2d1d6eb8d169a611a841a8d3acad3ef6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

VLBI @ Arecibo – T. Ghosh • What Arecibo’s 305 -m contributes to VLBI observations with the present equipment • Observations in 2009 • Some scientific results • Sensitivity upgrade: Bandwidth =>VLBI data Acquisition/recording Integration time (limited) - phase referenceing - slow slew rate of the 305 -m dish • Looking for a solution – the new 12 -m dish
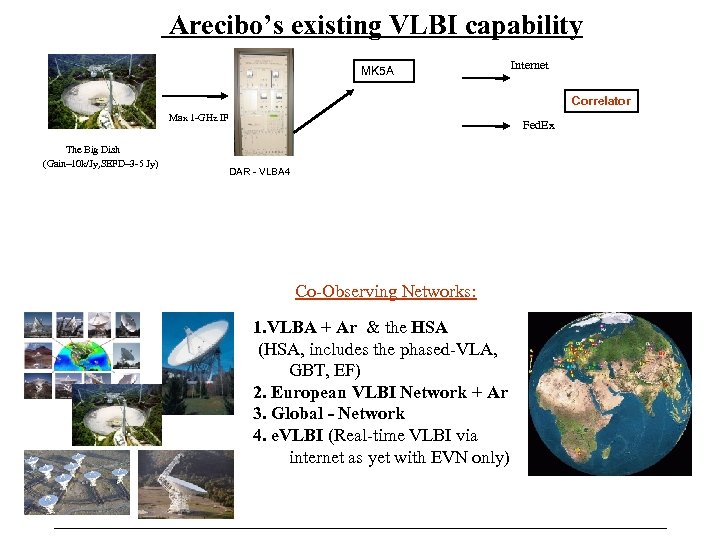
Arecibo’s existing VLBI capability MK 5 A Internet Correlator Max 1 -GHz IF The Big Dish (Gain~10 k/Jy, SEFD~3 -5 Jy) Fed. Ex DAR - VLBA 4 Co-Observing Networks: 1. VLBA + Ar & the HSA (HSA, includes the phased-VLA, GBT, EF) 2. European VLBI Network + Ar 3. Global - Network 4. e. VLBI (Real-time VLBI via internet as yet with EVN only)

Arecibo’s Contribution to the Arrays • A continuum observation, =18 -cm, data-rate=512 Mbps, i. e. 128 MHz of RF bandwidth, dual-polarization, = 120 minutes on source: • A spectral-line observation, =18 -cm, 64 channels over 1 -MHz, 2 pol, 120 mins.
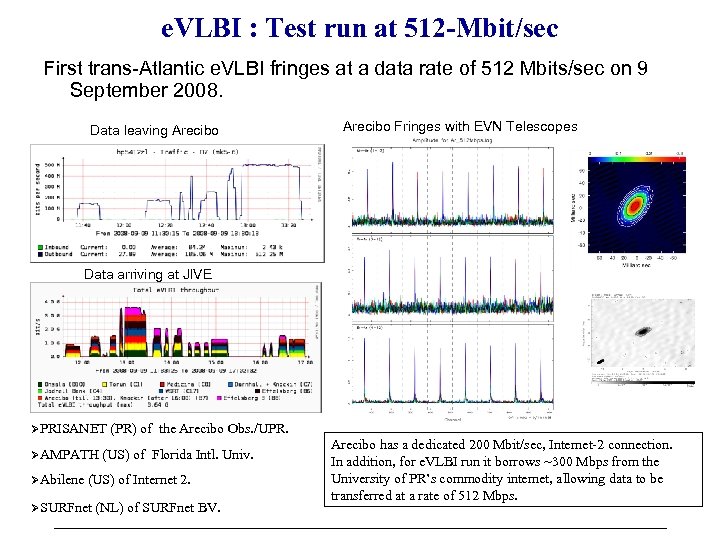
e. VLBI : Test run at 512 -Mbit/sec First trans-Atlantic e. VLBI fringes at a data rate of 512 Mbits/sec on 9 September 2008. Data leaving Arecibo Fringes with EVN Telescopes Data arriving at JIVE PRISANET AMPATH Abilene (PR) of the Arecibo Obs. /UPR. (US) of Florida Intl. Univ. (US) of Internet 2. SURFnet (NL) of SURFnet BV. Arecibo has a dedicated 200 Mbit/sec, Internet-2 connection. In addition, for e. VLBI run it borrows ~300 Mbps from the University of PR’s commodity internet, allowing data to be transferred at a rate of 512 Mbps.
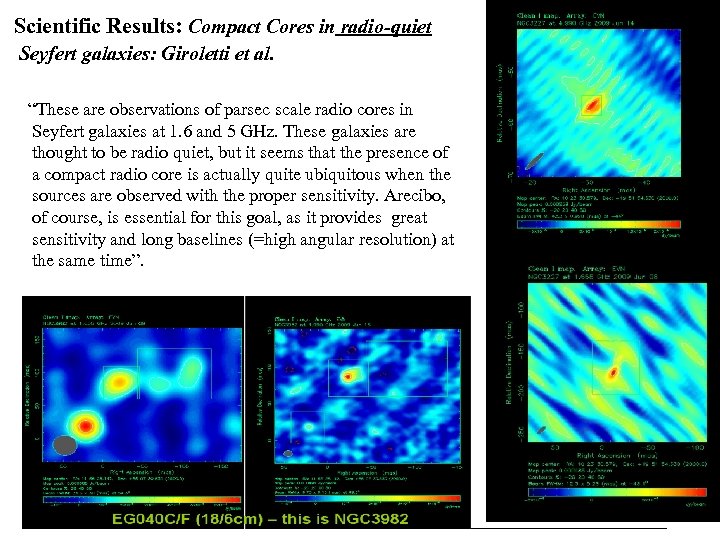
Scientific Results: Compact Cores in radio-quiet Seyfert galaxies: Giroletti et al. “These are observations of parsec scale radio cores in Seyfert galaxies at 1. 6 and 5 GHz. These galaxies are thought to be radio quiet, but it seems that the presence of a compact radio core is actually quite ubiquitous when the sources are observed with the proper sensitivity. Arecibo, of course, is essential for this goal, as it provides great sensitivity and long baselines (=high angular resolution) at the same time”.
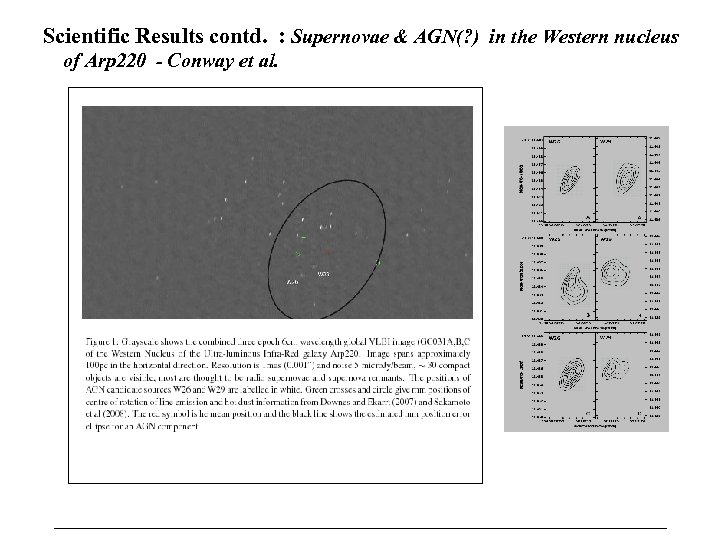
Scientific Results contd. : Supernovae & AGN(? ) in the Western nucleus of Arp 220 - Conway et al.
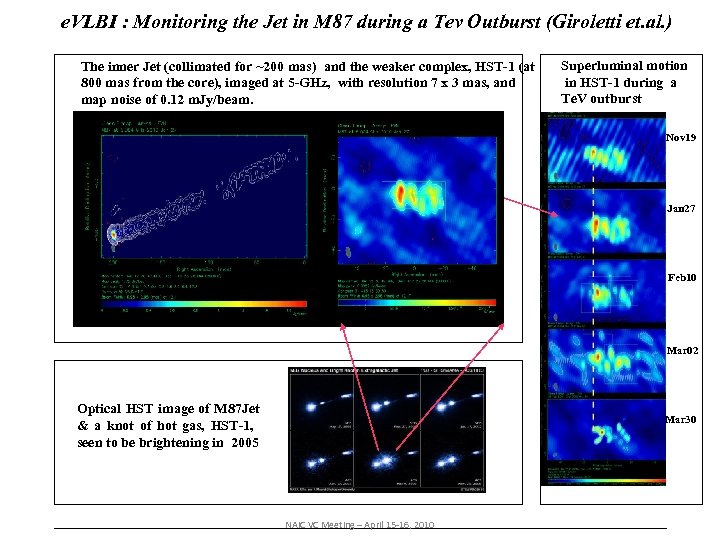
e. VLBI : Monitoring the Jet in M 87 during a Tev Outburst (Giroletti et. al. ) The inner Jet (collimated for ~200 mas) and the weaker complex, HST-1 (at 800 mas from the core), imaged at 5 -GHz, with resolution 7 x 3 mas, and map noise of 0. 12 m. Jy/beam. Superluminal motion in HST-1 during a Te. V outburst Nov 19 Jan 27 Nov 19 Feb 10 Mar 02 Optical HST image of M 87 Jet & a knot of hot gas, HST-1, seen to be brightening in 2005 Mar 30 NAIC VC Meeting – April 15 -16, 2010

VLBI Sensitivity pgrade Increasing the US VLBI data recording rate to at least 4 Gbps by 2010: Goal set by the Taylor Committee. Increase the bandwidth: Replace the analog DAR with RDBE. - The Digital Down Conversion (DDC) personality consists of four independently tunable sub-bands per IF, with bandwidths 0. 5 - 256 MHz. and output sample precision: 1 – 8 bits. There will also be a Polyphase Filter Bank personality (PFB) with 32 sub-bands spanning the entire 500 -MHz IF. Output will be via 10 Gigabit Ethernet transporting individual sub-band packet streams. Maximum data rate of 8 Gbps. Arecibo has placed an order with the NRAO for two RDBEs. Mark 5 C recording system developed by Haystack & Conduant Corp. Control software is still under development at Haystack. Arecibo has bought and received two Mark 5 C units.
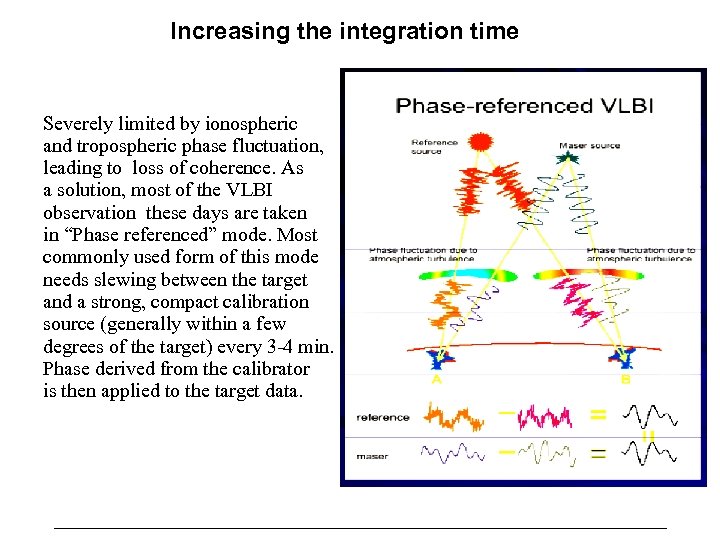
Increasing the integration time Severely limited by ionospheric and tropospheric phase fluctuation, leading to loss of coherence. As a solution, most of the VLBI observation these days are taken in “Phase referenced” mode. Most commonly used form of this mode needs slewing between the target and a strong, compact calibration source (generally within a few degrees of the target) every 3 -4 min. Phase derived from the calibrator is then applied to the target data.

The Small Antenna (12 -m? ) Problem for the Big Dish: Slow slew rate of 305 -m antenna can lead to >50% loss of time in phase referencing VLBI. Solution? The nearby small antenna will track the calibrator continually, while the 305 -m, tracks just the target, with occasional visits to the calibrator. Phase derived from the small antenna will be applied to the 305 -m data under the assumption that the same ionospheric correction applies to both data sets. How Big? - In order to provide a baseline sensitivity within a factor of 2 of an intra. VLBA baseline, the small antenna should be at least about 12 -m. With this, sources brighter than 110 m. Jy can be used as a phase referencing calibrator. Freq. Coverage - L, S, C & X bands are needed for astronomy; S/X for now. Eventually, 1 -12 GHz will be covered. Slew Rate - For geodetic use, az slew rates of 5 deg/sec are required.
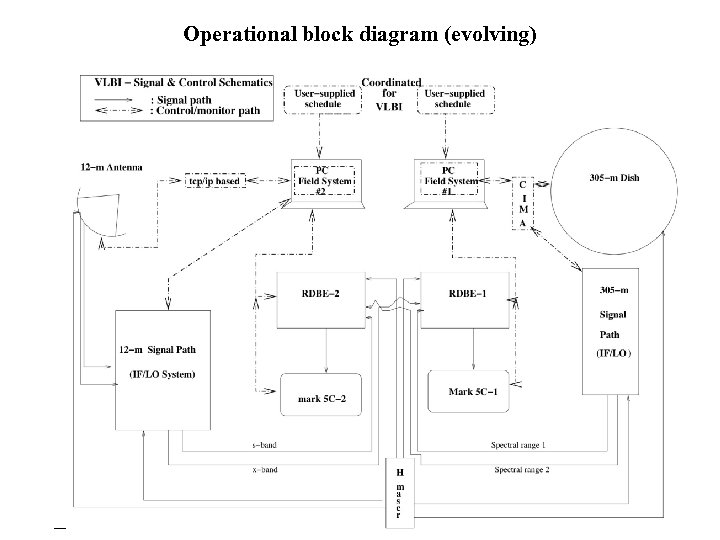
Operational block diagram (evolving)
The Arecibo 12 -m Antenna • Current Status – The antenna has arrived at the Observatory, site preparation is basically finished, assembly work is about to beging. When commissioned, it will primarily be used for VLBI phase referencing, enhancing astrometric work. (http: //www. aoc. nrao. edu/events/astrometry) • Freq. Coverage – An S/X receiver has been ordered from Patriot Antenna Systems Inc. This will be supplemented later by C- (and L-band) systems. It is intended that a broadband system will eventually be installed. • Single Dish Uses – Education and research applications with Puerto. Rican universities and other educational establishments. • Other Uses – (a) Participation in VLBI 2010; (b) At L-band, the voltage beam-width of a 12 -m antenna contains all seven beams of the ALFA receiver, opening up a possibility of multi-beam interferometric applications.

The 12 -m Site The AUT Patriot 12 -m Antenna Science Areas: Astronomical VLBI with 305 -m, Stand-alone VLBI for astronomy, astrometry & Geodesy, Single dish uses, and UG-teaching aid Timeline : 1. June 2010 – construction complete 2. Acceptance test using temporary backends, integrate RDBE+MK 5 C 3. Jan 2011 – test observations in VLBI mode at S/X 4. Wide band receivers by 2012
2d1d6eb8d169a611a841a8d3acad3ef6.ppt