968a4d772a649780f54ac41c415239bd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 96
VLF CABLE TESTING INCLUDING PARTIAL DISCHARGE & TANGENT DELTA Michael T. Peschel High Voltage, Inc. Copake, NY. USA www. hvinc. com 3/19/2018 1

SUBJECTS COVERED 3/19/2018 Review of DC Issues What Is VLF Applications IEEE Standards Lab and Field Results How To Perform The Test Myths about VLF Who Uses VLF Selecting a VLF Model Selecting A Cable Test Method VLF Conclusion Tan Delta Testing VLF Partial Discharge Testing 2

THIS CAN BE PREVENTED In-service failures cause great damage to faulted cables and adjacent cables. Not so if failed under a VLF test. 3/19/2018 3

WHY WAS DC USED DC hipots are small, portable, and economical. DC originally used with PILC cable and worked well. Same techniques used when HMW, XLPE, EPR, and other solid dielectric cables were installed. Years later DC was found to harm insulation and leakage current measurements are often ineffective for exposing defects. VLF work started. Until recently, AC field testing of cable was not practical. Now it is practical and economical. 3/19/2018 4

DC USE DISCOURAGED Worldwide consensus exists among engineering organizations, utilities, and cable manufacturers that typical DC test voltages of 4 – 5 Vo (4 – 5 x line-toground operating voltage) damage insulation, lead to failures, and leakage currents are often not indicative of insulation integrity. Using lower voltages renders test meaningless. 3/19/2018 5

Avoid DC Voltage On Service Aged, Solid Dielectric Insulation DC Voltage Polarizes Cable. Water trees trap space charges – leads to failures. 3/19/2018 6

WHY IS DC HARMFUL? WATER TREES Tree shaped channels are found within the insulation of operating cables resulting from the presence of moisture and electrical fields. l Prevalent in solid dielectric cables. l Eventually leads to the inception of PD. l Leads to insulation failure. l 3/19/2018 7
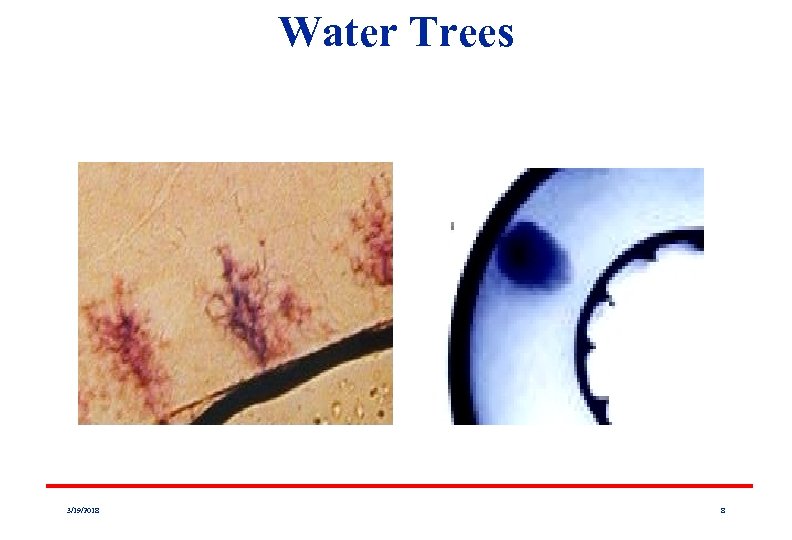
Water Trees 3/19/2018 8
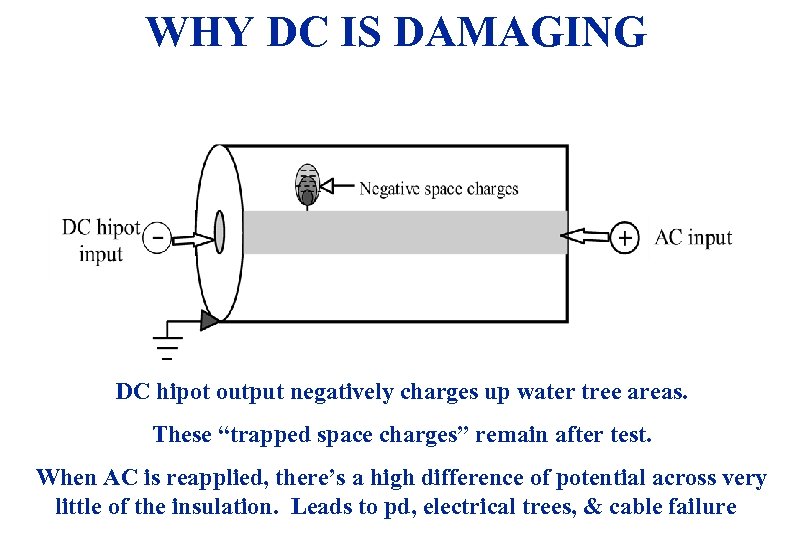
WHY DC IS DAMAGING DC hipot output negatively charges up water tree areas. These “trapped space charges” remain after test. When AC is reapplied, there’s a high difference of potential across very little of the insulation. Leads to pd, electrical trees, & cable failure 3/19/2018 9

UTILITIES RESPONSE TO DC CONCERNS l Typical DC test voltages were/are 4 - 5 times V 0. l At these high voltages, damage is done. l Some reduce voltage to 15 k. VDC on 15 k. V cable. l 15 k. V is only 30% above the peak AC stress in service. At this voltage, leakage currents are meaningless. l l Some do nothing, letting cables fail and then repair. Many have adopted VLF AC hipoting to expose bad insulation and accessories. VLF is the best splice checker. 3/19/2018 10

IF NOT DC - THEN WHAT? VLF – Very Low Frequency AC Advantages • Light Weight. • Low Cost. • Simple to Use. • Results are certain Disadvantages • Voltage Waveform in Some Designs – Can’t Use For TD & PD • Cable May Fail Under Test. • Perhaps Multiple Failures In Severely Deteriorated Insulation 3/19/2018 11

WHAT IS VLF? 3/19/2018 12

A VLF HIPOT IS SIMPLY AN AC OUTPUT INSTRUMENT BUT AT A LOWER FREQUENCY. THE LOWER THE FREQUENCY OUTPUT, THE LOWER THE CURRENT AND POWER REQUIRED TO TEST HIGH CAPACITANCE LOADS LIKE CABLES. DON’T OVERCOMPLICATE IT. IT’S A SIMPLE AC WITHSTAND TEST. VLF IS THE EASIEST, CHEAPEST, MOST CERTAIN WAY OF TESTING THE AC INTEGRITY OF A CABLE. 3/19/2018 13

DROP THE FREQUENCY Very Low Frequency: 0. 1 Hz and lower. By decreasing the frequency, it is possible to test miles of cable with a small and affordable unit. Output frequencies range from 0. 1 – 0. 01 Hz. IEEE 400. 2 recognizes frequencies as low as 0. 01 Hz. At 0. 1 Hz, it takes 600 times less power to test a cable, or any other high capacitance load, than at 60 Hz. At 0. 01 Hz, 6000 times higher capacitive loads can be tested than at 60 Hz with the same power consumption. 3/19/2018 14

VLF EXPLAINED Xc = 1 2 x pi x f x C The lower the frequency, the higher the capacitive reactance, or Xc. The higher Xc , or resistance across the power supply output, the lower the current/power needed to apply a voltage. 3/19/2018 15

60 Hz vs. 0. 1 Hz At 60 Hz. a 1 μF cable has an Xc of 2. 65 k. Ohms. At 22 k. V peak, it requires 8. 3 amps of current to test. Total power supply rating must be 183 k. VA. At 0. 1 Hz, the Xc is 1. 59 megohms. At 22 k. V, the current needed is 14 m. A. Total power supply needed is only. 304 k. VA. 3/19/2018 (22 k. V is the typical test voltage for 15 k. V cable) 16
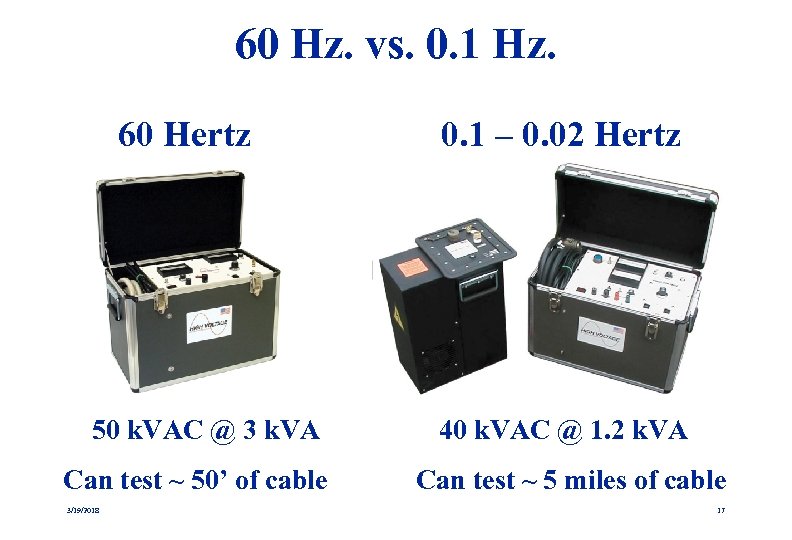
60 Hz. vs. 0. 1 Hz. 60 Hertz 0. 1 – 0. 02 Hertz 50 k. VAC @ 3 k. VA 40 k. VAC @ 1. 2 k. VA Can test ~ 50’ of cable 3/19/2018 Can test ~ 5 miles of cable 17

APPLICATIONS 3/19/2018 18

IEEE STANDARDS EXIST • Power Cable IEEE 400 -2001 & IEEE 400. 2 -2004 • Large Rotating Machinery IEEE 433 -1974 • Diagnostic Testing: 3/19/2018 Tan d Partial discharge 19

CAN OTHER LOADS BE VLF TESTED? Yes, but no standards exist that define the test. Most other loads are low in capacitance, permitting 60 Hz AC hipots to be used. Sometimes large insulators are VLF tested if a powerful enough 60 Hz hipot is not available. 3/19/2018 20

WHY TEST CABLES WITH AC VOLTAGE? Cables are designed to carry AC voltage. They are factory tested with AC voltage. Cables operate under AC voltage stress. Cables should be tested with AC voltage. Why would you not use AC if you could? 3/19/2018 21

Can Now AC Stress Test Cable l l With VLF, utilities, testing services, industrials, and others can now AC stress test cables in the field. Just like with vacuum bottle or rubber glove testing, now a go/no-go AC stress test can be performed on power cable. If a cable can’t hold 2 – 3 times normal voltage, it’s not healthy. Find the problem, make the repair, and move on. At the very least, every newly installed and repaired cable should be VLF tested before energizing, since many failures are due to installation damage, faulty workmanship, stress from in-service failures, or over voltage thumping. 3/19/2018 22

Other Methods Don’t Get It Done. DC Hipot 5 k. Vdc “Megger” DC Hot stick adaptor 24 hour soak 3/19/2018 23

VLF IT! 3/19/2018 24

IEEE STANDARDS 3/19/2018 25

NORTH AMERICAN STANDARDS FOR VLF TESTING IEEE 400 -2001 overall cable testing standard sanctions VLF testing of cables. IEEE 400. 2 -2004 standard for VLF cable testing IEEE 433 -1974 covers VLF testing for rotating machinery. Now being updated. Standard for smaller motors/gens. under consideration. 3/19/2018 26

MOTOR & GENERATOR TESTING • IEEE Std. 433 -1974 (1974) l Recommended Practice For Insulation Testing of Large AC Rotating Machinery with High Voltage VLF. l Refers to Large AC Machines 10 MVA/6 k. V & above. l Test Waveform: Must be Sinusoidal. l Test Frequency: 0. 1 Hz. l Test Voltage: 1. 63 x 60 Hz RMS Level 3/19/2018 27

CABLE TESTING IEEE 400. 2 -2004 l Recommends test voltage of 2 - 3 V 0 (V 0 equals line-to-ground voltage) l Test duration is 15 – 60 minutes l Best recommendation is for 30+ minutes 3/19/2018 28

IEEE 400. 2 FIELD TEST VOLTAGES For Shielded Power Cable Systems Using Sine Wave Output VLF ----------- 0. 1 Hz Test Voltage ----------System Voltage Installation Acceptance Maintenance phase to ground phase to ground k. Vrms/k. Vpeak 5 9/12 10/14 7/10 15 18/25 20/28 16/22 25 27/38 31/44 23/33 35 39/55 44/62 33/47 Test voltages are generally 2 – 3 time the line-to-ground system voltage. 3/19/2018 29
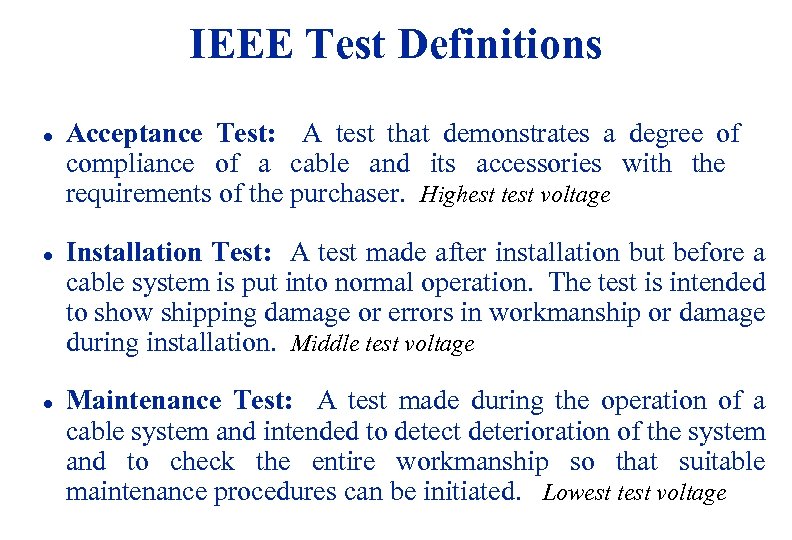
IEEE Test Definitions l l l Acceptance Test: A test that demonstrates a degree of compliance of a cable and its accessories with the requirements of the purchaser. Highest test voltage Installation Test: A test made after installation but before a cable system is put into normal operation. The test is intended to show shipping damage or errors in workmanship or damage during installation. Middle test voltage Maintenance Test: A test made during the operation of a cable system and intended to detect deterioration of the system and to check the entire workmanship so that suitable maintenance procedures can be initiated. Lowest test voltage 3/19/2018 30
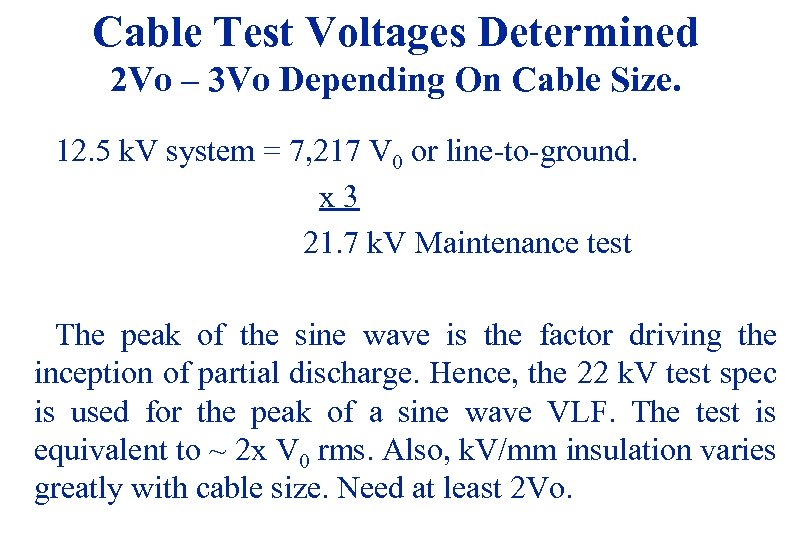
Cable Test Voltages Determined 2 Vo – 3 Vo Depending On Cable Size. 12. 5 k. V system = 7, 217 V 0 or line-to-ground. x 3 21. 7 k. V Maintenance test The peak of the sine wave is the factor driving the inception of partial discharge. Hence, the 22 k. V test spec is used for the peak of a sine wave VLF. The test is equivalent to ~ 2 x V 0 rms. Also, k. V/mm insulation varies greatly with cable size. Need at least 2 Vo. 3/19/2018 31

WHY 2 Vo – 3 Vo The IEEE standard says 2 – 3 V 0 for 15 - 60 minutes. Cables routinely see 2 x normal voltage due to reflected waves, transients, etc. VLF test voltage must be at least 2 x normal line-to-ground. Must use enough voltage for enough time to let the VLF do its job of growing electrical trees to failure. An abbreviated test or a test too low in voltage is worse than no test. 3/19/2018 32
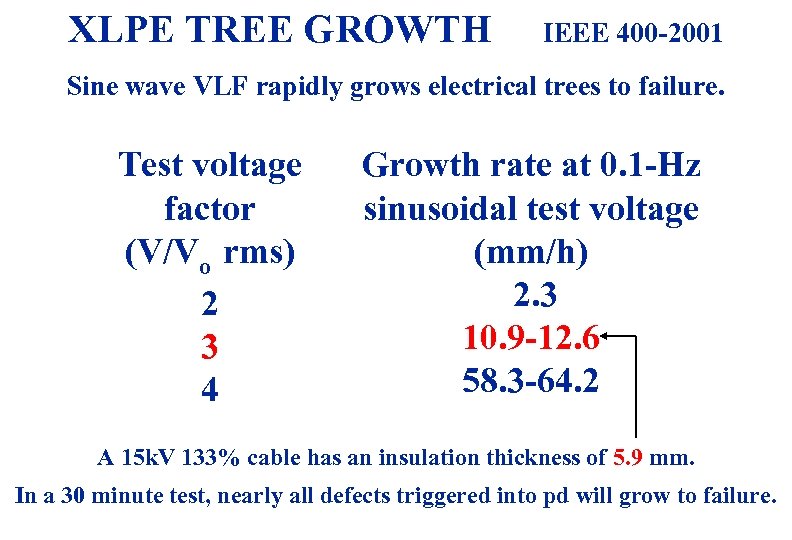
XLPE TREE GROWTH IEEE 400 -2001 Sine wave VLF rapidly grows electrical trees to failure. Test voltage factor (V/Vo rms) 2 3 4 Growth rate at 0. 1 -Hz sinusoidal test voltage (mm/h) 2. 3 10. 9 -12. 6 58. 3 -64. 2 A 15 k. V 133% cable has an insulation thickness of 5. 9 mm. In a 30 minute test, nearly all defects triggered into pd will grow to failure. 3/19/2018 33

RESULTS FROM FIELD USE AND LABORATORY RESEARCH 3/19/2018 34

VLF TEST RESULTS Numerous case studies show that if a cable passes a proper VLF test, there is a > 95% assurance of no in-service failure in the next few years. Nothing is perfect, but only a few percent possible failure rate post VLF testing is very good. Far better by multiples than with other testing methods. If a cable can hold 2 – 3 times normal voltage for 30 -60 minutes, it’s good for years. 3/19/2018 35
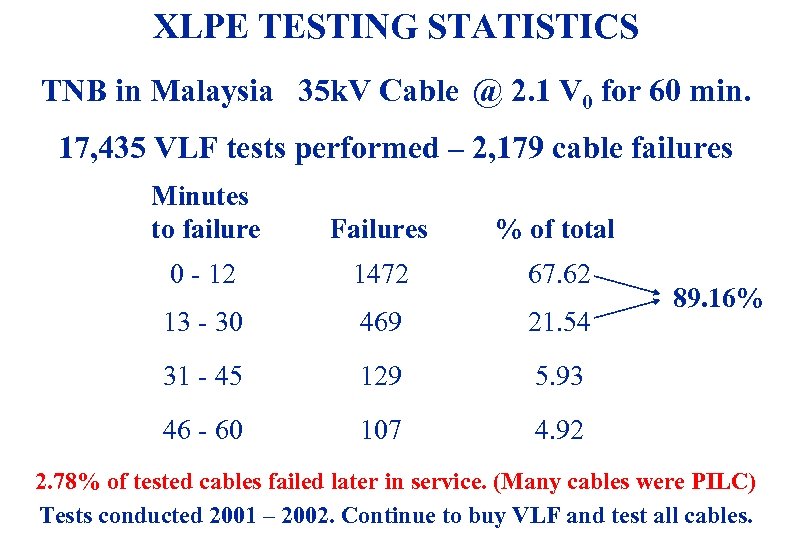
XLPE TESTING STATISTICS TNB in Malaysia 35 k. V Cable @ 2. 1 V 0 for 60 min. 17, 435 VLF tests performed – 2, 179 cable failures Minutes to failure Failures % of total 0 - 12 1472 67. 62 13 - 30 469 21. 54 31 - 45 129 5. 93 46 - 60 107 4. 92 89. 16% 2. 78% of tested cables failed later in service. (Many cables were PILC) Tests conducted 2001 – 2002. Continue to buy VLF and test all cables. 3/19/2018 36

XLPE TESTING STATISTICS Japan: Furukawa, Chubu & Tokyo Electric Research done to determine test voltage and duration versus expected life. Results were: A 33 k. V cable tested at 60 k. V peak @ 0. 1 Hz has a 97% probability of no failure for 3 years. 3/19/2018 37

Germany produced some of the first VLF products more than 20 years ago. German standard: 3 Vo rms for 60 minutes. 3/19/2018 38

Most US users test at the IEEE recommended voltages for 30 minutes. 3/19/2018 39

The World View Of VLF DC not recommended by cable companies for cables > 5 years & in moist environments IEEE 2 – 3 Vo for 15 -60 minutes 30+ minutes @ 3 Vo recommended. Germany 3 Vo for 60 minutes Japan 3 Vo for 15 minutes Malaysia 3 Vo for 60 minutes 3/19/2018 Over 60 countries have purchased the HVI VLF 40

HOW TO PERFORM A VLF TEST 3/19/2018 41

TEST PROCEDURE l l VLF testing is easier than DC testing. Isolate cable ends like with DC testing, although no cleaning and bagging is necessary. l Remove all arrestors, capacitors, transformers, etc. l Connect VLF HV lead to conductor & ground to shield. l After selecting appropriate test frequency, apply voltage l There are no leakage currents to read. Test is go/no-go l If cable holds, test is over. Cable is good for years. l If cable fails, make repairs and repeat test, or replace. l If second insulation failure occurs, maybe stop testing and replace. l Most models can test all three phases at once, saving time. 3/19/2018 42
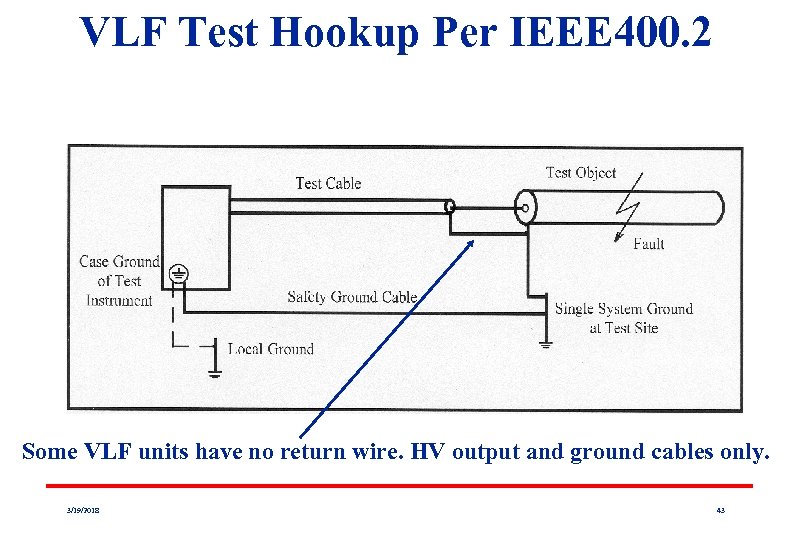
VLF Test Hookup Per IEEE 400. 2 Some VLF units have no return wire. HV output and ground cables only. 3/19/2018 43

CABLES INCLUDED WITH TWO PIECE MODEL Ground hook HV output from tank Cable connectors hook or clamp 3/19/2018 2 test leads for capacitance measurement Phase jumpers Interconnect with grounds Scope bnc 44

VLF-4022 CM 3/19/2018 45
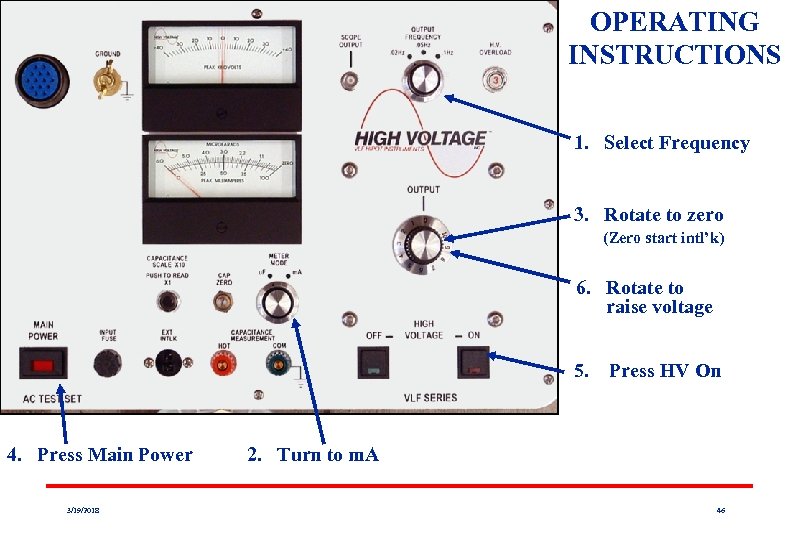
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS 1. Select Frequency 3. Rotate to zero (Zero start intl’k) 6. Rotate to raise voltage 5. Press HV On 4. Press Main Power 3/19/2018 2. Turn to m. A 46
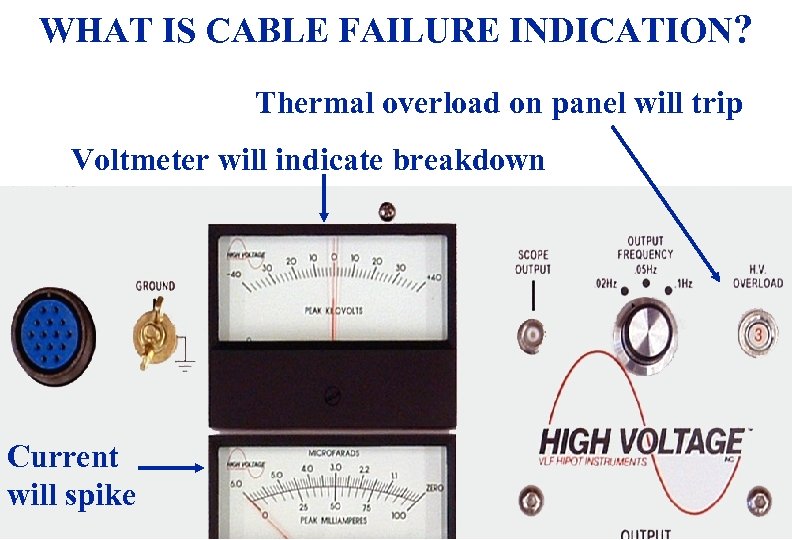
WHAT IS CABLE FAILURE INDICATION? Thermal overload on panel will trip Voltmeter will indicate breakdown Current will spike 3/19/2018 47

FAULT LOCATING NECESSARY When VLF testing, cable failures will occur. Someone has to find them. Testing contractors will need to use fault locators and should want to for increased billing. Thumpers, or VLF/thumpers must be purchased. 3/19/2018 48

COMMON VLF MYTHS 3/19/2018 49

VLF IS DESTRUCTIVE TO INSULATION. NOT TRUE. Cable is factory tested at voltages far higher than field VLF levels. VLF is destructive to existing defects that are severe enough to be triggered into partial discharge during the test. That’s the point of the test – light up defects and let them grow to failure. Minor defects and good insulation are not effected. 3/19/2018 50

VLF AGGRAVATES DEFECTS THAT FAIL LATER IN SERVICE Only if the test is not properly performed, like any testing method. The proper VLF voltage must be applied for a long enough time to permit defects triggered into pd to grow to failure. An improper test is worse than no test at all. The same can be said for 60 Hz hipoting, pd testing, and other tests. If done wrong, problems could result. If done correctly - positive results. 3/19/2018 51

VLF IS REALLY ALTERNATING DC Not true. At 0. 1 Hz there are polarity reversals every 5 seconds. Even at 0. 01 Hz there are reversals every 50 seconds. That does not compare at all to a 15 minute, constantly negative output DC hipot test. Space charges and traveling waves are not developed in insulation during a VLF test. The IEEE recognizes frequencies down to. 01 Hz as ok. 3/19/2018 52

VLF EFFECTIVENESS IS UNPROVEN Very wrong. Tell that to the hundreds of users over more than 15 years that have tested tens of thousands of cables with great success. Tell that to the IEEE, CEA, EPRI, cable companies, and many international organizations that have all endorsed VLF. A VLF instrument is just a low frequency AC hipot. Simple product – simple test – simple physics. There is nothing to not work. 3/19/2018 53
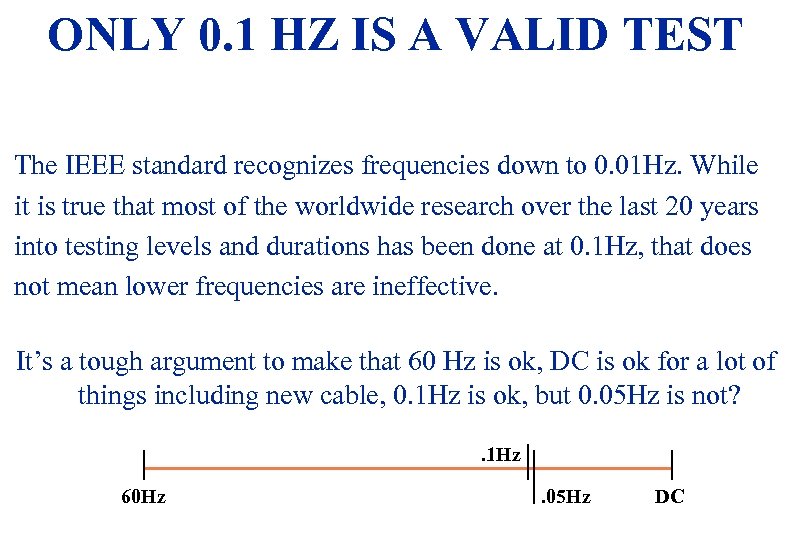
ONLY 0. 1 HZ IS A VALID TEST The IEEE standard recognizes frequencies down to 0. 01 Hz. While it is true that most of the worldwide research over the last 20 years into testing levels and durations has been done at 0. 1 Hz, that does not mean lower frequencies are ineffective. It’s a tough argument to make that 60 Hz is ok, DC is ok for a lot of things including new cable, 0. 1 Hz is ok, but 0. 05 Hz is not? . 1 Hz 3/19/2018 60 Hz . 05 Hz DC 54

ONE WAVEFORM OUTPUT IS BETTER THAN ANOTHER Of the three major VLF vendors, two output waveforms are offered: sine wave & cosine-rectangular (trapezoidal). Both work well to VLF hipot cable, although the sine wave output grows electrical trees faster - see IEEE 400. -However A sine wave VLF is better suited for use as a voltage source for tan delta and partial discharge testing, both desirable add-ons to VLF testing. Also, a sine wave is necessary for motor/generator testing per IEEE 433. 3/19/2018 55

WHO USES VLF 3/19/2018 56

UTILITIES TESTING SERVICES INDUSTRIALS CONTRACTORS Other methods of cable testing have their place, but VLF is embraced worldwide as the easiest, most effective, most economical method of cable testing. Over 800 VLF units have been shipped from High Voltage, Inc. over the last eight years, delivered to 54 countries and many US locations. Other VLF products have shipped from other vendors for even longer. 3/19/2018 57

COUNTRIES USING HVI VLF HVI has shipped over 800 VLF products to the following: USA Canada Taiwan Indonesia So. Korea Australia Saudi Arabia England Costa Rica Bolivia Israel 3/19/2018 So. Africa Singapore Hong Kong Belgium Puerto Rico Holland New Zealand Japan Malaysia Russia Spain Slovak Republic Czech Republic China UAE Vietnam Panama Jordan Germany Cyprus Honduras Lithuania Thailand Mexico India Bulgaria Fiji Venezuela Finland Greece Qatar Argentina Norway 58

SELECTING A VLF MODEL 3/19/2018 59
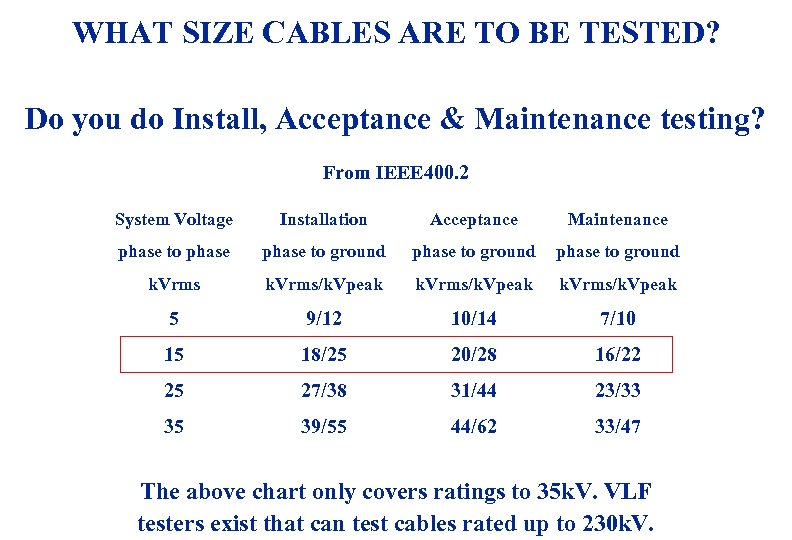
WHAT SIZE CABLES ARE TO BE TESTED? Do you do Install, Acceptance & Maintenance testing? From IEEE 400. 2 System Voltage Acceptance Maintenance phase to ground phase to ground k. Vrms/k. Vpeak 5 9/12 10/14 7/10 15 18/25 20/28 16/22 25 27/38 31/44 23/33 35 3/19/2018 Installation 39/55 44/62 33/47 The above chart only covers ratings to 35 k. V. VLF testers exist that can test cables rated up to 230 k. V. 60

WHAT CABLE LENGTHS ARE TO BE TESTED? VLF units are rated by the u. F of load they can test. Example: 15 k. V XLPE 750 mcm 220 mils ~. 1 uf/1000’ Model VLF-25 CM 0 - 25 k. V Peak 0. 1 Hz @ 0. 4 μf Load Can test up to 4000’ of 15 k. V cable depending on size. Perfect NETA model 3/19/2018 61
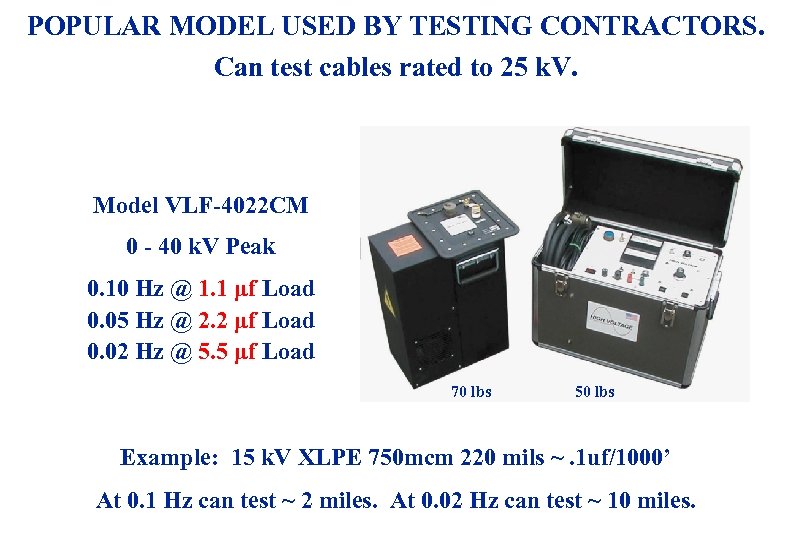
POPULAR MODEL USED BY TESTING CONTRACTORS. Can test cables rated to 25 k. V. Model VLF-4022 CM 0 - 40 k. V Peak 0. 10 Hz @ 1. 1 μf Load 0. 05 Hz @ 2. 2 μf Load 0. 02 Hz @ 5. 5 μf Load 70 lbs 50 lbs Example: 15 k. V XLPE 750 mcm 220 mils ~. 1 uf/1000’ At 0. 1 Hz can test ~ 2 miles. At 0. 02 Hz can test ~ 10 miles. 3/19/2018 62

MODEL SIZES AVAILABLE (all vendors included) Voltage ratings from 20 k. V – 200 k. V Load ratings from 0. 4 u. F – 50 u. F For a 15 k. V cable, 0. 4 u. F can test ~ 4000’ Some models can test > 30 miles of cable 3/19/2018 63

WILL IT BE USED FOR TAN DELTA & PD TESTING? Sine wave output is needed to use VLF as a voltage source for td and pd testing. IEEE 433 for VLF testing rotating machinery requires a sine wave output. Leave all your future testing options open by buying a sine wave VLF. 3/19/2018 64

Other Models 90 k. V peak 120 k. V peak up to 5. 5 u. F Up to 2. 75 u. F 60 k. V peak up to 5. 5 u. F 200 k. V soon available 65 k. V peak up to 22 u. F 3/19/2018 65

VLF THUMPER Complete URD Cable Care System Combination VLF AC Hipot and Thumper VLF Output: 0 - 33 k. VAC peak Load Rating: 1. 0 u. F @ 0. 1 Hz ~ 1. 5 miles of 15 k. V cable Discharge: 0 – 13 k. V @ 760 J VLF Cable Burning Mode 3/19/2018 Radar Ready 66

SELECTING A CABLE TEST METHOD 3/19/2018 67

CABLE TEST METHODS • • • 3/19/2018 AC Power Frequency. AC Series & Parallel Resonant. DC Hipot. Very Low Frequency (VLF) AC Hipot. Tan Delta, Partial Discharge, And Other Diagnostic Methods. 68

SEVERAL METHODS – WHAT TO USE? Ideally, VLF, Tan Delta, and Partial Discharge should all be used. However, there are real world factors affecting the decision. 1. 2. 3. Type of test results desired Ease of use Cost of equipment There is no one perfect method that does it all. A variety of approaches is needed to meet all the requirements encountered. 3/19/2018 69

WHAT’S THE GOAL? l Verify new installation? l Verify repaired cable? l Verify critical cable? l Help to prioritize cable replacement or injection? 3/19/2018 70

WHAT’S THE SITUATION? l Direct buried – must pinpoint problem to repair Cable in conduit or trench - replaceable Cable in raceways – visible and easily replaceable How old is cable What is the failure history How easy is it to repair Is there alternate feed should failure occur during test Is fault location and repair available? l How much downtime can be tolerated? l l l l 3/19/2018 71

EXAMPLES OF SITUATION vs. METHOD New Install: Diagnostic test not appropriate, the insulation is good. VLF it to make sure there are no installation flaws. Old suspect cable: There may be many defects, don’t VLF. Use TD to see how degraded cable is. If modest degradation, then PD possibly followed by VLF. Critical cable in conduit: PD test to expose location and severity of defects. If no PD tester available, VLF. Direct buried, hard to repair: TD test to evaluate condition to prioritize cable injection or replacment. Prioritization for replacement or injection: If a comparative condition assessment test is desired, tan delta is the easiest method. Post repair test: VLF repaired cable to make sure it holds – no further damage caused by over voltage thumping. 3/19/2018 72

SO, WHAT TO DO? NO SHORT AND EASY ANSWER. Depends on money and available people. A combination of methods is needed: some easy and economical (VLF) and some more complicated and more expensive (TD & PD), and each yielding different but important data about your cable. 3/19/2018 73

IT ALL STARTS WITH A VLF Fact: As more industrial customers, utilities, and specifying engineering companies spec VLF testing, per IEEE 400. 2, you will need a VLF. Fact: In addition to performing VLF AC stress tests, a VLF hipot is the foundation for other tests, like partial discharge and tan delta. You need VLF for pd and td. To learn the most about the health of your cable, all three tests, if economically and logistically feasible, are recommended. If not all possible, VLF should be the fallback, or nothing in old cable systems. 3/19/2018 74

SUMMARY & CONCLUSION 3/19/2018 75

VLF TESTING SUMMARY l Has the virtues of DC test equipment (low cost, small size, light weight, easy to use) but is AC. l Does not have the negative consequences of DC. l Requires 1/600 – 1/6000 of the k. VA of power frequency. l l Can be used for breakdown tests and predictive tests such as Tan Delta and Partial Discharge. (sine wave VLF units) Internationally accepted Standards exist and more are in the process of issuance. 3/19/2018 76

CONCLUSION The surest way to verify the AC integrity of any load is perform an AC stress test. It’s easy and certain. The load holds voltage or fails. VLF testing is easily performed with minimal training. Worldwide standards and decades of history exist. Some VLF models are very portable and affordable. VLF makes Tan Delta and Partial Discharge diagnostic testing easier and more economical. 3/19/2018 77

CONCLUSION VLF is suitable for use on cables and rotating machinery. IEEE, VDE, CEA, EPRI, other country’s engineering organizations, cable manufactures, and major utilities all recommend VLF. Hundreds of users worldwide have embraced VLF It! It’s economical, easy, and sure. 3/19/2018 78

OTHER CABLE TEST METHODS USING VLF 3/19/2018 79

YOU HAVE YOUR VLF. WHAT ELSE CAN YOU DO? Accessorize. Add on a Tan Delta measurement instrument. Partial Discharge detection instrument. 3/19/2018 80

TANGENT DELTA or TAN δ Dissipation Factor or Loss Angle Measurement For Power Cables Non Destructive Testing To Determine Insulation Quality (Similar to Power Factor Testing) 3/19/2018 81
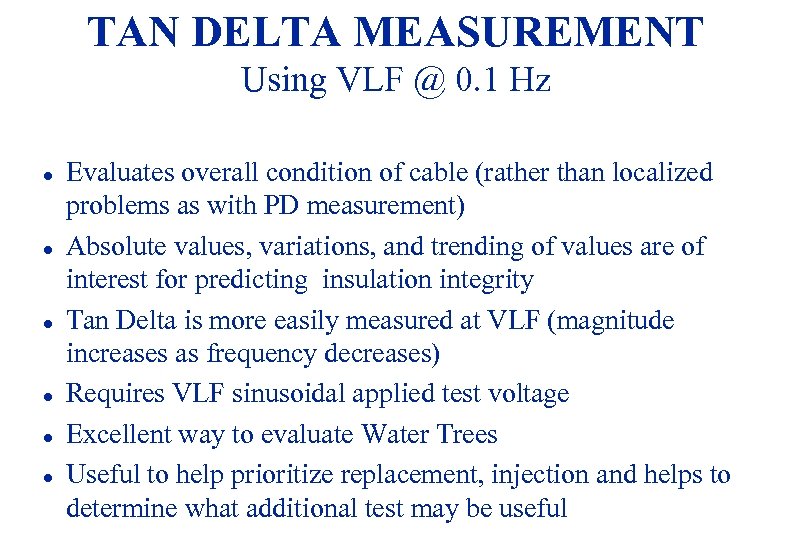
TAN DELTA MEASUREMENT Using VLF @ 0. 1 Hz l l l Evaluates overall condition of cable (rather than localized problems as with PD measurement) Absolute values, variations, and trending of values are of interest for predicting insulation integrity Tan Delta is more easily measured at VLF (magnitude increases as frequency decreases) Requires VLF sinusoidal applied test voltage Excellent way to evaluate Water Trees Useful to help prioritize replacement, injection and helps to determine what additional test may be useful 82
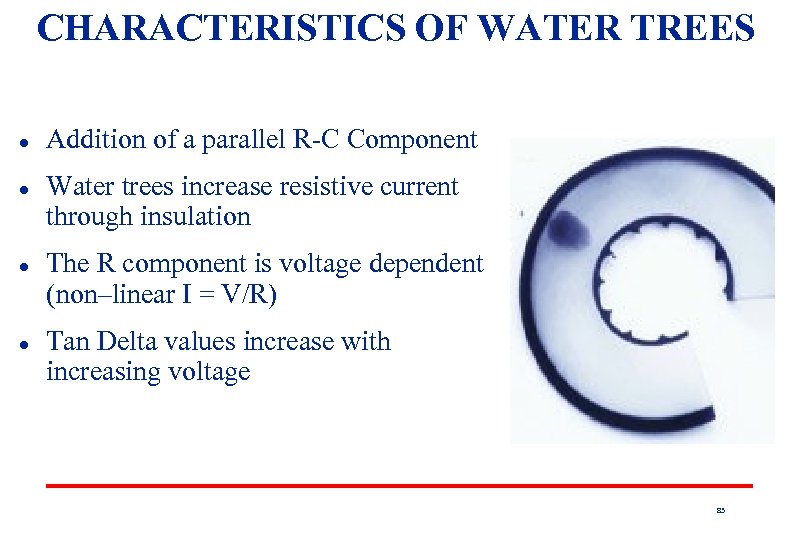
CHARACTERISTICS OF WATER TREES l l Addition of a parallel R-C Component Water trees increase resistive current through insulation The R component is voltage dependent (non–linear I = V/R) Tan Delta values increase with increasing voltage 83
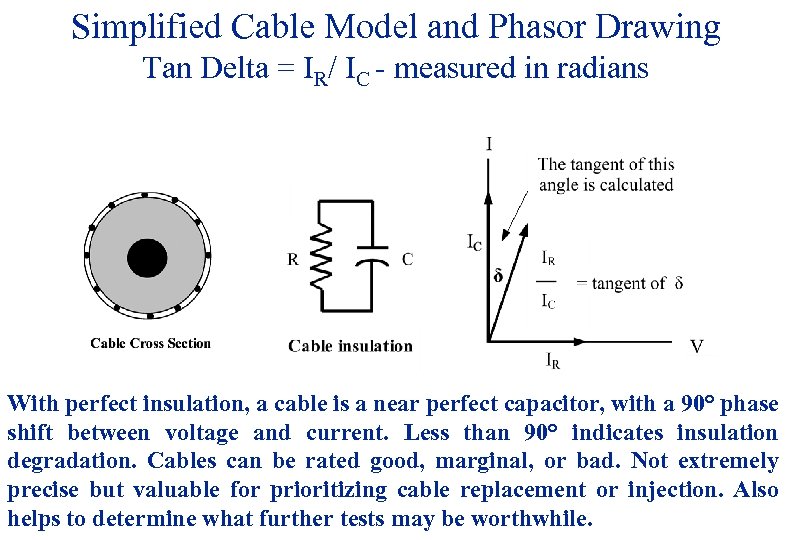
Simplified Cable Model and Phasor Drawing Tan Delta = IR/ IC - measured in radians With perfect insulation, a cable is a near perfect capacitor, with a 90° phase shift between voltage and current. Less than 90° indicates insulation degradation. Cables can be rated good, marginal, or bad. Not extremely precise but valuable for prioritizing cable replacement or injection. Also helps to determine what further tests may be worthwhile. 84
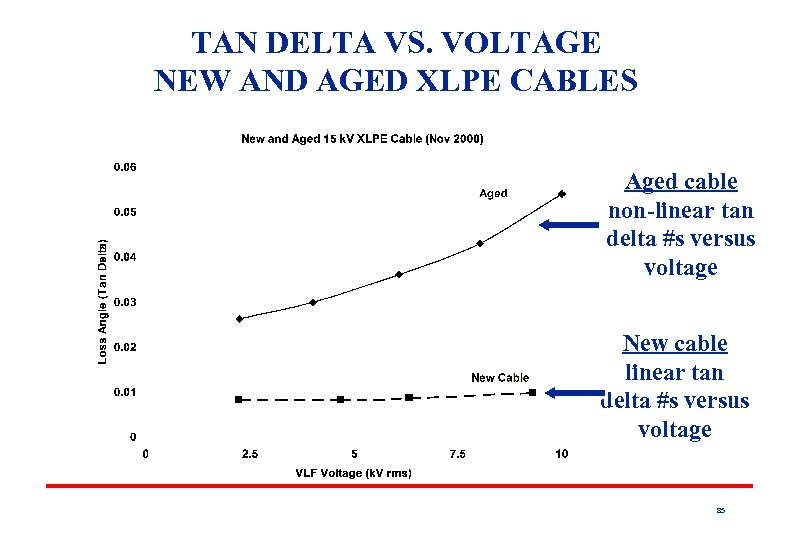
TAN DELTA VS. VOLTAGE NEW AND AGED XLPE CABLES Aged cable non-linear tan delta #s versus voltage New cable linear tan delta #s versus voltage 85
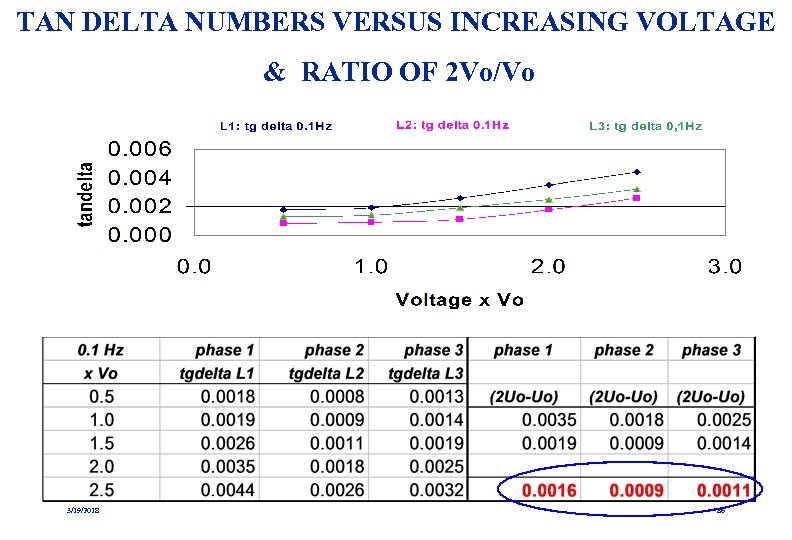
TAN DELTA NUMBERS VERSUS INCREASING VOLTAGE & RATIO OF 2 Vo/Vo 3/19/2018 86
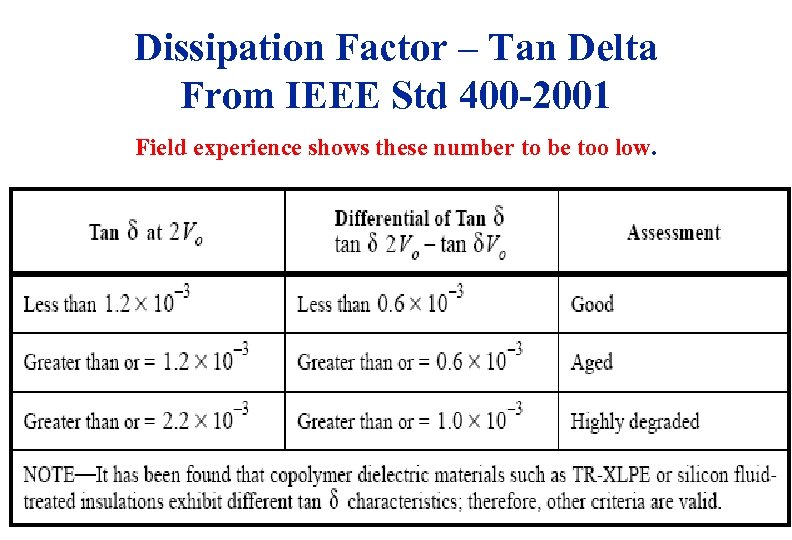
Dissipation Factor – Tan Delta From IEEE Std 400 -2001 Field experience shows these number to be too low. 3/19/2018 87

TAN DELTA LOSS ANALYZER 60 k. V model Used with VLF as voltage source 3/19/2018 HV Divider Signal analyzer/controller 88

TAN DELTA TESTING Advantages l l l Less destructive than VLF, DC, or 60 Hz testing Helps to prioritize cable replacement and/or injection Easier to use and interpret than other diagnostic methods Disadvantages l l Can be destructive if cable very degraded Gives overall condition of cable, not singularities Not best for mixed type cable runs More useful with historical data 3/19/2018 89

VLF PARTIAL DISCHARGE TESTING 3/19/2018 90

“SEE” UNDERGROUND CABLE FAULTS A PD detection system can show you the location and severity of insulation and accessory defects. Using a VLF as the voltage generator to apply voltages up to 2 Vo, long cables can be tested with portable equipment. 3/19/2018 91
OFF-LINE VS. ON-LINE PD TESTING Off-line testing using a VLF permits over voltage analysis. Can measure PDIV and PDEV up to 2 Vo. On-line pd testing can only detect pd at operating voltage, missing defects with a PDIV of 101% and above of operating voltage, yet cables routinely see twice normal voltage due to reflected waves, transients, switching surges, etc. Off-line testing may be less convenient, but the information gained is far more valuable. 3/19/2018 92

0. 1 Hz vs. 60 Hz PD TESTING Both frequencies initiate pd at defect locations. Both can measure PDIV, PDEV, magnitude, and location. The benefit of VLF is smaller size, lower weight, far lower cost, and can test longer cables. A 100 lb VLF can do the job of a 2000 lb 60 Hz series resonant unit. 3/19/2018 93

THE BEST OF EVERYTHING Start with a VLF tester to perform AC withstand testing. Add a Tan Delta accessory for evaluating the overall condition of a cable to help prioritize replacement, injection, or to determine what other tests might be helpful. Add a Partial Discharge accessory to map the location and severity of pd in the insulation and splices, or to determine what other tests might be helpful. Perform all three tests to get the most complete profile possible of your cable. 3/19/2018 94

Thank You Mike Peschel - High Voltage, Inc. www. hvinc. com 3/19/2018 95

3/19/2018 96
968a4d772a649780f54ac41c415239bd.ppt