And Diminishes In Deeper Tissue

Altering Current Density • Change The Spacing Of Electrodes – Moving Further Apart Increases Current Density In Deeper Tissues
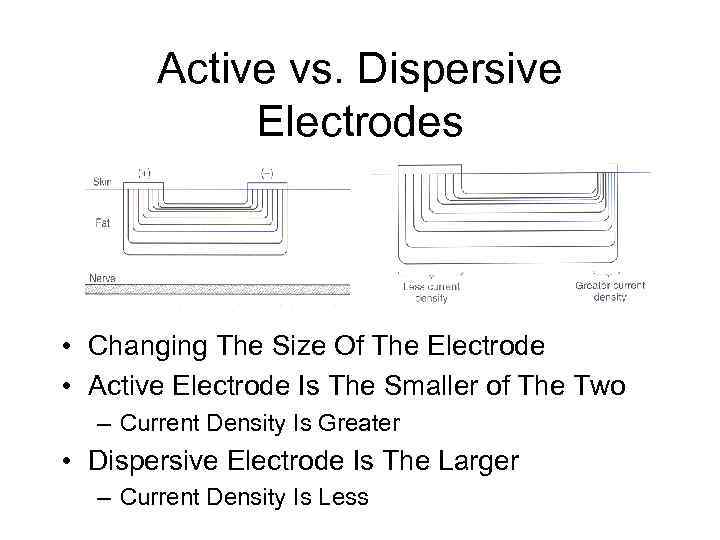
Active vs. Dispersive Electrodes • Changing The Size Of The Electrode • Active Electrode Is The Smaller of The Two – Current Density Is Greater • Dispersive Electrode Is The Larger – Current Density Is Less
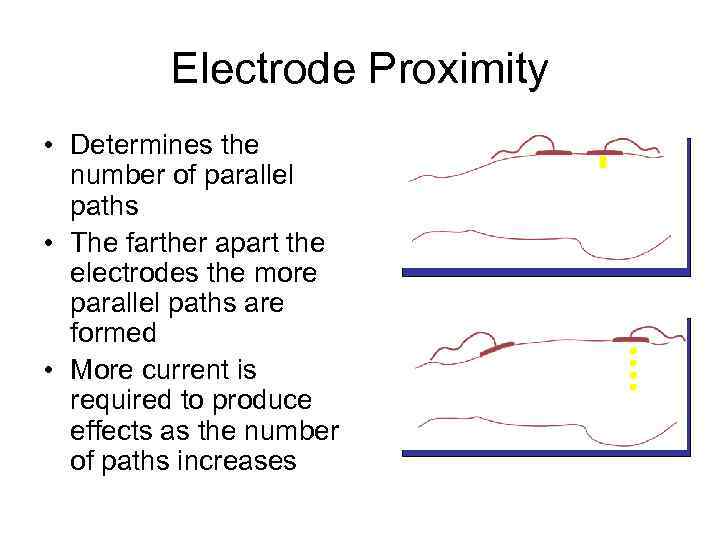
Electrode Proximity • Determines the number of parallel paths • The farther apart the electrodes the more parallel paths are formed • More current is required to produce effects as the number of paths increases

Path of Least Resistance • Ion flow will follow the path of least resistance – Nerves – Blood vessels • The current usually does not flow from electrode-toelectrode (the shortest path) • The path of least resistance is not necessarily the shortest path
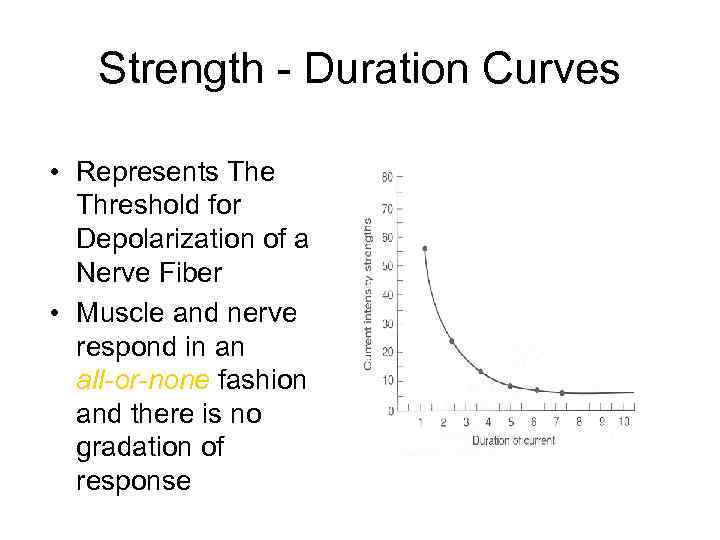
Strength - Duration Curves • Represents The Threshold for Depolarization of a Nerve Fiber • Muscle and nerve respond in an all-or-none fashion and there is no gradation of response
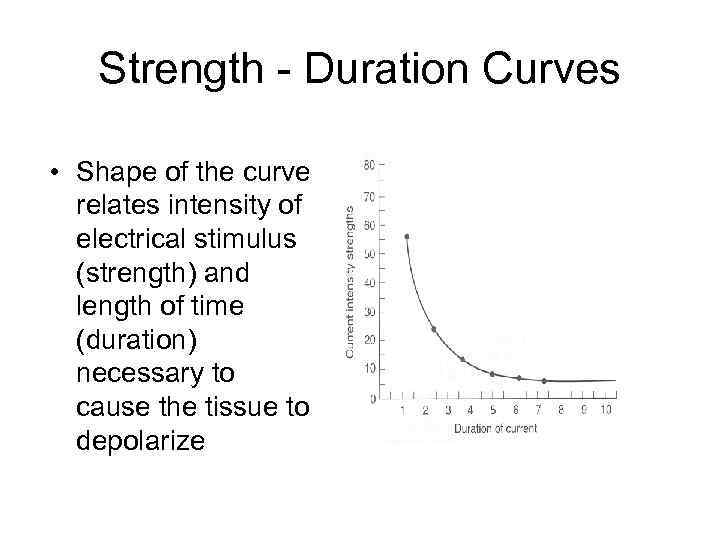
Strength - Duration Curves • Shape of the curve relates intensity of electrical stimulus (strength) and length of time (duration) necessary to cause the tissue to depolarize
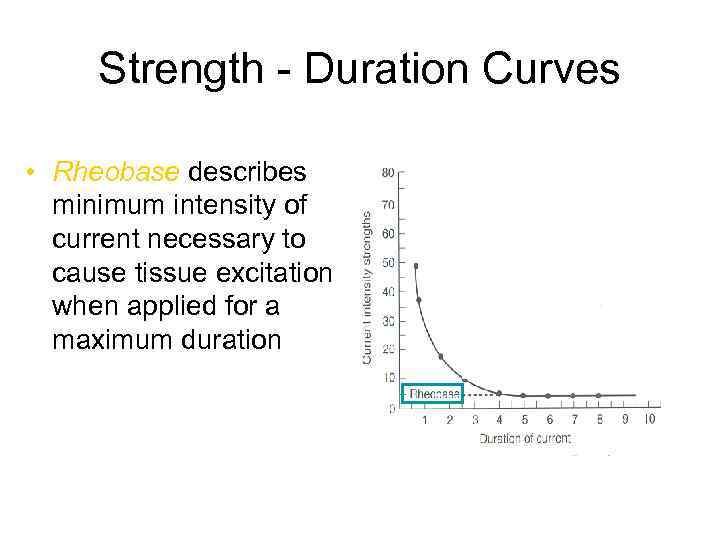
Strength - Duration Curves • Rheobase describes minimum intensity of current necessary to cause tissue excitation when applied for a maximum duration
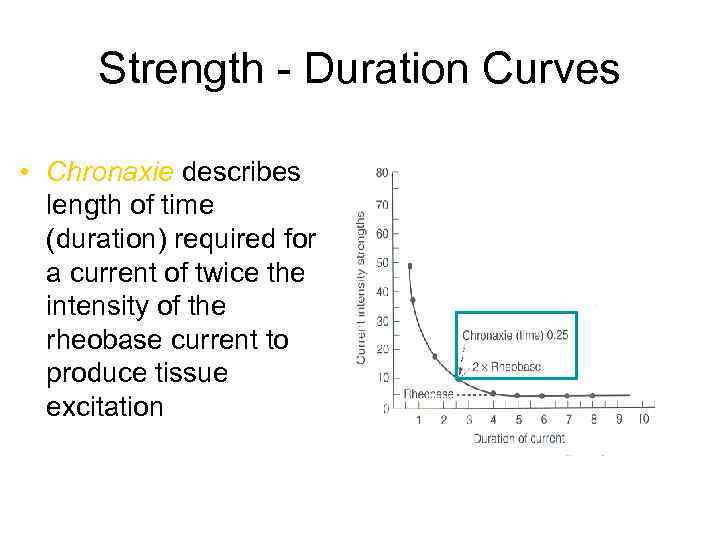
Strength - Duration Curves • Chronaxie describes length of time (duration) required for a current of twice the intensity of the rheobase current to produce tissue excitation
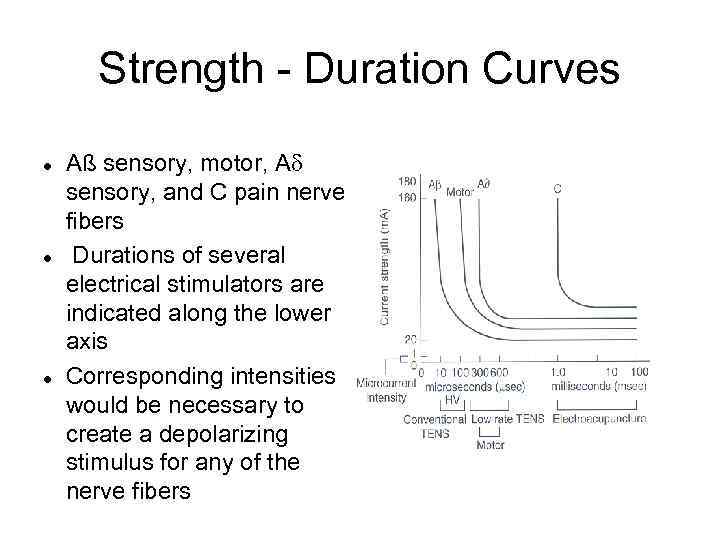
Strength - Duration Curves l l l Aß sensory, motor, A sensory, and C pain nerve fibers Durations of several electrical stimulators are indicated along the lower axis Corresponding intensities would be necessary to create a depolarizing stimulus for any of the nerve fibers


Гальванизация воздействие на пациента с лечебной целью постоянного электрического тока величиной до 50 м. А, плотностью тока не более 0, 1 м. А/см 2 и напряжением до 80 В. Проводится с помощью электродов, подключенных к источнику постоянного тока и накладываемых на кожу пациента. Основные биофизические эффекты, которые достигаются при гальванизации: • - внутритканевый электрофорез перемещения ионов, молекул под действием внешнего электрического поля; • - изменение мембранного потенциала клеток, возбудимости тканей, образование свободных радикалов; • - усиление микроциркуляции крови и лимфы.

Лекарственный электрофорез одновременное воздействие на организм постоянного электрического тока и лекарственного вещества, поступающего в организм с током через кожные покровы или слизистые оболочки. При электрофорезе между электродом и кожей помещают прокладку или гель, содержащие раствор лекарственного вещества. Обязательным требованием является диссоциация вещества на ионы в растворе. Лекарственные вещества, введенные с помощью постоянного тока, образуют кожно-ионное «депо» , из которого посредством крово - и лимфотока распределяются по всему организму.
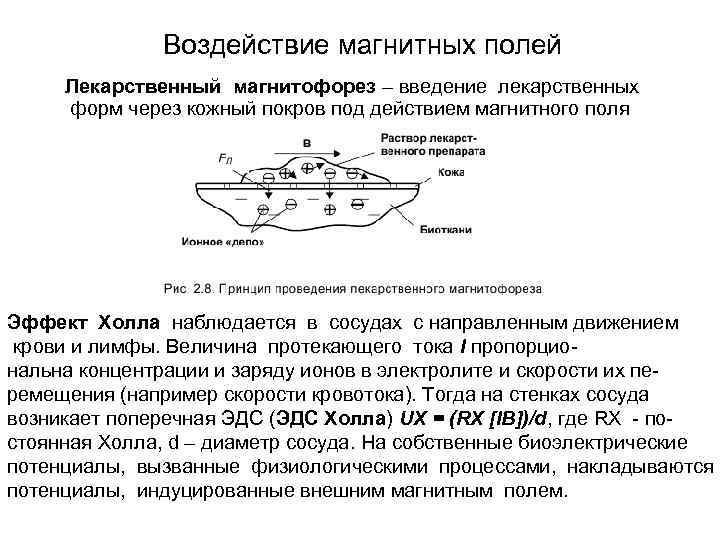
Воздействие магнитных полей Лекарственный магнитофорез – введение лекарственных форм через кожный покров под действием магнитного поля Эффект Холла наблюдается в сосудах с направленным движением крови и лимфы. Величина протекающего тока I пропорциональна концентрации и заряду ионов в электролите и скорости их перемещения (например скорости кровотока). Тогда на стенках сосуда возникает поперечная ЭДС (ЭДС Холла) UХ = (RХ [IB])/d, где RХ - постоянная Холла, d – диаметр сосуда. На собственные биоэлектрические потенциалы, вызванные физиологическими процессами, накладываются потенциалы, индуцированные внешним магнитным полем.
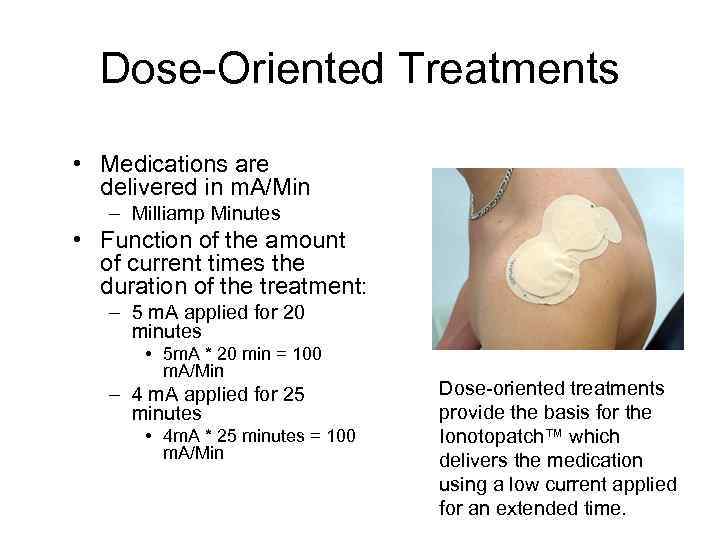
Dose-Oriented Treatments • Medications are delivered in m. A/Min – Milliamp Minutes • Function of the amount of current times the duration of the treatment: – 5 m. A applied for 20 minutes • 5 m. A * 20 min = 100 m. A/Min – 4 m. A applied for 25 minutes • 4 m. A * 25 minutes = 100 m. A/Min Dose-oriented treatments provide the basis for the Ionotopatch™ which delivers the medication using a low current applied for an extended time.

Uses • Delivers medication to the tissues to treat: – – – Acute inflammation Chronic inflammation Arthritis Myositis ossificans Myofascial pain syndromes Delivering local anesthetics before injection or other minor invasive procedures – Hyperhidrosis
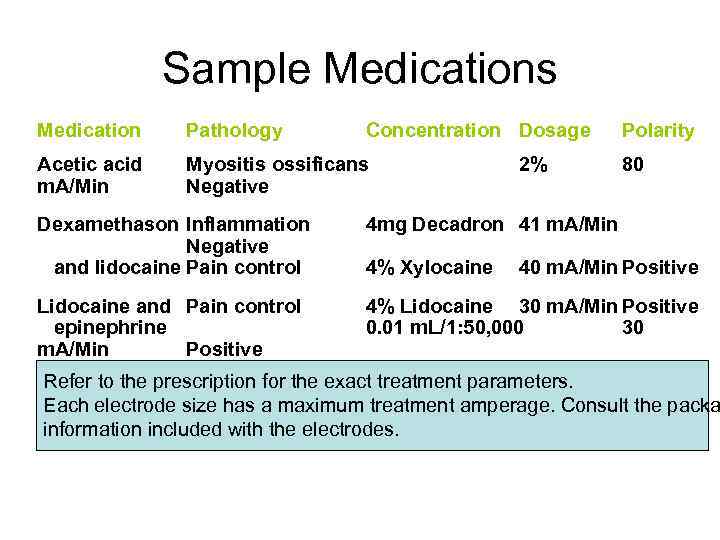
Sample Medications Medication Pathology Concentration Dosage Acetic acid m. A/Min Myositis ossificans Negative 2% Polarity 80 Dexamethason Inflammation Negative and lidocaine Pain control 4 mg Decadron 41 m. A/Min Lidocaine and Pain control epinephrine m. A/Min Positive 4% Lidocaine 30 m. A/Min Positive 0. 01 m. L/1: 50, 000 30 4% Xylocaine 40 m. A/Min Positive Refer to the prescription for the exact treatment parameters. Dexamethasone Inflammation 2 cc 4 mg/m. L Each electrode sizem. A/Min treatment 41 has a maximum Negative amperage. Consult the packa information included with the electrodes.

Notes and Precautions • Controlled medications require a physician’s prescription: – Each patient requires his/her own prescription – Follow any notes or instructions provided by the pharmacist. – State practice acts may further regulate the delivery of iontophoresis. • The exact medication dosage delivered is unknown. • Erythema under the electrodes is common • Too intense of a treatment dose can result in electrode burns • Do not reuse electrodes – Medications remain, contaminating the electrode

Электропунктурная диагностика метод исследования физиологического состояния пациента на основе измерения электрического сопротивления постоянному току в биологически активных точках. Для измерений используются микротоковые режимы, не вызывающие существенного энергетического воздействия на организм.

Методика тестирования Диагностика по Р. Фоллю 860 точек Давление на щуп 200 -300 г. Диагностика ВРТ 1 точка Давление на щуп 100 -150 г.
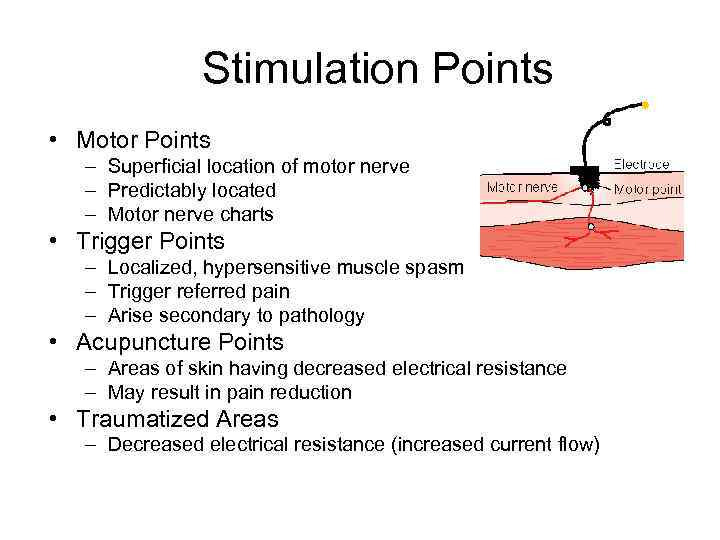
Stimulation Points • Motor Points – Superficial location of motor nerve – Predictably located – Motor nerve charts • Trigger Points – Localized, hypersensitive muscle spasm – Trigger referred pain – Arise secondary to pathology • Acupuncture Points – Areas of skin having decreased electrical resistance – May result in pain reduction • Traumatized Areas – Decreased electrical resistance (increased current flow)
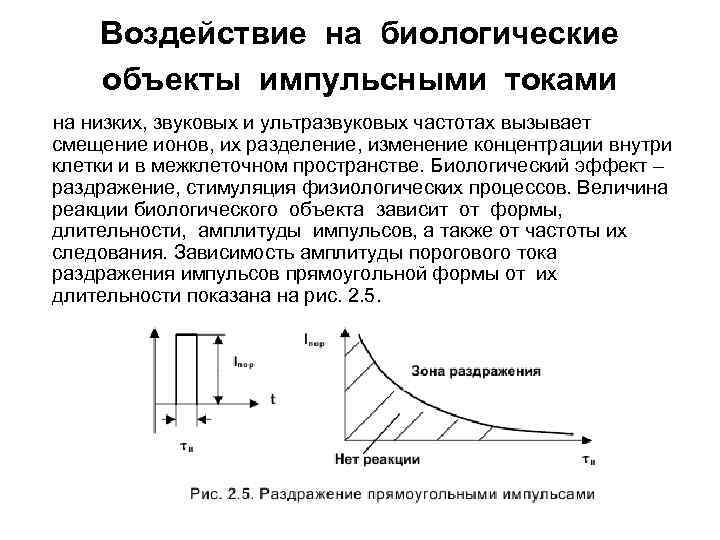
Воздействие на биологические объекты импульсными токами на низких, звуковых и ультразвуковых частотах вызывает смещение ионов, их разделение, изменение концентрации внутри клетки и в межклеточном пространстве. Биологический эффект – раздражение, стимуляция физиологических процессов. Величина реакции биологического объекта зависит от формы, длительности, амплитуды импульсов, а также от частоты их следования. Зависимость амплитуды порогового тока раздражения импульсов прямоугольной формы от их длительности показана на рис. 2. 5.
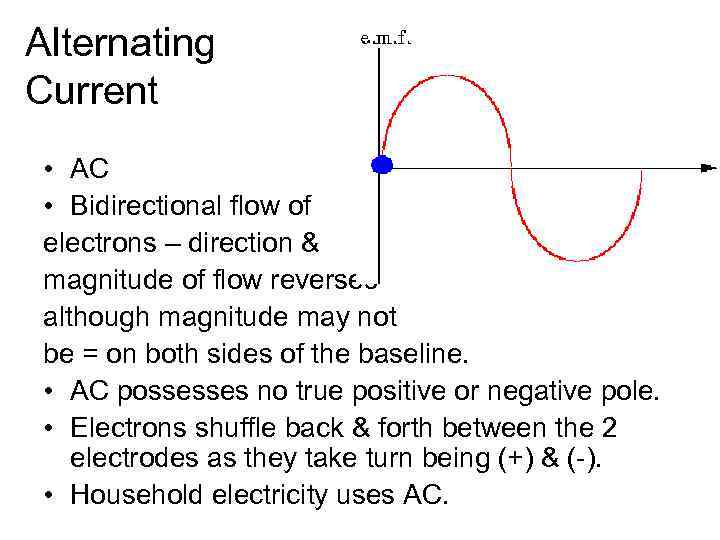
Alternating Current • AC • Bidirectional flow of electrons – direction & magnitude of flow reverses although magnitude may not be = on both sides of the baseline. • AC possesses no true positive or negative pole. • Electrons shuffle back & forth between the 2 electrodes as they take turn being (+) & (-). • Household electricity uses AC.
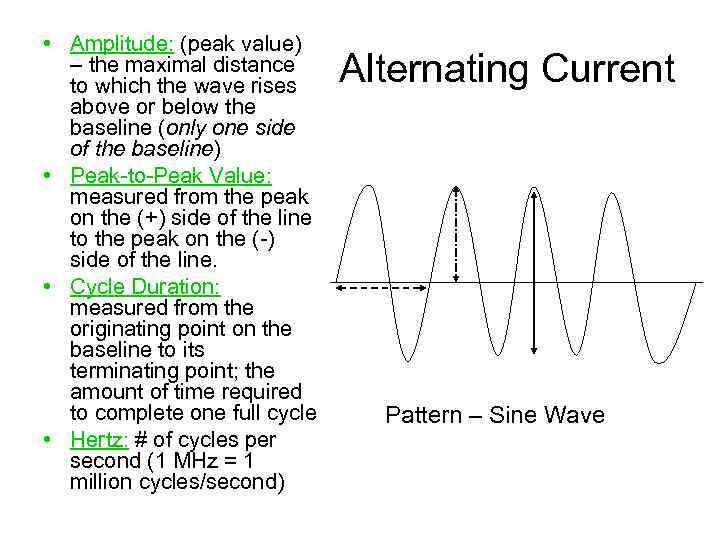
• Amplitude: (peak value) – the maximal distance to which the wave rises above or below the baseline (only one side of the baseline) • Peak-to-Peak Value: measured from the peak on the (+) side of the line to the peak on the (-) side of the line. • Cycle Duration: measured from the originating point on the baseline to its terminating point; the amount of time required to complete one full cycle • Hertz: # of cycles per second (1 MHz = 1 million cycles/second) Alternating Current Pattern – Sine Wave
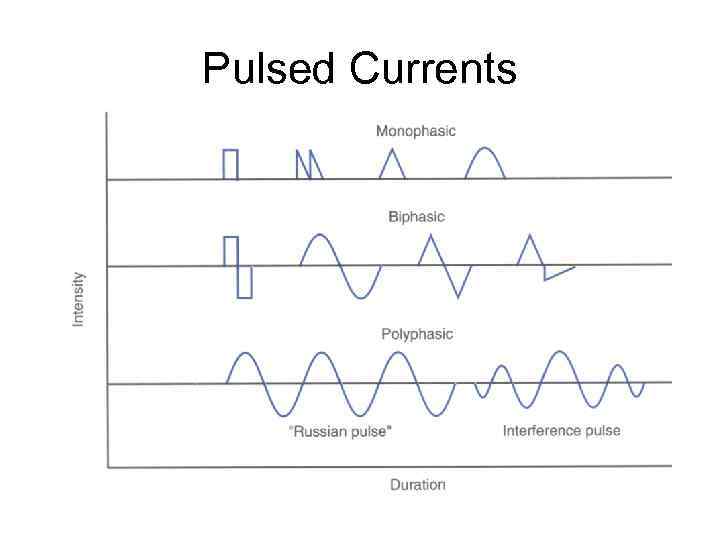
Pulsed Currents

Monophasic Current • Pulsed current • Unidirectional flow of electrons • Only one phase to a single pulse • With monophasic currents, “pulse”, “phase”, & “waveform” are the same.
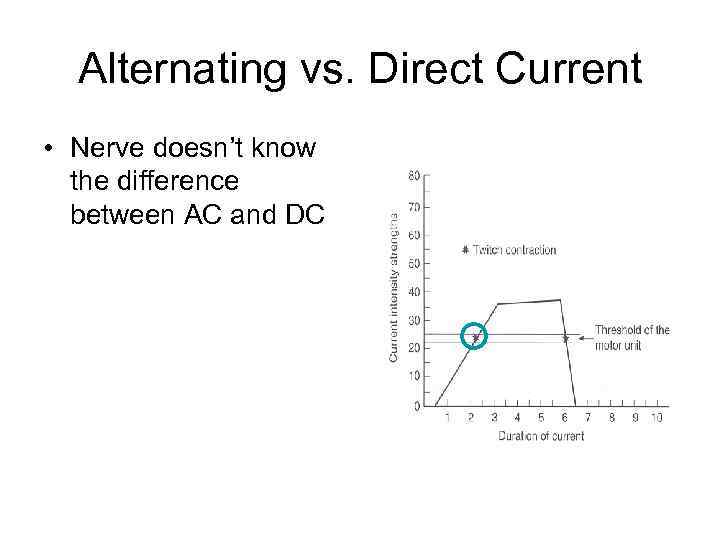
Alternating vs. Direct Current • Nerve doesn’t know the difference between AC and DC
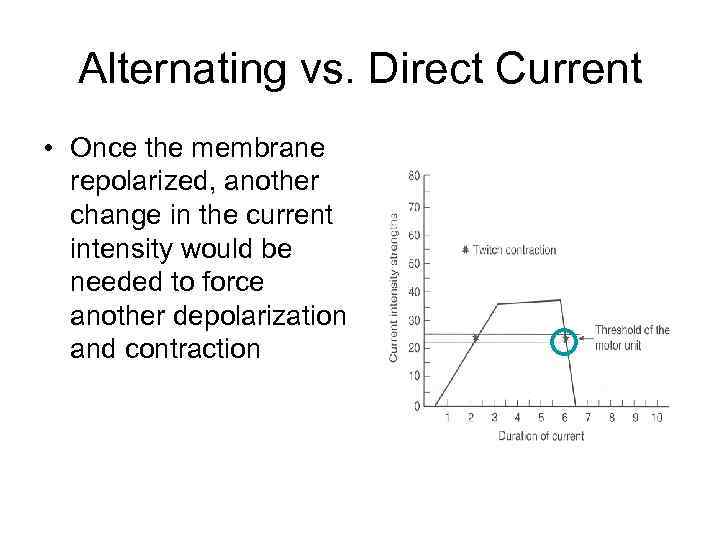
Alternating vs. Direct Current • Once the membrane repolarized, another change in the current intensity would be needed to force another depolarization and contraction
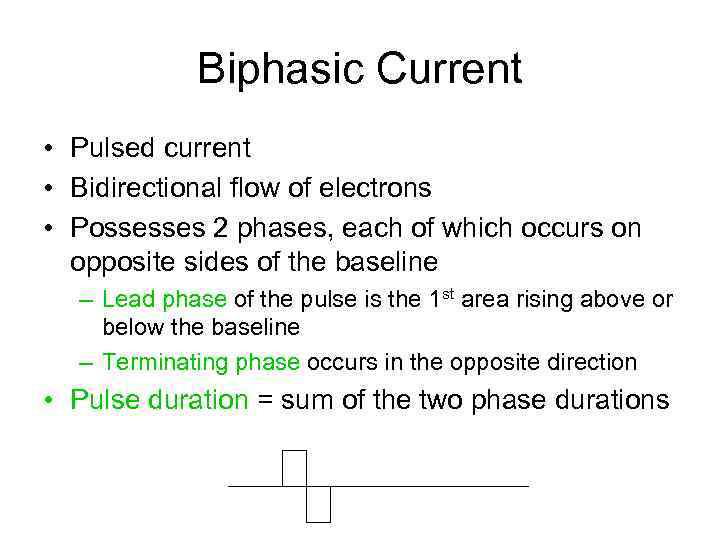
Biphasic Current • Pulsed current • Bidirectional flow of electrons • Possesses 2 phases, each of which occurs on opposite sides of the baseline – Lead phase of the pulse is the 1 st area rising above or below the baseline – Terminating phase occurs in the opposite direction • Pulse duration = sum of the two phase durations
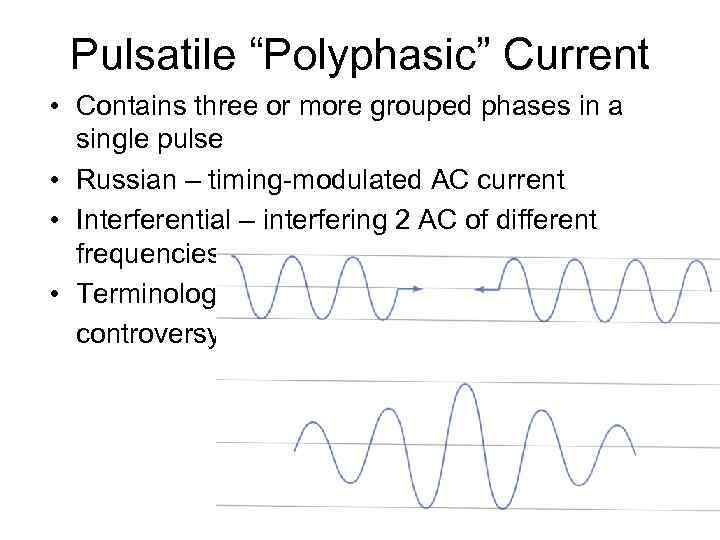
Pulsatile “Polyphasic” Current • Contains three or more grouped phases in a single pulse • Russian – timing-modulated AC current • Interferential – interfering 2 AC of different frequencies • Terminology controversy
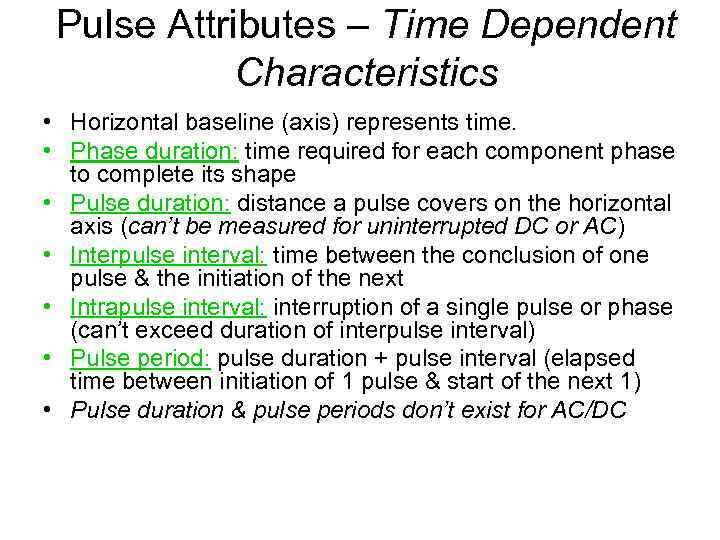
Pulse Attributes – Time Dependent Characteristics • Horizontal baseline (axis) represents time. • Phase duration: time required for each component phase to complete its shape • Pulse duration: distance a pulse covers on the horizontal axis (can’t be measured for uninterrupted DC or AC) • Interpulse interval: time between the conclusion of one pulse & the initiation of the next • Intrapulse interval: interruption of a single pulse or phase (can’t exceed duration of interpulse interval) • Pulse period: pulse duration + pulse interval (elapsed time between initiation of 1 pulse & start of the next 1) • Pulse duration & pulse periods don’t exist for AC/DC
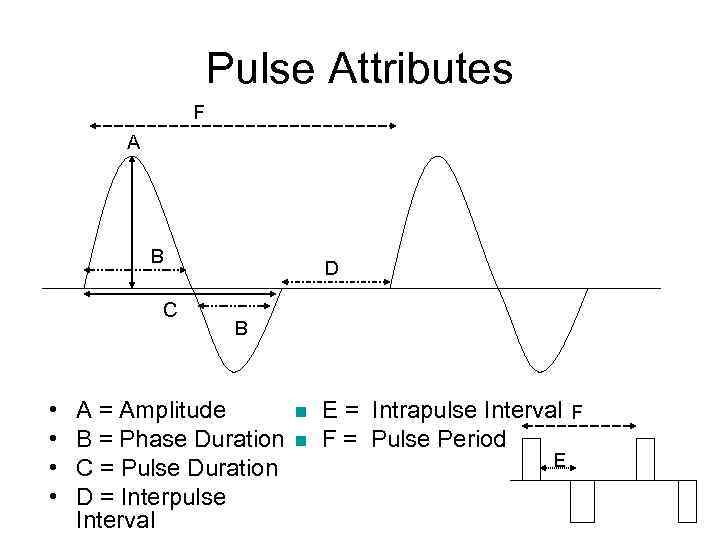
Pulse Attributes F A B C • • D B A = Amplitude B = Phase Duration C = Pulse Duration D = Interpulse Interval E = Intrapulse Interval F F = Pulse Period E
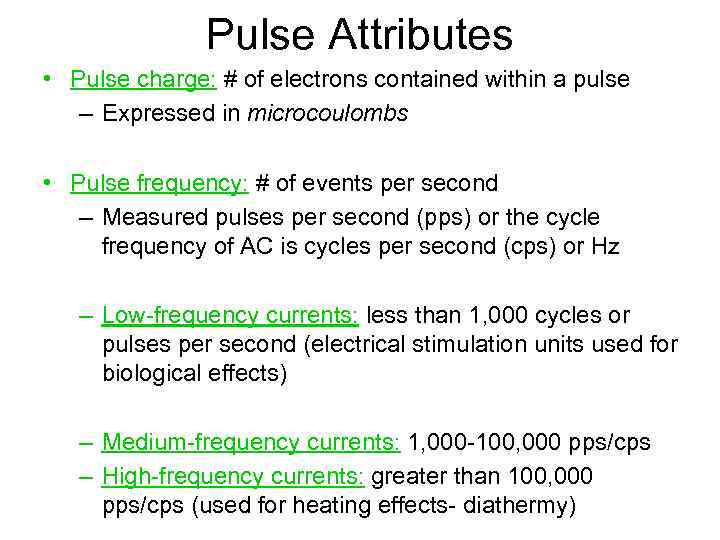
Pulse Attributes • Pulse charge: # of electrons contained within a pulse – Expressed in microcoulombs • Pulse frequency: # of events per second – Measured pulses per second (pps) or the cycle frequency of AC is cycles per second (cps) or Hz – Low-frequency currents: less than 1, 000 cycles or pulses per second (electrical stimulation units used for biological effects) – Medium-frequency currents: 1, 000 -100, 000 pps/cps – High-frequency currents: greater than 100, 000 pps/cps (used for heating effects- diathermy)

Pulse Attributes • Pulse Rise Time: amount of time needed for the pulse to reach its peak value (nanoseconds) – Rapidly rising pulses cause nerve depolarization • Pulse Decay Time: amount of time required for the pulse to go from its peak back to zero • Pulse Train: individual patterns of waveforms, durations &/or frequencies that are linked together (repeat @ regular intervals) – Amplitude Ramp: gradual rise &/or fall in amplitude of a pulse train (causes a gradual in the force of m. contractions by progressive recruitment of motor units)

Импульсные токи, используемые в лечебных целях - прямоугольной формы, частота повторения F = 1… 2 Гц, длительностьτи = 0, 8… 3 мс, применяются для электрокардиостимуляции; - прямоугольной формы, F = 1… 130 Гц, длительности = 0, 2… 2 мс (токи Ледюка), используются для получения состояния, аналогичного физиологическому сну (электросон); - треугольной формы, F = 100 Гц, длительностьτи = 1… 1, 5 мс, вызывают сокраще ние мышц; - экспоненциальной формы, F = 8… 100 Гц, длительностьτи = 2… 60 мс (токи Лапика), применяются для стимуляции мышц или электрогимнастики.
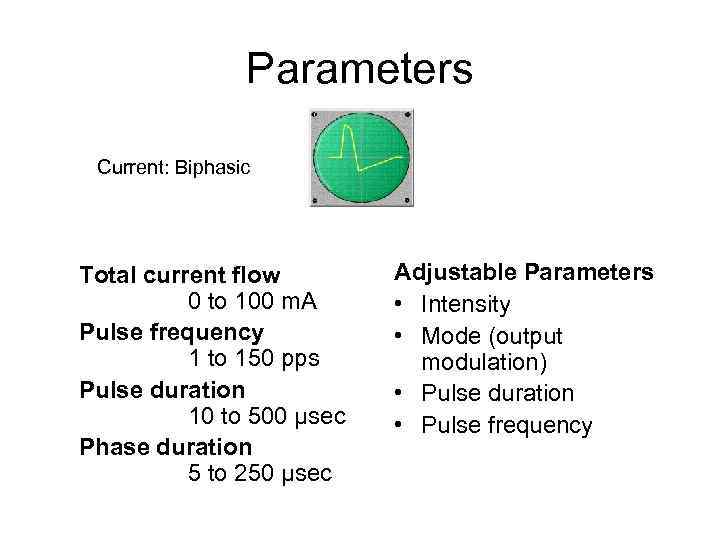
Parameters Current: Biphasic Total current flow 0 to 100 m. A Pulse frequency 1 to 150 pps Pulse duration 10 to 500 µsec Phase duration 5 to 250 µsec Adjustable Parameters • Intensity • Mode (output modulation) • Pulse duration • Pulse frequency

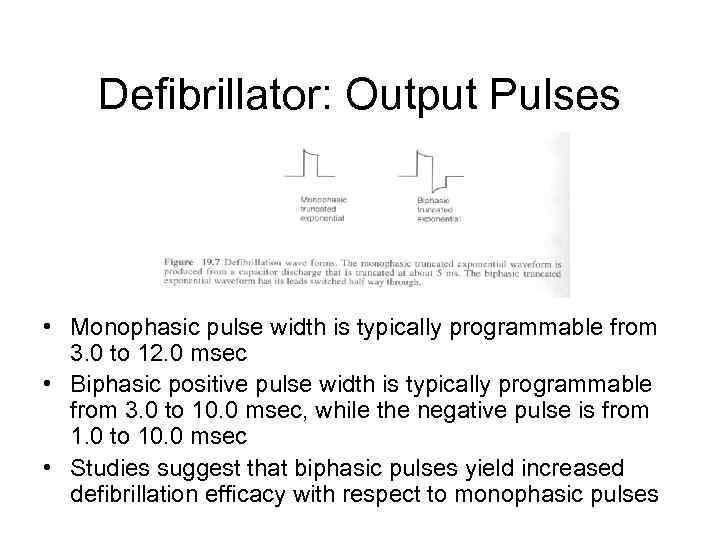
Defibrillator: Output Pulses • Monophasic pulse width is typically programmable from 3. 0 to 12. 0 msec • Biphasic positive pulse width is typically programmable from 3. 0 to 10. 0 msec, while the negative pulse is from 1. 0 to 10. 0 msec • Studies suggest that biphasic pulses yield increased defibrillation efficacy with respect to monophasic pulses

Defibrillator: Power Supply • Using this design, defibrillation uses: – 50 to 100 Joules of energy when electrodes are applied directly to the heart – Up to 400 Joules when applied externally • Energy stored in the capacitor follows: • Capacitors used range from 10 to 50μF • Voltage using these capacitors and max energy (400 J) ranges from 1 to 3 k. V • Energy loss result in the delivery of less than theoretical energy to the heart
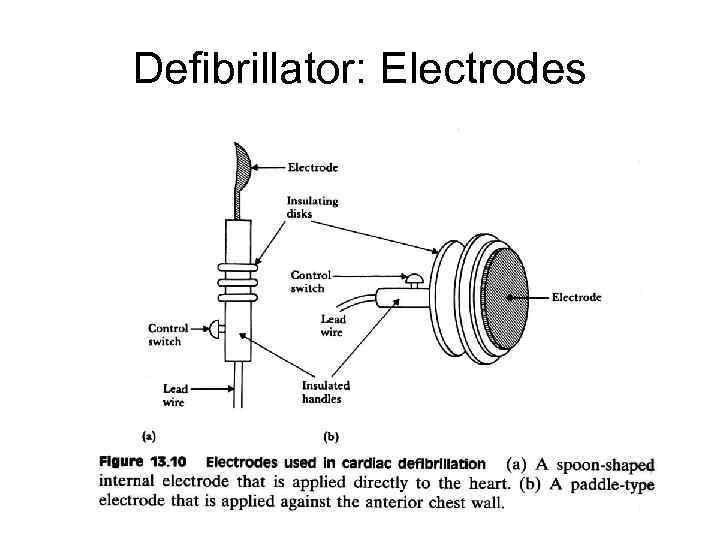
Defibrillator: Electrodes


Commercial Examples Taken from www. guidant. com Taken from www. medtronic. com
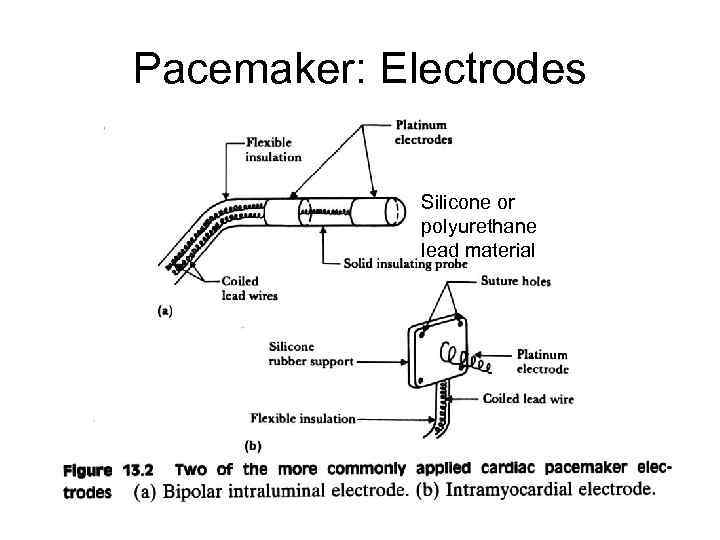
Pacemaker: Electrodes Silicone or polyurethane lead material

Pacemaker: Electrodes
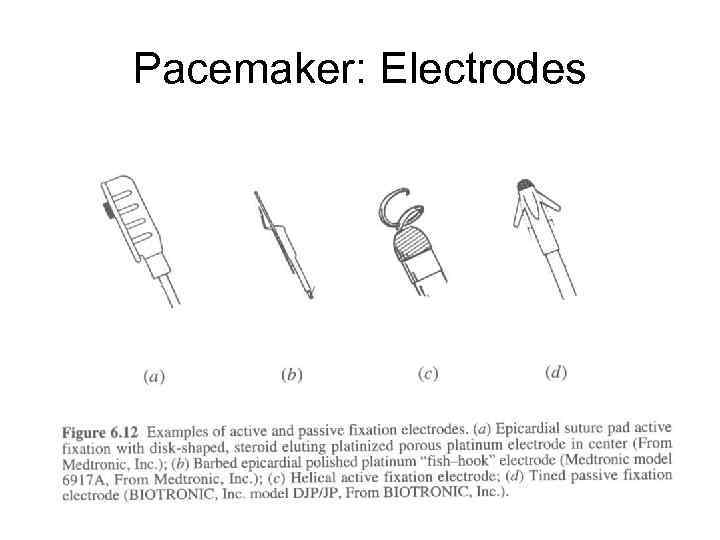
Pacemaker: Electrodes

Theory • Adjustable phase durations specifically target sensory, motor, and pain fibers • Phase duration is matched with pulse frequency to produce specific effects • Biphasic form prevents net residual charge
Uses • Control of acute or chronic pain • Management of postsurgical pain • Reduction of post-traumatic acute pain

Экспериментально установлено, что интервалы частот от 1 до 10 Гц оптимальны для возбуждения симпатических нервов; от 20 до 100 Гц – для парасимпатических; от 80 до 150 Гц – для угнетения болевой чувствительности. На основе этих данных было разработано несколько методов электролечения импульсными токами. Назовем некоторые из них.
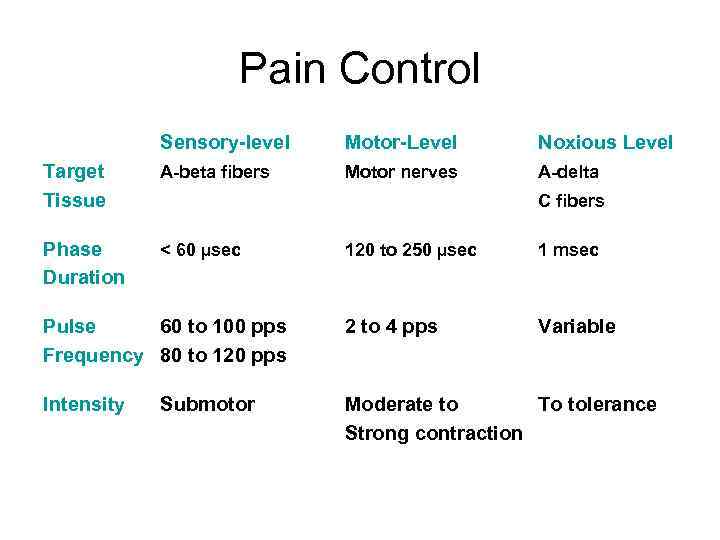
Pain Control Sensory-level Motor-Level Noxious Level Target Tissue A-beta fibers Motor nerves A-delta Phase Duration < 60 µsec C fibers 120 to 250 µsec 1 msec Pulse 60 to 100 pps Frequency 80 to 120 pps 2 to 4 pps Variable Intensity Moderate to To tolerance Strong contraction Submotor

Диадинамотерапия воздействие на организм двумя однополярными низкочастотными импульсными токами (50 и 100 Гц). Чередование частот импульсных токов специальной формы позволяет оптимизировать режимы стимуляции и болеутоления.

Амплипульстерапия воздействие высокочастотными токами (2… 5 к. Гц), модулированными по амплитуде сигналами частотой от 1 до 200 Гц. Этот метод позволяет стимулировать глубоко расположенные в организме ткани за счет снижения импеданса кожного покрова.
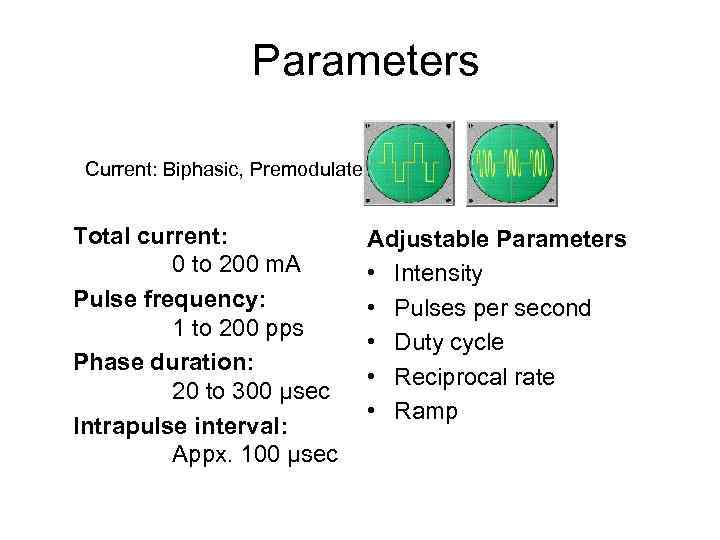
Parameters Current: Biphasic, Premodulated Total current: 0 to 200 m. A Pulse frequency: 1 to 200 pps Phase duration: 20 to 300 µsec Intrapulse interval: Appx. 100 µsec Adjustable Parameters • Intensity • Pulses per second • Duty cycle • Reciprocal rate • Ramp

Russian Currents • Deliver medium (2000 -10, 000 Hz) frequency polyphasic AC wave form • Pulse varies from 50 -250 µsec; the phase duration is half of the pulse duration or 25125 µsec • Two basic waveforms: sine wave or square wave cycles with a fixed intrapulse interval
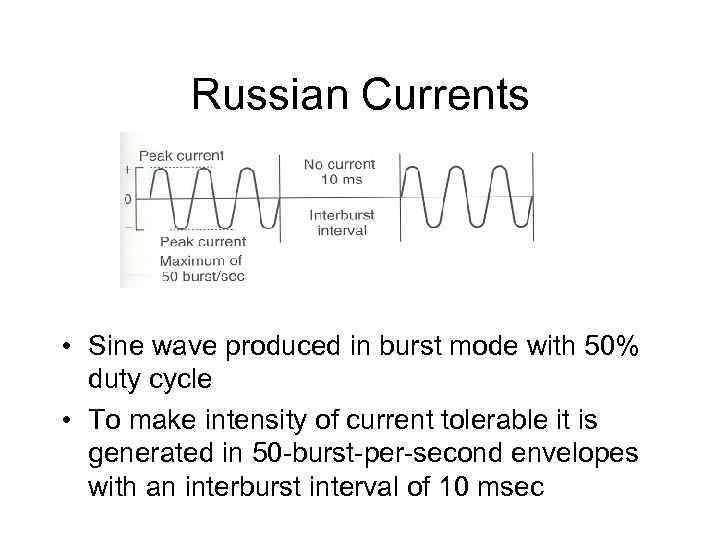
Russian Currents • Sine wave produced in burst mode with 50% duty cycle • To make intensity of current tolerable it is generated in 50 -burst-per-second envelopes with an interburst interval of 10 msec
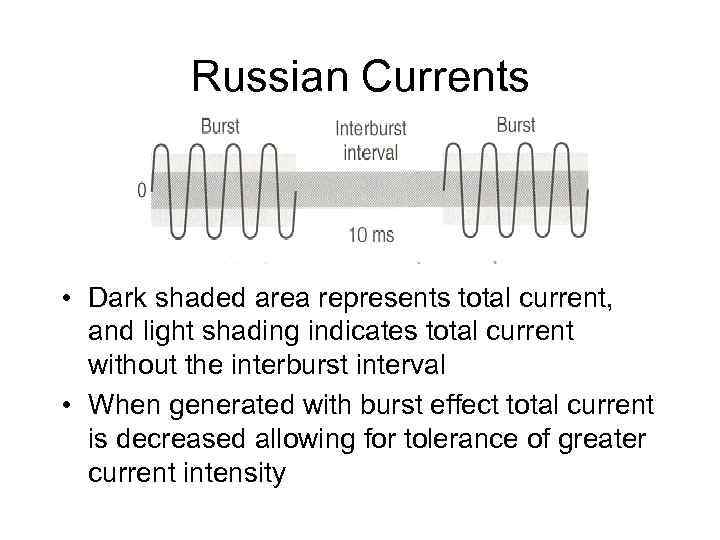
Russian Currents • Dark shaded area represents total current, and light shading indicates total current without the interburst interval • When generated with burst effect total current is decreased allowing for tolerance of greater current intensity

Russian Currents • Higher frequency currents reduce resistance to current flow making wave form comfortable enough to tolerate higher intensities • As intensity increases more motor nerves are stimulated increasing magnitude of the contraction

Russian Currents • Because it is a fast oscillating AC current, as soon as nerve repolarizes it is stimulated again, producing a current that will maximally summate muscle contraction

Uses • • • Maintaining range of motion Muscle reeducation Prevention of joint contractures Prevention of disuse atrophy Increasing local blood flow Decreasing muscle spasm

Effects • Can produce substantial muscular tension • Capable of increasing strength – Used when limb is immobilized – Also slows the onset of atrophy • Duty cycle is required to prevent fatigue

Интерференцтерапия одновременное воздействие двумя высокочастотными токами (3… 8 к. Гц), разность частот которых составляет ± 200 Гц (частоты биений). Отличием этого метода является локализация внутритканевой области стимуляции на частоте биений.
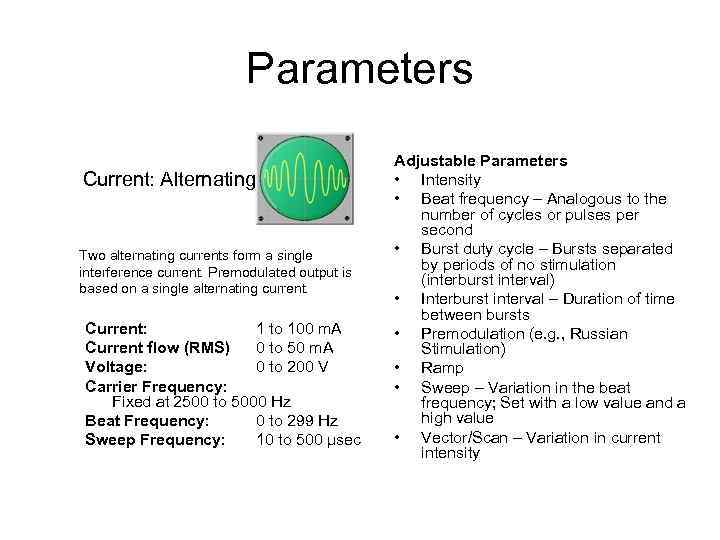
Parameters Current: Alternating Two alternating currents form a single interference current. Premodulated output is based on a single alternating current. Current: 1 to 100 m. A Current flow (RMS) 0 to 50 m. A Voltage: 0 to 200 V Carrier Frequency: Fixed at 2500 to 5000 Hz Beat Frequency: 0 to 299 Hz Sweep Frequency: 10 to 500 µsec Adjustable Parameters • Intensity • Beat frequency – Analogous to the number of cycles or pulses per second • Burst duty cycle – Bursts separated by periods of no stimulation (interburst interval) • Interburst interval – Duration of time between bursts • Premodulation (e. g. , Russian Stimulation) • Ramp • Sweep – Variation in the beat frequency; Set with a low value and a high value • Vector/Scan – Variation in current intensity

Interferential Currents • Make use of 2 separate generators • Produce sine waves at different frequencies
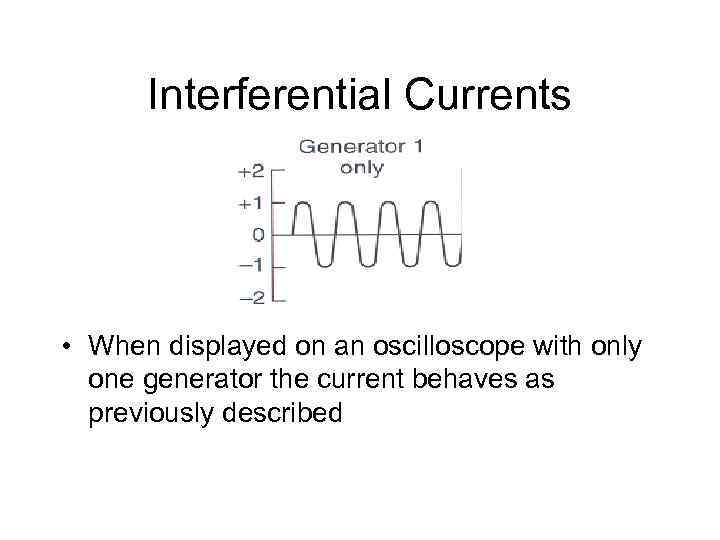
Interferential Currents • When displayed on an oscilloscope with only one generator the current behaves as previously described
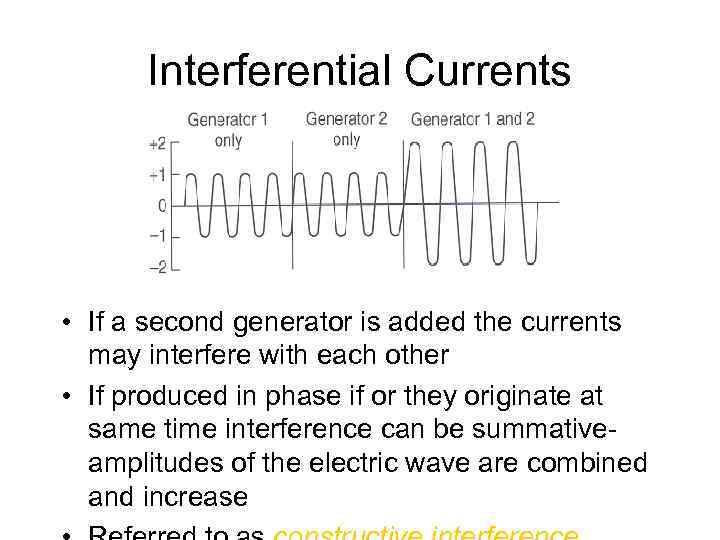
Interferential Currents • If a second generator is added the currents may interfere with each other • If produced in phase if or they originate at same time interference can be summativeamplitudes of the electric wave are combined and increase
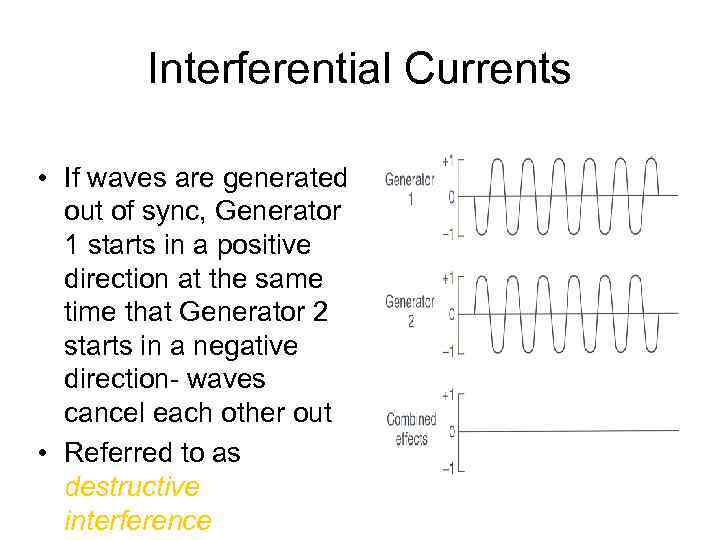
Interferential Currents • If waves are generated out of sync, Generator 1 starts in a positive direction at the same time that Generator 2 starts in a negative direction- waves cancel each other out • Referred to as destructive interference
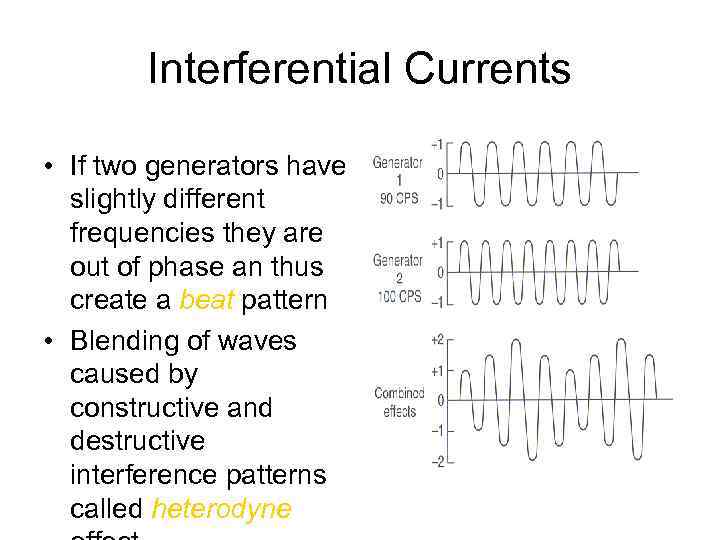
Interferential Currents • If two generators have slightly different frequencies they are out of phase an thus create a beat pattern • Blending of waves caused by constructive and destructive interference patterns called heterodyne

Interferential Currents • When using an interference current – Set intensity according to peak – Select the frequencies to create a beat frequency corresponding to choices of frequency when using other stimulators • 20 to 50 pps for muscle contraction • 50 to 120 pps for pain management • 1 pps for acustim pain relief
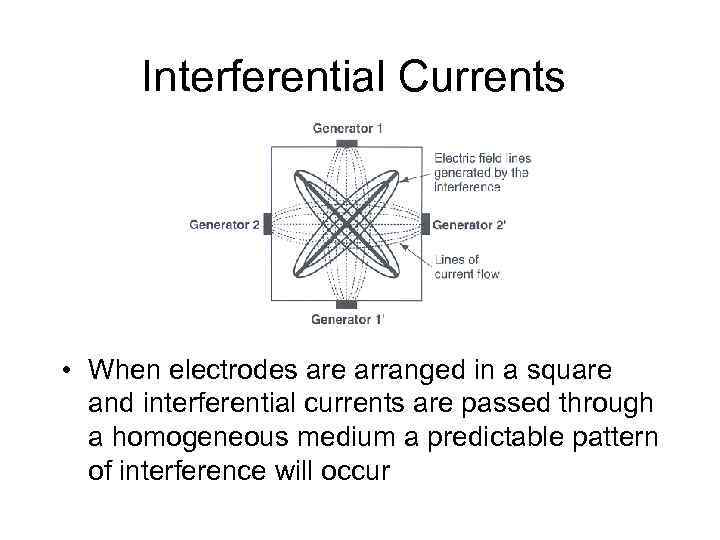
Interferential Currents • When electrodes are arranged in a square and interferential currents are passed through a homogeneous medium a predictable pattern of interference will occur
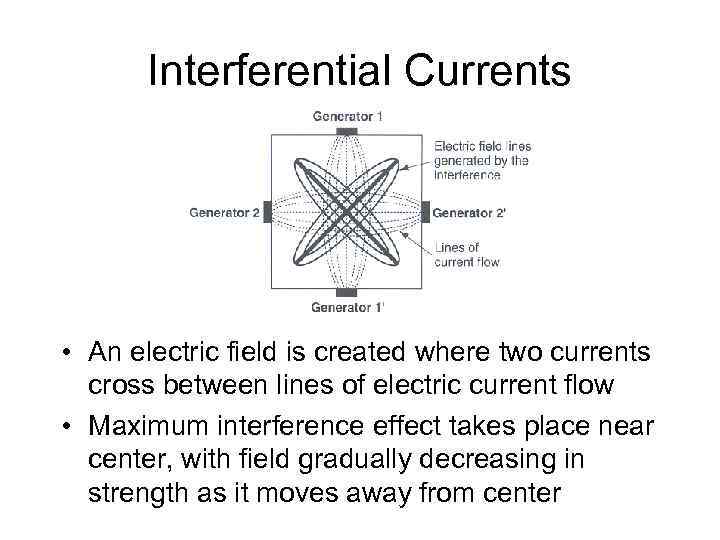
Interferential Currents • An electric field is created where two currents cross between lines of electric current flow • Maximum interference effect takes place near center, with field gradually decreasing in strength as it moves away from center
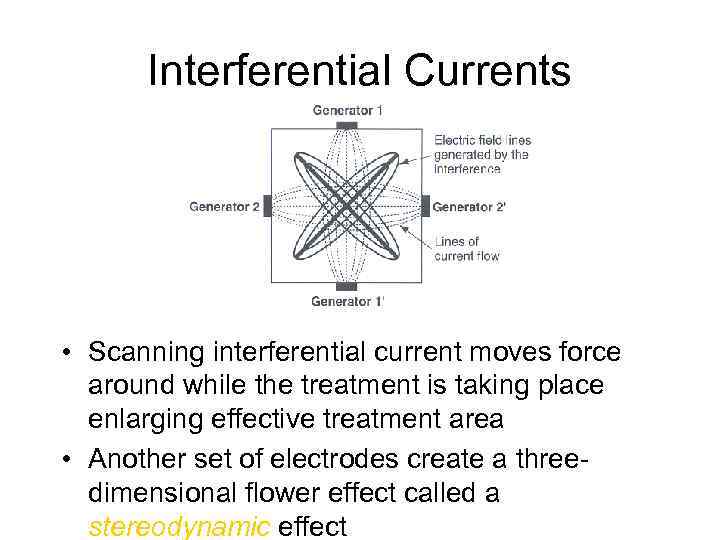
Interferential Currents • Scanning interferential current moves force around while the treatment is taking place enlarging effective treatment area • Another set of electrodes create a threedimensional flower effect called a stereodynamic effect
Uses • Acute pain • Chronic pain • Muscle spasm

Effects • Pain Control – Similar to TENS – Most frequently used for motor-level pain control • Muscle Contractions – Neuromuscular re-education – Edema reduction

Действие переменных токов в том числе и гармонических, на организм человека при низких, звуковых и ультразвуковых частотах характеризуется двумя пороговыми значениями: - порог ощутимого тока – наименьшая сила тока, от которого человек ощущает раздражение; - порог неотпускающего тока – минимальное значение силы тока, при котором наступает судорожное состояние (т. е. состояние, при котором человек не в состоянии самостоятельно освободиться от поражающего фактора).
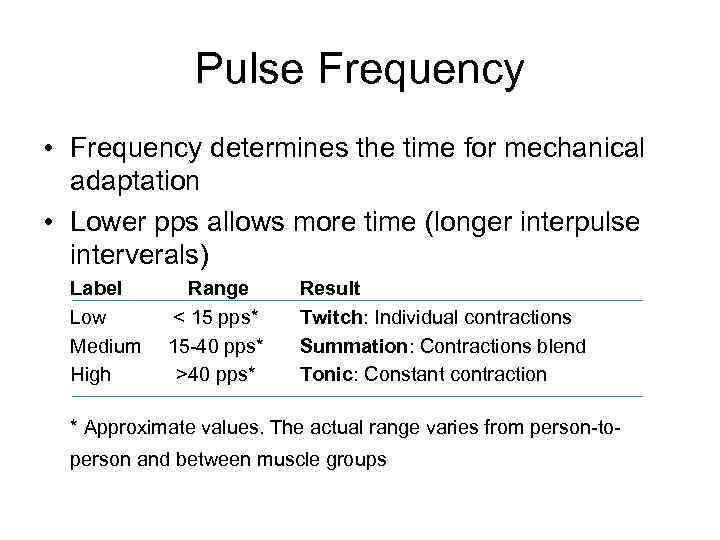
Pulse Frequency • Frequency determines the time for mechanical adaptation • Lower pps allows more time (longer interpulse interverals) Label Low Medium High Range < 15 pps* 15 -40 pps* >40 pps* Result Twitch: Individual contractions Summation: Contractions blend Tonic: Constant contraction * Approximate values. The actual range varies from person-toperson and between muscle groups
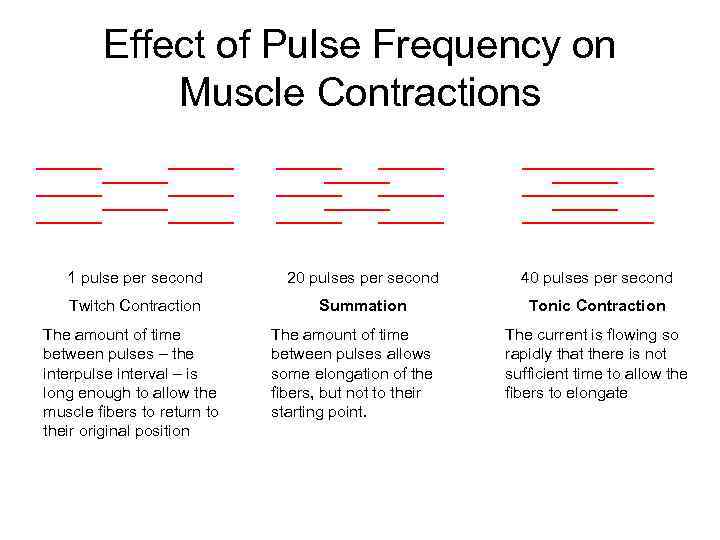
Effect of Pulse Frequency on Muscle Contractions 1 pulse per second 20 pulses per second 40 pulses per second Twitch Contraction Summation Tonic Contraction The amount of time between pulses – the interpulse interval – is long enough to allow the muscle fibers to return to their original position The amount of time between pulses allows some elongation of the fibers, but not to their starting point. The current is flowing so rapidly that there is not sufficient time to allow the fibers to elongate
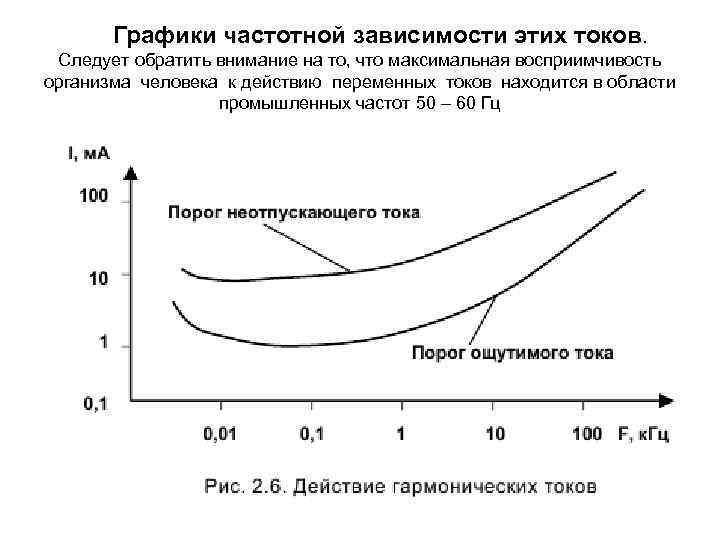
Графики частотной зависимости этих токов. Следует обратить внимание на то, что максимальная восприимчивость организма человека к действию переменных токов находится в области промышленных частот 50 – 60 Гц
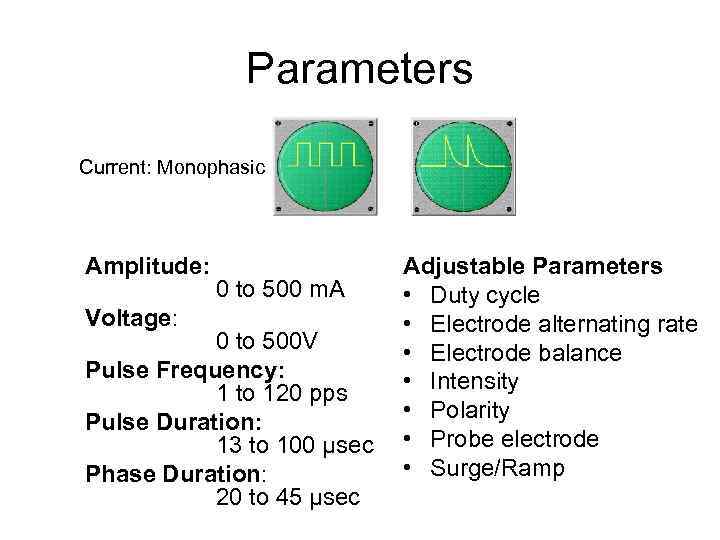
Parameters Current: Monophasic Amplitude: Voltage: 0 to 500 m. A 0 to 500 V Pulse Frequency: 1 to 120 pps Pulse Duration: 13 to 100 µsec Phase Duration: 20 to 45 µsec Adjustable Parameters • Duty cycle • Electrode alternating rate • Electrode balance • Intensity • Polarity • Probe electrode • Surge/Ramp

Theory • Short-duration, high amplitude (voltage) pulses can produce comfortable, moderate contractions. – Short phase duration targets sensory nerves and motor nerves – Wave form is modified to decrease total current to improve comfort • Each electrode has a known polarity – May cause galvanic (ion) changes – Short phase duration and long interpulse interval probably negates any effect

Нагревание биотканей токами высоких частот. При увеличении силы тока от остоянногодо ультразвуковых частот возникает явление электролиза, приводящее к разрушению тканей. Поэтому для прогревания тканей используют исключительно токи высокой частоты в диапазоне 0, 1… 10 МГц Диатермия – тепловое лечебное воздействие затухающими им пульсными токами частотой около 1 МГц, амплитудным начальным напряжением 100… 150 В и максимальным током в несколько ампер. Дарсонвализация – нетепловое воздействие высокочастотным (100… 400 к. Гц) импульсным током высокого напряжения (10… 100 к. В) и малой силой тока (10… 15 м. А) при воздействии кратковременными импульсами (длительность импульса составляет несколько периодов высокочастотного тока, а частота повторения – несколько десятков герц) выделение тепла будет минимальным. Поэтому основное действие таких токовраздражение рефлекторным путем, а лечебный эффект – болеутоление.


Прижигание, сваривание, рассечение Диатермокоагуляция – прижигание или «сваривание» биотканей токами высокой частоты. Необходимое нагревание достигается при плотности тока 6… 10 м. А/мм 2. Диатермотомия – метод рассечения биотканей токами высокой частоты с плотностью j ≥ 10 м. А/мм 2.






Действие переменных магнитных полей Индуктотермия – метод электролечения при воздействии на определенные участки тела высокочастотным (15… 50 МГц) магнитным полем. Лечебные уровни магнитного поля формируют индукторы (высокочастотные соленоиды), подключенные к генератору тока. Механизм лечебного действия основан на выделении тепла, оказывающего влияние на протекание биопроцессов. Тепло, образующееся на глубине 7 -8 см, является сильным раздражителем, вызывающим реакции многих систем организма. Низкочастотная магнитотерапия – применение с лечебной целью переменных, постоянно прерывистых и импульсных магнитных полей низкой частоты (50… 1000 Гц). Механизм лечебного воздействия обусловлен не величиной выделившегося тепла (оно мало вследствие низкой частоты поля), а его раздражающим действием.
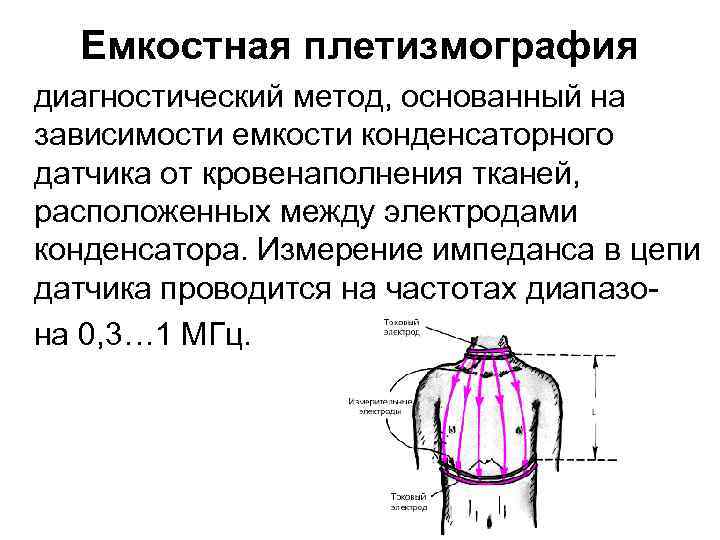
Емкостная плетизмография диагностический метод, основанный на зависимости емкости конденсаторного датчика от кровенаполнения тканей, расположенных между электродами конденсатора. Измерение импеданса в цепи датчика проводится на частотах диапазона 0, 3… 1 МГц.

• Если через какой-то участок тела пропускать безвредный для организма переменный электрический ток высокой частоты (порядка 500 к. Гц) и малой силы (не более 10 м. А) и одновременно регистрировать электрическое сопротивление этого участка, то окажется, что такое сопротивление будет постоянно меняться в связи с прохождением по тканям пульсовой волны. Чем больше кровенаполнение тканей, тем меньше их сопротивление. Таким образом, кривая изменения сопротивления хорошо отражает кровенаполнение тканей при прохождении по ним пульсовой волны. На этом основана методика реографии.

THANK YOU FOR ATTENDING OUR PRESENTATION Please Remember The Following: MAGNET THERAPY is a Godsend. It’s good for any condition and harmful to none!
Bioelectricity_12.ppt