90ef181df2a5ff1b4e866158d89e3136.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60

Visualizing Information Institute of Internal Auditors

Calibration Questions (Show of Hands) Who currently does process mapping or flow charting? How many use process mapping software? How many have the M/S Office suite?

Processes Defined “Simply” “It’s simple, you just take something and do something to it, and then do something else to it. Keep doing this, and pretty soon you’ve got something. ” -- Jasper Johns


Our Roadmap Process Mapping Overview Choosing the Tool to Use Reviewing Processes – Considerations – BOLO’s

Why Diagram Processes? "The first step in any organization is to draw a flow diagram to show each component depends on others. Then everyone may understand what his/her job is. If people do not see the process, they cannot improve it. " Paul Batalden quoting W. E. Deming

Two More Views “Any problem can be solved as long as it is stated properly. ” -- Dr. Edwin Land “A problem well-stated is a problem half-solved. ” -- John Dewey

Ways and Why We Visualize Information Partial List of Ways Why Affinity Diagrams (Fishbone) The 4 M’s: (Methods, Machines, Materials, Manpower) The 4 P’s: (Place, Procedure, People, Policies) The 4 S’s: (Surroundings, Suppliers, Systems, Skills) Cause & Effect Control Charts Force Field Analysis Graphs/Charts Pareto Process Maps Array information to enhance knowledge and understanding for action.
Process Maps Can Help Make the invisible — visible! – See Relationships – Builds Consensus – Compare & Contrast Perception/Reality/Ideal Improve Processes “As Is” “To Be” Training Inspections - Audits
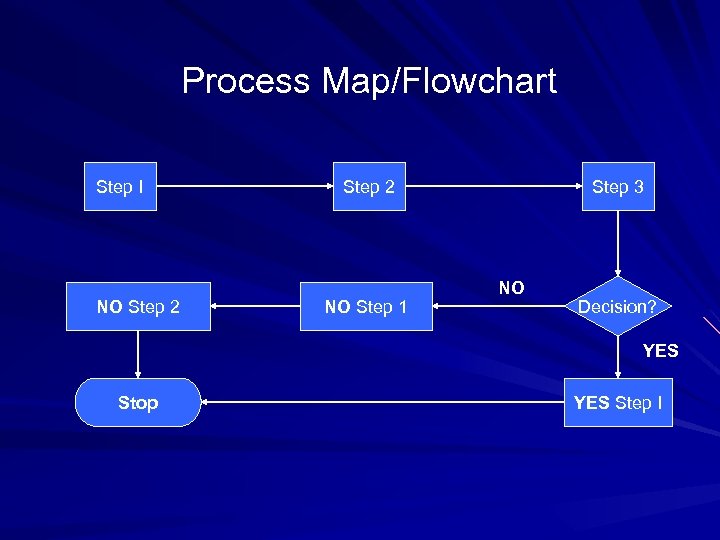
Process Map/Flowchart Step I NO Step 2 NO Step 1 Step 3 NO Decision? YES Stop YES Step I
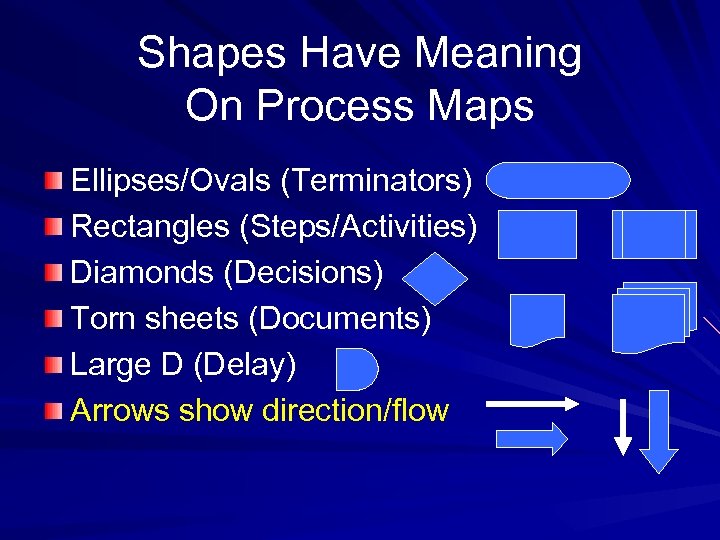
Shapes Have Meaning On Process Maps Ellipses/Ovals (Terminators) Rectangles (Steps/Activities) Diamonds (Decisions) Torn sheets (Documents) Large D (Delay) Arrows show direction/flow
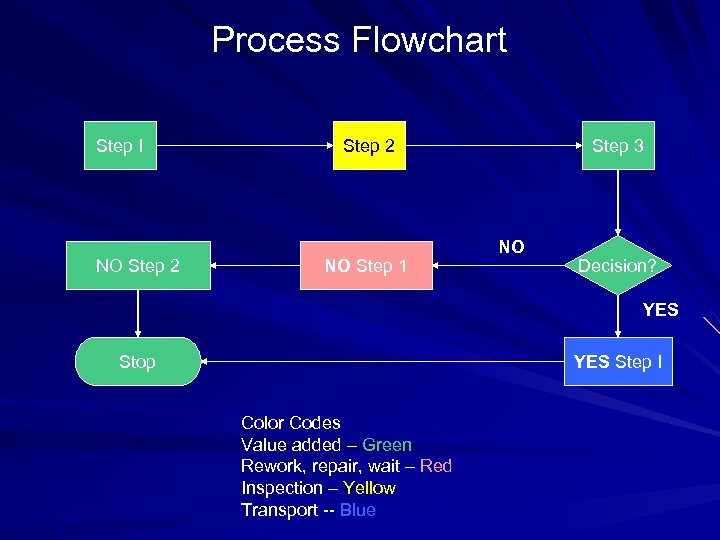
Process Flowchart Step I NO Step 2 NO Step 1 Step 3 NO Decision? YES Step I Stop Color Codes Value added – Green Rework, repair, wait – Red Inspection – Yellow Transport -- Blue
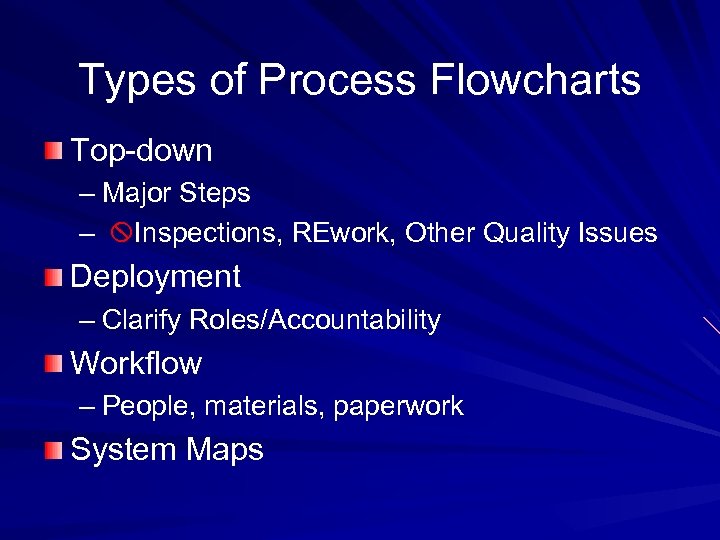
Types of Process Flowcharts Top-down – Major Steps – Inspections, REwork, Other Quality Issues Deployment – Clarify Roles/Accountability Workflow – People, materials, paperwork System Maps
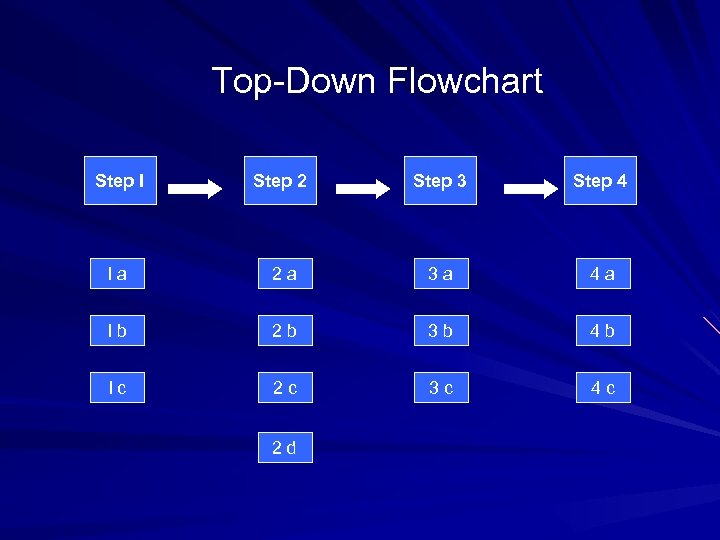
Top-Down Flowchart Step I Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 I a 2 a 3 a 4 a I b 2 b 3 b 4 b I c 2 c 3 c 4 c 2 d
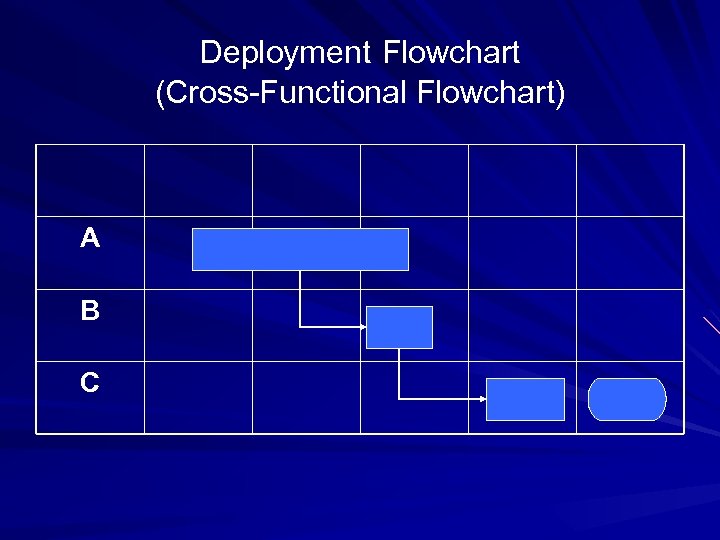
Deployment Flowchart (Cross-Functional Flowchart) A B C
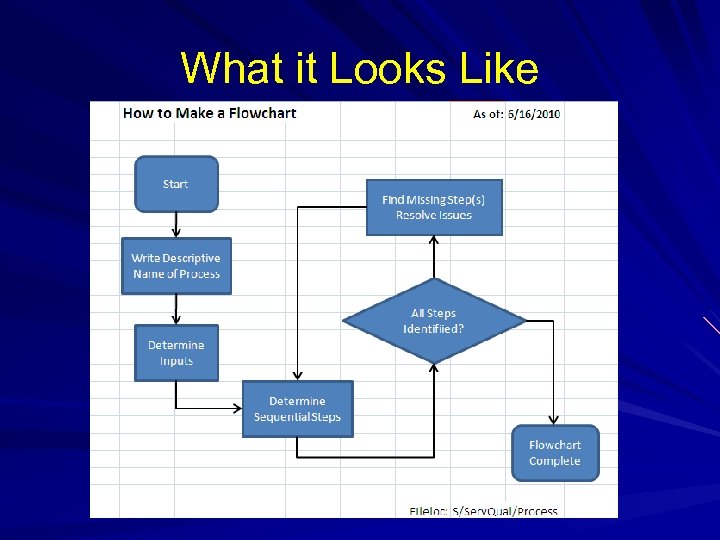
What it Looks Like
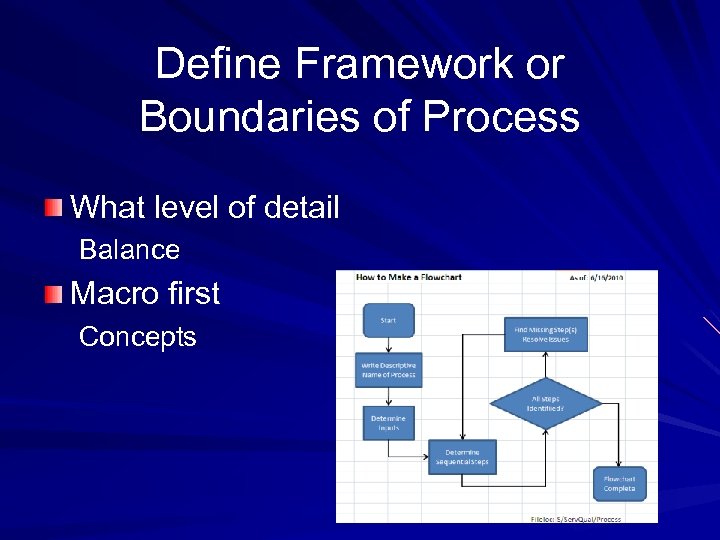
Define Framework or Boundaries of Process What level of detail Balance Macro first Concepts

Get It Down Right people Brainstorm all major activities – Determine shapes Describe process steps – Verb - Noun

Get It Right Sequence the steps Terminology – Revise and Edit – Variations Acknowledge them all—Resolve what you can Standardize—Note exceptions Document “Rules”—Who authorizes deviations? Identify “pre-defined” steps

Test Validate – Use people who were not part of initial team Seek out harshest critics – Capture their variations – Review, then appropriately incorporate Ensure correct use of symbols – Decisions may not be obvious All paths should close (loop) or terminate

A Most Common Gizmo Microsoft’s Drawing Tools

Drawing Tools (Word, Power Point, Excel) Cost Training Capability Most already have M/S Office Suite Minimal; Tool within an Application All Basic (28) Flow Charting Shapes Standardization Portability Doc Control Collaboration Unified Approach Interface with Other Office Applications

A Most Common Gizmo Microsoft’s Drawing Tools But which application?
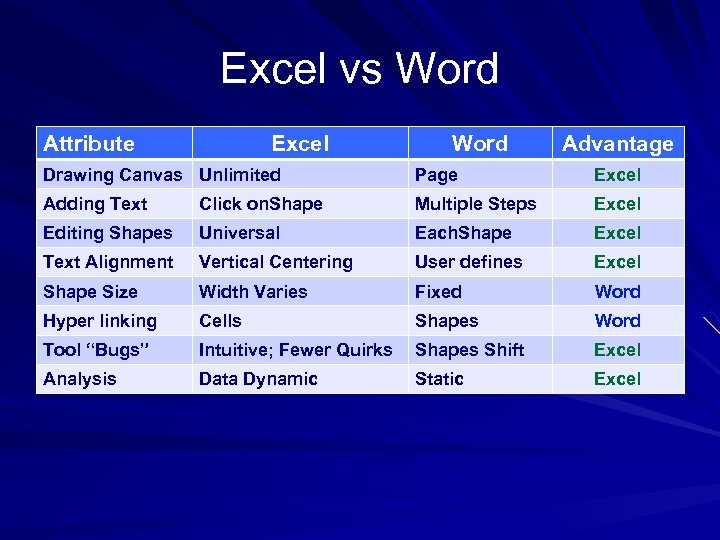
Excel vs Word Attribute Excel Word Advantage Drawing Canvas Unlimited Page Excel Adding Text Click on. Shape Multiple Steps Excel Editing Shapes Universal Each. Shape Excel Text Alignment Vertical Centering User defines Excel Shape Size Width Varies Fixed Word Hyper linking Cells Shapes Word Tool “Bugs” Intuitive; Fewer Quirks Shapes Shift Excel Analysis Data Dynamic Static Excel

M/S Autoshapes 28 Shapes available – Hover to see meanings Set Defaults – Center Justify – Font Size 10 *To change Auto. Shapes – 2003 Use Draw Menu – 2007 App Specific - Excel - Edit Shape
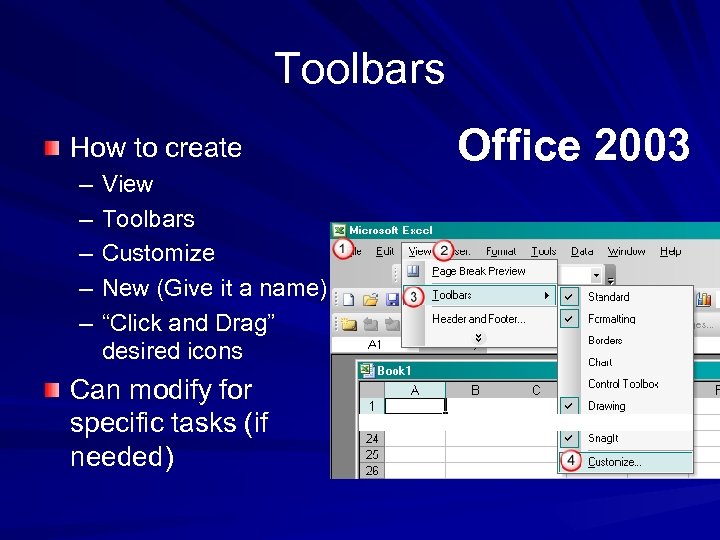
Toolbars How to create – – – View Toolbars Customize New (Give it a name) “Click and Drag” desired icons Can modify for specific tasks (if needed) Office 2003
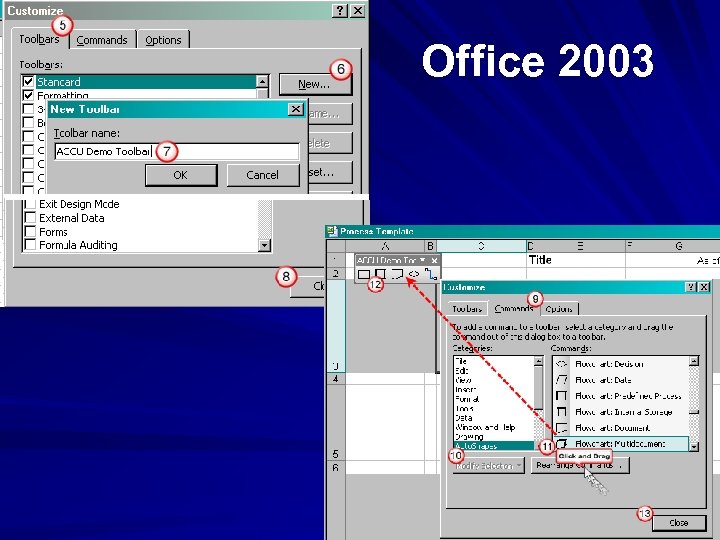
Office 2003
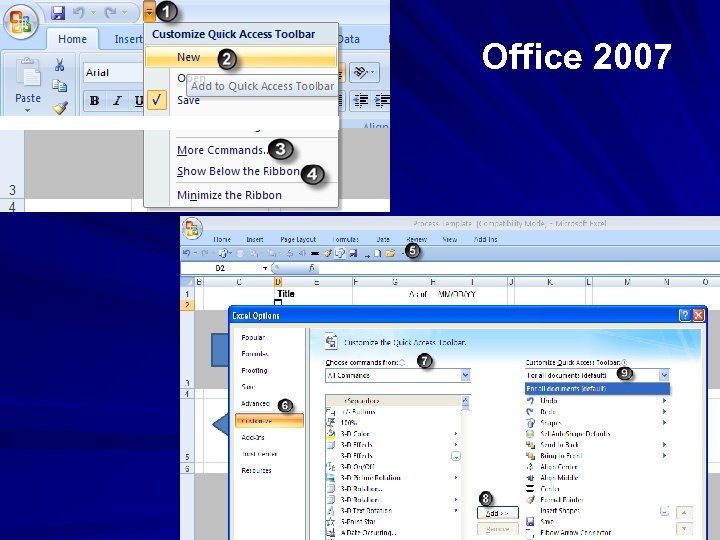
Office 2007

Helpful Hints Swim Lanes – – Column or Row Wide border by skinny Place shapes in wide spaces Move text vertically in a cell (Alt + Enter) Can Copy Shapes – Cntrl C (Cut) – Cntrl V (Paste) Link to Relevant Metrics – – – Hyperlink to worksheet Done via cells (not shapes) Remember to create a return path to process map As Of: Author:

Similar Processes? Work most complex (or Vanilla) first Copy worksheet “Boil off" excess (or add variations) Make other revisions q Deal with those “what if” situations

Improving Processes

Basic Steps Visualize the Process Identify Types, Numbers, & Impacts of Problems Identify Causes for Each Develop & Evaluate Solutions

Look for Opportunities to Measure** What indicates the process is effective or efficient? Should some parts of the process be examined with a Talley Sheet? Pareto Chart? A Run Chart? Use sample or All? Eliminate Does each step add value? Is there duplication? Can you eliminate or minimize delays? Inspections? Filing steps? Are some operations rework? Change How can the operation be changed? Different methods? Technology? Equipment? Less costly material or service? Reduce the frequency or the number of people receiving the service? Reduce the time it takes?

Look for Opportunities to Rearrange Is the layout or sequence the most efficient? Can you eliminate transport steps? Or method being used – electronic vs. physical? Combine Can any operations be combined? With a supplier's operation? With a customer's? Simplify What is the simplest way to achieve the objective(s) of the process? Are the instructions easy to understand? Imagine What would be the perfect process? Can you flowchart it? How much time would it take? A sub-process flow chart?
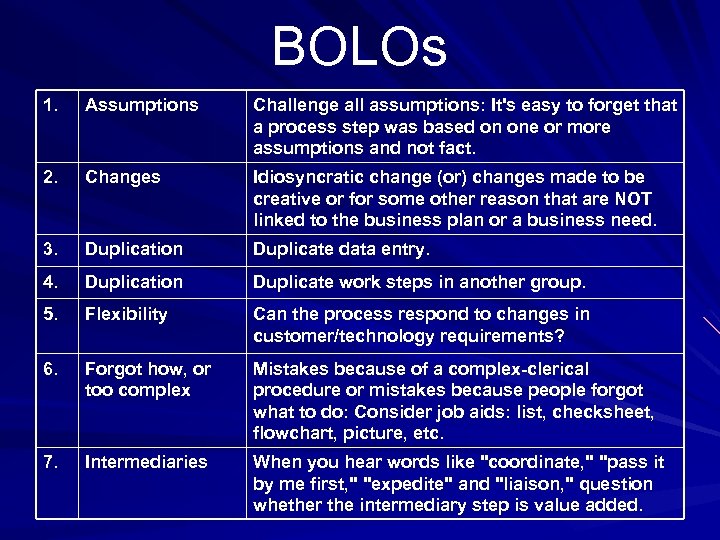
BOLOs 1. Assumptions Challenge all assumptions: It's easy to forget that a process step was based on one or more assumptions and not fact. 2. Changes Idiosyncratic change (or) changes made to be creative or for some other reason that are NOT linked to the business plan or a business need. 3. Duplication Duplicate data entry. 4. Duplication Duplicate work steps in another group. 5. Flexibility Can the process respond to changes in customer/technology requirements? 6. Forgot how, or too complex Mistakes because of a complex-clerical procedure or mistakes because people forgot what to do: Consider job aids: list, checksheet, flowchart, picture, etc. 7. Intermediaries When you hear words like "coordinate, " "pass it by me first, " "expedite" and "liaison, " question whether the intermediary step is value added.
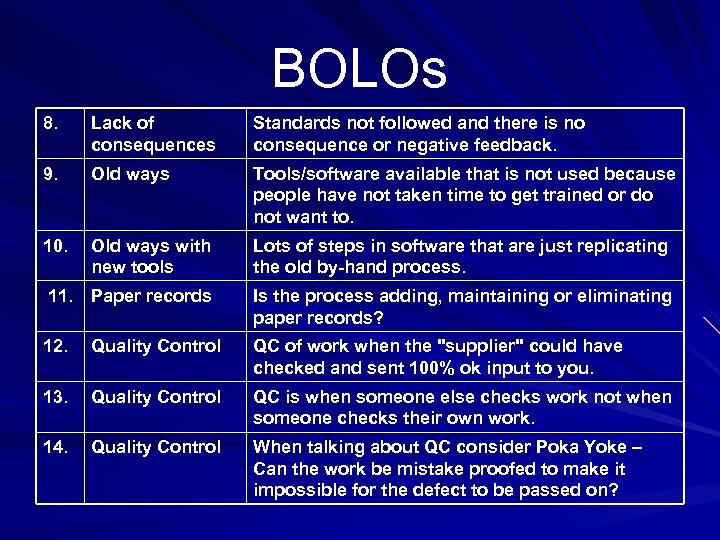
BOLOs 8. Lack of consequences Standards not followed and there is no consequence or negative feedback. 9. Old ways Tools/software available that is not used because people have not taken time to get trained or do not want to. 10. Old ways with new tools Lots of steps in software that are just replicating the old by-hand process. 11. Paper records Is the process adding, maintaining or eliminating paper records? 12. Quality Control QC of work when the "supplier" could have checked and sent 100% ok input to you. 13. Quality Control QC is when someone else checks work not when someone checks their own work. 14. Quality Control When talking about QC consider Poka Yoke – Can the work be mistake proofed to make it impossible for the defect to be passed on?
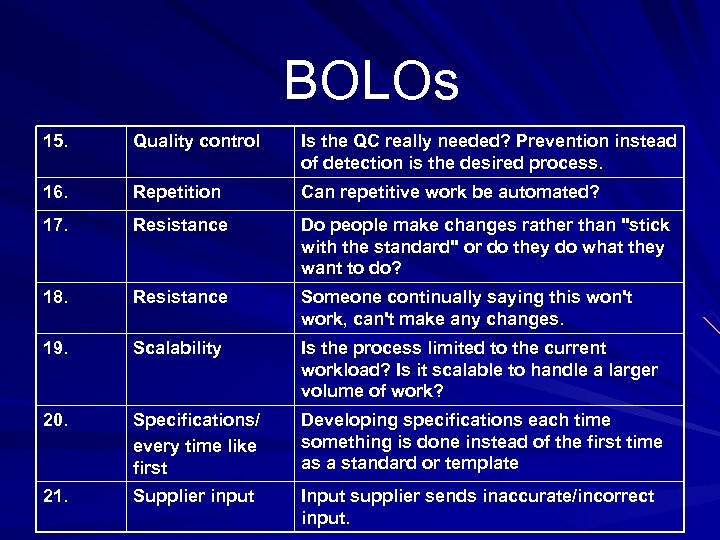
BOLOs 15. Quality control Is the QC really needed? Prevention instead of detection is the desired process. 16. Repetition Can repetitive work be automated? 17. Resistance Do people make changes rather than "stick with the standard" or do they do what they want to do? 18. Resistance Someone continually saying this won't work, can't make any changes. 19. Scalability Is the process limited to the current workload? Is it scalable to handle a larger volume of work? 20. Specifications/ every time like first Developing specifications each time something is done instead of the first time as a standard or template 21. Supplier input Input supplier sends inaccurate/incorrect input.

Bonus Round…
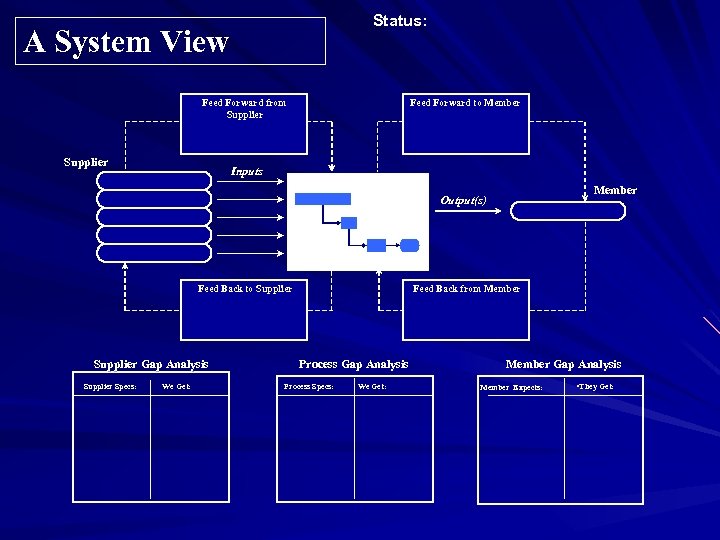
Status: A System View Feed Forward to Member Feed Forward from Supplier Inputs Member Output(s) Feed Back from Member Feed Back to Supplier Gap Analysis Supplier Specs: We Get: Process Gap Analysis Process Specs: We Get: Member Gap Analysis Member Expects: • They Get:

Shapes for Audit Processes

Which Aisle? Candy or Produce? 51

57

44

Closing Thoughts Accuracy is important Are you looking at symptoms or root causes? Consider other situations – Out of the ordinary – Emergencies Measures should be meaningful to users – Get a feel for best / worst cases and what is the average. How many of each? – Leading indicators are better than lagging ones

Final Wrap-up Introduction to Process Mapping Use M/S Draw Tools within Excel App Maps to Help Identify Improvement Areas

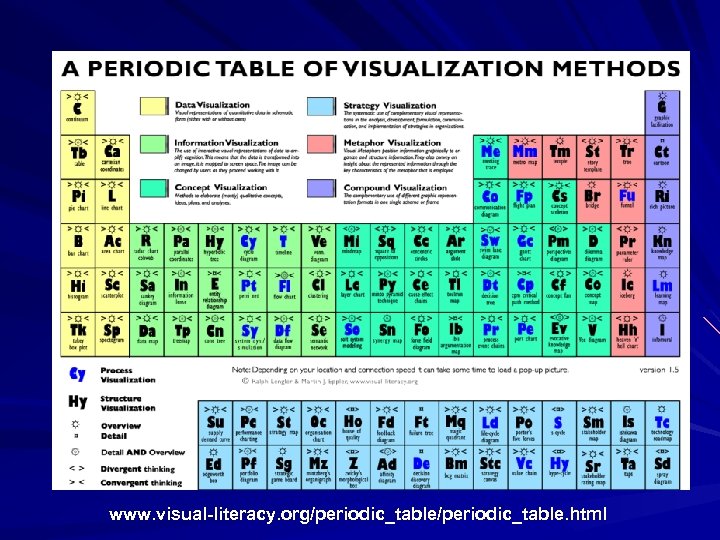
www. visual-literacy. org/periodic_table. html
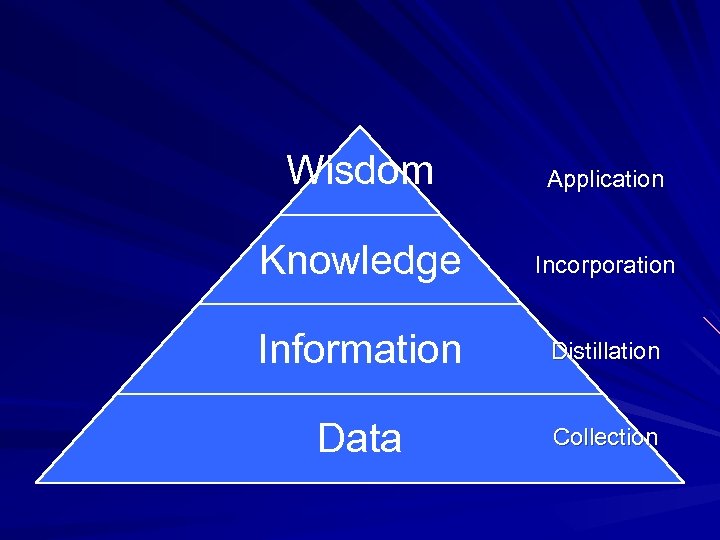
Wisdom Application Knowledge Incorporation Information Distillation Data Collection
90ef181df2a5ff1b4e866158d89e3136.ppt